English|中文
Website: openp2p.cn
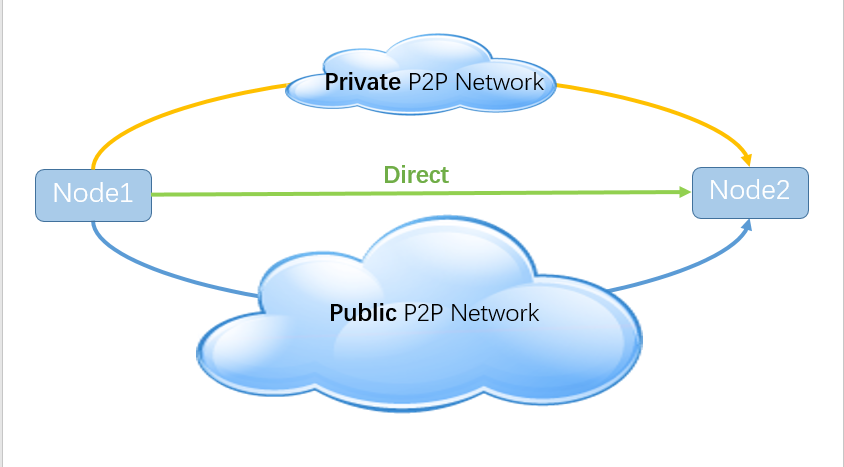
It is an open source, free, and lightweight P2P sharing network. Your devices will form a private P2P network, in which devices can directly access other members, or indirectly access through other members forwarding data. If the private network cannot complete the communication, it will go to the public P2P network to find a shared node to assist in the communication. Compared with the BT network used to share files, the OpenP2P network is used to share bandwidth. Our goal is to make full use of bandwidth, use shared nodes to relay data, and build a common infrastructure for remote connections.
Totaly free, fullfills most of users(especially free-rider). Unlike other similar products, OpenP2p doesn't need a server with public IP, and doesn't need to pay for services.By understanding its principle, you can understand why it can be done for free.
Your devices will form a private P2P network, share bandwidth between them, and provide network data forwarding services. When there is no node that can provide forwarding services in your private P2P network, you will try to find forwarding nodes in the public P2P network. 10mbps is its default setting of share speed limit. Only when you have shared their nodes, you are allowed to use others' shared nodes. This is very fair, and it is also the original intention of this project. We recommend that you join a shared network in a place with sufficient bandwidth (such as an office or home with 100M optical fiber). If you are not willing to contribute any node to the OpenP2P share network, please refer to the usage for your own setting.
The code is open source, the P2P tunnel uses TLS1.3+AES double encryption, and the shared node temporarily authorizes the use of the TOTP one-time password
2MB+ filesize, 2MB+ memory. It runs at appllication layer, no vitrual NIC, no kernel driver.
Benefit from lightweight, it easily supports most of major OS, like Windows, Linux, MacOS, also most of CPU architecture, like 386、amd64、arm、arm64、mipsle、mipsle64、mips、mips64.
P2P direct connection lets your devices make good use of bandwidth. Your device can be connected in any network environments, even supports NAT1-4 (Cone or Symmetric),UPNP,IPv6. Relying on the excellent congestion algorithm of the Quic protocol, high bandwidth and low latency can be obtained in a bad network environment.
Your applicaiton can call OpenP2P with a few code to make any internal networks communicate with each other.
Just 4 simple steps to use. Here's an example of remote work: connecting to an office Windows computer at home.
