一开始class属性爆红,cannot resolve class or package ppr和cannot resolve class Car
solution:一开始用的ppr.Car当 ,因为建包的时候右键new没有package
,因为建包的时候右键new没有package
solution:
因为在 Idea 中,编译器只会把 src/main/java 也就是源代码目录下的 .java 文件编译成 .class 文件然后放到 target 目录中,其他的默认不会。
- 把spring.xml复制一份放到target/classes目录下
solution:可以看出我写错地方了(classes\spring.xml),写在”java\spring.xml“就解决了
solution:漏了对括号
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
---------------pom.xml-------------------
--------------spring.xml--------------------
<bean id="vehicle" class="com.ppr.Car"></bean>package com.ppr;
public interface Vehicle {
public void drive();
}package com.ppr;
public class Car implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void drive() {
System.out.println("car is running");
}
}package com.ppr;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App {
public static void main(String[]args){
ApplicationContext context= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Vehicle vehicle=(Vehicle) context.getBean("vehicle");
vehicle.drive();
}
}-
ApplicationContext context= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");Vehicle vehicle=(Vehicle) context.getBean("vehicle");//objext->Vehicle -
过去想用别的接口实现类得在main方法里改,耦合高+得重新编译测试。现在只需在pring.xml文档中
class="com.ppr.Car“,把Car改成其他实现类即可。
public class Tyre {
private String brand;//成员/属性
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Tyre{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
'}';
}
}<bean id="tyre" class="com.ppr.Tyre">
<property name="brand" value="test"></property>
</bean>- 相当于setter
- < constructor-arg>
public Tyre() {//无参构造
}
public Tyre(String brand) {//加了构造器
this.brand = brand;
}<bean id="tyre" class="com.ppr.Tyre">
<constructor-arg value="aaa"></constructor-arg>
</bean>---------------------------E.G.1---------------------------------------
public class Samsung {
public void config(){
System.out.println("samsung--config--method--");
}
}public class App //主方法
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ApplicationContext factory= new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Samsung s1=factory.getBean(Samsung.class);
s1.config();
}
}@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public Samsung setSamsung(){
return new Samsung();
}
}-
ApplicationContext factory= new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); Samsung s1=factory.getBean(Samsung.class);- AppConfig是配置类,@Configuration,相当于xml配置文件
- @Bean,表示一个bean,相当于< bean/>
-------------------------------E.G.2----自动连线/装载(@Autowired)------------------------------------------
public class Samsung {
private Processor cpu;//属性
public Processor getCpu() {
return cpu;
}
public void setCpu(Processor cpu) {
this.cpu = cpu;
}
public void config(){
System.out.println("samsung--config--method--");
cpu.run();
}
}@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public Samsung setSamsung(){
return new Samsung();
}
@Bean
public Processor getCpu (){
return new BestProcessor();
}
}public interface Processor {//处理器接口
public void run();
}public class BestProcessor implements Processor{
//接口实现类
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("^^i am best cpu~~");
}
}可以在config类中不写具体的Bean
-
config类+注解:
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "org.example")- 通过此注解,Spring容器会自动扫描指定基础包及其子包下的所有类,并将其注册为Spring的Bean。所以就不用在config类里写”@Bean“了。
-
bean对应的类上面加注解:
@Component- 默认bean id为类名+第一个字母小写
- 自定义bean id: Component("xxx")
@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "org.example") public class AppConfig { /* @Bean public Samsung setSamsung(){ return new Samsung(); } @Bean public Processor getCpu (){ return new BestProcessor(); } */ }
@Component
public class Samsung {。。。。。。}@Component
public class BestProcessor implements Processor{
。。。}-
如果在5.的code基础上加一个Processor接口实现类SecondProcessor
-
@Component public class SecondProcessor implements Processor{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("&&2nd CPU**"); } }
报错:Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'org.example.Processor' available: expected single matching bean but found 2: bestProcessor,secondProcessor
-
solution1:@Primary
-
solution2:@Qualifier("bean的id")
-
自动装配(@Autowired)的时候(
-

-
ps:一开始写的SecondP...报错,改小写(默认bean的id)就ok了
-
-
在接口的实现类上使用
@Qualifier注解指定一个唯一的标识符,然后在注入时使用@Qualifier指定要注入的具体实现类。-
上面写的直接用是因为:没有人为起标识符,则该bean的id就是默认形式,自己起标识符也行
-
public interface MyInterface { // ... } @Component @Qualifier("implementation1") //自己起了一个标识 public class MyImplementation1 implements MyInterface { // ... } @Component @Qualifier("implementation2") //自己起了另一个标识 public class MyImplementation2 implements MyInterface { // ... } @Component public class MyComponent { @Autowired @Qualifier("implementation1") //用标识说明用的哪一个 private MyInterface myInterface; }
-
-
-
ApplicationContext是IOC容器接口
-
容器中的对象在容器创建好之后就创建了(比getBean的时候早
-
Bean的属性名由setter决定(去掉set后首字母小写
-
< proverty>--setter;< constructor-arg>--构造器(该构造器有几个写几个< constructor-arg>
-
先按类型去容器中找对应类型的组件
-
Autowired(required=false)找不到就null,避免报错
可以在接口的实现类上使用@Qualifier注解指定一个唯一的标识符,然后在注入时使用@Qualifier指定要注入的具体实现类。
public interface MyInterface {
// ...
