- Overview
- Configuration
- Upgrading your REDCap-Docker-Compose localhost installation
- FAQ and Other Information
- How do I upgrade to the latest version of redcap-docker-compose?
- How do I prevent SMS messages from going out?
- Does this work with ARM64 processors, like the M1 or M2 "Apple Silicon" MACs?
- Adminer
- How do I stop phpMyAdmin
- Connecting to the database
- Local URLS
- Logging
- I can't access my server at http://localhost even though docker is running!
- How do I make a custom localhost alias?
- Useful Docker-compose Commands
- Can I change the location of my webroot files?
- Can I run more than one instance of REDCap-Docker-Compose at the same time?
- Can you explain how I would change the PHP version?
- Shutting down
- Logging into the server
- How can I see what's running?
- If I remove my docker container will I loose my database?
- How can I REALLY delete everything?
- How can I switch mysql versions? For example, go from mySql 5.7 to mySql 8.0?
- Scanning External Modules for REPO Submission
- How do I work with git repositories as External Modules with Visual Studio Code (vsCode)?
- Any advice about working with repos you've cloned from GIT?
This docker-compose will build multiple docker containers as part of a server group to host REDCap on your local computer/server. The build consists of:
- The official PHP-Apache docker image (Currently version 8.3)
- The official MySql docker image (currently version 8.0)
- Mailpit (for capturing outbound emails from REDCap for your review)
- A basic alpine-based cron image (for running the REDCap cron and handling log rotation)
- (optional) The official alpine-based PhpMyAdmin web-based mysql tool for managing the database.
- This service is now commented out by default. If you wish to use phpMyAdmin you can uncomment the entries from the
docker-compose.ymlfile in the/rdc/directory
- This service is now commented out by default. If you wish to use phpMyAdmin you can uncomment the entries from the
The big advantage of this docker-based method is you can easily upgrade database versions, php versions, and see how these changes might affect your projects or custom code. It also provides a nice mechanism for you and your development team to work in identical environments for consistency. Further, with advanced installations you could run many versions of php or REDCap simultenaously for testing.
This docker-compose script relies on a number of underlying images which are build or pulled to build your containers
- docker-cron (built from Dockerfile)
- docker-web (built from Dockerfile)
- docker-db (built from Dockerfile as pulled official image)
- mailpit (built from official image)
- phpmyadmin image (pulled as official image)
Those images that use Dockerfiles can be modified by tweaking the Dockerfile or scripts in each folder. You must rebuild the container after modifying the Dockerfile.
Many of these docker containers are further customized through a series of startup scripts. The basic Docker-compose
is a LAMP stack that could be used for any project. However, the redcap-overrides and Docker-compose file provides
a mechanism to add addition REDCap-specific customizations.
For example, docker-web/container-config/php/70-sendmail_path sets up a generic msmtp mail service, but
redcap-overrides/web/php sets up typical REDCap php settings. It should be possible to reuse this framework to
create other version, such as SAML-enabled, or open-IDC containers for REDCap testing and production. The override
script merges the overrides into the default folders, so to remove a default you have to use the same filename.
-
Install docker on your machine.
- Docker now requires that you create a user account. Register.
- Download the latest version of docker desktop for your platform:
- For PC, I had to install the latest WSL2 Linux kernel update package and restart but gui walks you through the process. Also, upon launching VS Code, I installed the WSL extension.
-
Download a zip of this repository andy123/redcap-docker-compose to your computer. If you plan on contributing to the project, you may instead want to fork it and then clone your fork so you can push changes and issue a pull request to the main repo. Otherwise, just use the ZIP option. You can chose the Master branch of some of the few releases.
- A zip file of the latest commit is available here: zip download
- Unzip this into a good place on your computer (e.g. desktop or documents)
- On my Mac, I put it in a folder called 'redcap' under my user directory
~/REDCap/
- On my Mac, I put it in a folder called 'redcap' under my user directory
-
INSTALL A GOOD IDE. This really makes things easier. I can recommend:
- phpStorm,
- Visual Studio Code,
- and fancy editors like: Atom, etc... )
-
From your IDE, open the folder where redcap-docker-compose was placed:
-
Inside the
rdcfolder, find the.env-examplefile.- If you do not see the
.env-examplefile, you probably aren't using a real IDE. In windows and MAC, dot-files are hidden by default unless you tell it to show them.
- If you do not see the
-
Copy the
.env-examplefile to.env. -
Review the contents of the
.envfile, REALLY. This is where the majority of configuration changes are made. You should take a glance through so you understand what you can change.- If you are on a MAC, make sure you open your terminal and run
idto get your USER ID. Typically it will be 501-505 depending on how many users you have on your MAC. Make sure this value matches to reduce issues with file permissions in your mapped WEB directory. - If you are not running another local web-server or mysql server, your ports should be open. Otherwise,
you may have to change some of the ports for WEB or MYSQL services. You will get errors when building if the
ports are being used.