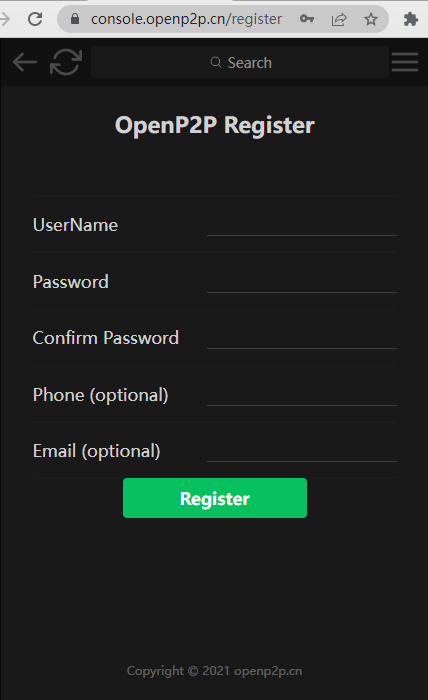
Go to https://console.openp2p.cn register a new user
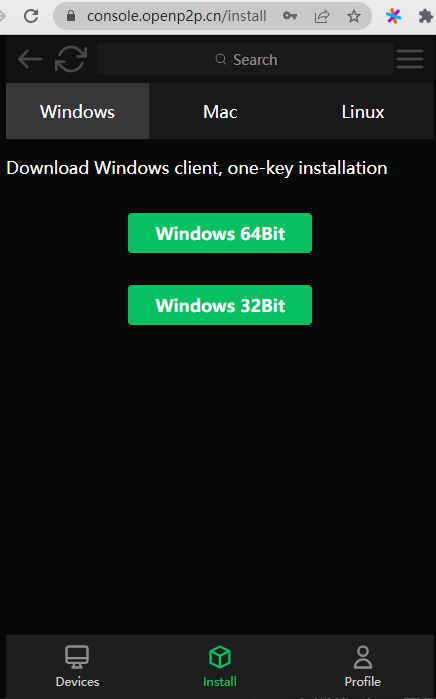
Download on local and remote computers and double-click to run, one-click installation
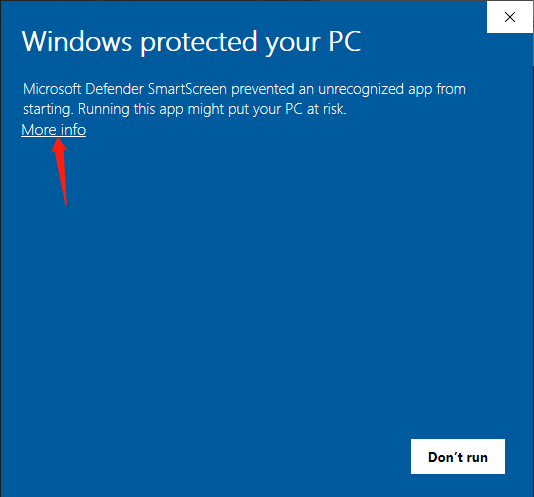
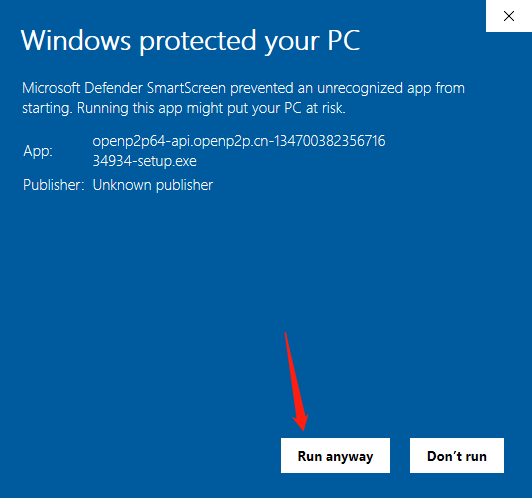
By default, Windows will block programs that have not been signed by the Microsoft's certificate, and you can select "Run anyway".
