Data for paper TL-Training: A Task-Feature-Based Framework for Training Large Language Models in Tool Use
Junjie Ye
Dec. 22, 2024
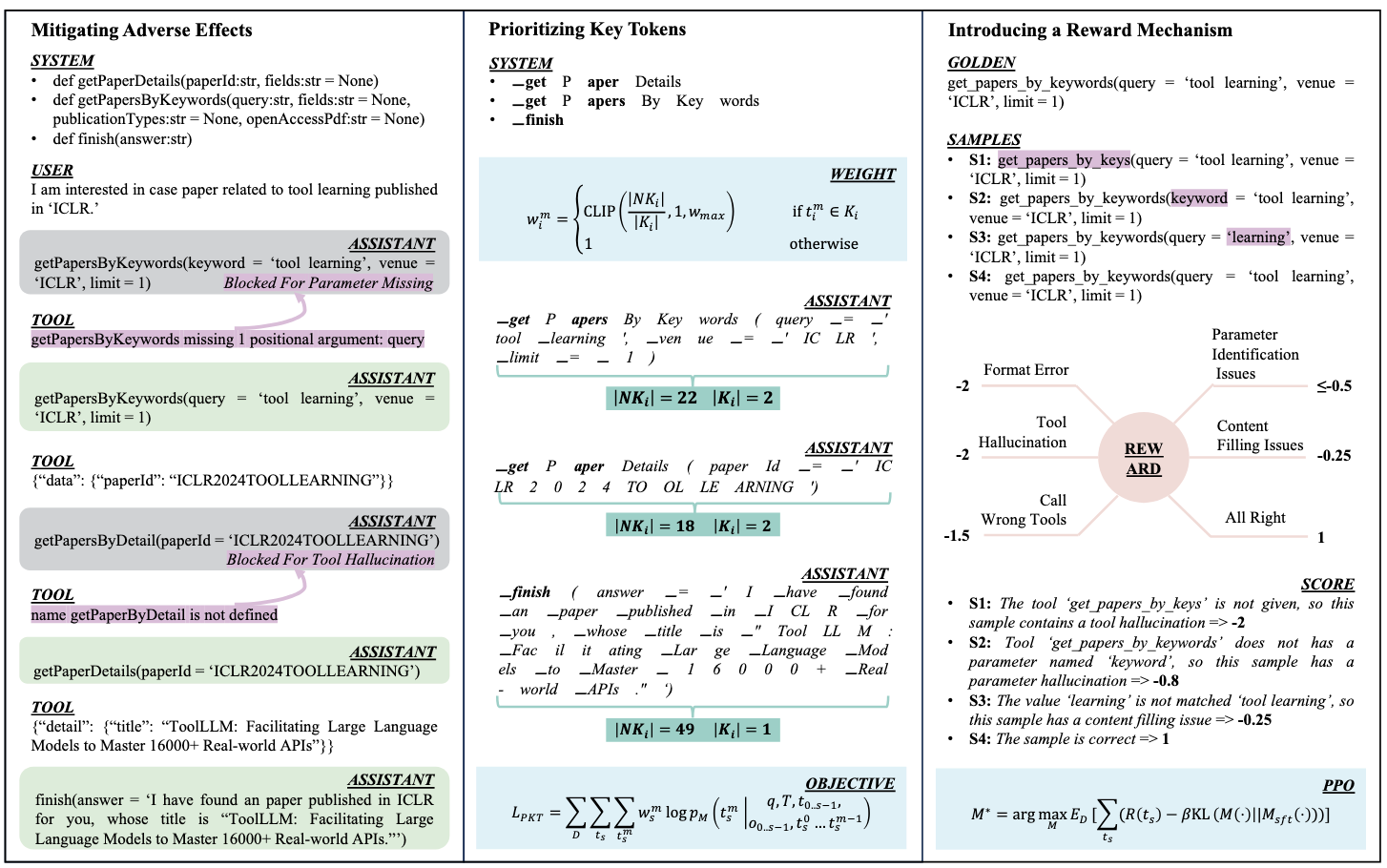
Large language models (LLMs) achieve remarkable advancements by leveraging tools to interact with external environments, a critical step toward generalized AI. However, the standard supervised fine-tuning (SFT) approach, which relies on large-scale datasets, often overlooks task-specific characteristics in tool use, leading to performance bottlenecks. To address this issue, we analyze three existing LLMs and uncover key insights: training data can inadvertently impede tool-use behavior, token importance is distributed unevenly, and errors in tool calls fall into a small set of distinct categories. Building on these findings, we propose TL-Training, a task-feature-based framework that mitigates the effects of suboptimal training data, dynamically adjusts token weights to prioritize key tokens during SFT, and incorporates a robust reward mechanism tailored to error categories, optimized through proximal policy optimization. We validate TL-Training by training CodeLLaMA-2-7B and evaluating it on four diverse open-source test sets. Our results demonstrate that the LLM trained by our method matches or surpasses both open- and closed-source LLMs in tool-use performance using only 1,217 training data points. Additionally, our method enhances robustness in noisy environments and improves general task performance, offering a scalable and efficient paradigm for tool-use training in LLMs.
- [2024.12.23] TL-CodeLLaMA-2 can be download from huggingface.
- [2024.12.23] Release the data and code for TL-Training.
- [2024.12.23] Paper available on Arxiv.