- On a MAC, you can test if your ports are open (default 80 for web and 3386 for mysql) with:
If you get nothing back, they are free. Otherwise, you can change the ports in your$ lsof -i tcp:80 $ lsof -i tcp:3386
.envfile.
- If you are on a MAC, make sure you open your terminal and run
-
Let's get ready to rumble. After you have reviewed your
.envwe are ready to build- Building the containers is required if you are upgrading, or else it might reuse an older container
If you got any errors here, stop and get help to resolve them. If you have made changes to the docker files or have upgrade to a newer version of redcap-docker-compose then I strong recommend you issue this command:
$ cd rdc $ docker compose builddocker compose build --no-cachewhich will ensure that all of your docker images are rebuilt from scratch
- Building the containers is required if you are upgrading, or else it might reuse an older container
-
Now that you have docker images (which you could see with the
docker images -acommmand, you need to make some docker containers. The first time you start your containers they may take a while- Bring up the container
$ cd rdc $ docker-compose up -d - You can tail the logs with
$ docker-compose logs -f
- Bring up the container
-
Hopefully you can now reach your server at
http://localhostorhttp://127.0.0.1- I prefer to access my 'local' redcap with a custom domain of 'redcap.local'.
- MAC Instructions: edit your /etc/hosts and append
redcap.localafter localhost (must be done as sudo):Then I access the server at http://redcap.local127.0.0.1 localhost redcap.local - PC Instructions: edit
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hostsand make the same change as above. You will have to be an administrator to save the file (or VS Code helps you) - If you want to be able to use SSL on your localhost without errors - there is now a special section with instructions
- MAC Instructions: edit your /etc/hosts and append
- I prefer to access my 'local' redcap with a custom domain of 'redcap.local'.
-
You need a copy of the REDCap Installer.
- If you are a member of the REDCap Consortium Community, you can:
- Download the latest full installer as a zip file.
- Alternately, if you know your community username and password, there is a built-in setup tool that can complete the installation for you.
- You can find your community username under your community profile (typically something like jane.b.doe)
- If you do not have an access code for the Community Consortium, you can ask your local site's REDCap administrator
to provide you with a copy of the latest FULL ZIP installer (provide the instructions above).
- If your institution has a license you should be able to install a local development version under that license
- If you represent your institution, you can request a community account here
- If you are not affiliated with an institution that has a license with REDCap, you CANNOT access the source code and will be unable to use this tool. You can contact REDCap to request a license here.
- If you are a member of the REDCap Consortium Community, you can:
-
Configure REDCap
- At this point, we assume that you have a running set of containers. Use the REDCap Setup tool to complete your
installation. Please note that you DO NOT need to create a new database user as the
.envand setup scripts for MySql have already done so. You can find the usernames and passwords in the.envfile.
- At this point, we assume that you have a running set of containers. Use the REDCap Setup tool to complete your
installation. Please note that you DO NOT need to create a new database user as the
If you would like to be able to access your localhost docker instance of REDCap via SSL, follow the following steps.
(This is based on an article from https://dockerwebdev.com/tutorials/docker-php-development/)
I use Homebrew for managing packages on my Mac laptop. So, these instructions are based on using a Mac and having installed Brew previously. If this isn't you, there are alternate install instructions for mkcert that provide many other methods.
brew install mkcert nss
mkcert -install
Next, make a locally trusted development certificate
mkcert localhost 127.0.0.1 ::1 (or add any other names you want to call your local server). In my case, I use redcap.local.
mkcert localhost 127.0.0.1 ::1 redcap.local
This will yield two new files in your current directory. Rename and move these files to the docker-compose continer inside the credentials folder.
mv localhost+3.pem /path_to_redcap_docker_compose/credentials/cert.pem
mv localhost+x-key.pem /path_to_redcap_docker_compose/credentials/cert-key.pem
Turn on the SSL site which is loaded in the redcap-overrides/web/apache2/sites-available/ssl.conf by setting
the .env variable WEB_ENABLE_SSL_SITE=true
Restart your docker containers with docker compose down; docker compose up -d
Try accessing your localhost with https protocol! If it works, you might need to change your REDCap base URL from http to https.
At this point, your local computer can connect to your locally running docker over https without warnings. This is because your local computer 'trusts' the signer which is itself. However, if your docker container trys to call itself or if the cron container were to try to call the web container with https, it would fail. This seldom happens, but some EM code calls the server itself and could end up trying to use https. To enable the docker web container to trust the certs we created on your laptop we have one more optional step.
Find the location of the root certificate used by mkcert on your local computer. This is done with:
mkcert -CAROOT
It will give a path like /Users/you/Library/Application Support/mkcert.
Inside that folder is a file called rootCA.pem. Lets copy that file to the credentials folder and rename it to rdc_rootCA.pem.
cp /Users/you/Library/Application Support/mkcert/rootCA.pem /path_to_redcap_docker_compose/credentials/rdc_rootCA.pem
There is a script in the redcap-overrides/web/startup-scripts that will, if the file rdc_rootCA.pem exists, install the crt into the trusted root chain so it will accept localhost calls.
