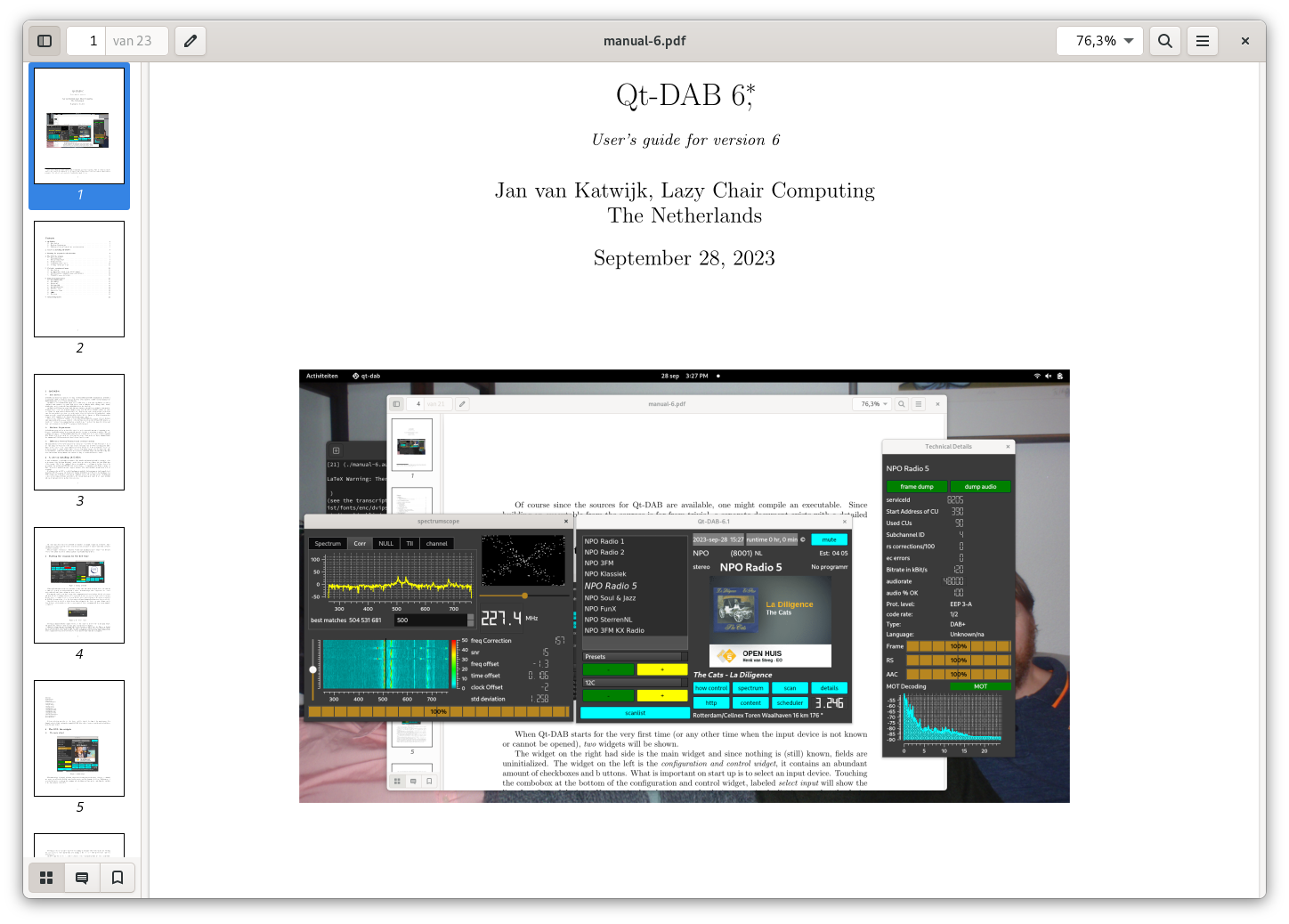
Qt-DAB-6 is software for Linux, Windows, MacOS and Raspberry Pi for listening to terrestrial Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB and DAB+).
The current version is 6.2, the versions 5.4 and 4.7 are still baing accessinle and maintained.
- Introduction
- Features
- Widgets and scopes
- Showing a map for TII
- Documentation
- Installation on Windows
- Installation on Linux
- Notes on building an executable
- Using user specified bands
- xml-files and support
- A Note on previous versions
- Copyright
Qt-DAB-XX is a rich implementation of a DAB decoder for use on Linux and Windows based PCs, including some ARM based boards, such as the Raspberry PI 2 and up. It can be used with a variety of SDR devices, including DABsticks, all models of the SDRplay, Airspy etc.
