Jumio’s products allow businesses to establish the genuine identity of their users by verifying government-issued IDs in real-time. ID Verification, Identity Verification and other services are used by financial service organizations and other leading brands to create trust for safe onboarding, money transfers, and user authentication.
- Release Notes
- Setup
- Dependencies
- Initialization
- Configuration
- Customization
- SDK Workflow
- Custom UI
- Callback
- Code Documentation
Please refer to our Change Log for more information. Current SDK version: 4.2.1
For breaking technical changes, please read our Transition Guide
The basic setup is required before continuing with the following setup for the Jumio SDK. If you are updating your SDK to a newer version, please also refer to:
➡️ Changelog
➡️ Transition Guide
The SDK Setup Tool is a web tool that helps determine available product combinations and corresponding dependencies for the Jumio SDK, as well as an export feature to easily import the applied changes straight into your codebase.
Below there is a list of dependencies the application will need to work in Android. Some modules are mandatory, others are optional. If an optional module is not linked, some functionalities such as certain methods may not be available, but the library size will be reduced. The Sample app apk size is currently around 17 MB.
dependencies {
implementation "com.jumio.android:core:4.2.1" // Jumio Core library
implementation "com.jumio.android:defaultui:4.2.1" // Jumio Default UI
implementation "com.jumio.android:mrz:4.2.1" // MRZ Scanning
implementation "com.jumio.android:nfc:4.2.1" // NFC Scanning
implementation "com.jumio.android:linefinder:4.2.1" // Linefinder Scanning
implementation "com.jumio.android:docfinder:4.2.1" // Generic ID Scanning (beta)
implementation "com.jumio.android:barcode:4.2.1" // Barcode scanning
implementation "com.jumio.android:barcode-mlkit:4.2.1" // Barcode scanning alternative
implementation "com.jumio.android:iproov:4.2.1" // Face Liveness library
implementation "com.jumio.android:datadog:4.2.1" // Analytics library
implementation "com.jumio.android:devicerisk:4.2.1" // Device fingerprinting library
The module com.jumio.android:docfinder offers a generic scanning method across all ID documents, providing a more seamless capture experience for the end user. The SDK will automatically detect which type of ID document is presented by the user and guide them through the capturing process with live feedback.
Jumio uses Certified Liveness technology to determine liveness. The iProov SDK is referenced as a transitive dependency within the com.jumio.android:iproov module.
If necessary, the iProov SDK version can be overwritten with a more recent one:
implementation "com.jumio.android:iproov:4.2.1"
implementation ("com.iproov.sdk:iproov:7.2.0"){
exclude group: 'org.json', module:'json'
}
As an alternative to the com.jumio.android:barcode dependency, you can substitute com.jumio.android:barcode-mlkit. This dependency includes com.google.android.gms:play-services-mlkit-barcode-scanning library - if your application includes other Google ML-kit libraries, it might be necessary to override meta-data specified in the application tag of the play-services-mlkit-barcode-scanning manifest by merging multiple manifests:
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.gms.vision.DEPENDENCIES"
android:value="barcode"
tools:replace="android:value"/>
Use JumioSDK.sdkVersion to check which SDK version is being used.
For security reasons, applications implementing the SDK should not run on rooted devices. Use either the below method or a self-devised check to prevent usage of SDK scanning functionality on rooted devices.
JumioSDK.isRooted(context: Context)
Use the method below to check if the current device platform is supported by the SDK.
JumioSDK.isSupportedPlatform(context: Context)
Using the SDK requires an activity declaration in your AndroidManifest.xml.
<activity
android:theme="@style/Theme.Jumio"
android:hardwareAccelerated="true"
android:name="com.jumio.defaultui.JumioActivity"
android:configChanges="orientation|screenSize|screenLayout|keyboardHidden"/>
You can specify your own theme (see chapter Customization). The orientation can be sensor based or locked with the attribute android:screenOrientation. Please note that some SDK screens will need portrait mode.
