This guide will cover how to configure Okta to issue SSH credentials to specific groups of users. When used in combination with role based access control (RBAC), it allows SSH administrators to define policies like:
- Only members of "DBA" group can SSH into machines running PostgreSQL.
- Developers must never SSH into production servers.
!!! warning "Version Warning": This guide requires a commercial edition of Teleport. The open source edition of Teleport only supports Github as an SSO provider.
First, configure Teleport auth server to use SAML authentication instead of the local
user database. Update /etc/teleport.yaml as shown below and restart the
teleport daemon.
auth_service:
authentication:
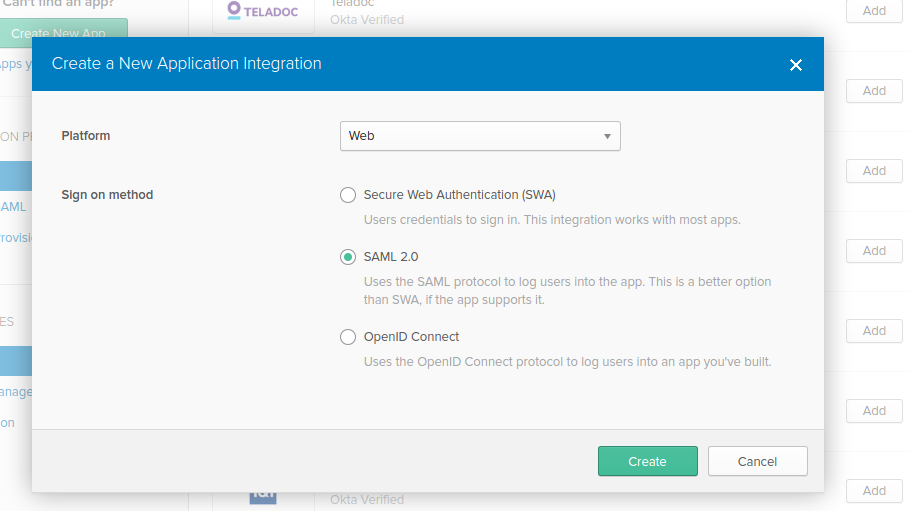
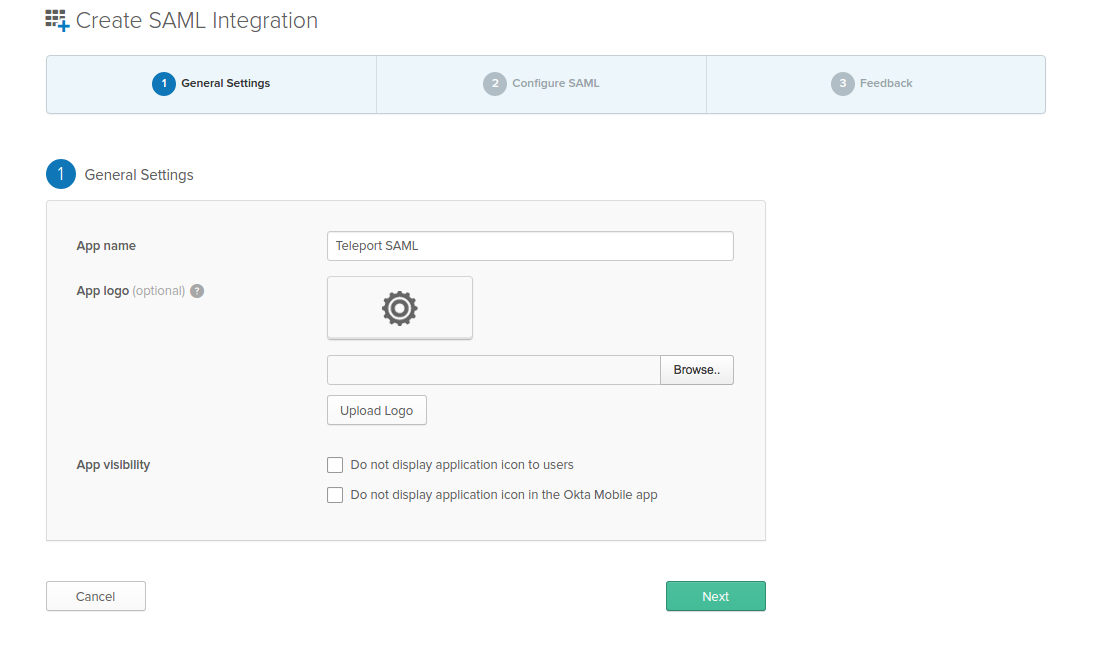
type: samlFirst, create a SAML 2.0 Web App in Okta configuration section
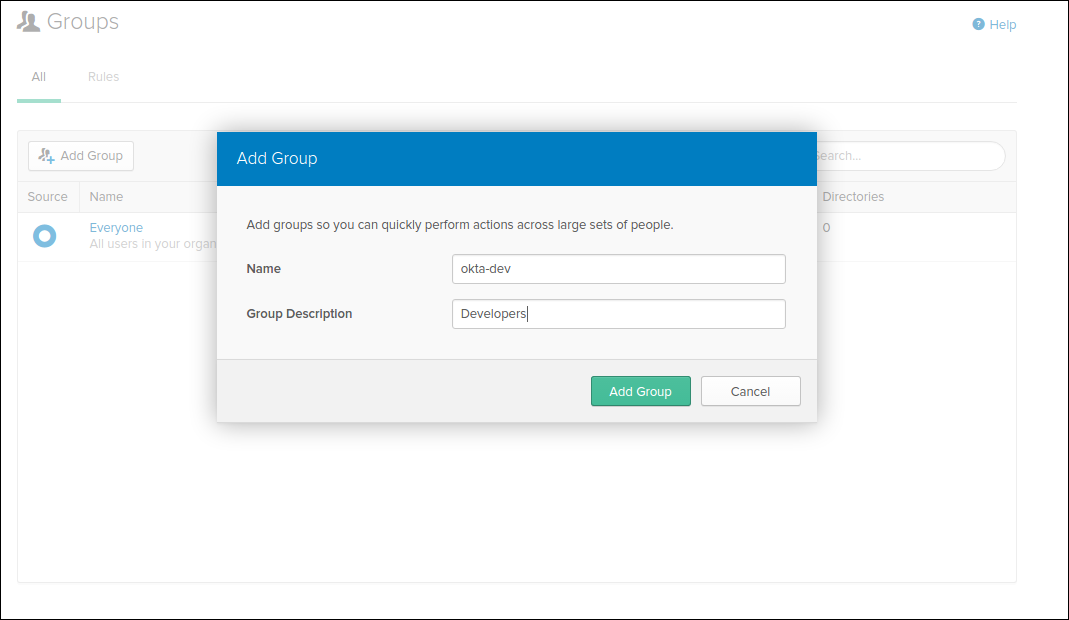
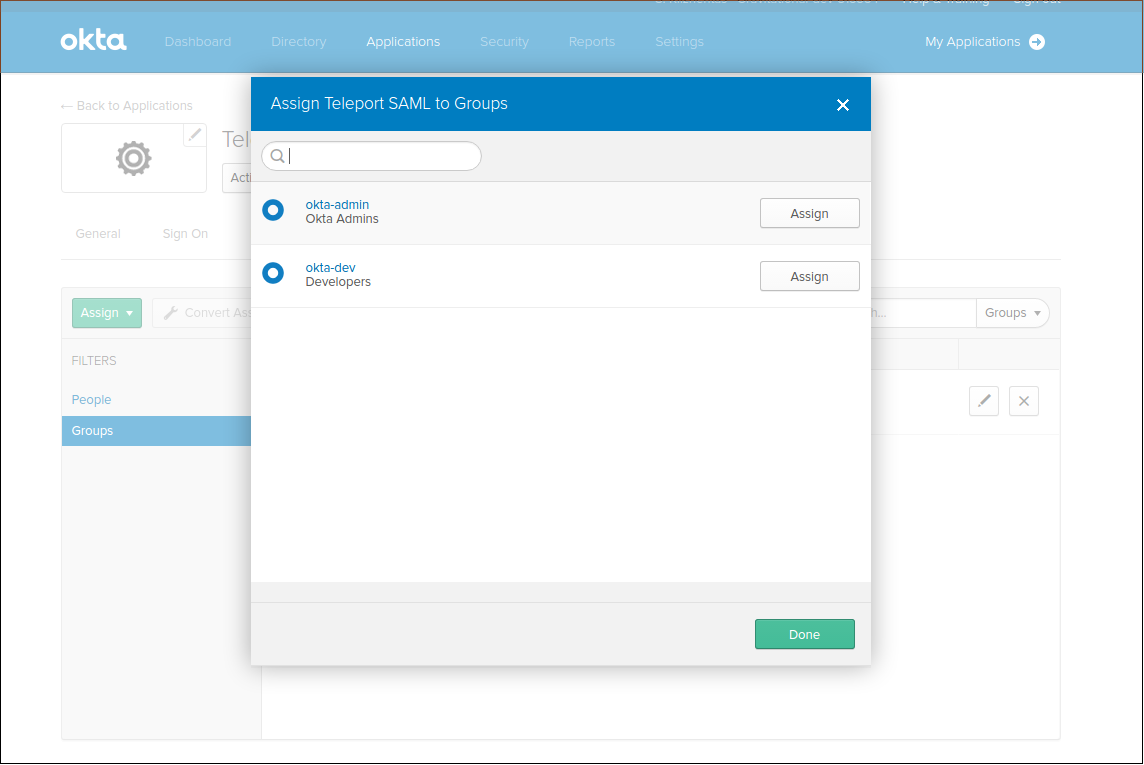
Create Groups
We are going to create two groups: "okta-dev" and "okta-admin":
...and the admin:
We are going to map the Okta groups we've created above to the SAML Attribute statements (special signed metadata exposed via a SAML XML response).