To test of this works, you can ssh into your web container and check. First, make sure you restart your containers with a docker-compose down; docker compose up -d;. Then, goto the rdc/ directory and connect to the web container as follows below:
Here is what it looks like when it isn't working:
$ docker compose exec web /bin/bash
root@7aeb61f66236:/var/www/html# cd /tmp
root@7aeb61f66236:/tmp# wget https://localhost
--2024-10-23 16:06:02-- https://localhost/
Resolving localhost (localhost)... ::1, 127.0.0.1
Connecting to localhost (localhost)|::1|:443... failed: Connection refused.
Connecting to localhost (localhost)|127.0.0.1|:443... connected.
ERROR: The certificate of 'localhost' is not trusted.
ERROR: The certificate of 'localhost' doesn't have a known issuer.
And, after:
--2024-10-23 16:47:50-- https://localhost/
Resolving localhost (localhost)... ::1, 127.0.0.1
Connecting to localhost (localhost)|::1|:443... failed: Connection refused.
Connecting to localhost (localhost)|127.0.0.1|:443... connected.
X-Debug allows you to insert breakpoints in your php code and evaluate variables from the server in your IDE. It has a small learning curve to pick up but is really helpful in the long run. I strongly encourage php developers to try and learn how to use this tool.
- After your docker server is up and running, open your project folder in PhpStorm (e.g.
~/redcap/) - In PhpStorm, goto
preferences -> PHP -> Serverand create new server.- Name the server whatever you like
- Set the hostname to be
localhost(or if you are using a host alias likeredcap.local, use that) and leave the port at '80' - Check the "Use Path Mapping" option to map your webroot (
www) in the redcap-docker-compose folder file to the docker container's webroot path which is/var/www/html.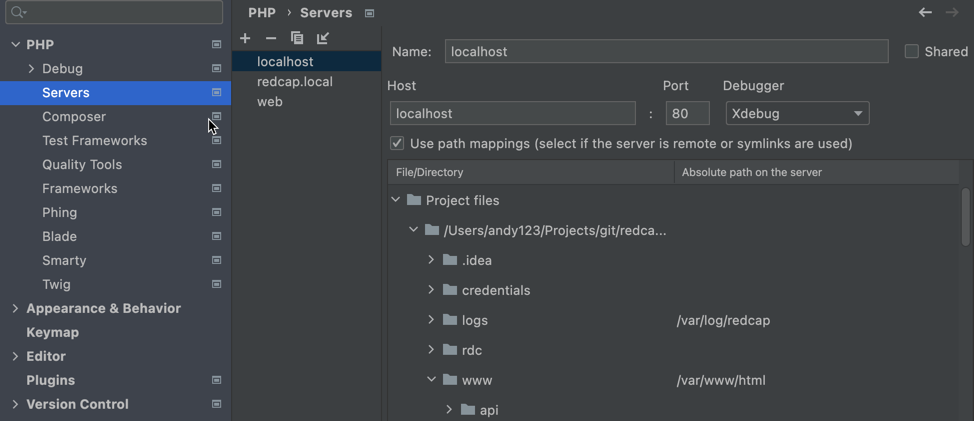
- After creating the server, goto the PHPStorm go to
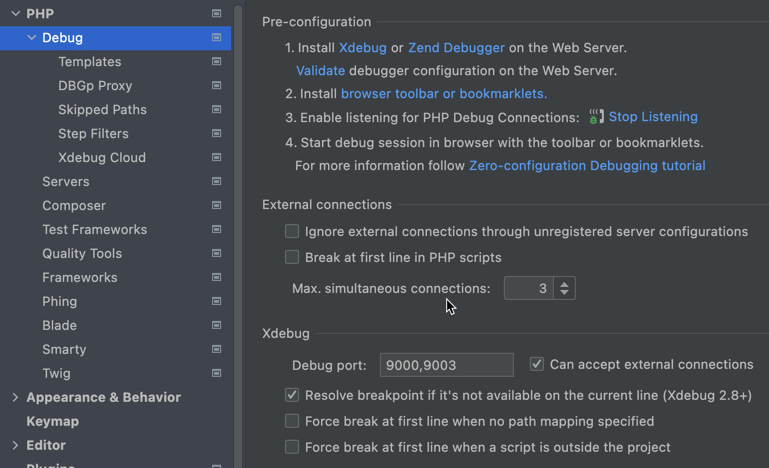
preferences > PHP -> Debugand review the settings for Xdebug. - Finally, install the PhpDebug Browser debugger extension
- This tool lets you decide when you want to debug. To debug you have to first make sure your debug server is listening in phpStorm (this is the phone icon in the top-right toolbar. Next, you need to make sure the toolbar extension is set to the green bug which sets a cookie that tells you to debug.
- I don't know if it matters, but in my toolbar configuration I set the IDEKEY to be 'PHPSTORM' but I don't think the IDEKEY is used any longer in phpStorm.