}
@Component
@Qualifier("implementation1")
public class MyImplementation1 implements MyInterface {
// ...
}
@Component
@Qualifier("implementation2")
public class MyImplementation2 implements MyInterface {
// ...
}
@Component
public class MyComponent {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("implementation1")
private MyInterface myInterface;
}@Autowired注解用于自动装配(自动注入)Spring容器中的Bean。通过使用@Autowired注解,可以方便地将依赖对象注入到需要使用它的地方,无需显式编写setter方法或构造函数。
@Autowired注解有以下几种使用方式:
- 根据类型自动装配:当只有一个与需求类型匹配的Bean存在时,Spring会自动将其注入。
@Autowired
private MyBean myBean;在上述示例中,MyBean类型的Bean将被自动注入到myBean字段中。
- 根据名称自动装配:当存在多个与需求类型匹配的Bean时,可以使用
@Qualifier注解配合@Autowired指定要装配的Bean的名称(通过唯一标识符或限定符)。
@Autowired
@Qualifier("myBean2")
private MyBean myBean;在上述示例中,根据@Qualifier("myBean2")指定要注入的Bean名称为"myBean2",从而解决了多个同类型Bean的命名歧义问题。
- 构造函数自动装配:可以在构造函数上使用
@Autowired注解,让Spring自动按照构造函数参数类型进行装配。
@Autowired
public MyClass(MyBean myBean) {
// ...
}在上述示例中,MyClass类的构造函数使用@Autowired注解,Spring将自动通过构造函数将MyBean类型的Bean注入到构造函数中。
@Autowired注解可以与@Component、@Service、@Repository和@Controller等注解一起使用,以便在组件扫描时自动装配Bean。当Spring容器实例化一个Bean,并发现有其他Bean依赖
1.一个类的成员是某个bean,自动注入
2.有多个满足类型查找的bean成员(如多个实现类)和@Qualifier 搭配使用,点明用哪个bean
3.构造方法自动装配。在创建实例时就已经完成了依赖注入。
- 对比1和3:①先创建myclass实例,检查@Autowired后发现mybean,后注入mybean ③创建实例时就完成依赖注入
方法上有@Autowired
1.这个方法在bean创建得时候自动运行
2.这个方法上每个参数都自动注入值
@Autowired,@Resource,@Injection都是自动装配
- @Resource:javaee自带,java标准--》扩展性强:如果换成别的容器框架也能用它
- @Autowired:spring框架的注解
@ContextConfiguration(locations="")指定spring的配置文件的位置
@RunWith(SpringJUnitClassRunner.class)指定用spring单元测试驱动来测试,以前默认是junit
不用再麻烦地getBean()来获取对象,可以在测试中使用自动装配
- 有Bookservice,Userservice两个bean(因为他俩都继承baseServlet<>相当于把里面代码复制粘贴过去
- --》在baseServlet<>写的@Autowired能正常运作
- @Autowired在上一行,--》自动装载了BaseDao< Book>对象,BaseDao< User>
- 去容器中按类型查找,即按BaseDao< Book>和BaseDao< User>分别查找,能匹配上唯一一个对象
- ioc是个容器,帮忙管理所有组件(@service等
- 某个组件要想使用spring提供的更多功能(ioc,aop),则必须加入容器中
- 容器底层其实是个map
- 源码调试思路:关键步骤打断点,进去看每一步具体咋执行
----》拿到代理对象,通过代理对象调用原来的方法。
缺点:jdk默认的动态代理,若目标对象未实现任何接口,则无法生成代理类
- 代理对象和目标对象唯一产生关联的地方:都实现了同样的接口
Spring实现AOP功能,底层就是动态代理,比动态代理简化。
- 通知方法--日志记录的方法
- 切面类--通知方法所在的类
- 连接点--原来的功能类可以写日志记录的地方
- 切入点--连接点中真正用了的地方
- 切入点表达式--表明在连接点中用了哪些切入点
1)将目标类和切面类加入ioc容器中(如@Service,@Component
2)告诉spring哪个类是切面类(@Aspect
3)告诉spring切面类中的通知方法都是什么时候运行
- @Before(切入表达式) 目标方法之前运行
- @After(切入表达式) 目标方法结束之后
- @AfterReturning(切入表达式) 目标方法正常返回之后
- @AfterThrowing (切入表达式) 目标方法异常之后
-

- 切入表达式
- "execution(public int 目标方法的全类名)"
- 从ioc容器中拿对象,如果按类型,用接口类型,不能用本类
- AOP通常基于代理模式实现,使用接口类型可以确保获取到的对象是代理对象
细节一:
如果把切面类的注解@Aspect(告诉Spring容器这是一个切面类)删掉,即没切入了,则bean还是苯类对象;但实现aop后就是动态代理对象。
细节七: 抽取可重用的切入点表达式(防止同样的切入点表达式,却不得不修改多处
- 写一个无返回值的方法
- 把重用的切入点表达式写入@Pointcut注解,原通知的切入点表达式处改为1.中的方法名()
public class logUtis {
@Pointcut("execution(public int com.calculator.impl.MyCal.*(int,int))")///
public void chongyong(){}///
@Before("chongyong()")///
public static void logStart(){
System.out.println("xx方法开始执行");
}
@After("chongyong()")///
public static void logEnd(){
System.out.println("xx方法结束");
}细节八: 环绕通知**@Around**
-
相当于Before,After,AfterThrowing,,AfterReturning四合一
-
通过反射调用目标方法
-
@Around能决定目标方法晕不晕行;但其他四个不能;--》比如做权限验证时,验证不过就不运行-->用@Around
无需牵扯目标方法的场景->用其他四个
-
有参数ProceedingJoinPiont pjp
- 是JoinPoint的子接口之一
- Object[] getArgs():获取连接点的参数数组。
- Object proceed(Object[] args):可以使用proceed()方法来控制目标方法的执行。当我们调用proceed()方法时,它会触发目标方法的执行,并返回目标方法的返回值(如果有)
@Pointcut("execution(public int com.calculator.impl.MyCal.*(int,int))")
public void chongyong(){}