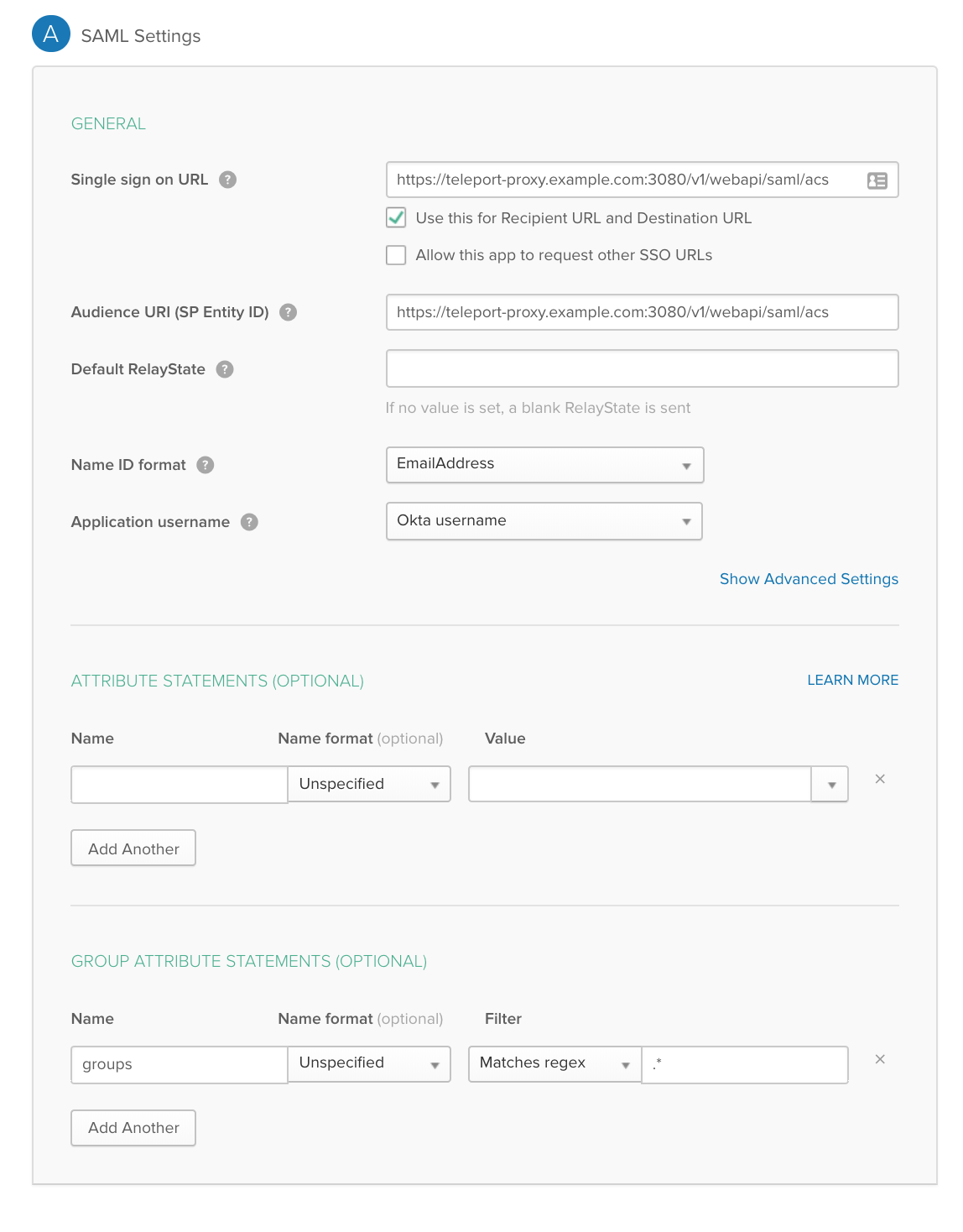
GENERAL
-
Single sign on URL
https://teleport-proxy.example.com:3080/v1/webapi/saml/acs -
Audience URI (SP Entity ID)
https://teleport-proxy.example.com:3080/v1/webapi/saml/acs -
Name ID format
EmailAddress -
Application username
Okta username
GROUP ATTRIBUTE STATEMENTS
-
Name:
groups| Name format:Unspecified -
Filter:
Matches regex|.*
!!! tip "Important": Notice that we have set "NameID" to the email format and mapped the groups with a wildcard regex in the Group Attribute statements. We have also set the "Audience" and SSO URL to the same value.
Assign groups and people to your SAML app:
Make sure to download the metadata in the form of an XML document. It will be used it to configure a Teleport connector:
Now, create a SAML connector resource:
# okta-connector.yaml
kind: saml
version: v2
metadata:
name: OktaSAML
spec:
# display allows to set the caption of the "login" button
# in the Web interface
display: "Login with Okta SSO"
acs: https://teleport-proxy.example.com:3080/v1/webapi/saml/acs
attributes_to_roles:
- {name: "groups", value: "okta-admin", roles: ["admin"]}