Your OAuth2 credentials are constructed using your previous API token as the Client ID and your previous API secret as the Client secret. You can view and manage your Client ID and secret in the Customer Portal under:
- Settings > API credentials > OAuth2 Clients
Client ID and Client secret are used to generate an OAuth2 access token. OAuth2 has to be activated for your account. Contact your Jumio Account Manager for activation. Send a workflow request using the acquired OAuth2 access token to receive the SDK token necessary to initialize the Jumio SDK. For more details, please refer to Authentication and Encryption.
const val YOUR_SDK_TOKEN = ""
const val YOUR_DATACENTER = ""
JumioSDK sdk = JumioSDK(context: Context)
sdk.token = "YOUR_SDK_TOKEN"
sdk.datacenter = "YOUR_DATACENTER"
Make sure that your SDK token is correct. If it isn't, an exception will be thrown. Then specify an instance of your activity and provide a reference to identify the scans in your reports (max. 100 characters or null). Data center is set to "US" by default. If your customer account is in the EU data center, use "EU" instead. Alternatively, use "SG" for Singapore.
Every Jumio SDK instance is initialized using a specific sdk.token. This token contains information about the workflow, credentials, transaction identifiers and other parameters. Configuration of this token allows you to provide your own internal tracking information for the user and their transaction, specify what user information is captured and by which method, as well as preset options to enhance the user journey. Values configured within the sdk.token during your API request will override any corresponding settings configured in the Customer Portal.
Use ID verification callback to receive a verification status and verified data positions (see API v3 Callback section). Make sure that your customer account is enabled to use this feature. A callback URL can be specified for individual transactions (for URL constraints see chapter Callback URL). This setting overrides any callback URL you have set in the Jumio Customer Portal. Your callback URL must not contain sensitive data like PII (Personally Identifiable Information) or account login. Set your callback URL using the callbackUrl parameter.
Use the correct workflow definition key in order to request a specific workflow. Set your key using the workflowDefinition.key parameter. For example: Use workflow 2 "ID Verification" to verify an ID document and extract data from that document. Use workflow 3 "ID and Identity Verification" to verify a photo ID document and extract data from that document, as well as compare the user's face with the photo on the ID and perform a liveness check to ensure the person is physically present.
'{
"customerInternalReference": "CUSTOMER_REFERENCE",
"workflowDefinition": {
"key": X,
},
"callbackUrl": "YOUR_CALLBACK_URL"
}'
For more details, please refer to our Workflow Description Guide.
ℹ️ Note: Identity Verification requires portrait orientation in your app.
There are several options in order to uniquely identify specific transactions. customerInternalReference allows you to specify your own unique identifier for a certain scan (max. 100 characters). Use reportingCriteria, to identify the scan in your reports (max. 100 characters). You can also set a unique identifier for each user using userReference (max. 100 characters).
For more details, please refer to our API Guide.
'{
"customerInternalReference": "CUSTOMER_REFERENCE",
"workflowDefinition": {
"key": X,
},
"reportingCriteria": "YOUR_REPORTING_CRITERIA",
"userReference": "YOUR_USER_REFERENCE"
}'
You can specify issuing country using ISO 3166-1 alpha-3 country codes, as well as ID types to skip selection during the scanning process. In the example down below, Austria ("AUT") and the USA ("USA") have been preselected. PASSPORT and DRIVER_LICENSE have been chosen as preselected document types. If all parameters are preselected and valid and there is only one given combination (one country and one document type), the document selection screen in the SDK can be skipped entirely.
For more details, please refer to our API Guide.
'{
"customerInternalReference": "CUSTOMER_REFERENCE",
"workflowDefinition": {
"key": X,
"credentials": [
{
"category": "ID",
"type": {
"values": ["DRIVING_LICENSE", "PASSPORT"]
},
"country": {
"values": ["AUT", "USA"]
}
}
]
}
}'
Use cameraFacing attribute of JumioScanView to configure the default camera and set it to FRONT or BACK.