@Around("chongyong()")
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();//获取目标方法参数
String name=pjp.getSignature().getName();//获取方法签名对象,通过签名对象获取方法名
Object proceed = null;
try{
//@Before
System.out.println(name+"xx方法开始执行");
proceed=pjp.proceed(args);//相当于目标方法的执行语句
//@AfterReturning
System.out.println(name+"xx方法正常返回");
}catch(Exception e){
//@AfterThrowing
System.out.println(name+"xx方法异常:"+e);
}finally{
//@After()
System.out.println(name+"xx方法结束");
}
return proceed;
}细节十: 多个切面执行顺序
add方法开始执行 [validate]add方法开始执行 [validate]add方法正常返回,结果是2 [validate]add方法结束 add方法正常返回,结果是2 add方法结束
Calculator接口
package com.calculator.infer;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
public interface Calculator {
public int add(int i,int j);
public int minus(int i,int j);
public int mul(int i,int j);
public int div(int i,int j);
}MyCal实现类
package com.calculator.impl;
import com.calculator.infer.Calculator;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MyCal implements Calculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result=i+j;
System.out.println(i+"+"+j+"="+result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int minus(int i, int j) {
return i-j;
}
@Override
public int mul(int i, int j) {
return i*j;
}
@Override
public int div(int i, int j) {
return i/j;
}
}Config配置类
package com.calculator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScans;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages ="com.calculator")
public class Config {
}logUtils切面类--添加日志
package com.calculator.utils;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy // 启用Spring的AOP功能*****
@Component
public class logUtis {
@Before("execution(public int com.calculator.impl.MyCal.*(int,int))")
public static void logStart(){
System.out.println("xx方法开始执行");
}
@After("execution(public int com.calculator.impl.MyCal.*(int,int))")
public static void logEnd(){
System.out.println("xx方法结束");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(public int com.calculator.impl.MyCal.*(int,int))")
public static void logReturn(){
System.out.println("xx方法正常返回");
}
@AfterThrowing(value="execution(public int com.calculator.impl.MyCal.*(int,int))",throwing="exception")
public static void logException(Exception exception){
System.out.println("xx方法异常:"+exception);
}
}依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.9.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.3.19</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>测试类
import com.calculator.Config;
import com.calculator.infer.Calculator;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test1 {
ApplicationContext ioc= new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
/*AnnotationConfigApplicationContext构造函数中传入的参数应该是配置类的类对象,
而不是配置类的名称。所以您需要将"Config.class"修改为Config.class。*/
@Test
public void test(){
Calculator bean= ioc.getBean(Calculator.class);//动态代理与接口实现类的唯一联系就是实现的接口,不能获取本类
bean.add(1,1);
bean.div(3,0);
}
}结果:
- 之前在test方法写了print语句,结果最后打印,我以为带上add()方法就会被日志方法夹在中间。其实只有在add方法体内写才还会有这种效果。chat道:
至于最后一行的"1+1=2"是您自己添加的输出语句,并不是切面逻辑产生的结果。
Aop使用场景
-
事务belike,异常-回滚,结束-关闭资源,返回 开始-提交
-
@Around能决定目标方法晕不晕行;但其他四个不能;--》比如做权限验证时,验证不过就不运行-->用@Around
无需牵扯目标方法的场景->用其他四个
配置:
- 加入ioc容器(bean tag
<bean id="myCal" class="com.calculator.impl.MyCal"></bean>
<bean id="logUtis" class="com.calculator.utils.logUtis"></bean>
<bean id="validateAspect" class="com.calculator.utils.validateAspect"></bean>2.告诉spring有哪些切面
<aop:config>
<!--指定切面-@Aspect-->
