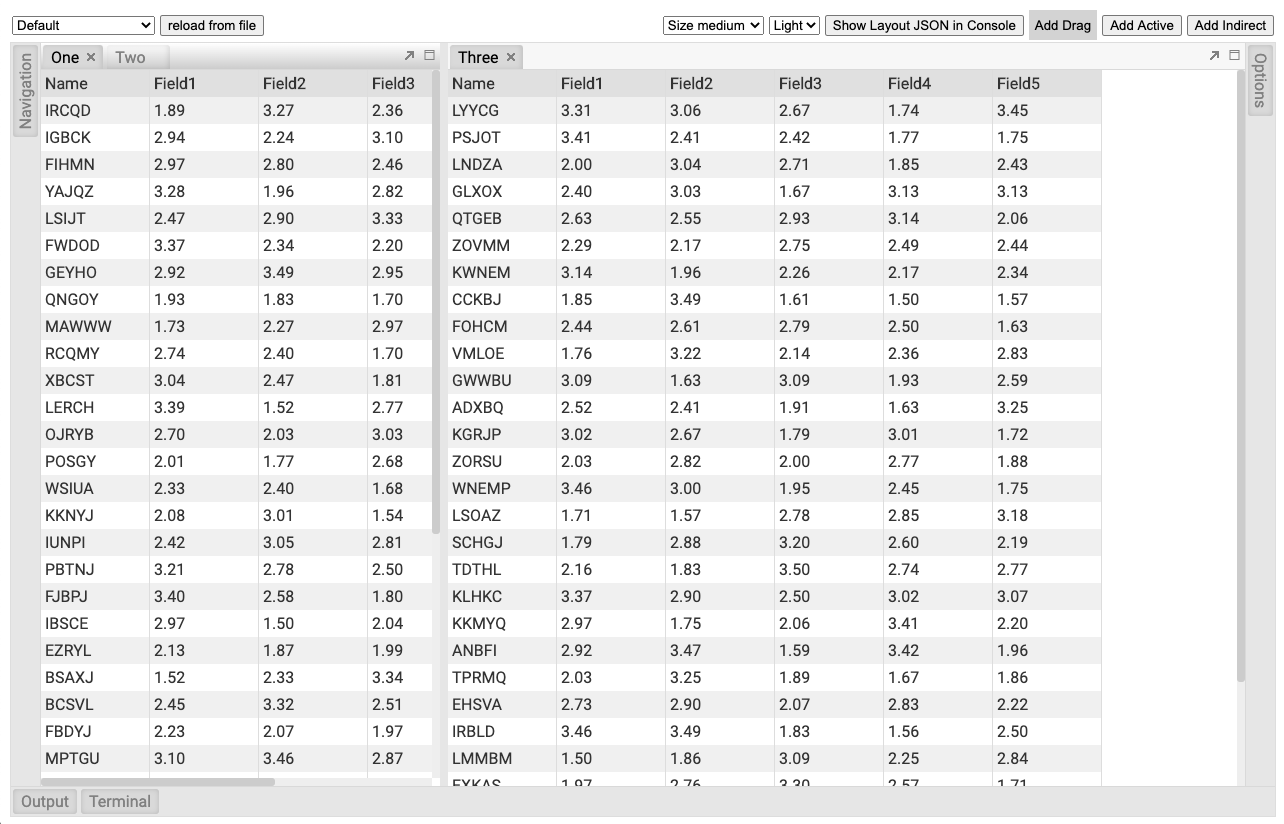
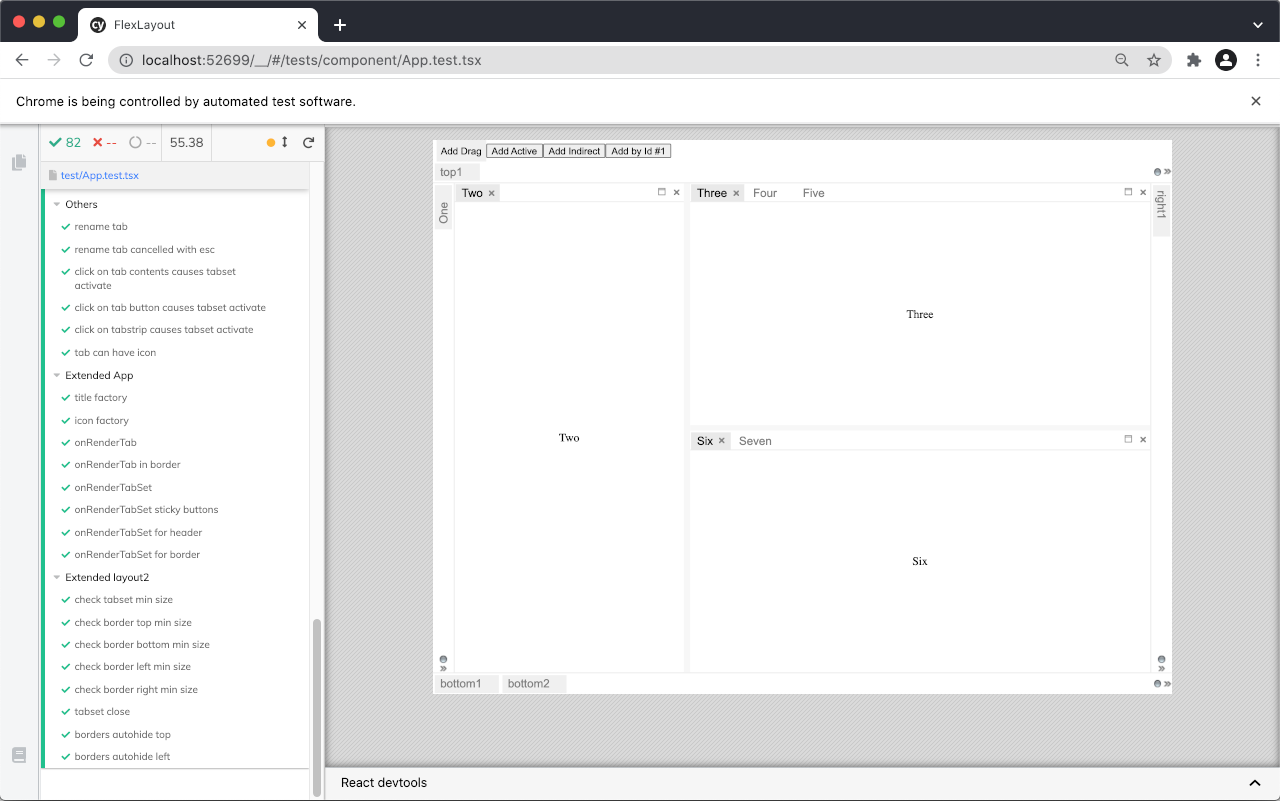
FlexLayout is a layout manager that arranges React components in multiple tab sets, tabs can be resized and moved.
Try it now using JSFiddle
Screenshot of Caplin Liberator Explorer using FlexLayout
FlexLayout's only dependency is React.
Features:
- splitters
- tabs
- tab dragging and ordering
- tabset dragging (move all the tabs in a tabset in one operation)
- dock to tabset or edge of frame
- maximize tabset (double click tabset header or use icon)
- tab overflow (show menu when tabs overflow, scroll tabs using mouse wheel)
- border tabsets
- popout tabs into new browser windows
- submodels, allow layouts inside layouts
- tab renaming (double click tab text to rename)
- theming - light, underline, gray and dark
- touch events - works on mobile devices (iPad, Android)
- add tabs using drag, indirect drag, add to active tabset, add to tabset by id
- preferred pixel size tabsets (try to keep their size when window resizes)
- headed tabsets
- tab and tabset attributes: enableHeader, enableTabStrip, enableDock, enableDrop...
- customizable tabs and tabset header rendering
- component state is preserved when tabs are moved
- typescript type declarations included
FlexLayout is in the npm repository. Simply install React and FlexLayout from npm:
npm install react
npm install react-dom
npm install flexlayout-react
Import React and FlexLayout in your modules:
import * as React from "react";
import { createRoot } from "react-dom/client";
import * as FlexLayout from "flexlayout-react";
Include the light, underline, gray or dark theme by either:
Adding an additional import:
import 'flexlayout-react/style/light.css';
or by adding the css to your html:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="node_modules/flexlayout-react/style/light.css" />
The <Layout> component renders the tabsets and splitters, it takes the following props:
| Prop | Description |
|---|---|
| model | the layout model |
| factory | a factory function for creating React components |
Additional optional props
The model is tree of Node objects that define the structure of the layout.
