| title | description | author | ms.author | ms.date | ms.topic | ms.service | services | ms.custom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Use Visual Studio and Visual Studio Code to build IoT Plug and Play Preview devices | Microsoft Docs |
Use Visual Studio and Visual Studio Code to accelerate authoring IoT Plug and Play device models and implementing the device code. |
liydu |
liydu |
12/26/2019 |
conceptual |
iot-pnp |
iot-pnp |
mvc |
The Azure IoT Tools for Visual Studio Code provides an integrated environment to author device capability models (DCM) and interfaces, publish to model repositories, and generate skeleton C code to implement the device application.
This article shows you how to:
- Generate device code and application project.
- Use the generated code in your device project.
- Iterate by regenerating the skeleton code.
To learn more about using the VS Code to develop IoT devices, see https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-iot-workbench.
Install Visual Studio Code.
Use the following steps to install the extension pack in VS Code.
- In VS Code, select Extensions tab.
- Search for and install Azure IoT Tools from the marketplace.
In VS Code, use Ctrl+Shift+P to open the command palette, enter IoT Plug and Play, and select Generate Device Code Stub to configure the skeleton code and project type. The following list describes each step in detail:
-
DCM file to be used for generating the code. To generate the skeleton device code, open the folder that contains the DCM and interface files it implements. If the code generator can't find an interface that a DCM requires, it downloads it from the model repository as needed.
-
Device code language. Currently, the code generator only supports ANSI C.
-
Project name. The project name is used as the folder name for the generated code and other project files. The folder is, by default, placed next to the DCM file. To avoid having to manually copy the generated code folder whenever you update your DCM and regenerate the device code, keep your DCM file in the same folder as the project folder.
-
Method to connect to Azure IoT. The generated files also contain code to configure the device to connect to Azure IoT Hub. You can choose to connect directly to Azure IoT Hub or use the Device Provisioning Service.
- Via IoT Hub device connection string: specify the device connection string for the device application to connect to IoT Hub directly.
- Via DPS symmetric key: specify the ID Scope, Symmetric Key and Device ID for the device application that are required to connect to IoT Hub or IoT Central using DPS.
-
Project type. The code generator also generates a CMake or Arduino project. Currently, the supported project types are:
- CMake Project on Windows: for a device project that uses CMake as build system on Windows. This option generates
CMakeLists.txtwith device SDK configurations in the same folder as the C code. - CMake Project on Linux: for a device project that uses CMake as build system on Linux. This option generates
CMakeLists.txtwith device SDK configurations in the same folder as the C code. - MXChip IoT DevKit project: for a device project that runs on an MXChip IoT DevKit device. This option generates an Arduino project that you can use in VS Code or in the Arduino IDE to build and run on an IoT DevKit device.
- CMake Project on Windows: for a device project that uses CMake as build system on Windows. This option generates
-
Device SDK type. If you select CMake as project type, this is the step to configure how generated code will include Azure IoT C device SDK in the
CMakeLists.txt:- Via Source Code: the generated code relies on the device SDK source code to include in and build together with it. This is recommended when you have customized the device SDK source code.
- Via Vcpkg: the generated code relies on the device SDK Vcpkg to include in and build together with it. This is the recommended way for devices running Windows, Linux or macOS.
[!NOTE] macOS support for Azure IoT C device SDK Vcpkg is working in progress.
The code generator tries to use DCM and interface files located in the local folder. If the interface files aren't in the local folder, the code generator looks for them in the public model repository or company model repository. Common interface files are stored in the public model repository.
After code generation finishes, the extension opens a new VS Code window with the code. If you open a generated file such as main.c, you may find that IntelliSense reports that it can't open the C SDK source files. To enable the correct IntelliSense and code navigation, use the following steps to include the C SDK source:
-
In VS Code, use Ctrl+Shift+P to open the command palette, type and select C/C++: Edit Configurations (JSON) to open the c_cpp_properties.json file.
-
Add the path of the device SDK in the
includePathsection:"includePath": [ "${workspaceFolder}/**", "{path_of_device_c_sdk}/**" ]
-
Save the file.
The following instructions describe how to use the generated code in your own device project on different development machine platforms. The instructions assume you're using an IoT Hub device connection string with the generated code:
To build the device code together with the device C SDK Vcpkg using CMake in a Linux environment such as Ubuntu or Debian:
-
Open a terminal application.
-
Install GCC, Git,
cmake, and all dependencies using theapt-getcommand:sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y git cmake build-essential curl libcurl4-openssl-dev libssl-dev uuid-dev
Verify the version of
cmakeis above 2.8.12 and the version of GCC is above 4.4.7.cmake --version gcc --version
-
Install Vcpkg:
git clone https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg.git cd vcpkg ./bootstrap-vcpkg.shThen, to hook up user-wide integration, run:
./vcpkg integrate install
-
Install Azure IoT C device SDK Vcpkg:
./vcpkg install azure-iot-sdk-c[public-preview,use_prov_client]
-
Create a
cmakesubdirectory in the folder contains the generated code stub, and navigate to that folder:mkdir cmake cd cmake -
Run the following commands to use CMake to build the device SDK and the generated code stub:
cmake .. -Duse_prov_client=ON -Dhsm_type_symm_key:BOOL=ON -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE="{directory of your Vcpkg repo}/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmake" cmake --build .
