- Offline Kernel-Aware Sparse Pattern Search
- MInference Benchmark Experiments
- MInference Downstream Tasks Experiments
You can use the following scripts to search for the optimal head sparse pattern:
cd experiments/infinite_bench
python run_infinitebench.py \
--task kv_retrieval \
--model_name_or_path gradientai/Llama-3-8B-Instruct-262k \
--data_dir ./data \
--output_dir ./results \
--max_seq_length 30000 \
--rewrite \
--is_search \
--start_example_id 3 \
--topk_dims_file_path Llama_3_8B_Instruct_262k_kv_out_v32_fit_o_best_pattern.json \
--num_eval_examples 20 --topk 1 --starting_layer 0 --attn_type minference
Note
All experiments were run on a single A100 GPU with 80GB of VRAM.
Environment parameters:
- CUDA 12.3
- Triton 2.1.0
To demonstrate the efficiency of our method, we conducted end-to-end latency tests using the LLaMA-3-8B-Instruct-1M model. The prompts were trimmed to different target token numbers, and we measured the pre-filling stage latency without using KV cache.
- Download the prompt:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FranxYao/chain-of-thought-hub/main/gsm8k/lib_prompt/prompt_hardest.txt- Run a single context window size test using one method:
# If the context window is greater than 700K, you need to enable kv_cache_cpu.
python experiments/benchmarks/benchmark_e2e.py --attn_type minference --context_window 1_000_000 --kv_cache_cpu
python experiments/benchmarks/benchmark_e2e.py --attn_type minference_with_dense --context_window 1_000_000 --kv_cache_cpu
python experiments/benchmarks/benchmark_e2e.py --attn_type minference --context_window 500_000- Run all latency experiments using different methods:
python experiments/benchmarks/benchmark_e2e.py --run_benchmark- After that, you should get the end-to-end latency results like this:
FlashAttention-2 StreamingLLM InfLLM MInference
1K 0.54565 1.07110 2.94495 2.96450
10K 0.97590 1.18339 2.21052 2.77618
50K 8.52933 5.47972 14.63624 7.54537
100K 24.88319 10.86379 27.67215 13.98508
200K 79.39184 21.61490 55.64703 26.81303
300K 169.62441 32.44844 80.74326 41.09374
500K 456.78353 54.15910 167.91472 66.27691
1000K 1765.56387 107.85639 328.58551 179.12031Tip
Based on our tests, a single A100 can support up to 1.8M context prompts during the pre-filling stage using LLaMA-3-8B-4M with bf16.
And we also built the End-to-End benchmark using vLLM. You can run it using the following scripts:
- Download the prompt:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FranxYao/chain-of-thought-hub/main/gsm8k/lib_prompt/prompt_hardest.txt- Run a single context window size test using one method:
python experiments/benchmarks/benchmark_e2e_vllm.py --attn_type minference --context_window 100_000Here are some vLLM latency data, for reference, on an A100:
FlashAttention-2 MInference
1K 0.08062 3.01744
10K 0.83215 2.76216
50K 7.71675 7.53989
100K 21.73080 14.08111
128K 32.86252 18.82662Please note that the current vLLM version only supports MInference and FlashAttention modes. Due to vLLM's PageAttention management of the KV cache, a single A100 can handle a maximum context window size of 130k.
Note
All of these experiments were run on one A100 GPUs with 80GB of VRAM. You may need to modify commands to fit your own computing environment (e.g., changing the batch size, the max memory per GPU, the number of GPUs, etc)
InfiniteBench is a benchmark tailored for evaluating the capabilities of language models to process, understand, and reason over super long contexts.
InfiniteBench consists of the following tasks: kv_retrieval, longbook_choice_eng, math_find, longbook_qa_chn, longbook_qa_eng, longdialogue_qa_eng, code_debug, longbook_sum_eng, number_string, passkey.
- Run InfiniteBench with
MInference:
bash experiments/infinite_bench/run_infinitebench.sh gradientai/Llama-3-8B-Instruct-262k 160000 -1 minference- Experimental results
| Methods | longbook_sum_eng | longbook_qa_eng | longbook_choice_eng | longdialogue_qa_eng | longbook_qa_chn | code_debug | math_find | passkey | number_string | kv_retrieval | Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Attention | 20.2 | 12.4 | 67.3 | 6.0 | 12.9 | 22.1 | 26.6 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 14.4 | 38.2 |
| Ours | 20.5 | 12.9 | 65.9 | 7.5 | 12.5 | 22.3 | 33.1 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 12.8 | 38.8 |
The RULER benchmark is a challenging long-context LLMs benchmark contains four task categories: Retrieval, Multi-hop Tracing, Aggregation, and Question Answering (QA). The retrieval tasks extend the needle-in-a-haystack (NIAH) test; Multi-hop Tracing involves resolving coreference chains; Aggregation requires identifying frequently occurring words; and QA adapts existing datasets with added distracting information to test models on extended contexts.
