< Previous Module - Home - Next Module >
To populate Azure Purview with assets for data discovery and understanding, you must register sources that exist across our data estate so that we can leverage the out of the box scanning capabilities. Scanning enables Azure Purview to extract technical metadata such as the fully qualified name, schema, data types, and apply classifications by parsing a sample of the underlying data.
In this module, you'll walk through how to register and scan data sources. You'll create a new collection for your first data source, upload data and configure scanning. By the end of this module you'll have technical metadata, such as schema information, stored in Purview. You can use this to start linking to business terms, allowing your team members to easier find data.
- An Azure account with an active subscription.
- An Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account (see module 00).
- An Azure Azure Purview account (see module 01).
- Azure Storage Explorer (Download and Install)
- Create a collection.
- Register and scan an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account using the Azure Purview managed identity.
| # | Section | Role |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Grant the Azure Purview Managed Identity Access | Azure Administrator |
| 2 | Upload Data to Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 Account | Azure Administrator |
| 3 | Create a Collection | Collection Administrator |
| 4 | Register a Source (ADLS Gen2) | Data Source Administrator |
| 5 | Scan a Source with the Azure Purview Managed Identity | Data Source Administrator |
| 6 | View Assets | Data Reader |
💡 Did you know?
To scan a source, Azure Purview requires a set of credentials. For Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, Azure Purview supports the following authentication methods.
- Managed Identity (recommended)
- Service Principal
- Account Key
In this module we will walk through how to grant the Azure Purview Managed Identity the necessary access to successfully configure and run a scan.
-
Navigate to your Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account (e.g.
pvlab{randomId}adls) and select Access Control (IAM) from the left navigation menu. -
Click Add role assignments.
-
Filter the list of roles by searching for
Storage Blob Data Reader, click the row to select the role, and then click Next. -
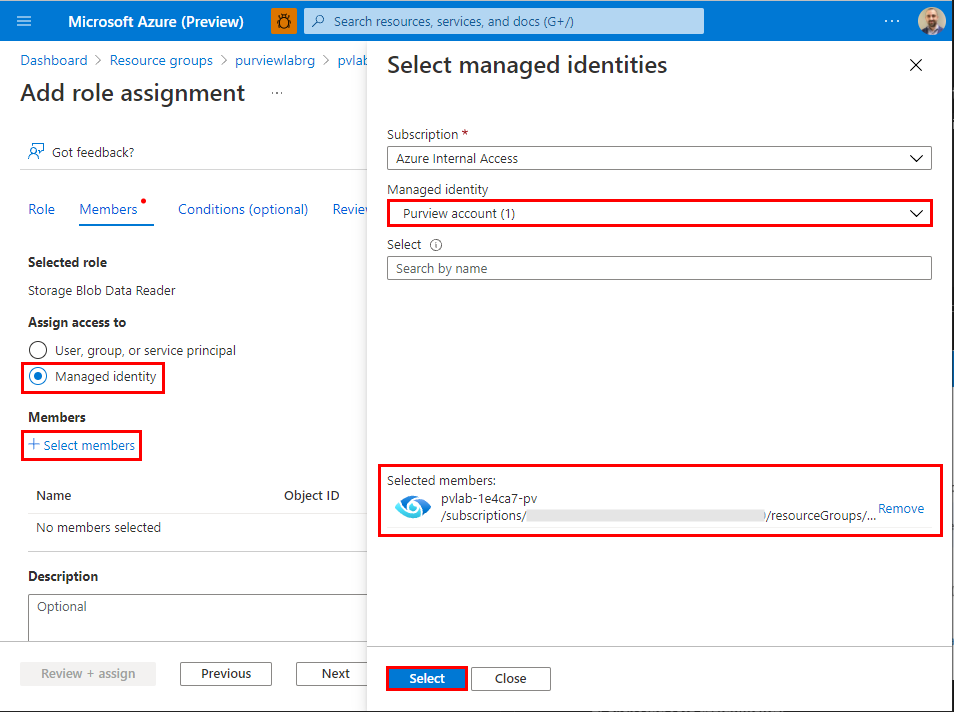
Under Assign access to, select Managed identity, click + Select members, select Purview account from the Managed Identity drop-down menu, select the managed identity for your Azure Purview account (e.g.
pvlab-{randomId}-pv), click Select. Finally, click Review + assign. -
Click Review + assign once more to perform the role assignment.