- This tool lets you decide when you want to debug. To debug you have to first make sure your debug server is listening in phpStorm (this is the phone icon in the top-right toolbar. Next, you need to make sure the toolbar extension is set to the green bug which sets a cookie that tells you to debug.
- Note: If you want to debug cron calls, you may have to do more!
- When the cron container calls the web container it uses the url of
http://web/cron.php. So, your xdebug server will not have a 'server' defined with a host ofweb. So, in my case, I made aq second Server (step 2 above) also called web with the same configuration. - Alternately, you could disable the cronjob container with
docker compose stop cronat the command prompt in the rdc folder and just make calls to the cron endpoint manually from your local browser (e.g.http://localhost/cron.phpto trigger and test a cron job. In this case, your normal xdebug server settings should capture the event)
- When the cron container calls the web container it uses the url of
- Xdebug's default mode is "debug". To profile the code instead of debug
- Create a new file "/usr/local/etc/php/conf.d/81-xdebug.ini"
- Edit the file to include the line
- xdebug.mode=profile
- Restart apache
- /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
- Set the Debug Browser Extension to "Profile". This may be optional.
- The output is captured at /tmp/cachegrind.out.##.gz (## refers to the numbers in the filename. One file is created per request)
- Copy the profile data to where PHP Storm can read it (Choose your location)
- cp /tmp/cachegrind.out.##.gz /var/www/html/
- In PHPStorm click on "Tools" choose "Analyze Xdebug Profiler Snapshot..."
- Choose the cachegrind.out file. No need to un-gzip it.
- After your docker web container is up and running, you should have access to a xdebug information page here: http://localhost/debug/xdebug_info.php
- Note that the settings for xdebug defalt via the injected override file located here
/rdc/redcap-overrides/web/php/80-xdebug.ini. If you want to make changes, you can EITHER edit this file and change the master values, or you can override them using then.envXDEBUG environmental variable. Be sure to rundocker compose down; docker compose up -dafter any changes and check the [xdebug_info]((http://localhost/debug/xdebug_info.php) page afterwards.
- Note that the settings for xdebug defalt via the injected override file located here
- In VS Code, install the OFFICIAL 'Php Debug' extension. (has 12.5M installs as of 10/2024)
- For Chrome, install the Xdebug helper extension. This will allow you to designate a page/session for debugging by setting a cookie
- The redcap-docker-compose repository already contains a .vscode folder with a launch.json which should create a launch open for starting a debug session. To do this:
- Click on the left-side 'Run and Debug' page in VSCODE that was added when you installed PHP Debug
- Click on the green play button for 'Listen for Xdebug'
- Now, goto your browser, using the new extension, set it to 'debug mode' and then refresh a page and you should see a debug session.
This new section is designed to help you perform an upgrade from an older version of REDCap Docker Compose. For clarity, I will refer
to the current folder where your old/existing redcap-docker-compose is located as ~/old_rdc/ so the folder with the docker-compose.yml
would be in ~/old_rdc/rdc/.
These are step-by-step - please reach out on the community consortium if you are having trouble.
Your current mysql database is stored on a docker volume. We are going to use the db container to generate a .sql.gz backup and copy it to your host laptop. In older versions of rdc, the database container mounted its logs as ~/old_rdc/logs/mysql or ~old_rdc/logs/. If you look there, you should see a mysql_error.log or mysql_slow.log file.
- Make sure your old redcap docker compose is running (e.g. you can access your local redcap).
- Backup your current redcap-docker-compose database with the following commands:
# Goto the folder with the docker-compose.yml file
$ cd ~/old_rdc/rdc
# Depending on how your LOGS_DIR is mounted to the db container, one of the following two commands should work to create a backup:
# For newer versions where the db container has logs mounted as: ${LOGS_DIR}:/var/log, this should work:
$ docker compose exec db bash -c 'mysqldump -u root --password=$MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD $MYSQL_DATABASE | gzip > /var/log/${DOCKER_PREFIX}_redcap_db_$(date +%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S).sql.gz'
# Alternately, for older versions of rdc, where the logs are mounted as ${LOGS_DIR}/mysql:/var/log or ${LOGS_DIR}/mysql:/var/log/mysql, this might work:
$ docker compose exec db bash -c 'mysqldump -u root --password=$MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD $MYSQL_DATABASE | gzip > /var/log/mysql/${DOCKER_PREFIX}_redcap_db_$(date +%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S).sql.gz'
- Check your
~/old_rdc/logs/...directory and try to find the new.sql.gzbackup. This command might take a while if your database is large. - Shut down your old rdc setup with
~/old_rdc/rdc> docker compose down
-
You can pull from the master branch or pick a newer release. I would default to trying the master branch, but it is up to you. In most cases, you want to pull the 'zip' version and not clone the repo unless you plan to make pull requests. Let's then unzip it into a new folder, e.g.