To run the RULER benchmark, you need first install the requirements:
pip install Cython
pip install nemo-toolkit[all]==1.21 --no-deps
pip install -r experiments/ruler/requirements.txt- Download required data files:
cd experiments/ruler/data/synthetic/json/
# download Paul Graham Essays for the needle test
python download_paulgraham_essay.py
# download SQuAD and HotpotQA for the QA test
bash download_qa_dataset.sh
# you will need nltk.download('punkt') as well
python -c "import nltk; nltk.download('punkt')"- Run RULER with
MInferenceandLlama-3-8B-Instruct-262k:
# under the experiments/ruler/ directory
bash run.shThe default output dir results/ruler, you use ROOT_DIR in run.sh to change the output dir.
- Experimental results
| Models | Claimed | Effective | 4K | 8K | 16K | 32K | 64K | 128K | Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Attention | 262K | 16K | 97.2 | 91.8 | 87.3 | 80.8 | 77.4 | 72.2 | 84.4 |
| Ours | - | 32K | 97.7 | 91.2 | 88.5 | 85.0 | 82.3 | 77.6 | 87.0 |
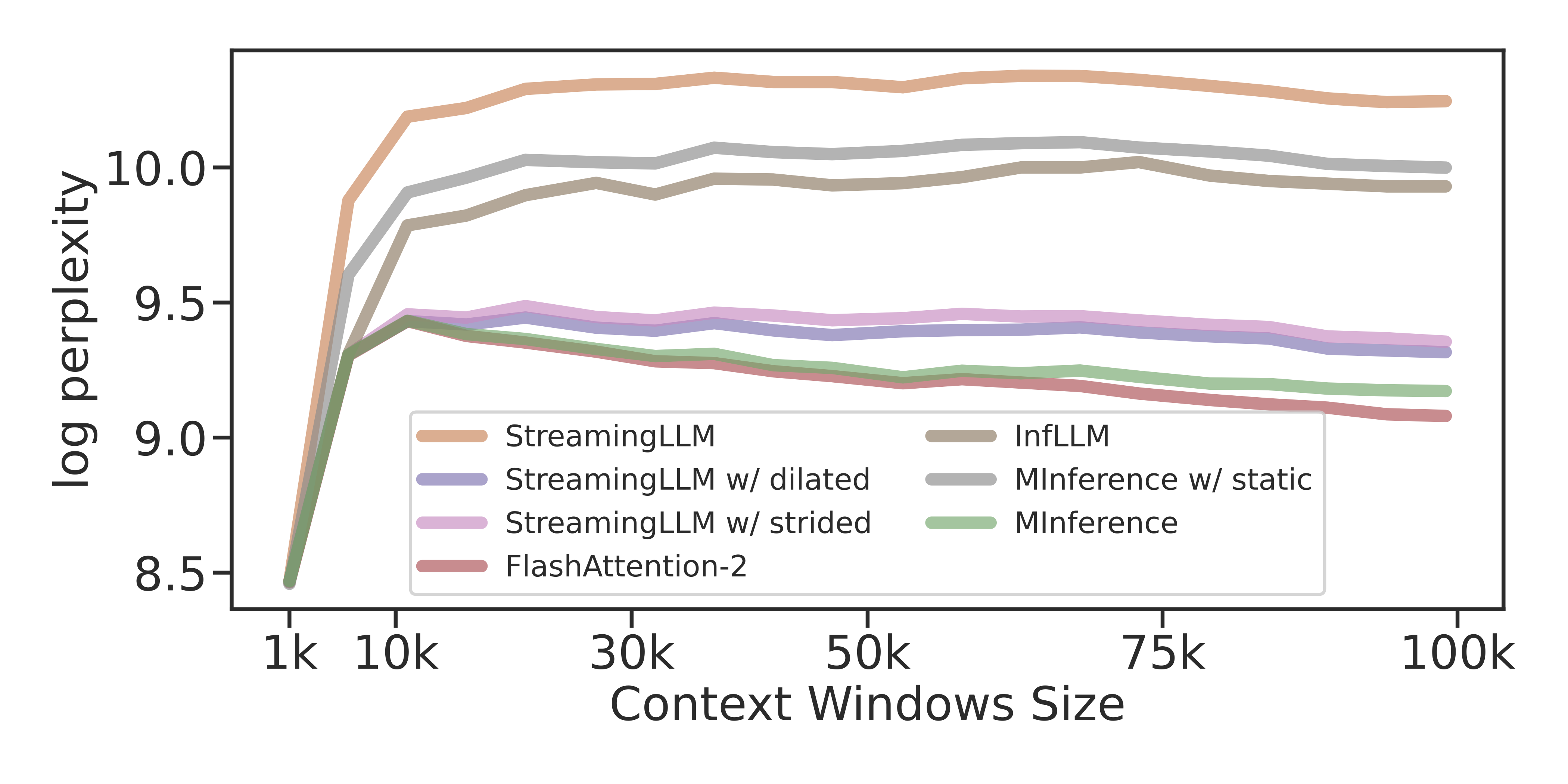
We use continues 100K text chunks samples from PG-19 for the perplexity evaluation.
