VSL is a Scientific Library with a great variety of different modules. Although most modules offer pure-V definitions, VSL also provides modules that wrap known C libraries that allow high performance computing as an alternative.
Visit vsl docs to know more about the supported features.
This library contains essential functions for linear algebra computations (operations between all combinations of vectors and matrices, eigenvalues and eigenvectors, linear solvers) and the development of numerical methods (e.g. numerical quadrature).
Optionally, we link VSL with existent libraries written in C and Fortran, such as Open BLAS and LAPACK. These existing libraries have been fundamental for the development of high-performant simulations over many years. We believe that it is possible to rewrite these libraries in native V and at the same time achieve the same speed delivered by them, but at the same time, we want to allow to the users of VSL the possibility to choose when to use these libraries as backend and when not. That is why each module documents the flags that allow this at the time of use.
It is possible to optimize certain modules using different backends. For this there are some C dependencies that can be installed optionally. If you want to use these C dependencies and other libraries, the easiest way to work with VSL is via Docker. Having Docker and VS Code installed, you can start developing powerful numerical simulations using VSL in a matter of seconds. Furthermore, the best part of it is that it works on Windows, Linux, and macOS out of the box.
- Install Docker
- Install Visual Studio Code
- Install the Remote Development extension for VS Code
- Clone https://github.com/ulises-jeremias/hello-vsl
- Create your application within a container (see gif below)
Done. And your system will remain "clean".
Our Docker Image also contains V and the V Tools for working with VS Code (or not). Below is a video showing the convenience of VS Code + the V tools + VSL.
It is enough to use the so convenient v install or vpkg get functionality for installing VSL.
Anyways, it is possible to optimize certain modules using different backends.
For this there are some C dependencies that can be installed optionally.
If you want to use these C dependencies and other libraries,
first we need to install some dependencies in order to
have VSL working as expected with these backends.
Debian/Ubuntu GNU Linux
libopenblas-dev is not needed when using the pure V backend.