- {name: "groups", value: "okta-dev", roles: ["dev"]}
entity_descriptor: |
<paste SAML XML contents here>Create the connector using tctl tool:
$ tctl create okta-connector.yaml
We are going to create 2 roles, privileged role admin who is able to login as root and is capable of administrating the cluster and non-privileged dev.
kind: role
version: v3
metadata:
name: admin
spec:
options:
max_session_ttl: 24h
allow:
logins: [root]
node_labels:
"*": "*"
rules:
- resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]The developer role:
kind: role
version: v3
metadata:
name: dev
spec:
options:
max_session_ttl: 24h
allow:
logins: [ "{{external.username}}", ubuntu ]
node_labels:
access: relaxed- Devs are only allowed to login to nodes labelled with
access: relaxedlabel. - Developers can log in as
ubuntuuser - Notice
{{external.username}}login. It configures Teleport to look at "username" Okta claim and use that field as an allowed login for each user. - Developers also do not have any "allow rules" i.e. they will not be able to see/replay past sessions or re-configure the Teleport cluster.
Now, create both roles on the auth server:
$ tctl create admin.yaml
$ tctl create dev.yaml
The Web UI will now contain a new button: "Login with Okta". The CLI is the same as before:
$ tsh --proxy=proxy.example.com login
This command will print the SSO login URL (and will try to open it automatically in a browser).
!!! tip "Tip":
Teleport can use multiple SAML connectors. In this case a connector name
can be passed via tsh login --auth=connector_name
!!! note "IMPORTANT": Teleport only supports sending party initiated flows for SAML 2.0. This means you can not initiate login from your identity provider, you have to initiate login from either the Teleport Web UI or CLI.
If you get "access denied errors" the number one place to check is the audit
log on the Teleport auth server. It is located in /var/lib/teleport/log by
default and it will contain the detailed reason why a user's login was denied.
Some errors (like filesystem permissions or misconfigured network) can be
diagnosed using Teleport's stderr log, which is usually available via:
$ sudo journalctl -fu teleport
If you wish to increase the verbosity of Teleport's syslog, you can pass
--debug flag to teleport start command.