Precompiled versions for Linux-x64 (AppImage) and Windows (an installer) are available.
Thanks to Richard Huber, Qt-DAB can be compiled on the Mac.
- DAB (mp2) and DAB+ (HE-AAC v1, HE-AAC v2 and AAC-LC) decoding
- MOT SlideShow (SLS)
- Dynamic Label (DLS) and the possibility of saving dynamic Labels - augmented with channel and time info - in a file,
- Both DAB bands (and user defined bands) are supported:
- VHF Band III (default),
- L-Band (obsolete now),
- a user defined Band
- Modes I, II and IV (Mode I default, Modes II and IV obsolete, but can be set in the
.inifile, - Views on the signal: spectrum view incl. constellation diagram, correlation result, TII spectrum and the SNR over time,
- automatic reconfiguration of services,
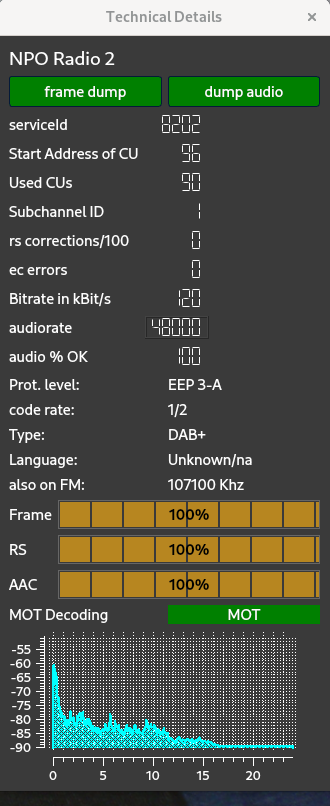
- Detailed information on reception and selected service (SNR, bitrate, frequency, ensemble name, ensemble ID, subchannel ID, used CUs, protection level, CPU usage, program type, language, alternative FM frequency if available, 4 quality bars),
- If configured, the TII data is mapped upon a transmitter's name, and display of TII (Transmitter Identification Information) data when transmitted,
- Possibility of displaying a map with position(s) of received transmitter(s),
- Presets for easy switching of programs in different ensembles (see section Presets),
- Dumping of the input data of the DAB channel (Warning: produces large raw files!) into
.sdrfiles or.xmlfile formats and playing them again later (see section on xml format), - Saving audio as uncompressed wave files, and Saving aac frames from DAB+ services for processing by e.g. VLC,
- Saving the ensemble content description: audio and data streams, including almost all technical data into a text file readable by e.g LibreOfficeCalc
- Advanced scanning function (scan the band, show the results on the screen and save a detailed description of the services found in a file),
- ip output: when configured the ip data - if selected - is sent to a specified ip address (default: 127.0.0.1:8888),
- TPEG output: when configured the data is sent to a specified ip address,
- EPG detection and building up a time table,
- Supports as input device:
- SDR DAB sticks (RTL2838U or similar),
- HACKRF One,
- Airspy, including Airspy mini,
- SDRplay (RSP I, RSP II, RSP Duo and RSP Dx), with separate entries for v2 and v3 library
- limeSDR,
- Adalm Pluto,
- Soapy (experimental, Linux only),
- ExtIO (experimental, Windows only),
- rtl_tcp servers.
- Always supported input from:
- prerecorded dump (
.raw,.iqand.sdr), .xmland.uffformat files.
- prerecorded dump (
- Clean device interface, easy to add other devices.
- Scheduling the start of (channel:service) pairs or operations as frame dump or audio dump, even for days ahead.
- Showing the name of the transmitter received as well as the distance to the receiver and the azimuth.
- background services. Since 4.351 it is possible to run an arbitrary number of DAB+ audioservices (from the current ensemble) as background service with the output sent to a file.
Partly implemented:
- TPEG: when configured, TPEG messages are being sent to a TCP port; sources for a simple client are part of the source distribution.
- Journaline (an untested Journaline implementation is part of the sources).
- Other bands than used for terrestrial broadcasting in Europe (like DAB over cable)
ℹ️ Note: While the 2.13 support for SDRplay devices is able to handle the RSP 1, RSP II, RSP Ia and RSP duo, the 3.0X support handles all SDRplay RSP's. It is recommended to use the 3.0X support library. Note further that when - on Windows - a 3.10 (or higher) library is installed (e.g. by installing SDRuno), the 2.13 library is not reachable.