scanView.cameraFacing = JumioCameraPosition.FRONT
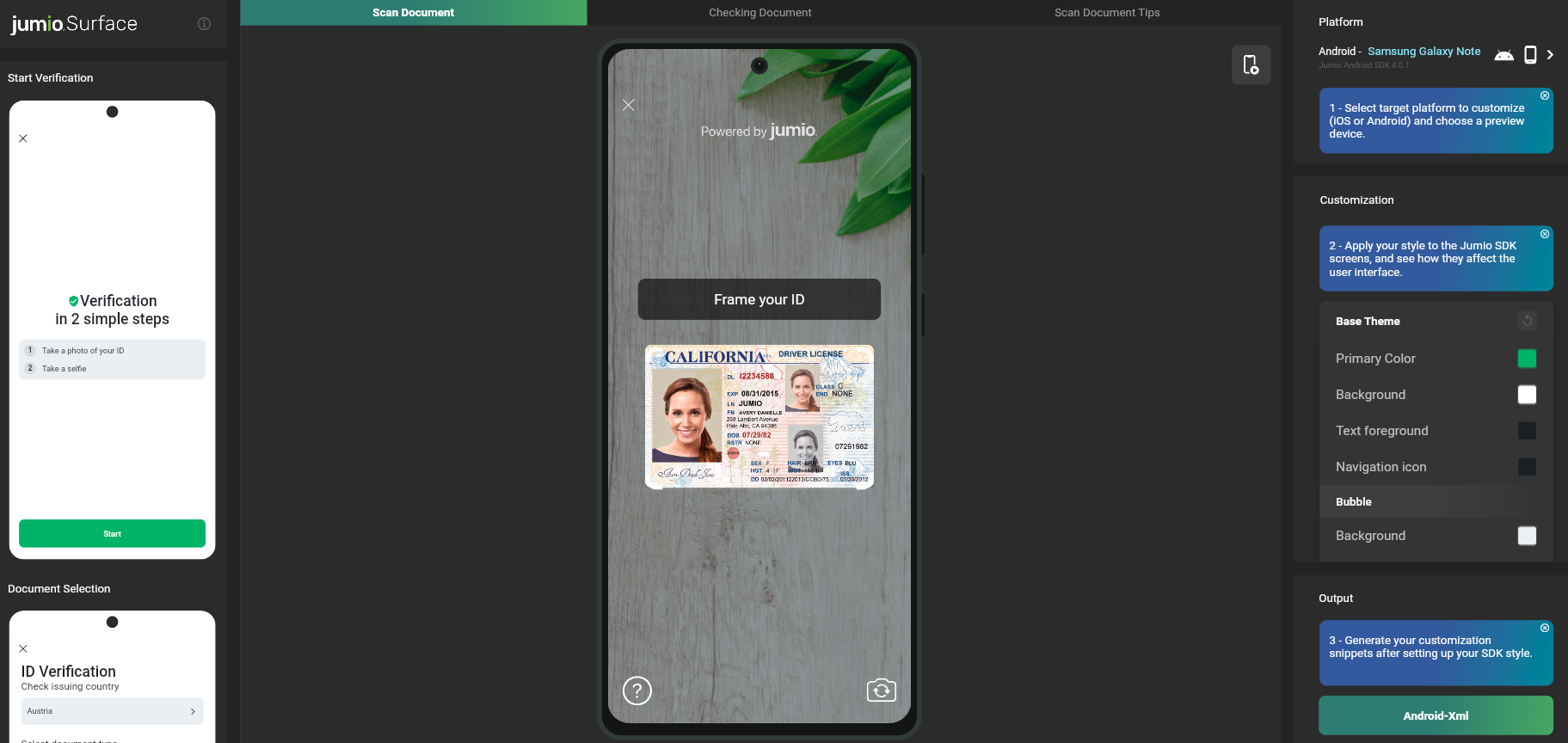
Jumio Surface is a web tool that offers the possibility to apply and visualize, in real-time, all available customization options for the Jumio SDK, as well as an export feature to import the applied changes straight into your codebase.
The surface tool lets you go through all available screens and visualizes all the colors that can be customized. As visualized in the code there, the SDK can be customized to fit your application's look and feel by specifying Theme.Jumio as a parent style and overriding attributes within this theme.
After customizing the SDK, you can click the Android-Xml button in the Output menu on the bottom right to copy the code from the theme AppThemeCustomJumio to your Android app's styles.xml file.
Apply the custom theme that you defined before by replacing Theme.Jumio in the AndroidManifest.xml:
<activity
android:name="com.jumio.defaultui.JumioAcitivty"
android:theme="@style/AppThemeCustomJumio"
... />
Theme.Jumio attributes can also be customized for dark mode. If you haven't done so already, create a values-night folder in your resources directory and add a new styles.xml file. Adapt your custom Jumio theme for dark mode. The SDK will switch automatically to match the system settings of the user device.
