EIP-6551 enhances the features of NFTs (ERC-721 tokens) by giving each token its own smart contract account, also known as token-bound accounts (TBA). These smart contract accounts equip NFTs with the ability to operate like traditional blockchain wallets, allowing state changes and features such as holding ERC-20 tokens, other NFTs, and ether. Programmable accounts open up a myriad of use cases, limited only by the developer's imagination and the protocol's constraints.
Importantly, EIP-6551 is backwards compatible and doesn't mandate custom logic within the NFT smart contract. This compatibility allows NFT projects that were created before the introduction of EIP-6551 to adopt smart contract accounts via a permissionless registry.
- Gaming - A character, represented as an NFT, can possess its own inventory (like weapons, gold, etc.) using a smart wallet
- Investing - Utilize NFTs and their smart contract accounts to organize assets and sell entire investment portfolios in a single transaction
- Social (DAOs) - NFTs representing DAO membership can now maintain their own transaction history
This guide demonstrates how to create and interact with three smart contracts:
- An ERC-721 smart contract that serves as our NFT.
- A registry contract that deploys smart contract account associated with a given ERC-721 and computes the token bound account address.
- A token bound account contract that can send and receive ether and other ERC-20 tokens.
We will use a few tools to write and deploy our smart contracts:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Hardhat | Helps deploy and interact with smart contracts |
| Node.js | Developer environment |
| OpenZeppelin | An open library for building secure smart contracts |
| Coinbase Wallet | Non-custodial wallet for creating accounts and interacting with the blockchain |
We will be deploying these smart contracts on the Base Goerli testnet allowing us to see transaction information on BaseScan.
Using a testnet requires us to obtain testnet funds from a faucet to deploy and interact with our smart contracts on that network.
Warning: This demo requires the use of private keys in order to effectively interact with the blockchain. For this demo, use newly created wallets as a safety measure.
Depending on system settings your wallet may look different
Open the Coinbase Wallet browser extension then click on the Settings tab
Select "Developer Settings"
Click on the Settings tab
Select "Networks"
Select "Testnets" tab
Click on the water (💧) icon
Request testnet funds
Alternatively, use the base faucet
Clone this repo
git clone https://github.com/base-org/guides.gitChange into the directory
cd base-guides/6551Initiate a node project and install dependencies:
The dependencies in this project are as follows:
| Dependencies | Description |
|---|---|
| hardhat | Helps deploy and interact with smart contracts |
| hardhat-toolbox | Bundles all the commonly used packages and Hardhat plugins we recommend to start developing with Hardhat. |
| dot-env | Dotenv is a zero-dependency module that loads environment variables from a .env file into process.env |
| openzeppelin/contracts | A library for secure smart contract development. |
Install them by running:
npm installAssuming you have set up your wallet (and safely stored away your seed phrase) and have some funds (testnet or mainnet), obtain the addresses and private keys needed for the demo.
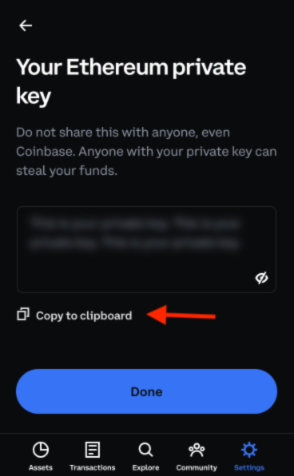
Do not share your private key with anyone.
Click on the Settings tab
Select "Developer Settings"
Click on "Show private key"
Enter password
Read disclaimer to copy address
Type the following command into your terminal application:
export WALLET_KEY=Paste the private key after export WALLET_KEY= within your terminal
Your terminal should look like this
export WALLET_KEY=0xde9be858da4a475276426320d5e9262ecfc3ba460bfac56360bfa6c4c28b4ee0Press enter/return on your keyboard to save the value
Verify your private key has been saved:
echo $WALLET_KEYSample output:
0xde9be858da4a475276426320d5e9262ecfc3ba460bfac56360bfa6c4c28b4ee0Note: Each account will need funds in order to deploy contracts and interact with Base.
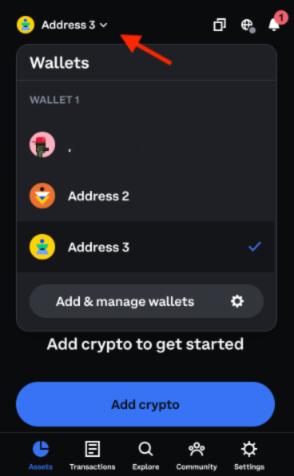
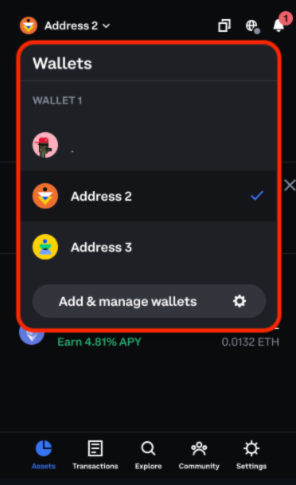
From the assets tab, click on the current address/account
Select another wallet/account
If you do not have an additional account click the "Add & manage wallets" button to create a new account.
