vue-chartjs is a wrapper for Chart.js in vue. You can easily create reuseable chart components.
- v1 later
@legacy- Vue.js 1.x
- v2 later
- Vue.js 2.x
After the final release of vue.js 2, you also get the v2 per default if you install vue-chartjs over npm. No need for the @next tag anymore. If you want the v1 you need to define the version or use the legacy tag. If you're looking for v1 check this branch
Simply run npm install vue-chartjs
You need to import the base chart class and extend it. This gives much more flexibility when working with different data. You can pass the data over props or vue-resource.
You can import the whole package or each module individual.
import VueCharts from 'vue-chartjs'
import { Bar, Line } from 'vue-chartjs'Just create your own component.
// CommitChart.js
import { Bar } from 'vue-chartjs'
export default Bar.extend({
mounted () {
// Overwriting base render method with actual data.
this.renderChart({
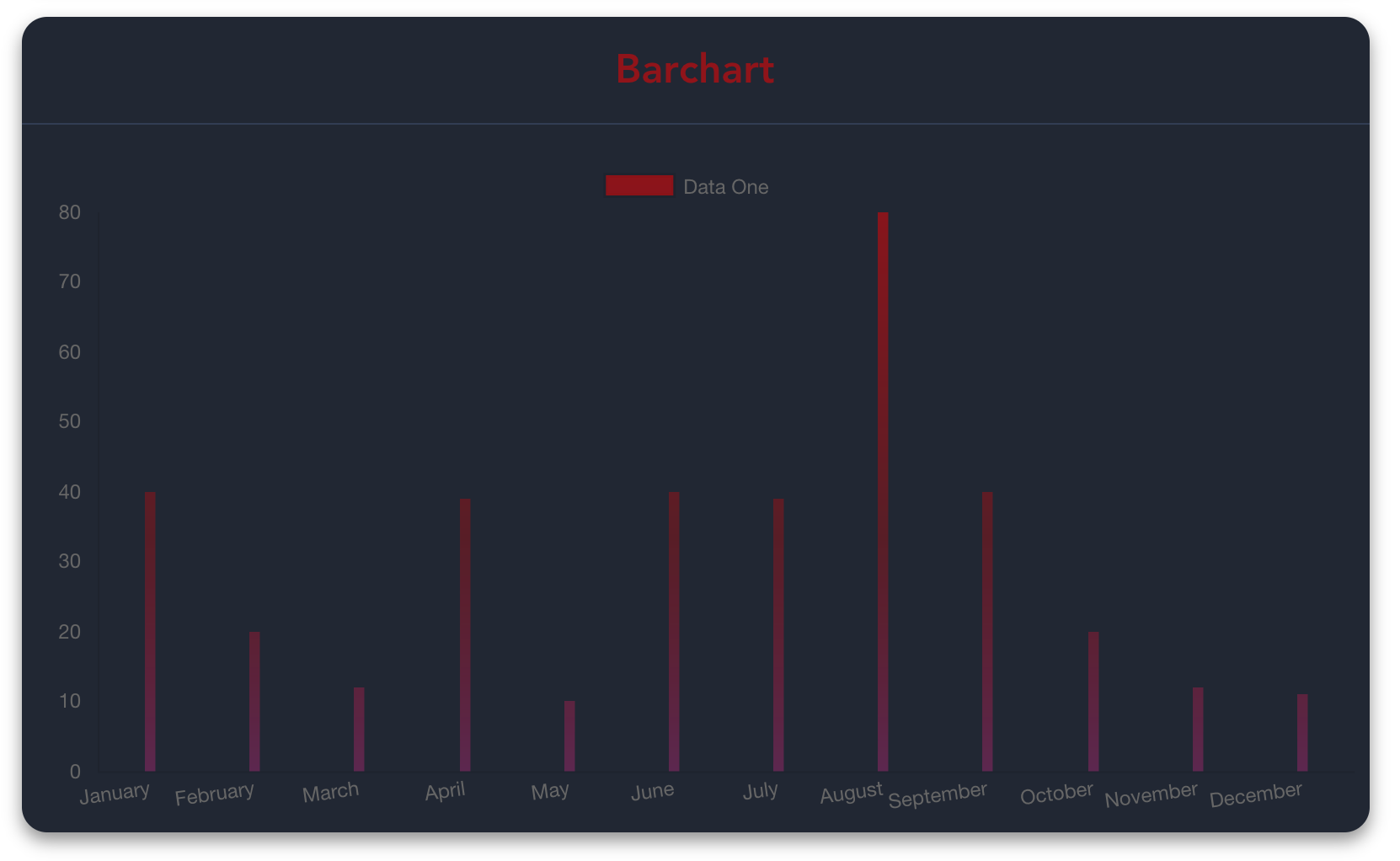
labels: ['January', 'February', 'March', 'April', 'May', 'June', 'July', 'August', 'September', 'October', 'November', 'December'],
datasets: [
{
label: 'GitHub Commits',
backgroundColor: '#f87979',
data: [40, 20, 12, 39, 10, 40, 39, 80, 40, 20, 12, 11]
}
]
})
}
})Then simply import and use your own extended component and use it like a normal vue component
import CommitChart from 'path/to/component/CommitChart'You can overwrite the default chart options. Just pass the options object as a second paramenter to the render method
// MonthlyIncome.js
import { Line } from 'vue-chartjs'
export default Line.extend({
props: ["data", "options"],
mounted () {
this.renderChart(this.data, this.options)
}
})Use it in your vue app
import MonthlyIncome from 'path/to/component/MonthlyIncome'
<template>
<monthly-income :data={....} />
</template>
<script>
export default {
components: { MonthlyIncome },
....
}
</script>Chart.js does not update or re-render the chart if new data is passed. However you can simply implement this by your own or use one of the two mixins which are included.
reactivePropreactiveData
Both are included in the mixins module.
The mixins automatically create chartData as a prop or data. And add a watcher. If data has changed, the chart will update.