The following tables give information on the specification of all data parameters and errors.
| Parameter | Type | Max. length | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| issuingCountry | String | 3 | Country of issue as ISO 3166-1 alpha-3 country code |
| idType | String | PASSPORT, DRIVER_LICENSE, IDENTITY_CARD or VISA as provided or selected | |
| firstName | String | 100 | First name of the customer |
| lastName | String | 100 | Last name of the customer |
| dateOfBirth | String | Date of birth | |
| issuingDate | String | Date of issue | |
| expiryDate | String | Date of expiry | |
| documentNumber | String | 100 | Identification number of the document |
| personalNumber | String | 14 | Personal number of the document |
| gender | String | Gender M, F or X | |
| nationality | String | Nationality of the customer | |
| placeOfBirth | String | 255 | Place of birth |
| country | String | Country of residence | |
| address | String | 64 | Street name of residence |
| city | String | 64 | City of residence |
| subdivision | String | 3 | Last three characters of ISO 3166-2:US or ISO 3166-2:CA subdivision code |
| postalCode | String | 15 | Postal code of residence |
| mrzLine1 | String | 50 | MRZ line 1 |
| mrzLine2 | String | 50 | MRZ line 2 |
| mrzLine3 | String | 50 | MRZ line 3 |
| rawBarcodeData | String | 50 | Extracted barcode data |
| extractionMethod | JumioScanMode | Extraction method used during scanning (MRZ, BARCODE, MANUAL, OCR_CARD, NFC) | |
| imageData | JumioImageData | Wrapper class for accessing image data of all credential parts from an ID verification session. This feature has to be enabled by your account manager. |
| Parameter | Type | Max. length | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| passed | Boolean | ||
| extractionMethod | JumioScanMode | Extraction method used during scanning (FACE_MANUAL, FACE_IPROOV) | |
| imageData | JumioImageData | Wrapper class for accessing image data of all credential parts from an ID verification session. This feature has to be enabled by your account manager. |
List of all possible reject reasons returned if Instant Feedback is used:
| Code | Message | Description | Check enabled server-side (2022-05-25) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 102 | BLACK_WHITE_COPY | Document appears to be a black and white photocopy | x |
| 103 | COLOR_PHOTOCOPY | Document appears to be a colored photocopy | |
| 104 | DIGITAL_COPY | Document appears to be a digital copy | x |
| 200 | NOT_READABLE | Document is not readable | |
| 201 | NO_DOC | No document could be detected | x |
| 206 | MISSING_BACK | Backside of the document is missing | x |
| 214 | MISSING_FRONT | Frontside of the document is missing | x |
| 2001 | BLURRY | Document image is unusable because it is blurry | x |
| 2003 | MISSING_PART_DOC | Part of the document is missing | x |