- To run the PPL test, simply run:
bash experiments/ppl/run_ppl.shThe result will be saved at results/long-ppl/, and the visualization will be saved as results/long-ppl/long-ppl-viz.png.
- Experimental results
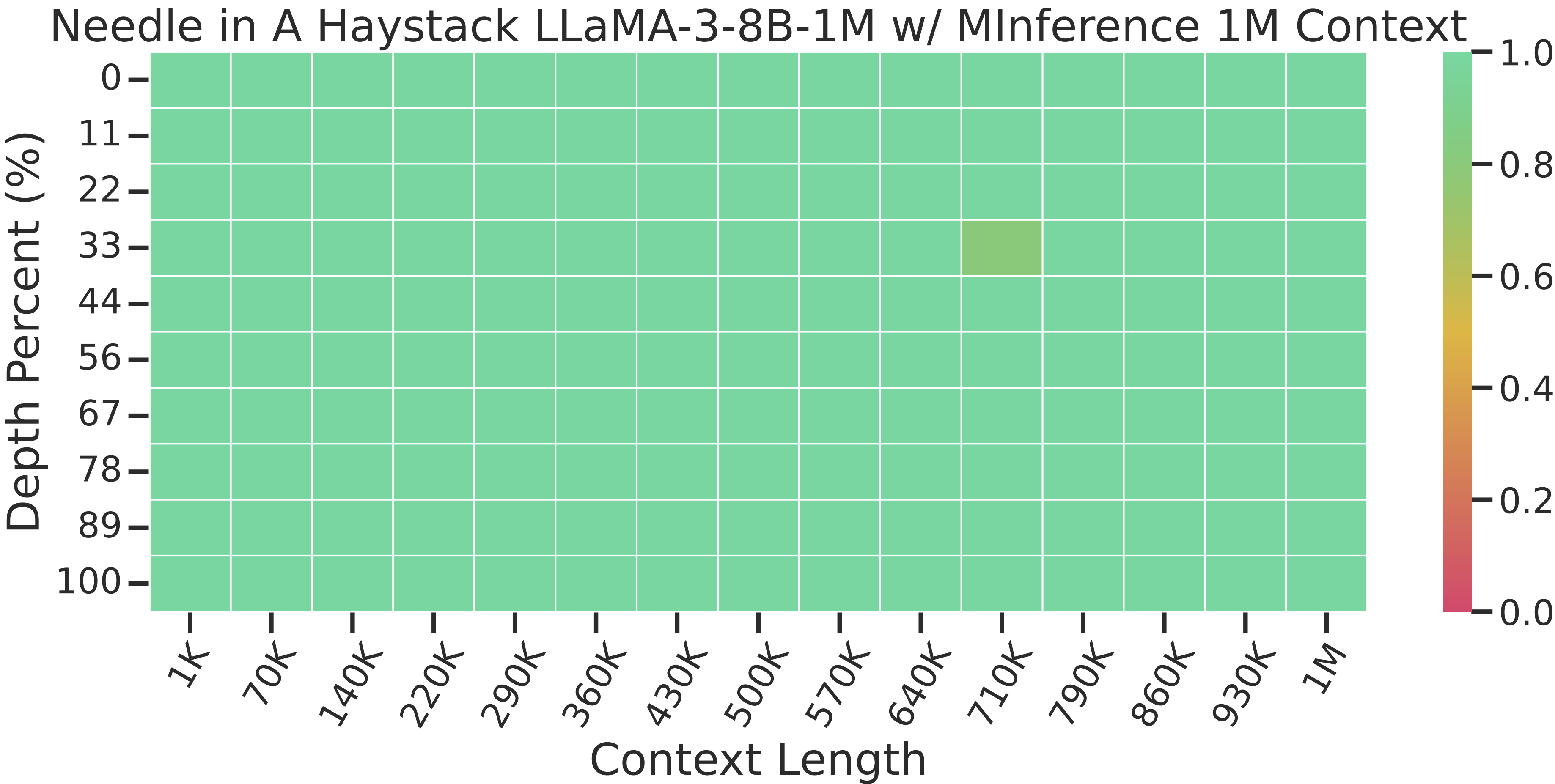
The Needle In A Haystack test is an evaluation method that randomly inserts key information into long texts to form prompts for large language models (LLMs). The test aims to detect whether large models can extract such key information from extensive texts, thereby assessing the models’ capabilities in processing and understanding long documents.
- Run the Needle in A Haystack test:
bash experiments/needle_in_a_haystack/run_needle.shThe results will be saved under ./needle directory.
- Our experimental results