However keep in mind the limitations of vue and javascript for mutations on arrays and objects. More info here
// MonthlyIncome.js
import { Line, mixins } from 'vue-chartjs'
export default Line.extend({
mixins: [mixins.reactiveProp],
props: ["chartData", "options"],
mounted () {
this.renderChart(this.chartData, this.options)
}
})The mixins module is included in the VueCharts module and as a seperate module.
Some ways to import them:
// Load complete module with all charts
import VueCharts from 'vue-chartjs'
export default VueCharts.Line.extend({
mixins: [VueCharts.mixins.reactiveProp],
props: ["chartData", "options"],
mounted () {
this.renderChart(this.chartData, this.options)
}
})// Load speperate modules
import { Line, mixins } from 'vue-chartjs'
export default Line.extend({
mixins: [mixins.reactiveProp],
props: ["chartData", "options"],
mounted () {
this.renderChart(this.chartData, this.options)
}
})// Load speperate modules with destructure assign
import { Line, mixins } from 'vue-chartjs'
const { reactiveProp } = mixins
export default Line.extend({
mixins: [reactiveProp],
props: ["chartData", "options"],
mounted () {
this.renderChart(this.chartData, this.options)
}
})If you use import VueCharts from 'vue-chartjs' you will mostly import the UMD build of vue-chart.js
This is because of compatibility reasons. This approach however has a downside: vue.js and chart.js are bundled into the file.
And you end up with two vue instances.
If you're using webpack 2 however, it will automatically import the transpiled ES sources. If you know what you're doing you can import directly from the transpiled es sources:
import { Line } from 'vue-chartjs/es'
# install dependencies
npm install
# serve with hot reload at localhost:8080
npm run dev
# build for production with minification
npm run build
# run unit tests
npm run unit
# run e2e tests
npm run e2e
# run all tests
npm testFor detailed explanation on how things work, checkout the guide and docs for vue-loader.
- Fork it ( https://github.com/apertureless/vue-chartjs/fork )
- Create your feature branch (
git checkout -b my-new-feature) - Commit your changes (
git commit -am 'Add some feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin my-new-feature) - Create a new Pull Request
This software is distributed under MIT license.