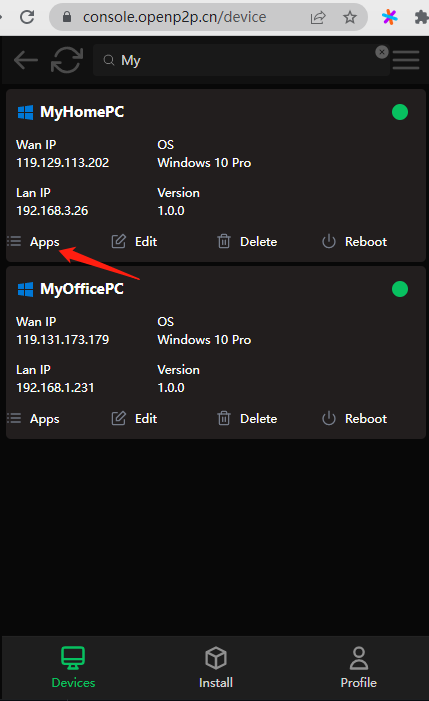
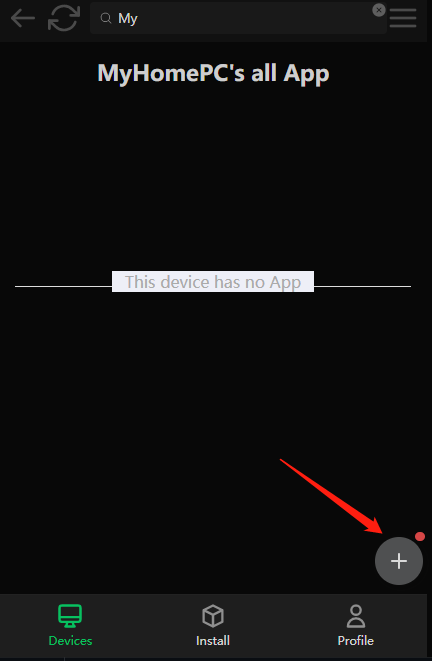
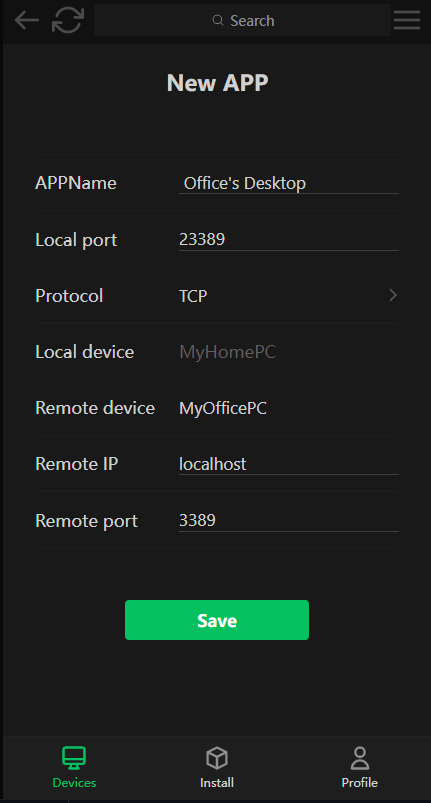
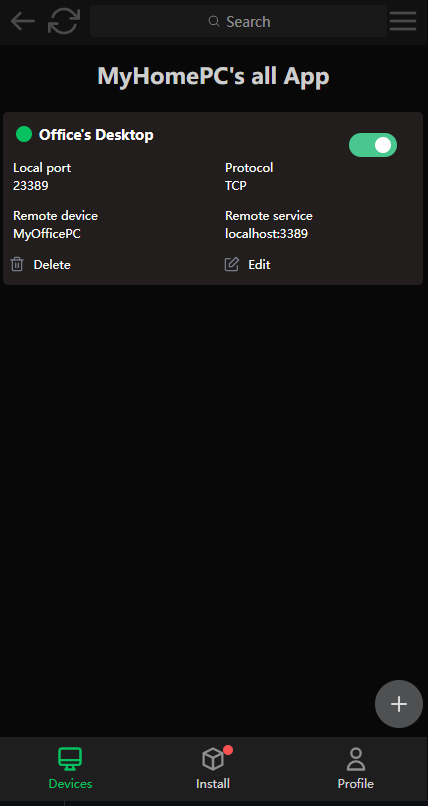
You can see the P2P application you just created on the "MyHomePC" device, just connect to the "local listening port" shown in the figure below.
On MyHomePC, press Win+R and enter MSTSC to open the remote desktop, input 127.0.0.1:23389 /admin
Here describes how to run manually
Especially suitable for large traffic intranet access.