- Run the command to install the packages required.
pip install -r requirements.txt
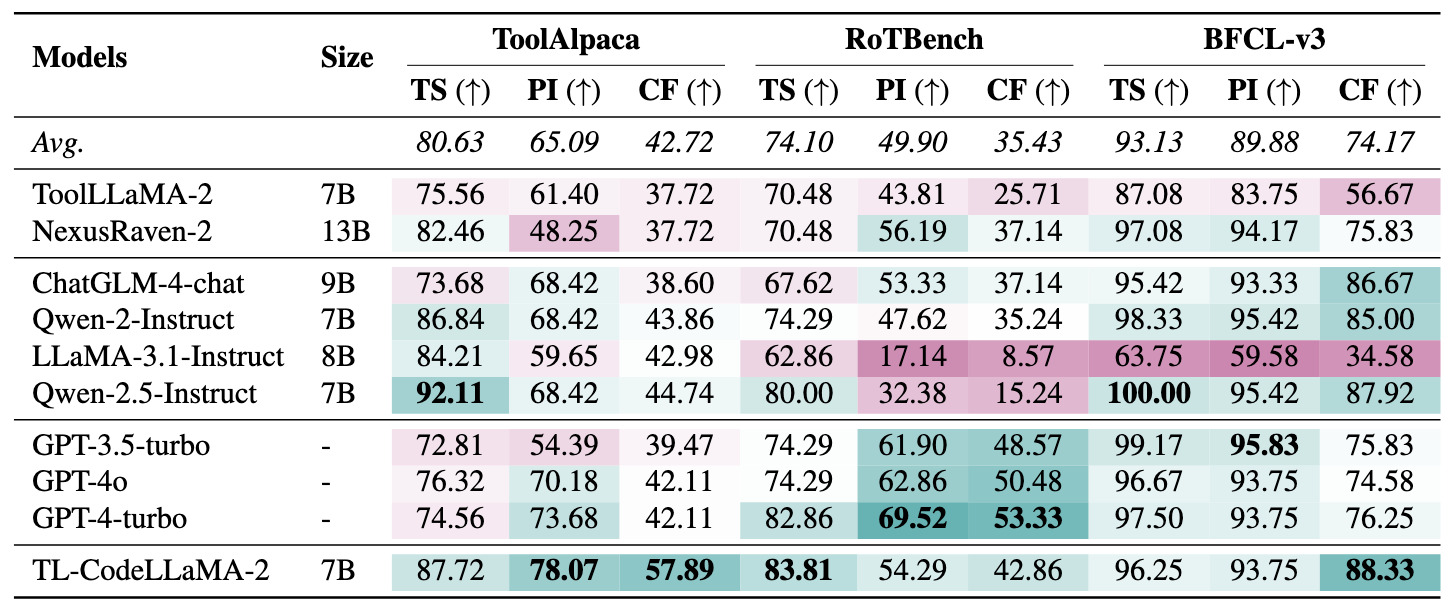
We evaluate the performance of various LLMs on three single-turn tool-use test sets and one multi-turn tool-use test set.
To assess the individual contributions of the three components in our design that enhance LLMs' tool-use capabilities, we conduct ablation studies, comparing model performance across various scenarios.
-
Apply MAE
cd code python mae.py --is_mae -
Apply PKT
cd pkt bash finetune.sh -
Apply IRM
cd irm bash RL_run.sh
After run these codes, the model will be found in ../../save_models/irm_model
If you want to use the model (TL-CodeLLaMA-2) for inference, please follow the format below:
[
{
"role": "System",
"content": "Function:\ndef random_advice():\n \"\"\"\n Returns a random advice slip as a slip object.\n \"\"\"\n\nFunction:\ndef advice_by_id(slip_id:str):\n \"\"\"\n If an advice slip is found with the corresponding {slip_id}, a slip object is returned.\n\n Args:\n slip_id (string): The unique ID of this advice slip.\n \"\"\"\n\nFunction:\ndef search_advice(query:str):\n \"\"\"\n If an advice slip is found, containing the corresponding search term in {query}, an array of slip objects is returned inside a search object.\n\n Args:\n query (string): The search query provided.\n \"\"\"\n\nFunction:\ndef ask_to_user(question:str):\n \"\"\"\n You can ask user for guidance when you think you need more information to handle the task, but you should use this tool as less as you can.\n\n Args:\n question (string): The question you want to ask to user.\n \"\"\"\n\nFunction:\ndef finish(answer:str):\n \"\"\"\n Finish the task and give your answer.\n\n Args:\n answer (string): Your answer for the task.\n \"\"\"\n\n"
},
{
"role": "User",
"content": "Could you give me some advice about 'love'?"
},
{
"role": "Assistant",
"content": "search_advice(query = 'love') "
},
{
"role": "Output",
"content": "..."
}
]The chat template is:
{% for message in messages %}{{message['role'] + ': ' + message['content']}}{% if loop.last %}{% if add_generation_prompt %}{{ '\nAssistant:' }}{% else %}{{ '</s>'}}{% endif %}{% else %}{{ '\n' }}{% endif %}{% endfor %}If you find this project useful in your research, please cite:
@misc{TL-Training,
title={TL-Training: A Task-Feature-Based Framework for Training Large Language Models in Tool Use},
author={Junjie Ye and Yilong Wu and Sixian Li and Yuming Yang and Tao Gui and Qi Zhang and Xuanjing Huang and Peng Wang and Zhongchao Shi and Jianping Fan and Zhengyin Du},
year={2024},
eprint={2412.15495},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.15495},
}