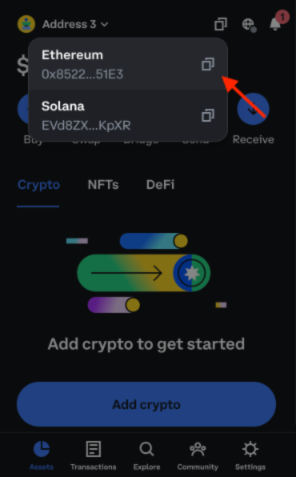
Copy the address of the newly selected account
Type the following command into your terminal application
Your terminal should look like this:
export WALLET2_ADDR=Paste the address as an environment variable within your terminal
export WALLET2_ADDR=0xf39Fd6e51aad88F6F4ce6aB8827279cffFb92266Press enter/return on your keyboard to save the value
Verify the account address has been saved:
echo $WALLET2_ADDRSample output:
0xf39Fd6e51aad88F6F4ce6aB8827279cffFb92266Save the private key of the currently selected account
Each account has its own private key.
This wallet will be the original owner of the NFT minted later in this tutorial. You will need the private key of the currently selected wallet in order to transfer the ownership of the NFT.
Refer to the previous steps for obtaining and copying your private keys and save them as an environment variable WALLET2_KEY using your terminal.
Example:
export WALLET2_KEY=0x5de4111afa1a4b94908f83103eb1f1706367c2e68ca870fc3fb9a804cdab365aVerify your private key has been saved:
echo $WALLET2_KEYSample output:
0x5de4111afa1a4b94908f83103eb1f1706367c2e68ca870fc3fb9a804cdab365aThe following script will deploy three smart contracts and save their deployment information in a file called deploymentData.json.
Once you become comfortable deploying contracts on a testnet, you may deploy contracts on the Base mainnet by replacing --network base-goerli with --network base-mainnet .
npx hardhat run scripts/01_deploy_contracts.js --network base-goerli
ERC-721 Contract deployed at: 0xECD4b1C01a0aF70C7Ee985db389E294D01DffEC0
Saved deployment data to a new file: deploymentData.json
Deployed registry contract at: 0x58B2EAe6f05abf9C1e1566AD9307C67B41627A1e[
{
NftContract: {
address: '0xECD4b1C01a0aF70C7Ee985db389E294D01DffEC0',
deployer: '0xB6d00D83158feE6695C72ff9c5E915478A465724',
deploymentHash: '0xedacc11c5268b155a9a6918b5e1cc19031343f41519f596eb264ef6ca3feaeb4'
}
},
{
ERC6551Registry: {
address: '0x58B2EAe6f05abf9C1e1566AD9307C67B41627A1e',
deployer: '0xB6d00D83158feE6695C72ff9c5E915478A465724',
deploymentHash: '0xcf45022f97e682eccc87c903c6eff38ba2c080aeb69c69da4662914aacf4f481'
}
}
] Deployment data saved to: deploymentData.json
Deploying Token Bound Account
Token bound account deployed at: 0xdAcaEDF79Fa33405446F2B9Fbf820Cef84507f22[
{
NftContract: {
address: '0xECD4b1C01a0aF70C7Ee985db389E294D01DffEC0',
deployer: '0xB6d00D83158feE6695C72ff9c5E915478A465724',
deploymentHash: '0xedacc11c5268b155a9a6918b5e1cc19031343f41519f596eb264ef6ca3feaeb4'
}
},
{
ERC6551Registry: {
address: '0x58B2EAe6f05abf9C1e1566AD9307C67B41627A1e',
deployer: '0xB6d00D83158feE6695C72ff9c5E915478A465724',
deploymentHash: '0xcf45022f97e682eccc87c903c6eff38ba2c080aeb69c69da4662914aacf4f481'
}
},
{
ERC6551Account: {
address: '0xdAcaEDF79Fa33405446F2B9Fbf820Cef84507f22',
deployer: '0xB6d00D83158feE6695C72ff9c5E915478A465724',
deploymentHash: '0xbfe9ab08951e07660c2d3a6e9b16e6e959a174530f1e28aba9c98a19c381f586'
}
}
]Deployment data saved to: deploymentData.jsonThis script will mint an NFT and assign its ownership to the WALLET2_ADDR account
npx hardhat run scripts/02_mint_nft.js --network --network base-goerli0xECD4b1C01a0aF70C7Ee985db389E294D01DffEC0
Minting NFT...
TokenId 0 is owned by address: 0x9eEd71442F60440b39Def927047e5823c0b208D4This script will create and compute the address for a smart contract wallet (token bound account)
npx hardhat run scripts/03_create_account.js --network base-goerliComputed Address: 0xA5153E5D9A384e519fEa64D228797edb4a448d45
This script will send funds from WALLET_KEY to the token bound account and transfer ownership of the NFT from WALLET2_ADDR to WALLET_KEY.
npx hardhat run scripts/04_account_interaction.js --network base-goerliCurrent owner of tokenId 0 is 0x9eEd71442F60440b39Def927047e5823c0b208D4
Token account has 0 ETH
New owner of tokenId 0 is 0xB6d00D83158feE6695C72ff9c5E915478A465724
Token account has 12500000000000000 ETH
Clear the private keys from your environment variables by running this command:
export WALLET_KEY=nil
export WALLET2_KEY=nil