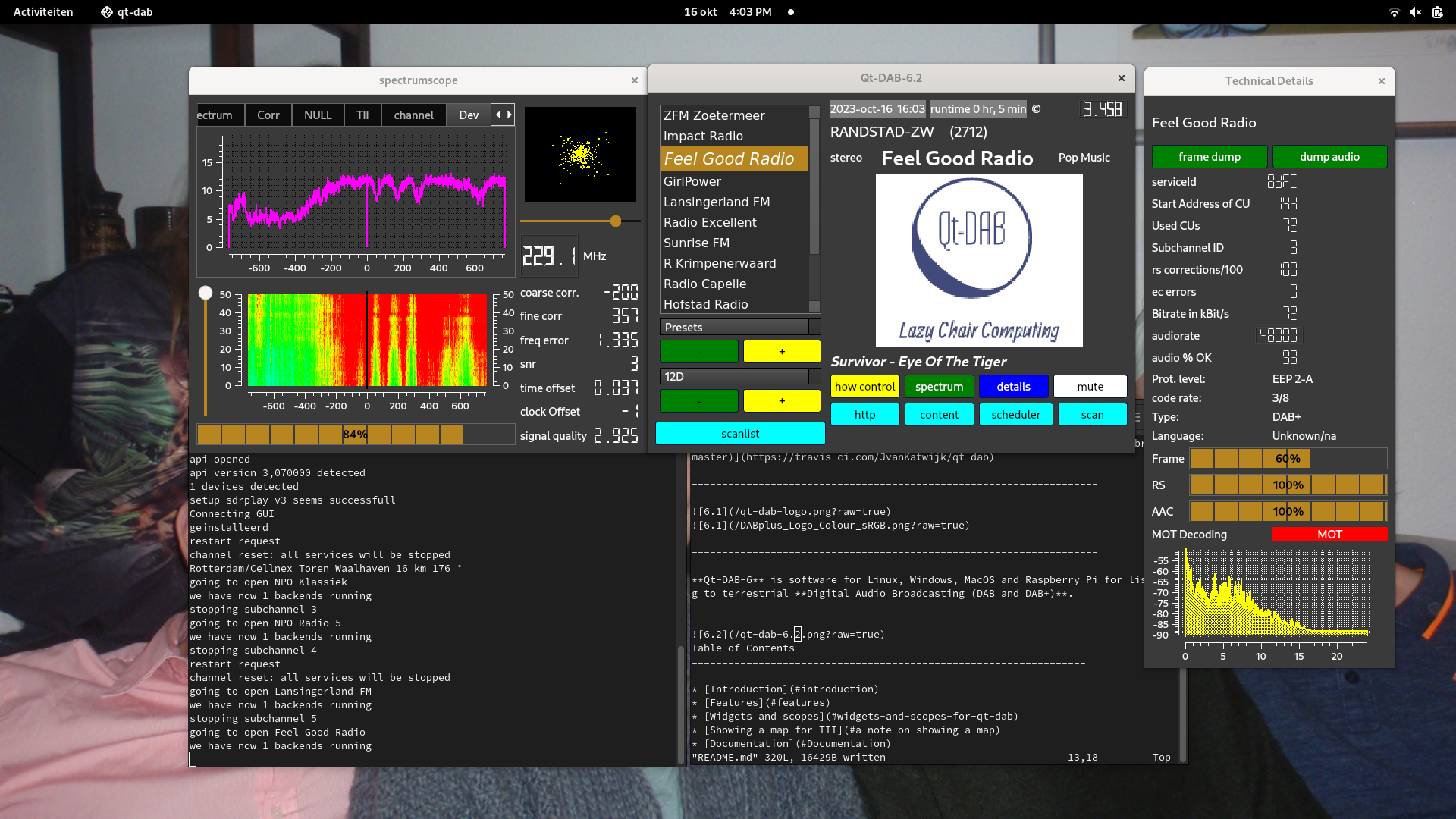
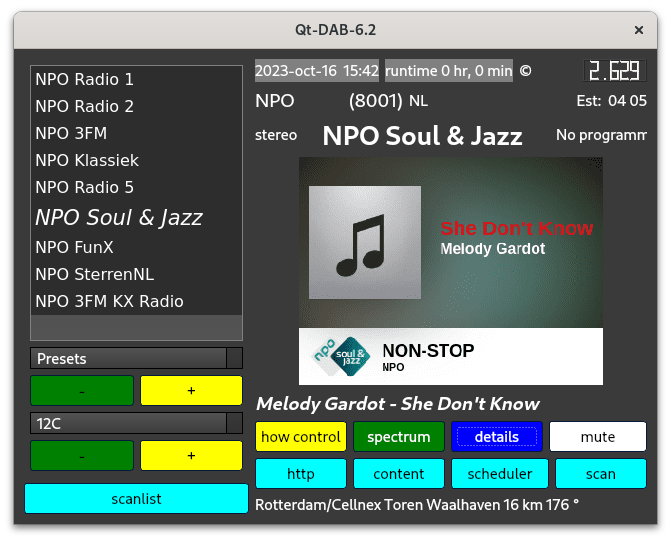
The main widget of Qt-DAB provides all means for selecting a channel, and selecting a service. Furthermore, it provides full control over the visibility of the other widgets of the GUI.