<aop:aspect ref="logUtis">
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect ref="validateAspect">
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>3.before,after之类的执行位置
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="globalpoint" expression="execution(int com.calculator.impl.MyCal.*(int,int))"/>
<!--指定切面-@Aspect-->
<aop:aspect ref="logUtis">
<aop:pointcut id="mypointcut" expression="execution(int com.calculator.impl.MyCal.*(int,int))"/><!--切面表达式,免得复制粘贴好几行-->
<aop:before method="logStart" pointcut-ref="mypointcut"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="logEnd" pointcut="execution(int com.calculator.impl.MyCal.*(int,int))"></aop:after>
<aop:after-throwing method="logException" pointcut-ref="mypointcut" throwing="exception"></aop:after-throwing>
<aop:after-returning method="logReturn" pointcut-ref="mypointcut" returning="result"></aop:after-returning>
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect ref="validateAspect">
<aop:before method="logStart" pointcut-ref="globalpoint"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="logEnd" pointcut-ref="globalpoint"></aop:after>
<aop:after-throwing method="logException" pointcut-ref="globalpoint" throwing="exception"></aop:after-throwing>
<aop:after-returning method="logReturn" pointcut-ref="globalpoint" returning="result"></aop:after-returning>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>-
public void checkout(String isbn,String username){ /*** * 购买图书操作 */ int price=bookDao.getBookPrice(isbn);//查价格 bookDao.updateBalance(username,price);//-余额 bookDao.updateStock(isbn);//-库存 }
上述业务操作,如若-库存的sql语句写错了,则没修改库存,但是账户余额已经改了--》不应该改,回滚之类的--》事务
-

-
-
①配置事务管理器(切面)让其进行事务控制--加入ioc容器--bean tag
-
控制住数据源
-
控制事务--控制连接--而从数据源获取连接connection--控制住数据源--加入属性
-
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean>
-
-
②开启基于注解的事务控制模式 依赖tx名称空间
-
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
-
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
-
-
③给事务方法加注解
-
@Transactional public void checkout(String isbn,String username){ }
but报错
通配符的匹配很全面, 但无法找到元素 'tx:annotation-driven' 的声明solution:->
xsi:schemaLocation后加了一个http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd -
-
isolation-Isolation 事务隔离级别
propagation-Propagation 事务传播行为
noRollbackFor-Class[] 哪些异常事务可以不回滚
boRollbackForClassName-String[](String全类名)
rollbackFor-Class[] 哪些异常事务要回滚
rollbackForClassName-String[]
readOnly-booolean 设置事务为只读【【可以进行事务优化:加快查询速度∵不执行增删改了】】
timeout-int (秒)事务超出指定执行时长后自动终止并回归
@Transactional(timeout = 3)@Transactional(timeout = 3)
public void checkout(String isbn,String username){
/***
* 购买图书操作
*/
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);//毫秒
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
。。。。。}- 运行时异常:可以不用处理【默认都回滚】
- 编译时异常:必须trycatch或throws【默认不回滚】
noRollbackFor让原来必须回滚的不回滚
@Transactional(timeout = 3,noRollbackFor = {ArithmeticException.class})//让数学异常可以不回滚
//noRollbackFor-Class[]
public void checkout(String isbn,String username){
/***
* 购买图书操作
*/
int price=bookDao.getBookPrice(isbn);//查价格
bookDao.updateBalance(username,price);//-余额
bookDao.updateStock(isbn);//-库存
int x=10/0;/////数学异常
}- 脏读不可以出现,其他的允许存在
- 都是读事务(readonly)与写事务之间
起始code:
public class BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
BookService(BookDao bookDao){
this.bookDao=bookDao;
}
/**隔离级别:可读未提交**/
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITTED)
public int getPrice(String isbn){