~/REDCap_2025_01/. -
Set up the new
.envfile. Copy.env-exampleto.envand set up all the values. -
Make sure the value for the
DOCKER_PREFIXvariable in the new.envis different than in your old one. This will ensure you don't accidentally overwrite a docker volume that might contain data from your previous RDC install.
$ cat .env | grep "DOCKER_PREFIX"
DOCKER_PREFIX=rc_v2 (or whatever)
- Turn on your new rdc with
docker compose up. This should create an empty database and you should be able to access the setup page athttp://localhost.
- Copy the
.sql.gzbackup created from your old instance to thelogsdirectory of the new rdc folder (and rename itredcap_restore.sql.gz).
$ cp /path/to/old_rdc/logs/(?mysql)/prefix_redcap_db_2024-xx-xx_xxxxxx.sql.gz /path/to/latest/redcapdockercompose/logs/redcap_restore.sql.gz
- Next, lets tell the database container to import the backup:
~/new_rdc/rdc> $ docker compose exec db bash -c 'zcat /var/log/redcap_restore.sql.gz | mysql -u root --password=$MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD ${MYSQL_DATABASE}'
This might take a while, but when done you should see all your database tables. You can verify with http://localhost/debug/adminer.php and then use db as the server name and root / root as the user/password.
If all worked, your new rdc instance is a copy of your old database, but it is missing the www directory. So, copy over all the /www/ files from the old install to the new one.
- Copy files (via command line or by drag and drop)
$ cp -r /path/to/old/rdc/www/* /path/to/latest/redcapdockercompose/rdc/www
Now, you should be ready to go with the new version. If you don't like what you get, you can always shut it down (e.g. docker compose down) and start up the old one again. Or, if you want to run both instances simultaneously, you simply need to change the values for the WEB_PORT and WEB_SSL_PORT and MYSQL_PORT in the .env files so they do not overlap and you can run both versions at the same time on different ports (but you might need to change your REDCap base URL in control center / general configuration)
We periodically make improvements to this package and if you are not careful, simply bringing up the latest version of this framework on your old docker volumes could lead to corruption. There are many permutations here so I would reach out for advice but in general I would follow a process like this:
Ideally, do a CLEAN new development environment. This means that you bring down your current docker compose,
otherwise you will get a port conflict error. Alternately, you can change the public ports in the .env file for
the new environment. You also want to MAKE SURE you change the DOCKER_PREFIX variable in the new .env to be
different from your existing environment. Otherwise docker may reuse the same volumes which can corrupt your database.
I would probably try a process like the following:
- First, make a backup of your current development server database. This can easily be done with phpmyadmin (check your docker-compose.yml file if you commented it out) and then dump your redcap database to a .sql or .sql.gz file.
- Take note of your current redcap version number (e.g. 12.2.1).
- Shut down your current docker rdc environment (e.g.
docker compose down). This will free the local ports on your system. - Follow the clean start directions to download the latest RDC version from github and unzip in a new location
- Copy the new default
.env-exampleto.envin the fresh download folder. Don't try to move your old.envas there could be some changes in the new version. - Compare your old
.envwith the latest.envto update variables as necessary. There may be some changes here so look carefully. - IMPORTANT Make sure you change the
DOCKER_PREFIXin your new.envas this is used to name the volumes Docker creates. If you try to make a NEW instance of your development environment with the sameDOCKER_PREFIXyour new instance will use the same volume for things like the mysql database which could lead to corruption.
- Copy the new default
- Copy the webroot (
/www) contents from your old environment to the new one - Rebuild your images (e.g.
docker compose build --no-cache) - Bring up the new environment (e.g.
docker compose up -d) and goto phpmyadmin again. - Restore your backed up database to overwrite the REDCap database
- Make sure you move your redcap web folders into the www directory (or download a clean install version of the same version of redcap you had previously in your database).
If you do not want your local instance to be able to send text messages, you can:
- uncomment the block of code in the web container (remove the
#)# extra_hosts: # - "api.twilio.com:127.0.0.1" # - "www.twilio.com:127.0.0.1" # - "taskrouter.twilio.com:127.0.0.1" # - "lookups.twilio.com:127.0.0.1" # - "event-bridge.twilio.com:127.0.0.1" - Then restart the web container with
docker-compose up -d --no-deps --build web
Having recently switched to an M2 MAC, I found that I had to make some subtle changes. I was able
to identify multi-platform images for most dependencies except for phpmyadmin. So, if you are using
an ARM64 processor, you will have to modify the docker-compose.yml file and switch the images
command to look like this:
# image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
image: arm64v8/phpmyadminAdminer is an alternate solution for phpMyAdmin since phpMyAdmin is no longer supported and maintained. I selected a fork of adminer here https://github.com/adminerevo/adminerevo/ and the setup process copies the file to the /debug/ folder of your local server on setup.
You can access adminer at http://localhost/debug/adminer.php.