| 2005 | DAMAGED_DOCUMENT | Document appears to be damaged | |
| 2004 | HIDDEN_PART_DOC | Part of the document is hidden | |
| 2006 | GLARE | Document image is unusable because of glare | x |
List of all error codes that are available via the code and message property of the JumioError object. The first letter (A-J) represents the error case. The remaining characters are represented by numbers that contain information helping us understand the problem situation([x][yyyy]).
| Code | Message | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A[x][yyyy] | We have encountered a network communication problem | Retry possible, user decided to cancel |
| B[x][yyyy] | Authentication failed | Secure connection could not be established, retry impossible |
| C[x]0401 | Authentication failed | API credentials invalid, retry impossible |
| E[x]0000 | No Internet connection available | Retry possible, user decided to cancel |
| F00000 | Scanning not available at this time, please contact the app vendor | Resources cannot be loaded, retry impossible |
| G00000 | Cancelled by end-user | No error occurred |
| H00000 | The camera is currently not available | Camera cannot be initialized, retry impossible |
| I00000 | Certificate not valid anymore. Please update your application | End-to-end encryption key not valid anymore, retry impossible |
| J00000 | Transaction already finished | User did not complete SDK journey within session lifetime |
| N00000 | Scanning not available at this time, please contact the app vendor | Required images are missing to finalize the acquisition |
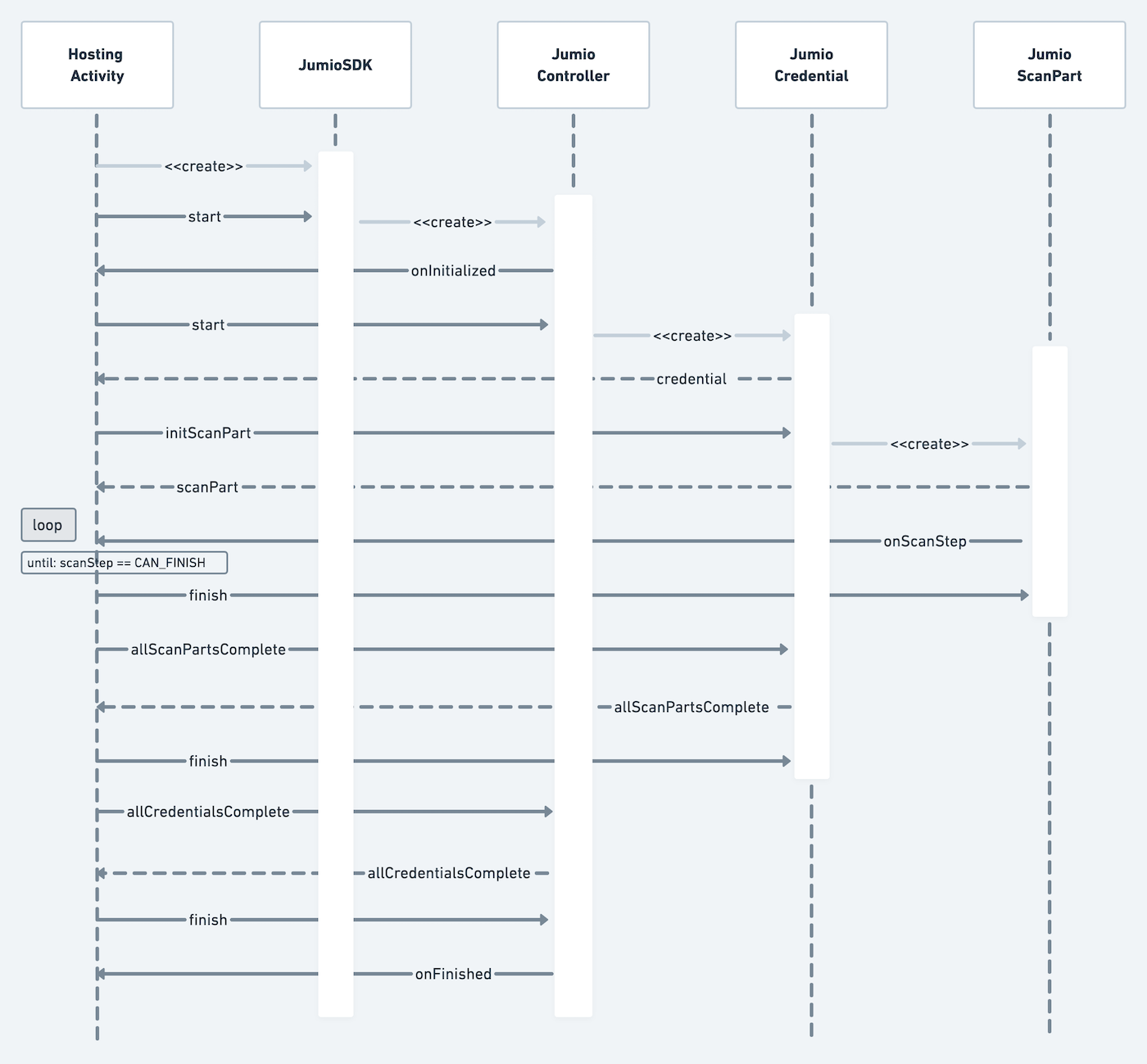
ID Verification can be also implemented as a custom scan view. This means that only the scan view (including the scan overlays) are provided by the SDK. The handling of the lifecycle, document selection, readability confirmation, intermediate callbacks, and all other steps necessary to complete a scan have to be handled by the client application that implements the SDK.
The following sequence diagram outlines components, callbacks and methods for a basic ID Verification workflow:
CustomUI enables you to use a custom scan view with a plain scanning user interface. Initialize the Jumio SDK and set sdk.token and sdk.datacenter and specify an instance of your class that implements JumioControllerInterface.
sdk = JumioSDK(context: Context)
sdk.token = "YOUR_SDK_TOKEN"
sdk.datacenter = JumioDataCenter.YOUR_DATACENTER
JumioDataCentervalues:US,EU,SG
Start the SDK by passing context and the JumioControllerInterface instance. You will receive a JumioController object in return.
val jumioController: JumioController = sdk.start(context, jumioControllerInterface)
When the jumioController is initialized, the following callback will be triggered:
onInitialized(credentials: List<JumioCredentialInfo>, policyUrl: String?)