The technical widget - the visibility of which depends on the settings in the main widget, gives full information about the selected audio service. (Of course the color(s) used in the spectrum display can be set by the user).
Different from previous versions, a single widget, the spectrum widget, contains (almost) all of the scopes and displays. It is set up as a tabbed widget - the 5 or 6 scopes (depending on the configuration) show the various aspects of the DAB signal. Furthermore, it contains an IQscope, showing the constellation of the decoded data or the constellation of the data before decoding. A waterfall scope shows the progress in time of the data that is displayed in the selected scope.
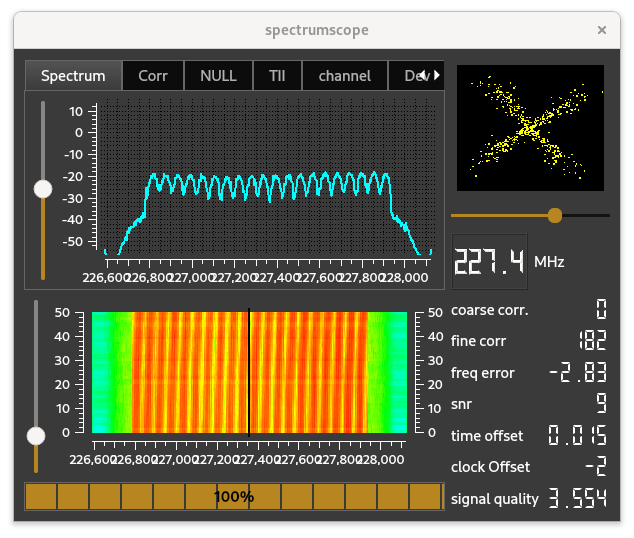
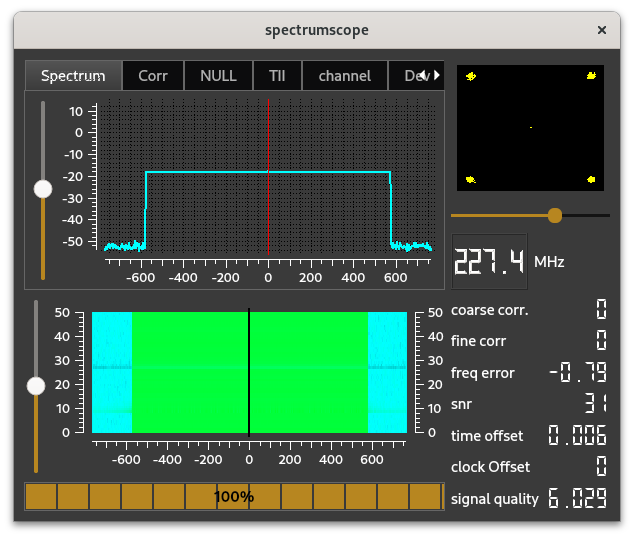
The spectrum scope shows - in numbers - some quality indicators for the raw DAB signal.
The progress indicator at the bottom shows the quality of the FIC decoding, where FIC can be seen as the directory data of the contents of the DAB transmission
(Note that - obviously - the colors of the scopes can be set to different colors than shown here).
The spectrum scope shows the spectrum of the incoming DAB signal. One sees clearly that the width of the signal is app 1.5 MHz.
The ideal form of the spectrum - and the signal constellation as shown in the IQScope - is not seen often.