-
To confirm the role has been assigned, navigate to the Role assignments tab and filter the Scope to
This resource. You should be able to see that the Azure Purview managed identity has been granted the Storage Blob Data Reader role.
Before proceeding with the following steps, you will need to:
- Download and install Azure Storage Explorer.
- Open Azure Storage Explorer.
- Sign in to Azure via View > Account Management > Add an account....
-
Download a copy of the Bing Coronavirus Query Set to your local machine. Note: This data set was originally sourced from Microsoft Research Open Data.
-
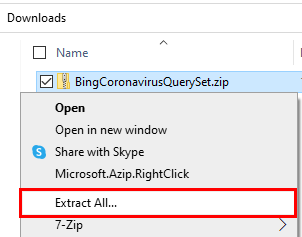
Locate the downloaded zip file via File Explorer and unzip the contents by right-clicking the file and selecting Extract All....
-
Click Extract.
-
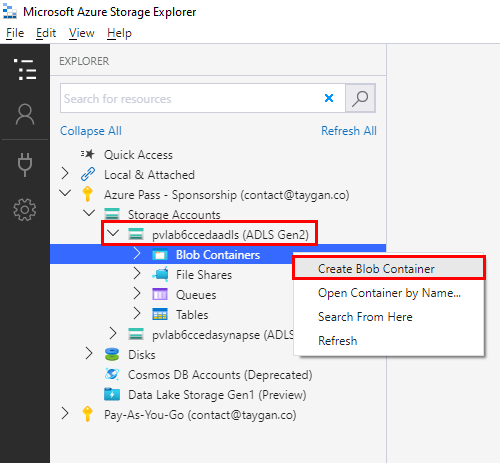
Open Azure Storage Explorer, click on the Toggle Explorer icon, expand the Azure Subscription to find your Azure Storage Account. Right-click on Blob Containers and select Create Blob Container. Name the container raw.
-
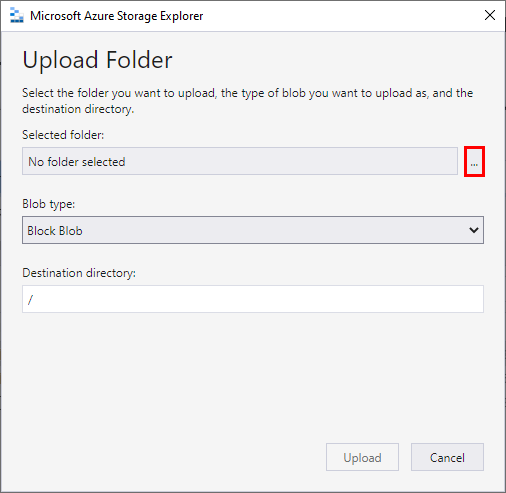
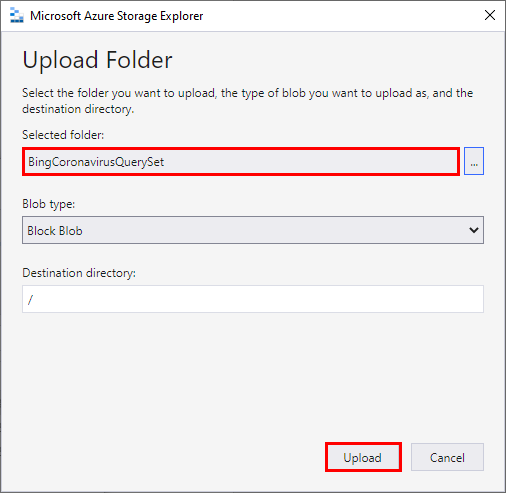
With the container name selected, click on the Upload button and select Upload Folder....
-
Click on the ellipsis to select a folder.
-
Navigate to the extracted BingCoronavirusQuerySet folder (e.g. Downloads\BingCoronavirusQuerySet) and click Select Folder.
-
Click Upload.
-
Monitor the Activities until the transfer is complete.
💡 Did you know?
Collections in Azure Purview can be used to organize data sources, scans, and assets in a hierarchical model based on how your organization plans to use Azure Purview. The collection hierarchy also forms the security boundary for your metadata to ensure users don't have access to data they don't need (e.g. sensitive metadata).
For more information, check out Collection Architectures and Best Practices.
