给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个单词(字符串)列表 words, 返回所有二维网格上的单词 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过 相邻的单元格 内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母在一个单词中不允许被重复使用。
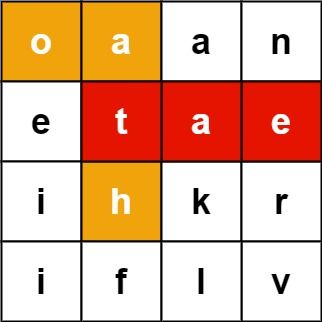
示例 1:
输入:board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"] 输出:["eat","oath"]
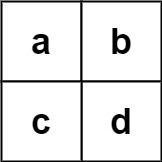
示例 2:
输入:board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"] 输出:[]
提示:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 12board[i][j]是一个小写英文字母1 <= words.length <= 3 * 1041 <= words[i].length <= 10words[i]由小写英文字母组成words中的所有字符串互不相同
方法一:前缀树 + DFS
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.children = [None] * 26
self.w = ''
def insert(self, w):
node = self
for c in w:
idx = ord(c) - ord('a')
if node.children[idx] is None:
node.children[idx] = Trie()
node = node.children[idx]
node.w = w
class Solution:
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
def dfs(node, i, j):
idx = ord(board[i][j]) - ord('a')
if node.children[idx] is None:
return
node = node.children[idx]
if node.w:
ans.add(node.w)
c = board[i][j]
board[i][j] = '0'
for a, b in [[0, -1], [0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and board[x][y] != '0':
dfs(node, x, y)
board[i][y] = c
trie = Trie()
for w in words:
trie.insert(w)
ans = set()
m, n = len(board), len(board[0])
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
dfs(trie, i, j)
return list(ans)class Trie {
Trie[] children = new Trie[26];
String w;
void insert(String w) {
Trie node = this;
for (char c : w.toCharArray()) {
c -= 'a';
if (node.children[c] == null) {
node.children[c] = new Trie();
}
node = node.children[c];
}
node.w = w;
}
}
class Solution {
private Set<String> ans = new HashSet<>();
private int m;
private int n;
private char[][] board;
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
Trie trie = new Trie();
for (String w : words) {
trie.insert(w);
}
m = board.length;
n = board[0].length;
this.board = board;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dfs(trie, i, j);
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(ans);
}
private void dfs(Trie node, int i, int j) {
int idx = board[i][j] - 'a';
if (node.children[idx] == null) {
return;
}
node = node.children[idx];
if (node.w != null) {
ans.add(node.w);
}
char c = board[i][j];
board[i][j] = '0';
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] != '0') {
dfs(node, x, y);
}
}
board[i][j] = c;
}
}class Trie {
public:
vector<Trie*> children;
string w;
Trie()
: children(26)
, w("") { }
void insert(string& w) {
Trie* node = this;
for (char c : w) {
c -= 'a';
if (!node->children[c]) node->children[c] = new Trie();
node = node->children[c];
}
node->w = w;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
vector<string> findWords(vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<string>& words) {
Trie* trie = new Trie();
unordered_set<string> res;
for (auto& w : words) trie->insert(w);
for (int i = 0; i < board.size(); ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].size(); ++j)
dfs(trie, i, j, board, res);
vector<string> ans;
for (auto& w : res) ans.emplace_back(w);
return ans;
}
void dfs(Trie* node, int i, int j, vector<vector<char>>& board, unordered_set<string>& res) {
int idx = board[i][j] - 'a';
if (!node->children[idx]) return;
node = node->children[idx];
if (node->w != "") res.insert(node->w);
char c = board[i][j];
board[i][j] = '0';
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < board.size() && y >= 0 && y < board[0].size() && board[x][y] != '0') dfs(node, x, y, board, res);
}
board[i][j] = c;
}
};type Trie struct {
children [26]*Trie
w string
}
func newTrie() *Trie {
return &Trie{}
}
func (this *Trie) insert(word string) {
node := this
for _, c := range word {
c -= 'a'
if node.children[c] == nil {
node.children[c] = newTrie()
}
node = node.children[c]
}
node.w = word
}
func findWords(board [][]byte, words []string) []string {
trie := newTrie()
for _, w := range words {
trie.insert(w)
}
m, n := len(board), len(board[0])
res := map[string]bool{}
var dfs func(node *Trie, i, j int)
dfs = func(node *Trie, i, j int) {
idx := board[i][j] - 'a'
if node.children[idx] == nil {
return
}
node = node.children[idx]
if node.w != "" {
res[node.w] = true
}
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
c := board[i][j]
board[i][j] = '0'
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && board[x][y] != '0' {
dfs(node, x, y)
}
}
board[i][j] = c
}
for i, row := range board {
for j := range row {
dfs(trie, i, j)
}
}
var ans []string
for v := range res {
ans = append(ans, v)
}
return ans
}