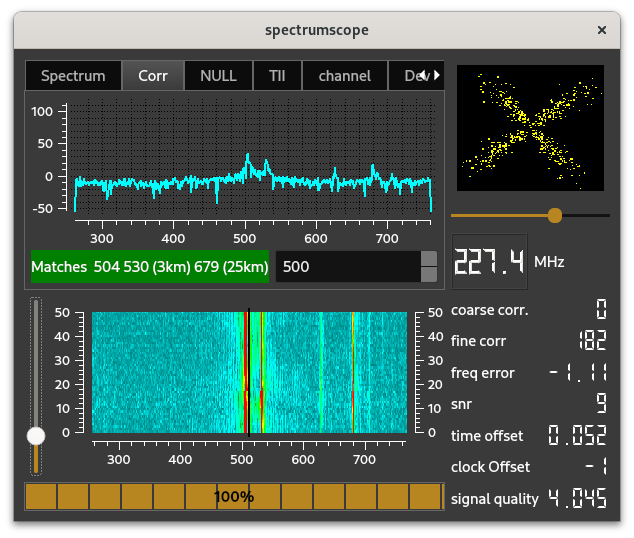
The correlation scope shows the correlation between the incoming signal and some predefined data. It is helpful in finding the precise start of the (relevant) data in the input stream. The picture shows that the signal from more than one transmitter is received. If the distance to the current transmitter is known, the display shows the estimated distances - from the receiver location - to the other peaks as well.
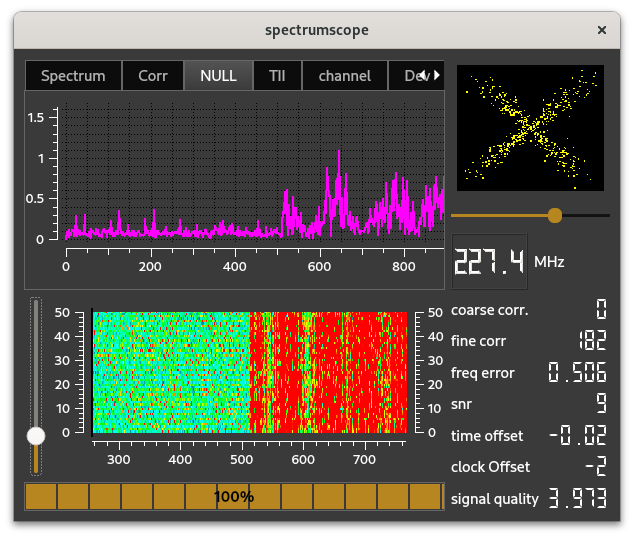
The NULL scope shows the samples in the transition from NULL period to the first data block of a DAB frame;
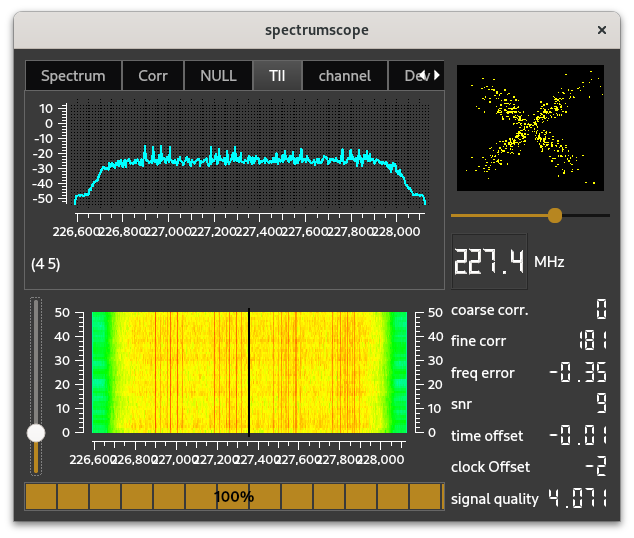
The TII scope shows the spectrum of the data in the NULL period, since that data contains the TII (Transmitter Identification Information) data in an encoded form;
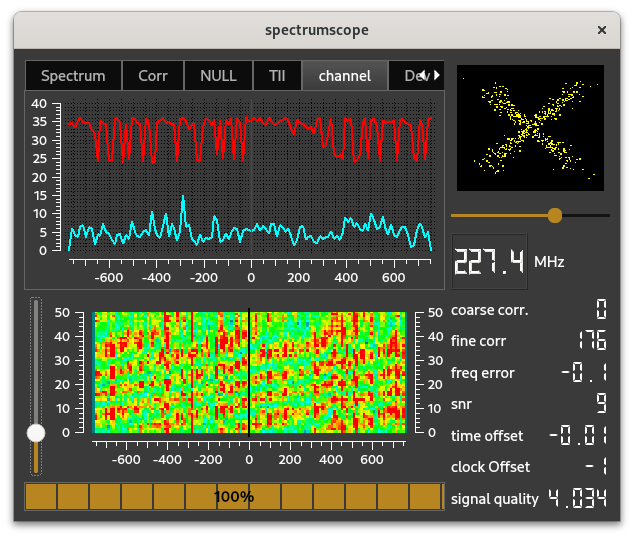
The channel scope shows the channel effect on the transmitted data, i.e. the deformation of the transmitted signal. The picture shows the cyan colored line, i.e. the channel effects (i.e. the deformation) on the amplitudes, and the red line, i.e. the channel effects on the phase of the samples. (The "jumps in the red line indicate the modulo 2*PI effect.)