-
Open Purview Studio, navigate to Data Map > Collections, and click Add a collection.
-
Provide the collection a Name (e.g. Contoso) and click Create.
-
Open Purview Studio, navigate to Data Map > Sources, and click on Register.
-
Select Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 and click Continue.
-
Select the Azure subscription, Storage account name, Collection, and click Register.
💡 Did you know?
At this point, we have simply registered a data source. Assets are not written to the catalog until after a scan has finished running.
-
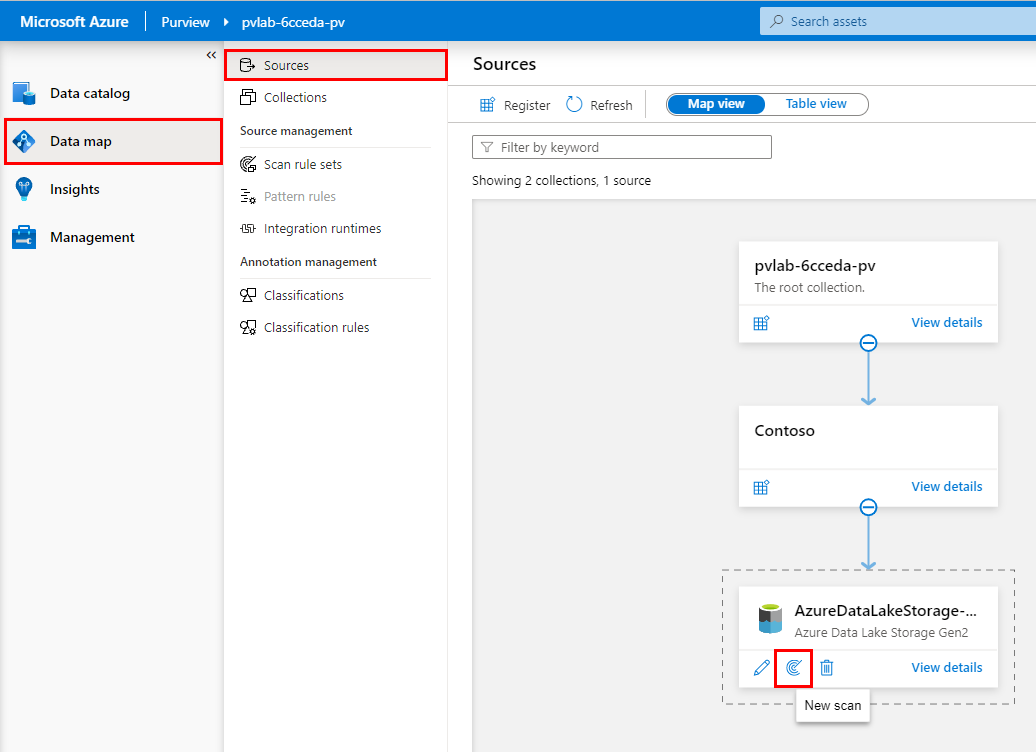
Open Purview Studio, navigate to Data Map > Sources, and within the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 tile, click the New Scan button.
-
Click Test connection to ensure the Azure Purview managed identity has the appropriate level of access to read the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account. If successful, click Continue.
-
Expand the hierarchy to see which assets will be within the scans scope, and click Continue.
-
Select the system default scan rule set and click Continue.
💡 Did you know?
Scan Rule Sets determine which File Types and Classification Rules are in scope. If you want to include a custom file type or custom classification rule as part of a scan, a custom scan rule set will need to be created.