If a user’s consent is required, the parameter policyUrl will provide a valid URL that will redirect the user to Jumio’s consent details. User can open and continue to this link if they choose to do so. If the user consents to the Jumio policy, jumioController.userConsented() is required to be called internally before any credential can be initialized and the user journey can continue. If no consent is required, the parameter policyUrl will be null.
policyUrl is not null, the user is legally required to actually consent to Jumio's policy. Do not accept automatically without showing the user any terms.
Create a JumioCredential which will contain all necessary information about the scanning process. For ID verification you will receive a JumioIDCredential, for Identity Verification a JumioFaceCredential, and so on. Initialize the necessary credential and check whether the credential is already preconfigured. If this is the case, the parameter isConfigured will be true. In this case, the credential can be started right away.
currentCredentialInfo: val currentCredential = jumioController.start(currentCredentialInfo!!)
currentCredential?.isConfigured == true
If the credential is not configured yet, the credential needs some more configuration before scan parts can be initialized.
JumioCredentialCategoryvalues =ID,FACE,DOCUMENT
In case of JumioIDCredential, query the available country and document combinations by checking the countries map provided by the credential. After that, specify country and document details by setting the credential configuration to receive all relevant scan parts for your chosen document. Use setConfiguration() to set a valid country / document combination from that list:
val countries:Map<String, List<JumioDocument>> = (currentCredential as JumioIDCredential)?.countries
val country = “USA”
val jumioDocument = countries.get(“USA”)
(currentCredential as JumioIDCredential).setConfiguration(country, jumioDocument)
-
JumioDocumentvalues:JumioDocumentType,JumioDocumentVariant -
JumioDocumentTypevalues:PASSPORT,VISA,DRIVING_LICENSE,ID_CARD -
JumioDocumentVariantvalues:PAPER,PLASTIC
Retrieve the first credential part of the credential to start the scanning process by calling:
val credentialPart = currentCredential?.credentialParts?.first()
currentCredential?.initScanPart(credentialPart, yourScanPartInterface)
JumioDataCredential is used for the device fingerprinting. There are some optional configurations you can do to enhance it's behaviour.
- Add the following Android permissions to your AndroidManifest.xml, if not already added:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" /> // Get user's GPS Location.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" /> // Get user's GPS Location.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" /> // Get User's Wifi name and Status.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" /> // Get User's Network information and State.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE" /> // Get Phone and Network information (MNC, MCC, IMEI, Phone Number, Phone Type (GSM/CDMA), SIM Number, ...etc).
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.USE_BIOMETRIC" /> // Get user's Biometric authentication settings (Face or Fingerprint authentication).
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.USE_FINGERPRINT" /> // Get user's Biometric authentication settings (Face or Fingerprint authentication).