The first time you use adminer, you will have to connect. Server = db (this is the name inside the redcap-docker network as defined in the docker-compose.yml file), Username, Password, and Database are all specified in your .env file.
If you are using an older install of redcap-docker-compose, you may have to copy over the debug folder from /rdc/redcap-overrides/web/webroot/ to your local webroot at /www/.
If you have another mysql admin tool you'd prefer to use, you can prevent your docker-compose from instantiating the phpMyAdmin container. Either:
- After startup (e.g.
docker-compose up -d) you could rundocker-compose stop phpmyadmin - Alternately, you can comment out the phpmyadmin section of the
docker-compose.ymlfile with#before each line. If you don't use it, you might as well turn it off so it isn't running all the time. - NOTE that phpMyAdmin is commented out by default since the introduction of adminer. You will have to edit your docker-compose.yml file to re-enable the phpMyAdmin container
There are at least three ways to connect to your database:
- You can connect to the database from your client using any database tool (dataGrip, phpWorkbench, etc). The default
port is 3306 but you can change this in the
.envfile. - You have phpMyAdmin running inside this service - simply visit http://localhost/phpmyadmin/
- Note that the trailing slash is required!
- You can connect to the database from the command line as illustrated in the example below:
$ docker-compose exec db mysql -u redcap -predcap123
redcap-docker-compose$ docker-compose exec db mysql -u redcap -predcap123
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Server version: 5.7.23-log MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>- You can access your webroot at http://localhost or http://127.0.0.1
- If this isn't working, see FAQ below
- You can access your mail via proxy at http://localhost/mail/
- (don't forget the trailing slash)
- You can access your phpMyAdmin via proxy at http://localhost/phpmyadmin/
- (don't forget the trailing slash)
- Some logs (like apache access and cron) are passed through to the docker runtime and can be viewed by calling
docker-compose logsor can be viewed using a gui tool. - Other log files (like mysql slow queries and php_errors.log) are mapped through to a log volume on your computer for
easy monitoring using tools like notepad++ (pc), console (mac), or just
tail -f *from the terminal. - Custom application logs should be written to
/var/log/redcapinside the web image that maps to the$LOG_DIRas configured in the.envfile. - Log rotation can be configured so your log files don't grow too large - see
redcap-overrides/cron/logrotatefor an example.
I can't access my server at http://localhost even though docker is running!
- On some macs, we've seen issues with using the name
localhost. If you are unable to resolve a webpage with http://localhost/ you can try http://127.0.0.1.- On my mac, I have edit the local hosts file and created an entry called
redcap.local. To do this, typesudo open -e /etc/hostsand make the line for 127.0.0.1 look like:127.0.0.1 localhost redcap.localYou should now be able to open up your localhost docker with http://redcap.local
- On my mac, I have edit the local hosts file and created an entry called
I prefer to use http://redcap.local for my local server. On my MAC, I accomplish this by editing my hosts file.
$ cat /etc/hosts
...
127.0.0.1 localhost
...I then modify this to read as:
127.0.0.1 localhost redcap.local
Please note that all commands must be run from the root directory where the docker-compose.yaml file is
located (unless you specify additional parameters).
docker-compose up -d- this will run and detach form the containers leaving them to run in the background. This is the most common way I run these containers. You can view the status and logs from otherdocker-composecommands or from the GUI of docker-compose tools like Kitematicdocker-compose up- this will run the containers in the current window. If you close your window the containers will be stopped. I sometimes do this the first time.docker-compose up -d --force-recreate- This should be run if you modify the .env file or other custom override files and need those changes to be incorporated into the containers -- otherwise your changes will not appear in the running images.docker-compose up -d --no-deps --build <CONTAINER_NAME>- If you just want to rebuild one container and not all of them. Valid names areweb,db,cron,mailpit,phpmyadminandstartup)docker-compose stop- this will stop the docker process (which would be good to do if you want to save battery)docker-compose down- this will stop and remove the containers - meaning the next time you call up they will be recreated (this is similar to the --force-recreate tag)docker-compose down -v- this will stop and remove the containers along with their internal volumes. For example, if you call this any saved email messages would be removed.docker ps- shows you all running containers - see the docker command referencedocker ps -a- shows you all running and stopped containers.
By default, this package uses the www folder in the parent directory to the rdc folder. You can, however, easily point
to a different location by changing the WEBROOT_DIR in the .env file and re-starting with docker-compose up -d
I have seen file permission issues at times when mapping local directories to the docker containers. This is the point
of specifying the APACHE_RUN_USER_ID on MACs.
Yes you can, but you want to make sure they don't clobber each other. The safe way to do this is to make a complete copy of the redcap-docker-compose folder and then modify the rdc/.env file. Each version of the rdc folder must have a different value in the DOCKER_PREFIX variable of the .env file. This will ensure
that the networks and volumes are uniquely named and do not collide. If you want to run both instances simultaneously
you will have to change the ports on one so they are unique, such as 81 for web and 3387 for database.