-
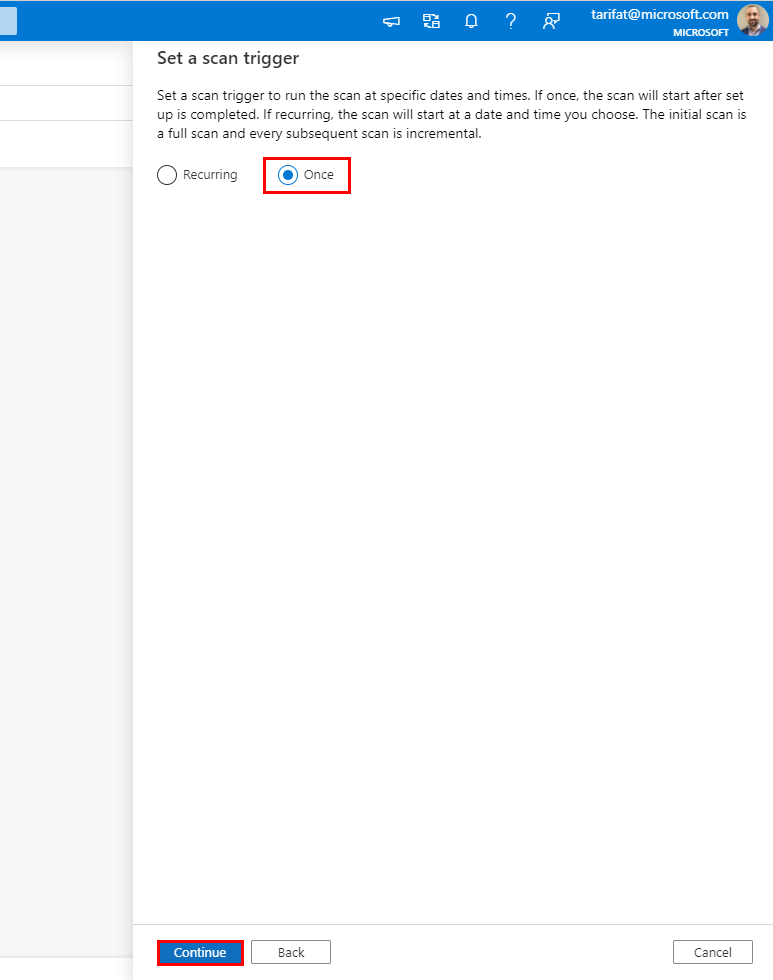
Select Once and click Continue.
-
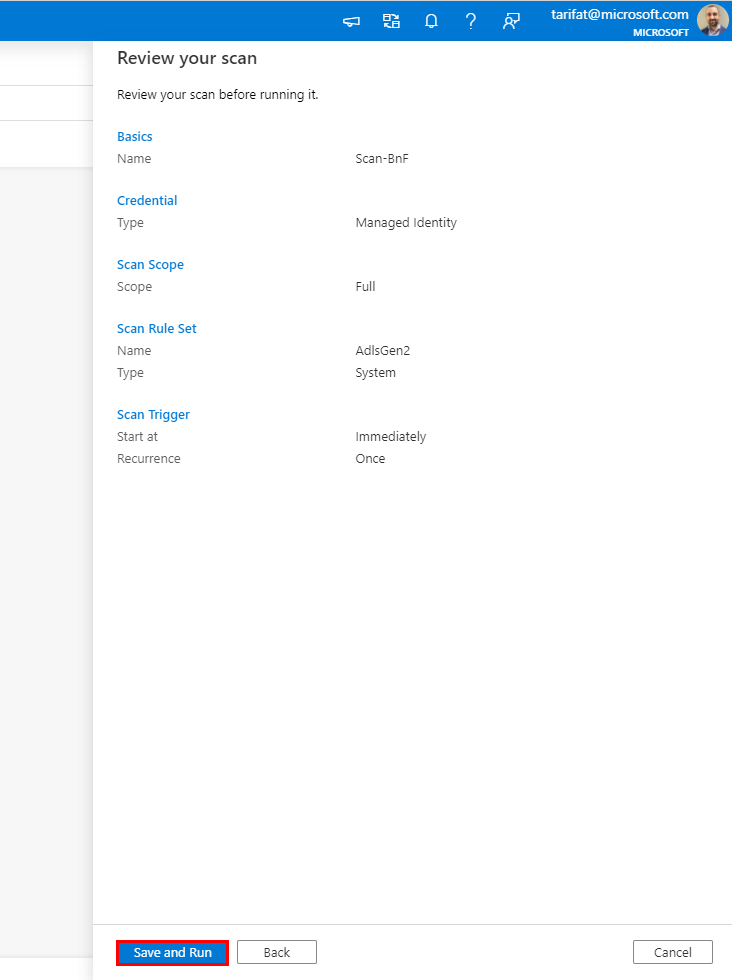
Click Save and Run.