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /> // Write data into device to check re-installation behaviour.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /> // Get External storage status, total size, free size...etc.
<uses-permission android:name="com.google.android.providers.gsf.permission.READ_GSERVICES" /> // Get GSFID (Google Services Id) for accurate identification for unique users.
Note:
- the reason for the requirement of the given permission is added as inline comment
- some of them are
dangerouspermissions, and you have to ask for the permission from the user. More information about permissions can be found in the official Android documentation - The above permissions imply to add some features to your manifest file:
<uses-feature
android:name="android.hardware.location"
android:required="false" />
<uses-feature
android:name="android.hardware.telephony"
android:required="false" />
<uses-feature
android:name="android.hardware.wifi"
android:required="false" />
- If you use proguard for obfuscation, you have to add some rules to your proguard-rules.pro configuration file:
-keep com.google.android.gms.*
-keep com.google.android.gms.tasks.*
-keep com.google.android.gms.ads.identifier.AdvertisingIdClient
The following sequence diagram outlines an overview of ScanPart handling details:
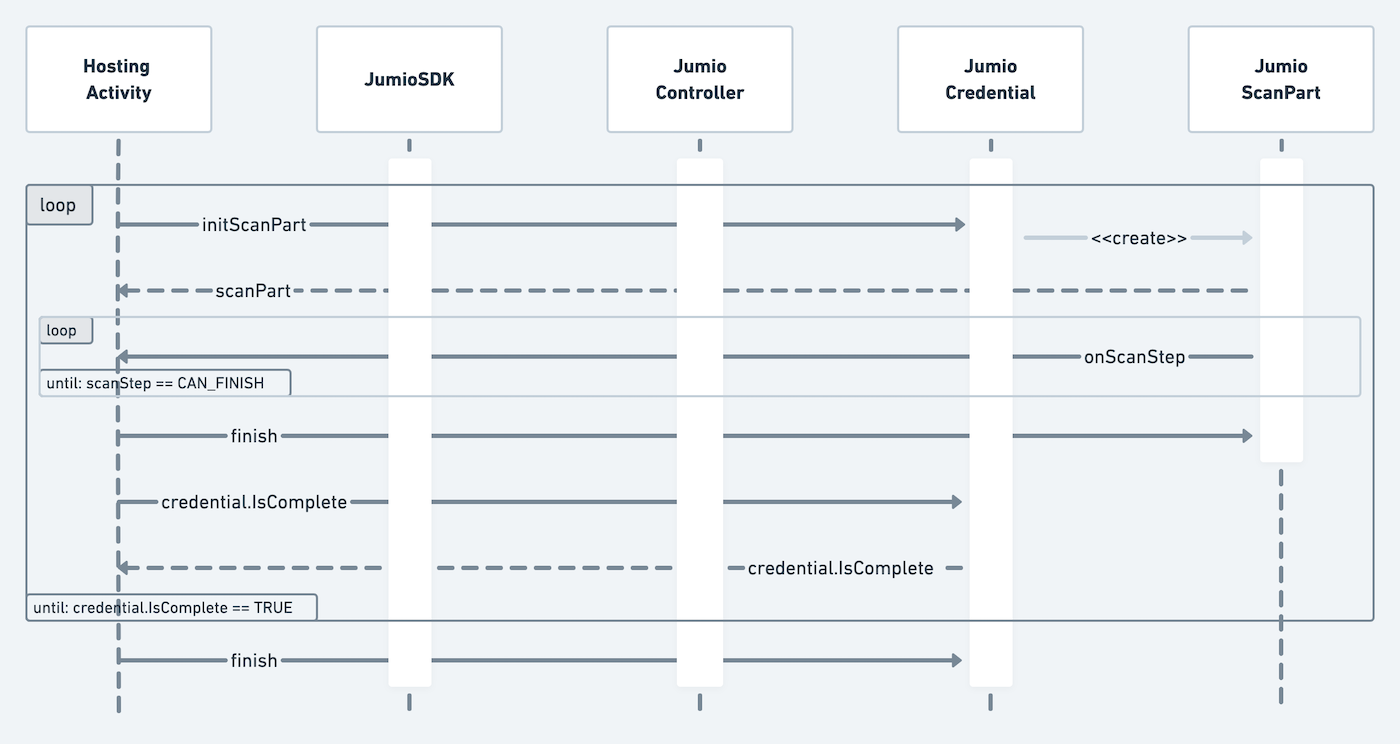
Start the scanning process by initializing the scan part. Provide a JumioCredentialPart from the list below:
currentScanPart = currentCredential?.initScanPart(credentialPart, yourJumioScanPartInterface)
JumioCredentialPartvalues:FRONT,BACK,FACE,DOCUMENT,NFC,DEVICE_RISK
When the scanning is done, the parameter JumioScanStep.CAN_FINISH will be received and the scan part can be finished by calling currentScanPart?.finish().
Check if the credential is complete by calling currentCredential?.isComplete and finish the current credential by calling currentCredential?.finish().
Continue that procedure until all needed credentials (e.g. ID, FACE, DOCUMENT) are finished. Check if all credentials are finished with controller.isComplete, then call jumioController?.finish() to finish the user journey.
The callback onFinished() will be received after the controller has finished:
override fun onFinished(result: JumioResult) {
log("onFinished")
sdkResult.value = result
}
During the scanning process, use the scanPart method onScanStep() to check on the scanning progress. The scan step CAN_FINISH indicates that the scanning process for this part is done.
JumioScanStep covers lifecycle events which require action from the customer to continue the process.
JumioScanStepvalues:PREPARE,STARTED,ATTACH_ACTIVITY,SCAN_VIEW,IMAGE_TAKEN,PROCESSING,CONFIRMATION_VIEW,REJECT_VIEW,RETRY,CAN_FINISH,ADDON_SCAN_PART
PREPARE is only sent if a scan part requires upfront preparation and the customer should be notified (e.g. by displaying a loading screen):
JumioScanStep.PREPARE -> {
showLoadingView()
}
STARTED is always sent when a scan part is started. If a loading spinner was triggered before, it can now be dismissed:
JumioScanStep.STARTED -> {
hideLoadingView()
}
IMAGE_TAKEN is triggered as soon as the image is taken and has been uploaded to the Jumio server. The camera preview is stopped during that step
When background processing is executed, JumioScanStep.PROCESSING is triggered.