- Remote work: Windows MSTSC, VNC and other remote desktops, SSH, various ERP systems in the intranet
- Remote access ERP systems in the intranet
- Remote access NAS: Manage a large number of videos and pictures
- Remote access camera
- Remote flashing phone
- Remotely data backup
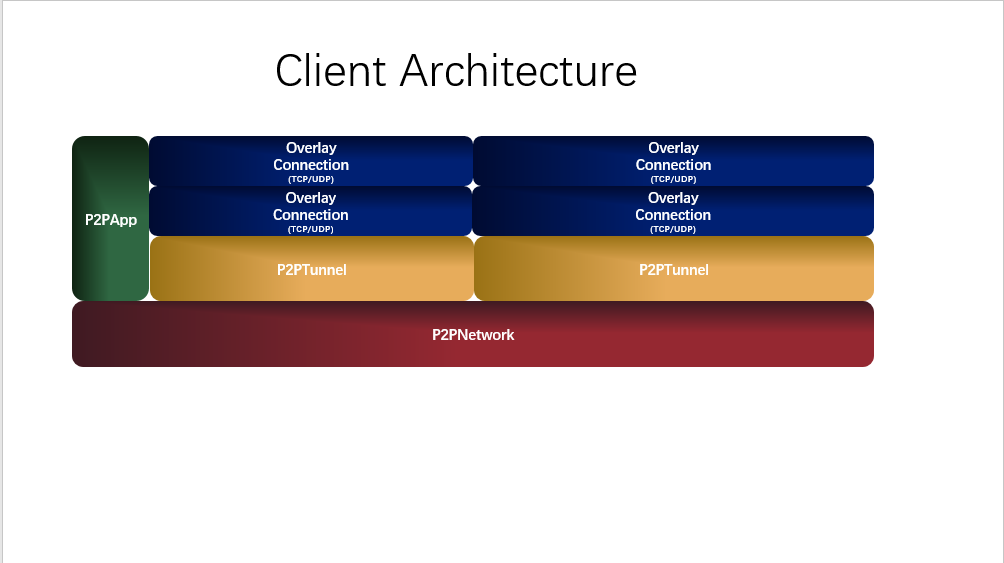
P2PAPP is the most import concept in this project, one P2PApp is able to map the remote service(mstsc/ssh) to the local listening. The main job of re-development or restful API we provide is to manage P2PApp.
The nodes which have joined the OpenP2P share network can vist each other by authentications. Shared nodes will only relay data, and others cannot access any resources in the intranet.
The communication data between the two nodes uses the industry's most secure TLS1.3 channel. The communication content will also use AES encryption, double security, the key is exchanged through the server. Effectively prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
That's right, the relay node is naturally an man-in-middle, so AES encryption is added to ensure the security of the communication content. The relay node cannot obtain the plaintext.
The server side has a scheduling model, which calculate bandwith, ping value,stability and service duration to provide a well-proportioned service to every share node. It uses TOTP(Time-based One-time Password) with hmac-sha256 algorithem, its theory as same as the cellphone validation code or bank cipher coder.
go version go1.18.1+
cd root directory of the socure code and execute
export GOPROXY=https://goproxy.io,direct
go mod tidy
go build
Short-Term:
- Support IPv6.(100%)
- Support auto run when system boot, setup system service.(100%)
- Provide free servers to some low-performance network.(100%)
- Build website, users can manage all P2PApp and devices via it. View devices' online status, upgrade, restart or CURD P2PApp .(100%)
- Provide wechat official account, user can manage P2PApp nodes and deivce as same as website.
- Provide WebUI on client side.
- Support high concurrency on server side.
- Optimize our share scheduling model for different network operators.
- Provide REST APIs and libary for secondary development.
- Support UDP at application layer, it is easy to implement but not urgent due to only a few applicaitons using UDP protocol.(100%)
- Support KCP protocol underlay, currently support Quic only. KCP focus on delay optimization,which has been widely used as game accelerator,it can sacrifice part of bandwidth to reduce timelag.
- Support Android platform, let the phones to be mobile gateway.
- Support SMB Windows neighborhood.
- Direct connection on intranet, for testing.
Long-Term:
- Use blockchain technology to decentralize, so that users who share equipment have benefits, thereby promoting more users to share, and achieving a positive closed loop.
- Enterprise-level product can well manage large scale equipment and ACL.
If the items in TODO or ISSUE is your domain, or you have sepical good idea, welcome to join this OpenP2P project and contribute your code. When this project grows stronger, you will be the major outstanding contributors. That's cool.
QQ Group: 16947733
Email: [email protected] [email protected]
This project is open source for everyone to learn and use for free. It is forbidden to be used for illegal purposes. Any loss caused by improper use of this project or accident, this project and related personnel will not bear any responsibility.