As of this writing, these ports are defined in .env
WEB_PORT=80
WEB_SSL_PORT=443
MYSQL_PORT=3306
PHPMYADMIN_PORT=8080
When you go to pick port numbers, it is generally safest to pick from the range 1024 - 65535. Each of the values selected for these port numbers needs to be unique to across the running instances.
If you want to run a lot of instances at once, consider a pattern for setting the ports wherein the REDCap version forms the last 3 or 4 digits of the port number while the first digit indicates which of the 4 assignments is which. You could work the DOCKER_PREFIX into the pattern as well. e.g., REDCap 9.4.2 would get these parameters:
DOCKER_PREFIX=rc942
WEB_PORT=1942
MYSQL_PORT=2942
PHPMYADMIN_PORT=3942
You can paste a block of parameters like this at the end of the .env file to override all of the parameters above.
Once you have changed the WEB_PORT to something other than 80, you'll need to append a ":" and the port number to "localhost" in all of URLs examples in this document that use no port number. e.g. Using the above port example, the installation step would require you to visit http://localhost:1942/. The proxy service in the web container would make phpMyAdmin accessible at http://localhost:1942/phpmyadmin/, but it's also accessible at http://localhost:3942 because of the port definition above. Use whichever method works best for you.
Sure. Say you want to test out a new version of PHP and see if your External Module will continue to run.
- The quick way:
-
Modify the
Dockerfileindocker-weband change theFROM: php:7.3-apacheto the version you want to run. You can see a list of options here: docker php -
Execute this one statement from the
rdcdirectory in your terminal (assuming you're already running):docker-compose up -d --no-deps --build web
-
- Alternately, you can stop ALL your services, make changes, and restart. This would go something like:
- Stop your Docker-compose by opening a terminal in the
rdcfolder and runningdocker-compose stop. - Modify the
docker-web/Dockerfileor other changes - Rebuild the modified containers by running
docker-compose build <<CONTAINER NAME>> - Restart all of the containers with
docker-compose up -d
- Stop your Docker-compose by opening a terminal in the
Note: The X-Debug version corresponds to the PHP version. Switching major version of PHP requires the X-Debug to changed. To downgrade from PHP8 to PHP7 X-Debug is downgraded from version 3 to version 2.
To load a specific version of X-Debug, modify the Dockerfile in docker-web and change the RUN yes | pecl install xdebug \ to RUN yes | pecl install xdebug-2.9.8 \.
You can shut down your servers by pressing ctrl-c in the window where you ran docker-compose up. After a few seconds
it should report all are off.
^CGracefully stopping... (press Ctrl+C again to force)
Stopping redcap ... done
This stops your running containers but does not delete them. If you run docker-compose up again, they will resume.
You can remove the containers by docker-compose down or docker-compose rm.
Try restarting again with docker-compose up -d - it should be MUCH faster after the initial load. Adding the -d means
detached so you can close your terminal window and the service will continue to run.
To get a bash shell as root in the redcap server, you can run:
$ docker compose exec web /bin/bash
root@5af71d765e77:/#
# become the apache user instead of root to avoid file permission issues
root@5af71d765e77:/# sudo www-data
www-data@5af71d765e77:~/html$
# Insert a file into the /var/www/html directory to test that it is syncing with my local www folder
www-data@5af71d765e77:~/html$ echo "Hello" > /var/www/html/test.html
# Look at my logs, which should match my log folder on my laptop
www-data@5af71d765e77:~/html$ ls -la /var/log/redcap/
# All done
www-data@5af71d765e77:~/html$ exit
root@5af71d765e77:/# exitKeep in mind any changes you make will be transitory and lost if you ever recreate the container
The command docker ps shows what containers are running. If your server is up, they will appear here.
The command docker ps -a shows all containers regardless of run state.
No, by default the database is stored in a docker volume. You can see the docker volumes with:
andy123 redcap-docker-compose rdc $ docker volume ls
DRIVER VOLUME NAME
local redcap_logs-volume
local redcap_mysql-volume
# Delete a volume (such as your mysql database)
andy123 redcap-docker-compose rdc $ docker volume rm redcap_mysql-volumeIf you remove a container, by default it DOES NOT remove the volumes.
See the question above -- basically the volumes that docker-compose creates are normally not deleted. To really clean
out and restart your docker-compose, you may have to remove them all. You can also remove the network with the
equivalent docker network ls and docker network rm redcap_network
This docker-compose has been tested to work with mySql 8. To make the switch you are going to have to regenerate your mysql database and volume. So, follow these steps:
- Make a backup of your local mysql database. This is most easily done using phpmyadmin.
- Goto http://localhost/phpmyadmin/ (if you don't have phpmyadmin running, make sure it isn't disabled in your docker-compose.yml file.
- Select Export -> Custom -> select redcap -> set compression to gzip -> and press go!
- Stop your database container.