When a confirmation view should be displayed, depending on the outcome either JumioScanStep.CONFIRMATION_VIEW or JumioScanStep.REJECT_VIEW is displayed. To display the ScanPart in the confirmation or reject view, simply attach the views once the steps are triggered:
JumioScanStep.CONFIRMATION_VIEW -> {
confirmationView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE)
confirmationView.attach(scanPart!!)
}
JumioScanStep.REJECT_VIEW -> {
rejectView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE)
rejectView.attach(scanPart!!)
}
The scan part can be confirmed by calling confirmationView.confirm() or retaken by calling confirmationView.retake() or rejectView.retake()
The retry scan step returns a data object of type JumioRetryReason. On RETRY, a retry has to be triggered on the credential.
if (data is JumioRetryReason) {
log("retry reason: ${data.code}")
log("retry message: ${data.message}")
}
As soon as the scan part has been confirmed and all processing has been completed CAN_FINISH is triggered. scanPart.finish() can now be called. During the finish routine the SDK checks if there is an add-on functionality for this part available, e.g. possible NFC scanning after an MRZ scan part. In this case ADDON_SCAN_PART will be called
When an add-on to the current scan part is available, JumioScanStep.ADDON_SCAN_PART is sent. The add-on scan part can be retrieved using the method addonScanPart = currentCredential?.getAddonPart().
JumioScanUpdate covers scan information that is relevant and might need to be displayed during scanning.
JumioScanUpdatevalues:LEGAL_HINT,CAMERA_AVAILABLE,FALLBACK,NFC_EXTRACTION_STARTED,NFC_EXTRACTION_PROGRESS,NFC_EXTRACTION_FINISHED
Instead of using the standard method onActivityResult(), implement the following methods within your jumioControllerInterface for successful scans and error notifications:
The method onFinished(result: JumioResult) has to be implemented to handle data after a successful scan.
override fun onFinished(result: JumioResult) {
val data = result
// handle success case
finish()
}
The method onError(error: JumioError) has to be implemented to handle data after an unsuccessful scan. Check the parameter error.isRetryable to see if the failed scan attempt can be retried.
override fun onError(error: JumioError) {
if(error.isRetryable) {
// retry scan attempt
} else {
// handle error case
}
log(String.format("onError: %s, %s, %s", error.code, error.message, if
(error.isRetryable) "true" else "false" )
}
If an error is retryable, jumioController.retry() should be called to execute a retry.
The use of Instant Feedback provides immediate end user feedback by performing a usability check on any image the user took and prompting them to provide a new image immediately if this image is not usable, for example because it is too blurry. Please refer to the JumioRejectReason table for a list of all reject possibilities.
All SDK related traffic is sent over HTTPS using TLS and public key pinning. Additionally, the information itself within the transmission is also encrypted utilizing Application Layer Encryption (ALE). ALE is a Jumio custom-designed security protocol that utilizes RSA-OAEP and AES-256 to ensure that the data cannot be read or manipulated even if the traffic was captured.
The software contains third-party open source software. For more information, see licenses.
This software is based in part on the work of the Independent JPEG Group.
If you have any questions regarding our implementation guide please contact Jumio Customer Service at [email protected]. The Jumio online helpdesk contains a wealth of information regarding our services including demo videos, product descriptions, FAQs, and other resources that can help to get you started with Jumio.
© Jumio Corporation, 395 Page Mill Road, Suite 150, Palo Alto, CA 94306
The source code and software available on this website (“Software”) is provided by Jumio Corp. or its affiliated group companies (“Jumio”) "as is” and any express or implied warranties, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose are disclaimed. In no event shall Jumio be liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, special, exemplary, or consequential damages (including but not limited to procurement of substitute goods or services, loss of use, data, profits, or business interruption) however caused and on any theory of liability, whether in contract, strict liability, or tort (including negligence or otherwise) arising in any way out of the use of this Software, even if advised of the possibility of such damage.
In any case, your use of this Software is subject to the terms and conditions that apply to your contractual relationship with Jumio. As regards Jumio’s privacy practices, please see our privacy notice available here: Privacy Policy.