Note that the implementation of this scope requires some additional libraries, therefore this scope is not part of the default configuration, although it is included in the precompiled versions.
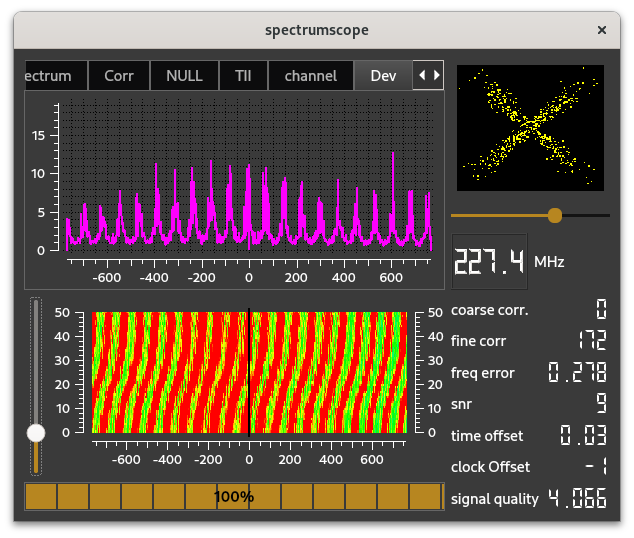
The deviation scope shows the mean deviation on the carriers in the decoded signal, before mapping the carriers to bits. The Y-axis is in Hz.
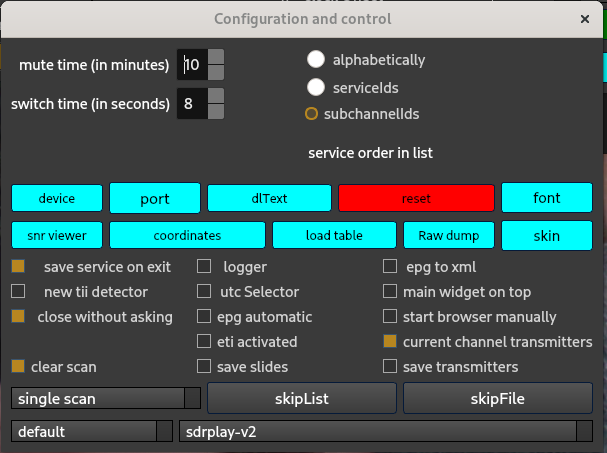
The configuration and control widget contains check boxes and buttons with which the configuration of the decoding process can be influenced.
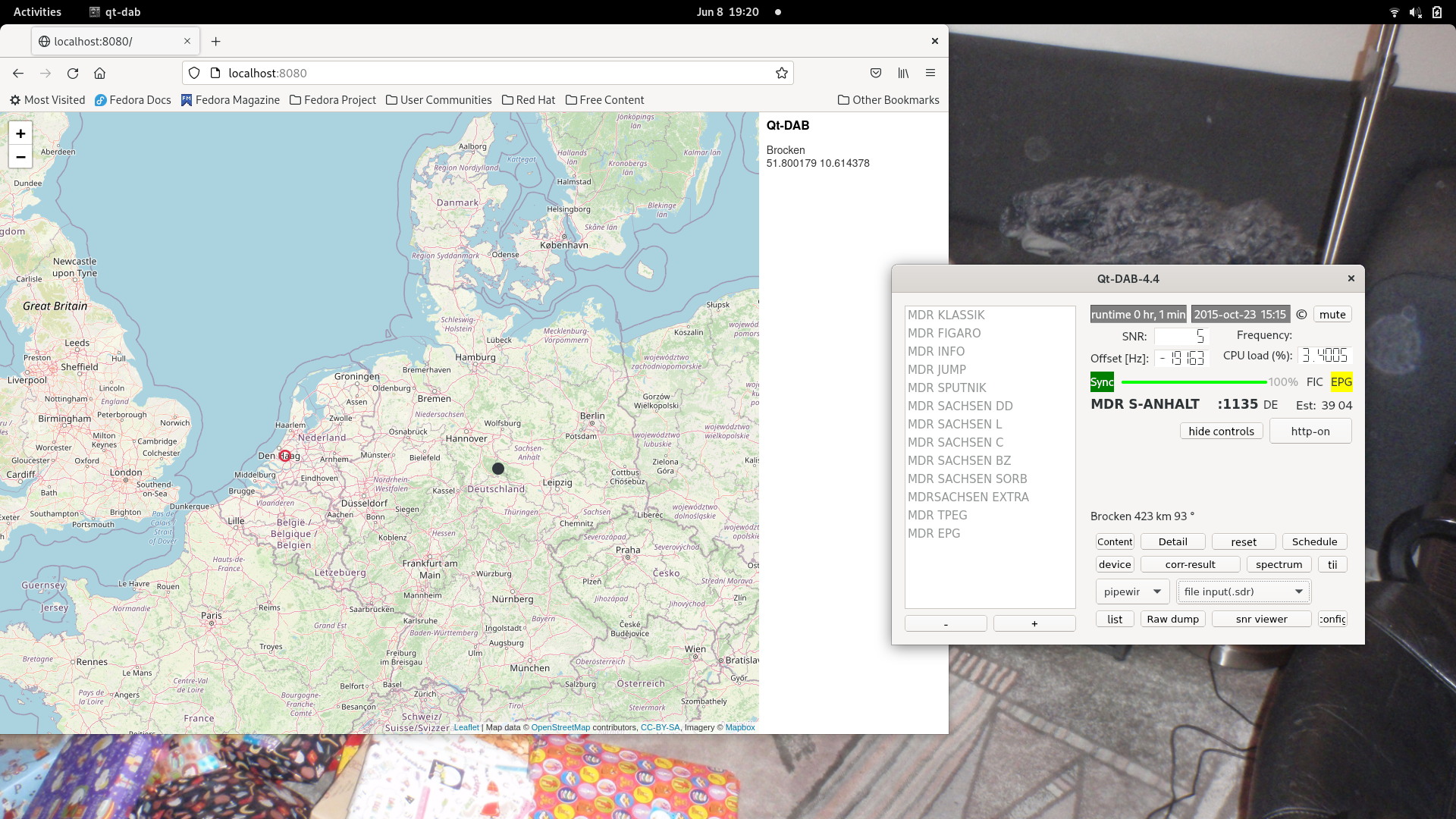
Since some time the Qt-DAB versions have a button labeled http, when touched, a small webserver starts that can show the position(s) of the transmitter(s) received on the map.
By default, on starting the server, the "standard" browser on the system will be invoked, listening to port 8080. The configuration (configuration/control) widget contains a selector for switching this off, so that one might choose his/hers own browser.
The feature will not work if
- handling the TII database is not installed on the system, and/or
- you did not provide your "home" coordinates.
The latter is easily done by touching the button "coordinates" on the configuration and control widget.
An extensive user's guide - in PDF format - for the 6.1 version can be found in the "docs" section of the source tree. The documentation contains a complete description of the widgets, of the values in the .ini file, on configuring for creating an executable (Linux), and even a complete description on how to add a device to the configuration.
For Windows an installer can be found in the releases section, https://github.com/JvanKatwijk/qt-dab/releases. The installer will install the executable as well as required libraries.
The installer will also call the official installer for the dll implementing the 2.3 api for getting access to the SDRplay devices.
For Linux-x64 systems, an appImage can be found in the releases section, https://github.com/JvanKatwijk/qt-dab/releases. The appImage contains next to the executable qt-dab program, the required libraries.
Of course it is possible to generate an executable, the manual contains a complete script for Ubuntu type Linux versions.
While for Linux-x64 and Windows there are precompiled versions, there may be reasons to build an executable. Building an executable is not very complicated, it is described in detail in the manual. Since it is customary to avoid reading a manual, here are the basic steps for the build process. Iy is strongly advised to use qmake/make in the process, since the number of configuration options is larger and selecting configuration options is much easier.
- ℹ️ Note that the sources for 4.4.x are now in the subdirectory
qt-dab-s4and for qt-dab-5.x in the subdirectoryqt-dab-s5 - Install required libraries, see section 5.5.3 (page 29) of the manual.
- :information: It turns out that in recent versions of Debian (and related) distributions the lib
qt5-defaultdoes not exist as as separate library.
- It seems to be part of another of the qt5 packages that is installed.