$ sudo apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends \
gcc \
gfortran \
liblapacke-dev \
libopenblas-dev \
libssl-dev \Arch Linux/Manjaro GNU Linux
$ sudo pacman -S opensslThe best way of installing OpenBlas/LAPACK is using openblas-lapack.
$ yay -S openblas-lapackor
$ git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/openblas-lapack.git /tmp/openblas-lapack
$ cd /tmp/openblas-lapack
$ makepkg -siVia vpm
$ v install vslVia vpkg
$ vpkg get https://github.com/vlang/vslDone. Installation completed.
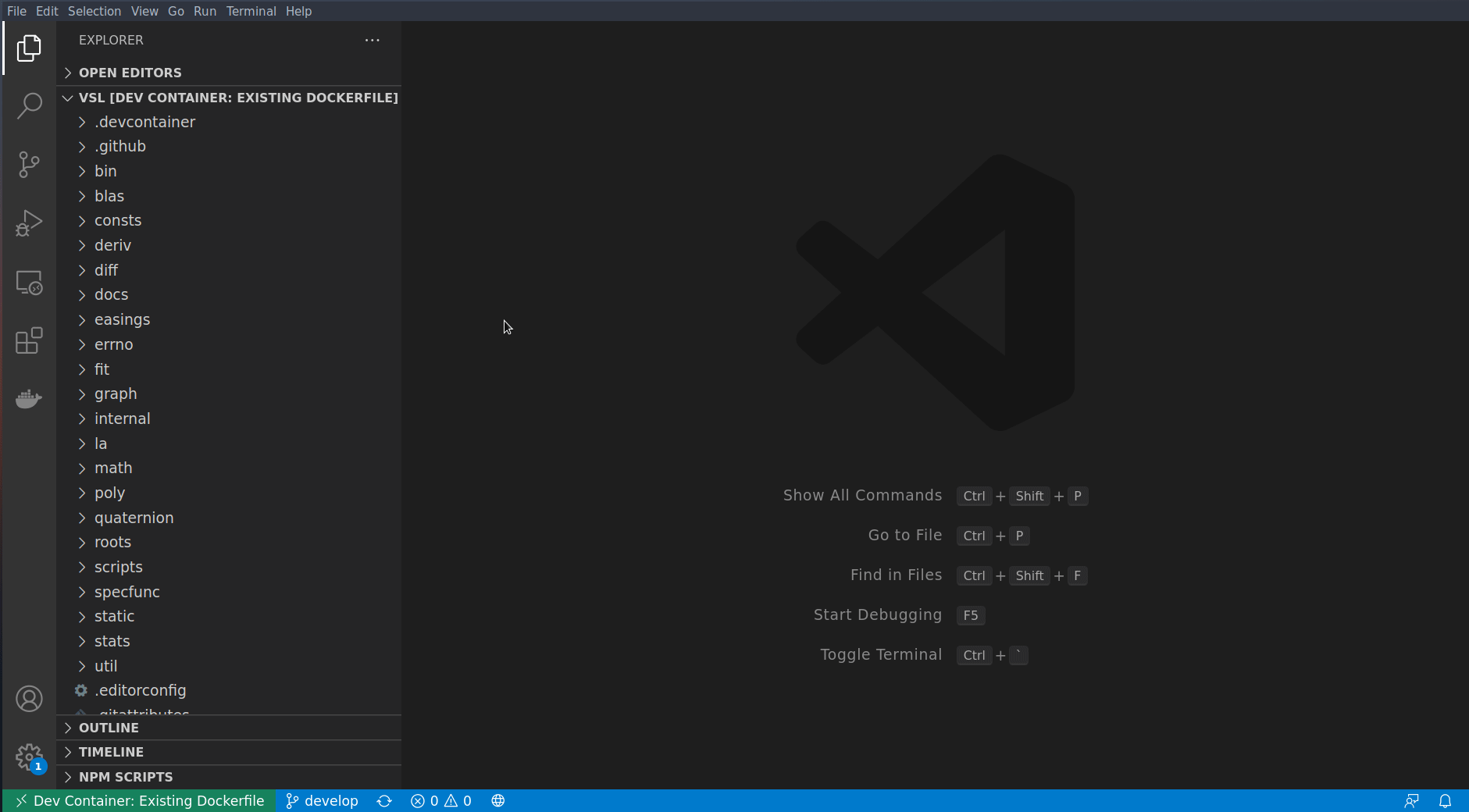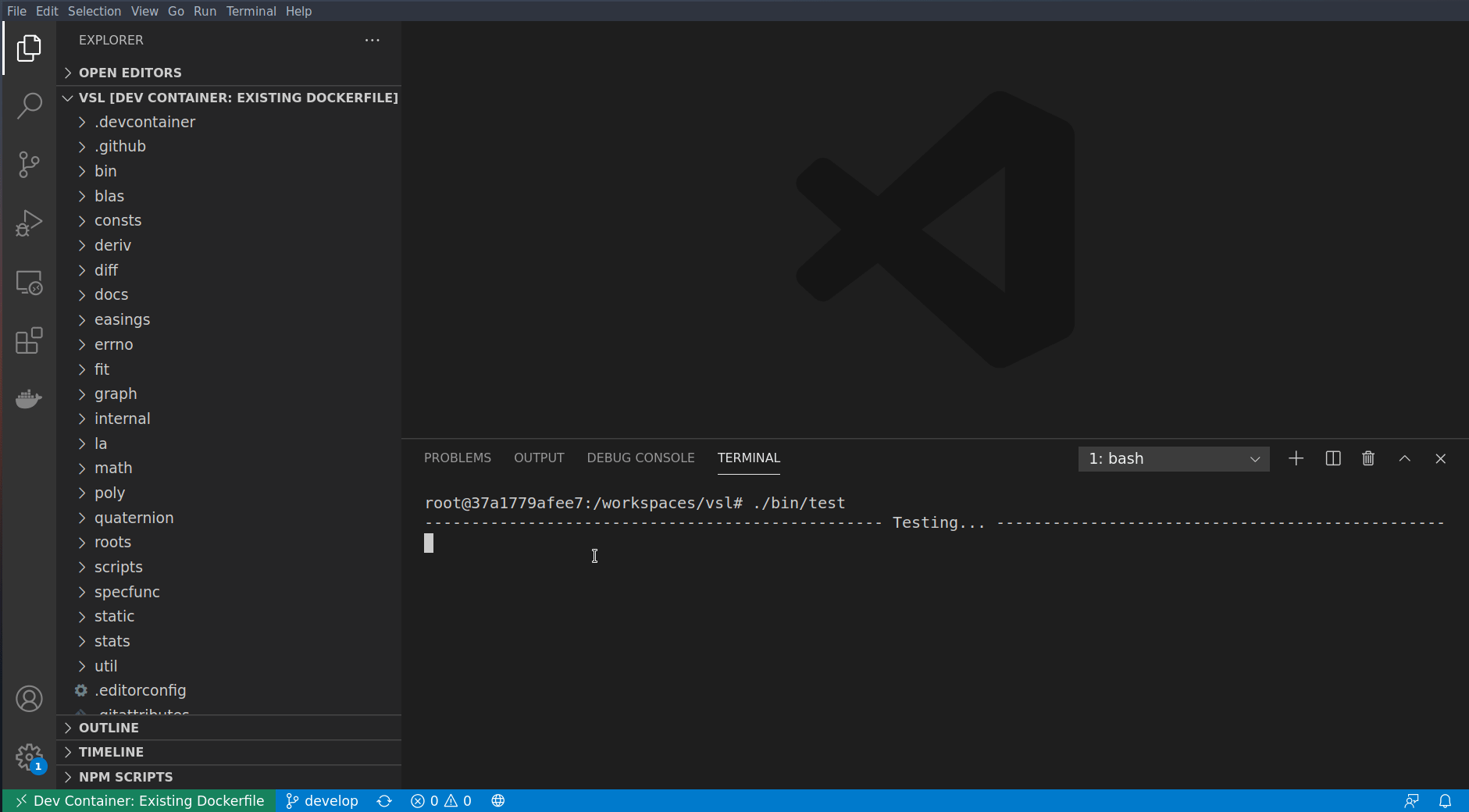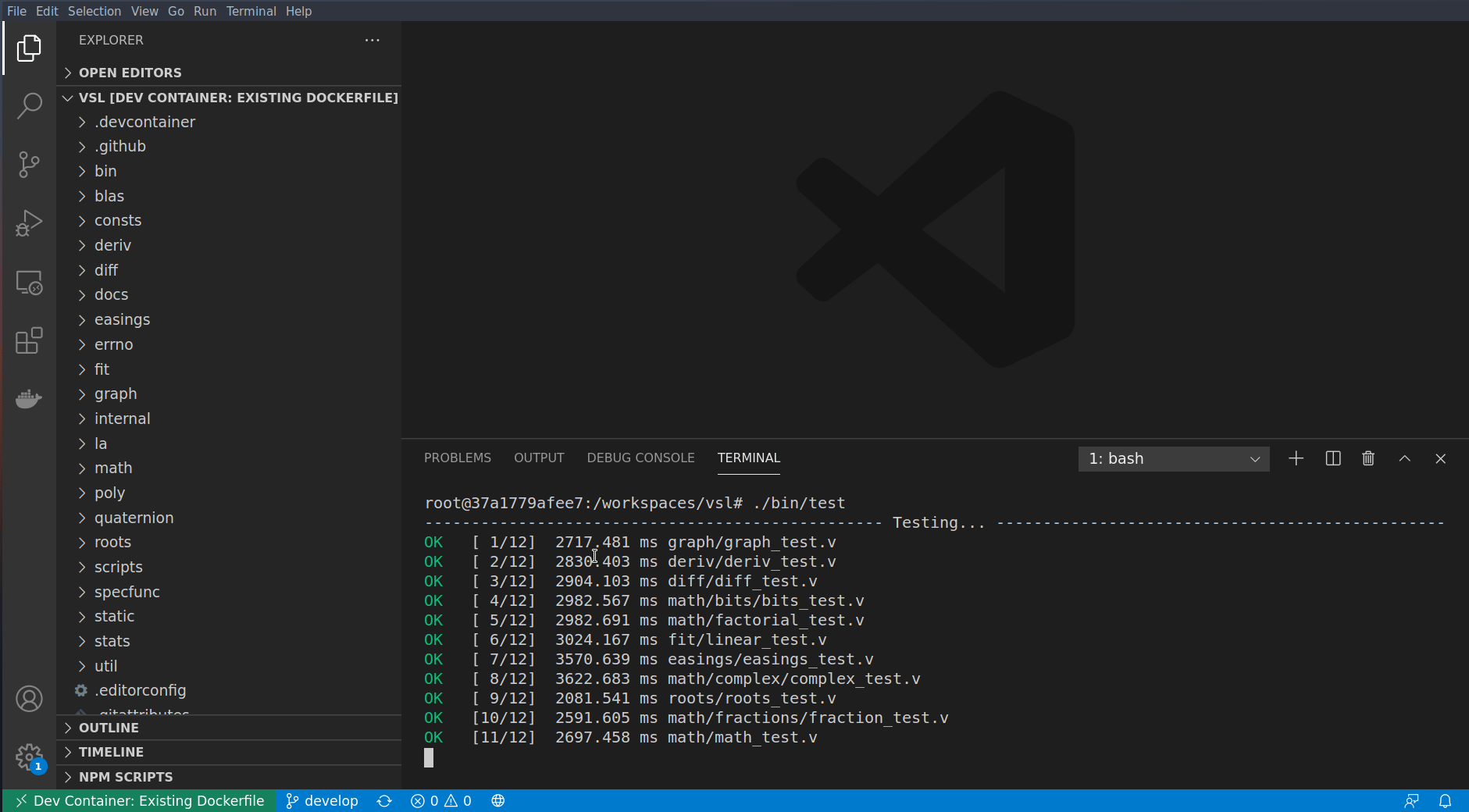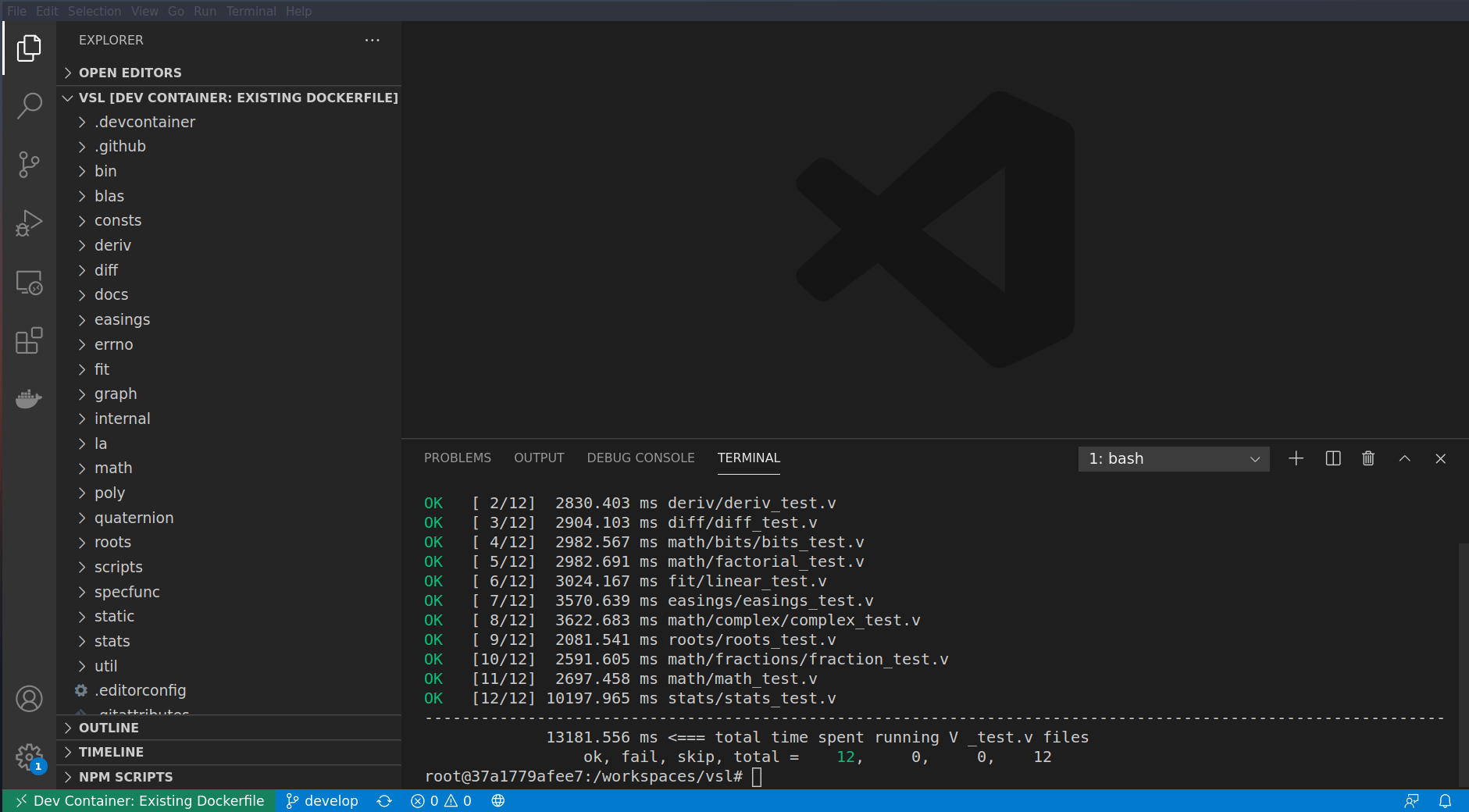
To test the module, just type the following command:
$ ./bin/test # execute `./bin/test -h` to know more about the test commandMade with contributors-img.