return bookDao.getBookPrice(isbn);
}
}@Test
public void test02(){
BookService bean = ioc.getBean(BookService.class);
System.out.println("ISBN-001单价"+bean.getPrice("ISBN-001"));
}结果:ISBN-001单价100
开启事务:
mysql> use tx
Database changed
mysql> start transaction;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> update book set price=999 where isbn="ISBN-001";
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 再执行测试test02时:ISBN-001单价999
回滚:
mysql> rollback;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) 再执行test:ISBN-001单价100
如果用回滚前的数据 进行一系列操作,显然是脏数据,产生一系列错误。
select @@transaction_isolation;
+-------------------------+
| @@transaction_isolation |
+-------------------------+
| REPEATABLE-READ |
+-------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> set session transaction isolation level read committ
ed;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select @@transaction_isolation;
+-------------------------+
| @@transaction_isolation |
+-------------------------+
| READ-COMMITTED |
+-------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)5.读已提交
- 第二次查询应该不变(因为另一个事务改了之后并没提交
- 问题原因:mysql自动提交
solution:SET autocommit=0;关闭自动提交
public void test02(){
BookService bean = ioc.getBean(BookService.class);
//System.out.println("ISBN-001单价"+bean.getPrice("ISBN-001"));
System.out.println(bean.getClass());//*
}①把BookService类中所有@Transactional都注释掉(即没有事务
class com.service.BookService
②取消注释掉的@Transactional
class com.service.BookService$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$b3a08004
-
当事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,必须指定事务应该如何传播
class A{ tran(){//事务tran里嵌有事务b和事务c b(){} c(){} } }
Q:事务c出异常了后事务b要不要回滚
A:可以靠设置 E.G.假设用的是REQUIRED b,c和tran共享事务(共享一个数据库连接),就是同一个事务--》完蛋一起完蛋--》∴b需要回滚

图解***********
- 因为小事务和大事务一起提交(执行完了还没提交),所以后边出了错能都滚蛋
@Service
public class MulService {
@Autowired
BookService bk;
@Transactional
public void mulTx(){
//@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
bk.checkout("ISBN-002","Tom");
//@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
bk.updatePrice("ISBN-003",99);
}
}@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
BookService(BookDao bookDao){
this.bookDao=bookDao;
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void checkout(String isbn,String username){
int price=bookDao.getBookPrice(isbn);//查价格
bookDao.updateBalance(username,price);//-余额
bookDao.updateStock(isbn);//-库存
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void updatePrice(String isbn,int price){
bookDao.updatePrice(isbn, price);
int i=10/0;///异常
}
}@Test
public void test03(){
MulService bean = ioc.getBean(MulService.class);
bean.mulTx();
}结果:因为updatePrice异常,打包滚蛋都回滚了,数据库数据并没有被修改。
- 历史遗留问题:第一次的时候异常语句写的sout(10/0),额,,没有都回滚,数据库还是被修改了,问了chatgpt说的也是前后矛盾,,说什么没被捕获之类的,但好像sout(10/0)和int i=10/0都是runtimeException,,
- checkout自己启动了自己的新事务后,执行完就立马提交了,所以就算后面大事务所在的事务回滚也不关他的事。
- 下图为两个小事务都是_NEW
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
doStuff();
}
public static void doStuff() {
doMoreStuff();
}
public static void doMoreStuff() {
System.out.println(10/0);
}
}方法调用时main->doStuff->doMoreStuff
RuntimeException的抛出顺序是从当前方法开始顺着调用栈向上传播
-
doMoreStuff()方法中有一个算术操作System.out.println(10/0),它会抛出一个ArithmeticException。但没捕获没处理,异常开始向上传播,离开
doMoreStuff()方法,并返回到doStuff()方法。 -
由于
doStuff()方法没有捕获这个异常,它会继续向上传播,离开doStuff()方法,并返回到main方法。 -
main方法也没有捕获异常,所以异常继续向上传播,离开main方法。 -
当异常离开
main方法时,程序终止,并在控制台打印异常信息和堆栈跟踪。
①
@Service
public class MulService {
........