- Be aware that different distributions store qt files on different locations, adapt the INCLUDEPATH setting in the
.profile if needed.
While there are dozens of configuration options, take note of the following ones:
-
Note on configuring DABsticks (i.e. RTLSDR type devices). The Windows support library does not seem to be vapable of closing the library and reopening it on switching channels. Therefore a special version of the library is made, that is used for both Windows and Linux.
-
For including "soapy" in the configuration, soapy software should have been installed, so leave them commented out when not available. iF
ℹ️ Note that "pluto-2" can be compiled in: as the other support programs, when the device is selected, the support program will (try to) read in the functions of the device library.
For X64 PC's one may choose the option CONFIG+=PC (for selecting SSE instructions). If unsure, use CONFIG+=NO_SSE.
For letting the software show the transmitter and the azimuth, choose CONFIG += tiiLib (see step 4).
ℹ️ Note that the file converted_map.h is a generated file that contains a binary version of the HTML/javascript code for the server.
run qmake (variants of the name are qt5-qmake, qmake-qt5) which generates a Makefile and then run make.
Unpack file .txdata.tii (which contains the database data for finding the transmitter's name and location) from tiiFile.zip into the user's home directory. If Qt-DAB cannot find the file, it will just function without showing the names and without "maps" option.
If running on an x64 PC or bullseye on the RPI you might consider to install libtii-lib.so in /usr/local/lib from dab-maxi/library.
ℹ️ Note however that this library needs curl to be installed and source code for libtii-lib.so is not free. libtii-lib.so contains functionality for uploading a new database version (the "load" button on the configuration widget). If Qt-DAB cannot find the library, it will just function without the additional functionality.
ℹ️ Note: Building a version on a fresh install of "bullseye" on the RPI gave a version that wouldn't run: The Qt_PLUGIN_PATH was not set. Setting it as given below solved - for me - the problem:
Qt_5= /usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabihf/qt5
export QT_PLUGIN_PATH=$Qt_5/plugins
While it is known that the DAB transmissions are now all in Band III, there are situations where it might is desirable to use other frequencies. Qt-DAB provides the opportunity to specify your own band. Specify in a file a list of channels, e.g.
jan 227360
twee 220352
drie 1294000
vier 252650
and pass the file on with the -A command line switch. The channel name is just any identifier, the channel frequency is given in kHz. Your SDR device obviously has to support the frequencies for these channels.
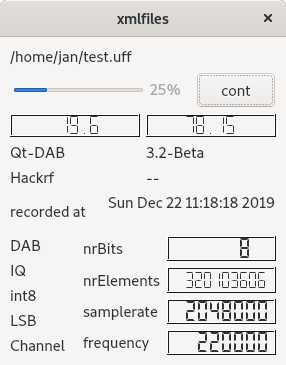
Clemens Schmidt, author of the QiRX program (https://qirx.softsyst.com/) and me defined a format for storing and exchanging "raw" data: .xml-files. Such a file contains in the first bytes - up to 5000 - a description in xml - as source - of the data contents. This xml description describes in detail the coding of the elements.
As an example, a description of data obtained by dumping Airspy input:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<SDR>
<Recorder Name="Qt-DAB" Version="3.2-Beta"/>
<Device Name="AIRspy" Model="I"/>
<Time Value="Wed Dec 18 12:39:34 2019" Unit="UTC"/>
<!--The Sample information holds for the whole recording-->
<Sample>
<Samplerate Value="2500000" Unit="Hz"/>
<Channels Bits="12" Container="int16" Ordering="LSB">
<Channel Value="I"/>
<Channel Value="Q"/>
</Channels>
</Sample>
<!--Here follow one or more data blocks-->
<Datablocks>
<Datablock Number="1" Count="375783424" Unit="Channel">
<Frequency Value="227360" Unit="KHz"/>
<Modulation Value="DAB"/>
</Datablock>
</Datablocks>
</SDR>
The device handlers in Qt-DAB support the generation of such an .xml file.
While the current implementation for reading such files is limited to a single data block, the reader contains a cont button that, when touched while playing the data, will cause continuous playing of the data in the data block.
The picture shows the reader when reading a file, generated from raw data emitted by the HackRF device.
Previous versions V5.4 and V4.7 will be maintained. Note that the different versions use the same sourcetree, the - almost - only difference being the GUI and its control.
Copyright (C) 2016 .. 2024
Jan van Katwijk ([email protected])
Lazy Chair Computing
The Qt-DAB software is made available under the GPL-2.0.
The SDR-J software, of which the Qt-DAB software is a part,
is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.