-
After the build succeeds, run the application specifying the IoT Hub device connection string as parameter.
./{generated_code_project_name} "[IoT Hub device connection string]"
To build the device code together with the device C SDK on Windows using CMake and the Visual Studio C/C++ compilers at the command line, see the IoT Plug and Play quickstart. The following steps show you how to build the device code together with the device C SDK Vcpkg as CMake project in Visual Studio.
-
Follow the steps in the quickstart to install the Azure IoT device SDK for C via Vcpkg.
-
Install Visual Studio 2019 (Community, Professional, or Enterprise) - make sure that you include the NuGet package manager component and the Desktop Development with C++ workload.
-
Open Visual Studio, choose File > Open > CMake... to open the
CMakeLists.txtin the folder contains generated code. -
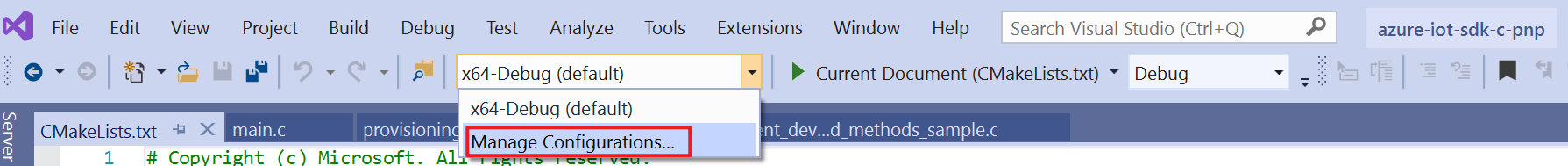
In the General toolbar, find the Configurations dropdown. Select Manage Configuration to add the CMake setting for your project.
-
In the CMake Settings, add a new configuration and select x86-Debug as target.
-
In CMake Command Arguments, add following line:
-Duse_prov_client=ON -Dhsm_type_symm_key:BOOL=ON
-
Save the file.
-
Switch to x86-Debug in the Configurations dropdown. It needs a few seconds for the CMake to generate the cache for it. View the Output window to see the progress.
-
In the Solution Explorer, right-click on the
CMakeLists.txtin the root folder, and select Build from the context menu to build the generated code stub with the device SDK. -
After the build succeeds, at the command prompt, run the application specifying the IoT Hub device connection string as a parameter.
.\out\build\x86-Debug\{generated_code_project_name}.exe "[IoT Hub device connection string]"
Tip
To learn more about using CMake in Visual Studio, see Build CMake project .
The following steps show you how to build the device code together with the device C SDK source code on macOS using CMake:
-
Open terminal application.
-
Use Homebrew to install all the dependencies:
brew update brew install git cmake pkgconfig openssl ossp-uuid
-
Verify that CMake is at least version 2.8.12:
cmake --version
-
Patch CURL to the latest version available.
-
In the folder that contains the generated code, clone the Azure IoT C SDK repository:
git clone https://github.com/Azure/azure-iot-sdk-c --recursive -b public-preview
You should expect this operation to take several minutes to complete.
-
Create a folder called
cmakeunder the folder that contains the generated code, and navigate to that folder.mkdir cmake cd cmake -
Run the following commands to use CMake to build the device SDK and the generated code stub:
cmake -Duse_prov_client=ON -Dhsm_type_symm_key:BOOL=ON -DOPENSSL_ROOT_DIR:PATH=/usr/local/opt/openssl .. cmake --build . -
After the build succeeds, run the application specifying the IoT Hub device connection string as parameter.
cd {generated_code_folder_name}/cmake/ ./{generated_code_project_name} "[IoT Hub device connection string]"
The code generator can regenerate the code if you update your DCM or interface files. Assuming you already generated your device code from a DCM file, to regenerate the code:
-
With the folder with DCM files open, use Ctrl+Shift+P to open the command palette, enter IoT Plug and Play, and select Generate Device Code Stub.
-
Choose the DCM file you updated.
-
Select Re-generate code for {project name}.
-
The code generator uses the previous setting you configured and regenerates the code. However, it doesn't overwrite the files that may contain user code such as
main.cand{project_name}_impl.c.
Note
If you update the URN id in your interface file, it's treated as a new interface. When you re-generate the code, the code generator generates code for interface but doesn't overwrite the original one in the {project_name}_impl.c file.
Azure IoT Tools is an open-sourced project on GitHub. For any issues and feature requests, you can create an issue on GitHub.
In this how-to article, you've learned how to use the Visual Studio and Visual Studio Code to generate skeleton C code to implement the device application. A suggested next step is to learn how to Install and use Azure IoT explorer tool.