@Transactional
public void mulTx(){
//REQUIRED_NEW
bk.checkout("ISBN-002","Tom");
//REQUIRED
bk.updatePrice("ISBN-003",99);//有算数异常
}
}- checkout把numTx挂起,自己另开了一个事务,执行完立马给自己提交了,然后mulTx又开启,mulTx事务的大家一起提交。所以在updatePrice和mulTx一起滚蛋(整个事务内的)的时候,不管他事。
②
@Service
public class MulService {
........
@Transactional
public void mulTx(){
//REQUIRED
bk.checkout("ISBN-002","Tom");
//REQUIRED_NEW
bk.updatePrice("ISBN-003",99);//有算术异常
}
}- updatePrice()中的异常未被捕获,继续往上找到mulTx()导致这个事务一起完蛋(都没提交,∵大事务还没执行完),所以在这个事务中(REQUIRED)的checkout()会一起回滚。
③
@Service
public class MulService {
........
@Transactional
public void mulTx(){
//REQUIRED_NEW
bk.checkout("ISBN-002","Tom");
//REQUIRED_NEW
bk.updatePrice("ISBN-003",99);
int i=10/0;//数学异常(在mulTx事务内
}
}- 作为 _NEW,两个小事务都把mulTx挂起,自己的事务执行完立马提交了。∴执行到mulTx内的异常时,他俩不会回滚。
- 小事务相当于继承的大事务的
REQUIRED:将之前事务用的connection传递给这个方法使用
REQUIRED_NEW:这个方法直接使用新的connection
-
上图在BookService中直接写mulTx,无法实现创自挤的事务
-

-
因为是调用事务方法实现的,而在本类内直接写没有动态代理对象,实现不了这种效果。
[^]: 事务细节3.7:bean.getClass()-》class com.service.BookService$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$b3a08004
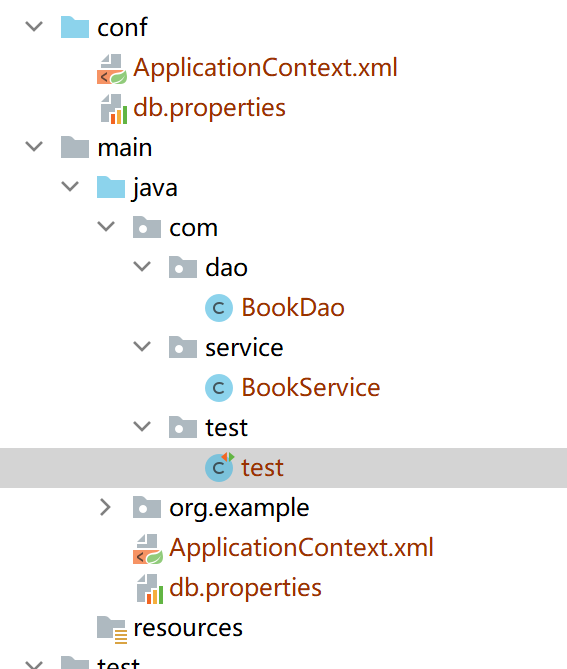
main包下的xml是我从conf下复制的,而test中ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext.xml");用的是原来conf目录下的xml--》致使后来加上<context:component-scan base-package="com.*" />后也找不到bean--》最后靠在原来路径的xml加<context:component-scan base-package="com.*" />解决
-
<context:component-scan base-package="com.*" />- 告诉Spring在指定的包及其子包中自动扫描并注册带有特定注解的组件。(即告诉他我用了注解没写bean标签,去读取去)