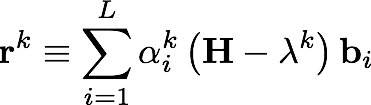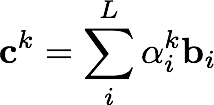A common problem in quantum chemistry is the need to compute a few eigenvalues of a very large matrix -- far too large to store entirely in core memory. In 1975, Ernest Davidson published a robust algorithm1 to solve this problem, and it has been used in electronic structure software packages ever since. A few years later, Bowen Liu extended the algorithm to allow computation of several eigenvalues simultaneously rather than one at a time2. The purpose of this project is to illustrate the use of what is now called the Davidson-Liu algorithm in the context of a CIS computation.
This is an outline of the essential aspects of the Davidson-Liu algorithm. There are many ways to tweak the approach to improve its rate of convergence or efficiency, and for details I recommend David Sherrill's excellent CI review article3, from which also we take our notation below.
Compute a set of L orthonormal guess eigenvectors, {bi} --- at least one for every desired root. A simple choice is a set of unit vectors, or one can taken them from another level of theory or perhaps the eigenvectors from a well-chosen subspace of the full determinantal space.
Compute a representation of the Hamiltonian within the space of guess vectors,
and then diagonalize this so-called "subspace Hamiltonian",
where M is the number of roots of interest. The current estimate of each of the M eigenvectors we want is a linear combination of the guess vectors, with the αk subspace eigenvectors providing the coefficients, viz.
The dimension of G is typically very small (perhaps a dozen times the number of guess vectors, L), so one can used a standard diagonalization package (such as DSYEV in LAPACK) for this task. Note that the most expensive part of the Davidson-Liu algorithm is the computation of σ, the products of the Hamiltonian matrix with the guess vectors. In some of the largest CI calculations, the Hamiltonian cannot even be stored on disk and its elements must be computed "on the fly" during the computation of each σ.
Build a set of "correction vectors",
where the "residual" vectors are defined as
and N is the dimension of the Hamiltonian (i.e. the number of determinants). The inverse appearing in the definition of the correction vectors is commonly referred to as the "preconditioner". Notice that the residual vectors are so named because they would be zero if the guess vectors, bi, were the true eigenvectors. Thus, convergence of the algorithm is checked at this point, based on the norms of the residual vectors (one for each desired root) and the change in the corresponding eigenvalue between each iteration.
Normalize each correction vector, fδk, then orthogonalize it against the existing set of guesses, bi, using the Schmidt Orthogonalization procedure, for example. If the orthonormalized correction vector has a norm larger than some chosen threshold (e.g. 10-3), include it in the set of guess vectors. If not, discard it. (Thus, the dimension of the guess space, L, gradually increases in each iteration.)
Return to step #2 and continue.
We will focus on the spin-adapted singlet formulation of CIS, for which the σ = H c equation was given in Project 12:
What should we choose for guess vectors? As noted above, the simplest choice
is probably a set of unit vectors, one for each eigenvalue you want. But in
what position of the vector should we put the 1? For a hint, look at the
structure of the spin-adapted singlet CIS Hamiltonian
for the H2O STO-3G test case and note that it is
strongly diagonally dominant. Thus, if the diagonal elements are reasonable
approximations to the true eigenvalues, and we want to compute only the lowest
M eigenvalues, then our guess unit vectors should have a 1 in the position
corresponding to the row/column of the smallest elements of the Hamiltonian.
If the number of guess vectors grows to be too large, we may need to reduce its dimension to something more manageable before continuing the Davidson-Liu algorithm. A typical choice is to collapse to the current best set of guesses using the equation given above for the current final eigenvectors:
- 1: E.R. Davidson, "The iterative calculation of a few of the lowest eigenvalues and corresponding eigenvectors of large real-symmetric matrices," J. Comput. Phys. 17, 87 (1975). (return to text)
- 2: B.Liu, "The simultaneous expansion method for the iterative solution of several of the lowest eigenvalues and corresponding eigenvectors of large real-symmetric matrices," Technical Report LBL-8158, Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, 1978. (return to text)
- 3: C.D. Sherrill, "The Configuration Interaction Method: Advances in Highly Correlated Approaches," Adv. Quantum Chem. 34, 143 (1998). (return to text)