$ docker-compose stop db
- Delete the docker volume that contains your actual database data
$ docker volume ls // Look for the volume like redcap-mysql_volume $ docker volume rm redcap-mysql_volume - Modify the version of mySql you want to run. Goto the mysql docker page: https://hub.docker.com/_/mysql and pick a
version, something like
8.0 - Open the
docker-mysql/Dockerfilein therdcdirectory and change theFROM mysql:5.7to your new versionFROM mysql:8.0 #FROM mysql:5.7 - Now rebuild your mysql image
$ docker-compose build db
- Now run it
$ docker-compose up db -d // Follow the logs if you like... $ docker-compose logs -f - Restore your backup using phpmyadmin. Open http://localhost/phpmyadmin/ Choose IMPORT and then
Choose Fileto select your redcap.sql.gz from step 1.
At this point you should be running your dev server on a new version of mySql. You can use the same process to change your database version anytime.
- How can I use Docker to run various commands against my database?
# SEE THE NETWORK FOR YOUR DOCKER-COMPOSE CONTAINERS (e.g. rdc_default) docker network list # BASIC TEST OF CONNECTION docker run --rm \ --network=rdc_default \ imega/mysql-client \ mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root --execute='show databases;' # GET A SHELL docker run -it \ --network=rdc_default \ --volume $(pwd):/mysqldump \ imega/mysql-client \ /bin/sh # GET A MYSQL SHELL docker run -it \ --network=rdc_default \ --volume $(pwd):/mysqldump \ imega/mysql-client \ mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root # GET A MYSQL DUMP docker run --rm \ --network=rdc_default \ --volume $(pwd):/mysqldump \ imega/mysql-client \ /bin/sh -c "mysqldump --host=db --user=root --password=root redcap > /mysqldump/redcap_backup.sql" # GET A MYSQL DUMP GZIPPED (doing the sh -c seemed necessary as volume wasn't otherwise immediately ready?) docker run --rm \ --network=rdc_default \ --volume $(pwd):/mysqldump \ imega/mysql-client \ /bin/sh -c "mysqldump --host=db --user=root --password=root redcap | gzip > /mysqldump/redcap_backup.sql.gz" # RESTORE A MYSQL DUMP FROM sql.gz FILE docker run -it \ --network=rdc_default \ --volume $(pwd):/mysqldump \ imega/mysql-client \ /bin/sh -c "mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root --execute 'create database if not exists new_db'; gunzip < /mysqldump/redcap_backup.sql.gz | mysql --host=db --user=root --password=root new_db"
How do I run Vanderbilt's static analysis checker Psalm, required when submitting to their EM repo?
With modern REDCap, the scan tool is now built into REDCap's release. When you go to submit to the repository, you will be asked about having run the scanner.
Keep in mind that in order to use the scanning tool with REDCap Docker Compose, you need to execute the scan inside the web container directly. There are two ways to do this:
First get a command prompt for your web container, from the rdc folder:
$ docker compose exec -it web /bin/bash
alternately, you can view all of your docker containers and execute the same command without compose as:
$ docker ps
$ docker exec -it WEB_CONTAINER_ID /bin/bash
You can then install the scan script the first time with:
$ php <redcap-root>/redcap_v13.3.1/ExternalModules/bin/install-scan-script.php
And, finally, execute the scan with:
$ <redcap-root>/bin/scan <path-to-module>
Although, it appears that the scan tool will now auto-install on its own, so the installer might not be necessary.
You can also run the scan from your parent operating system terminal as a larger docker command, such as:
$ docker compose exec -it web /var/www/html/bin/scan modules-lab/realtime_randomization_v9.9.9
or
$ docker exec -it 1dc2023b8753 /var/www/html/bin/scan modules-lab/realtime_randomization_v9.9.9
where 1dc... is the container ID from the docker ps command.
By default, Visual Studio only scans for git repositories in the root directory of your workspace. So, if you have cloned a git repository for an external module into www/modules/my_module_v0.0.0 it will NOT appear as a git module in vsCode by default. This can thankfully be easily fixed.
- Open your vsCode settings (command-comma) and search for
git.repositoryScanMaxDepth- change it from 1 (default) to 3 - Restart your vsCode project and it should now detect the git repos for your EMs.
Funny you should ask! If I am making my own repo from GIT, I will typically create the repo and pull it into my modules folder with:
> cd www/modules
www/modules> git clone [email protected]:123andy/my_external_module.git my_external_module_v0.0.0Note that I use version 0.0.0... This means I'm running off of a git repo and not from a fixed release. After a while, you might end up with a lot of repos in your
modules folder. In order to pull all of them so they are up-to-date with the repo HEAD, I created a script that you can use. First, you can check to see if you
have any repos that need updating from the web browser via http://localhost/debug/update_pull.php -- this will just tell you what, if anything, needs updating.
To actually do the update, you have to execute the command from the command line (because you might need to authenticate to github via ssh and the web container likely
isn't authenticated).
> cd www/debug
www/debug> php update_pull.php // This is a dry run and will not actually do any git pulls
www/debug> php update_pull.php true // This command will run git pull on any behind repo