-
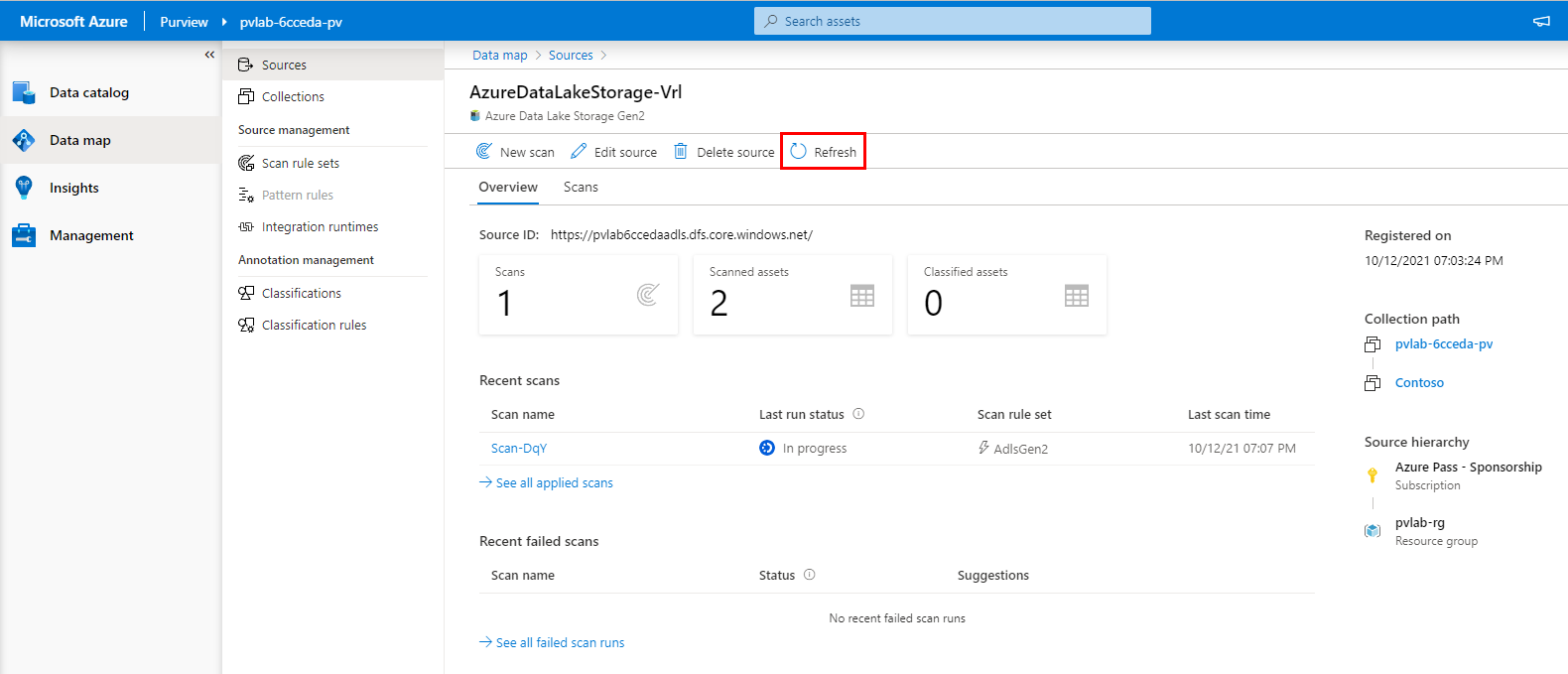
To monitor the progress of the scan run, click View Details.
-
Click Refresh to periodically update the status of the scan. Note: It will take approximately 5 to 10 minutes to complete.
-
Navigate to Purview Studio > Data catalog, and perform a wildcard search by typing the asterisk character (
*) into the search box and hitting the Enter key to submit the query. -
You should be able to see a list of assets within the search results, which is a result of the scan.
-
What type of object can help organize data sources into logical groups?
A ) Buckets
B ) Collections
C ) Groups -
At which point does Azure Purview begin to populate the data map with assets?
A ) After an Azure Purview account is created
B ) After a Data Source has been registered
C ) After a Data Source has been scanned -
Which of the following attributes is not automatically assigned to an asset as a result of the system-built scanning functionality?
A ) Technical Metadata (e.g. Fully Qualified Name, Path, Schema, etc)
B ) Glossary Terms (e.g. columnSales Taxis tagged with theSales Taxglossary term)
C ) Classifications (e.g. columnccnumis tagged with theCredit Card Numberclassification)
This module provided an overview of how to create a collection, register a source, and trigger a scan.