The factory is a function that takes a Node object and returns a React component that should be hosted by a tab in the layout.
The model can be created using the Model.fromJson(jsonObject) static method, and can be saved using the model.toJson() method.
this.state = {model: FlexLayout.Model.fromJson(json)};
render() {
<FlexLayout.Layout model={this.state.model} factory={factory}/>
}var json = {
global: {},
borders: [],
layout: {
type: "row",
weight: 100,
children: [
{
type: "tabset",
weight: 50,
children: [
{
type: "tab",
name: "One",
component: "button",
}
]
},
{
type: "tabset",
weight: 50,
children: [
{
type: "tab",
name: "Two",
component: "button",
}
]
}
]
}
};import * as React from "react";
import { createRoot } from "react-dom/client";
import * as FlexLayout from "flexlayout-react";
class Main extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {model: FlexLayout.Model.fromJson(json)};
}
factory = (node) => {
var component = node.getComponent();
if (component === "button") {
return <button>{node.getName()}</button>;
}
}
render() {
return (
<FlexLayout.Layout model={this.state.model} factory={this.factory}/>
)
}
}
const root = createRoot(document.getElementById("container"));
root.render(<Main/>);
The above code would render two tabsets horizontally each containing a single tab that hosts a button component. The tabs could be moved and resized by dragging and dropping. Additional grids could be added to the layout by sending actions to the model.
Try it now using JSFiddle
A simple Typescript example can be found here:
https://github.com/nealus/FlexLayout_cra_example
The model is built up using 4 types of 'node':
-
row - rows contains a list of tabsets and child rows, the top level 'row' will render horizontally (unless the global attribute rootOrientationVertical is set) , child 'rows' will render in the opposite orientation to their parent.
-
tabset - tabsets contain a list of tabs and the index of the selected tab
-
tab - tabs specify the name of the component that they should host (that will be loaded via the factory) and the text of the actual tab.
-
border - borders contain a list of tabs and the index of the selected tab, they can only be used in the borders top level element.
The main layout is defined with rows within rows that contain tabsets that themselves contain tabs.
The model json contains 3 top level elements:
- global - where global options are defined
- layout - where the main row/tabset/tabs layout hierarchy is defined
- borders - (optional) where up to 4 borders are defined ("top", "bottom", "left", "right").
Weights on rows and tabsets specify the relative weight of these nodes within the parent row, the actual values do not matter just their relative values (ie two tabsets of weights 30,70 would render the same if they had weights of 3,7).
NOTE: the easiest way to create your initial layout JSON is to use the demo app, modify one of the existing layouts by dragging/dropping and adding nodes then press the 'Show Layout JSON in console' button to print the JSON to the browser developer console.
example borders section:
borders: [
{
type: "border",
location: "left",
children: [
{
type: "tab",
enableClose: false,
name: "Navigation",
component: "grid",
}
]
},
{
type: "border",
location: "right",
children: [
{
type: "tab",
enableClose: false,
name: "Options",
component: "grid",
}
]
},
{
type: "border",
location: "bottom",
children: [
{
type: "tab",
enableClose: false,
name: "Activity Blotter",
component: "grid",
},
{
type: "tab",
enableClose: false,
name: "Execution Blotter",
component: "grid",
}
]
}
]
To control where nodes can be dropped you can add a callback function to the model:
model.setOnAllowDrop(this.allowDrop);
example:
allowDrop(dragNode, dropInfo) {
let dropNode = dropInfo.node;
// prevent non-border tabs dropping into borders
if (dropNode.getType() == "border" && (dragNode.getParent() == null || dragNode.getParent().getType() != "border"))
return false;
// prevent border tabs dropping into main layout
if (dropNode.getType() != "border" && (dragNode.getParent() != null && dragNode.getParent().getType() == "border"))
return false;
return true;
}
By changing global or node attributes you can change the layout appearance and functionality, for example:
Setting tabSetEnableTabStrip:false in the global options would change the layout into a multi-splitter (without tabs or drag and drop).
global: {tabSetEnableTabStrip:false},
Tabs can be rendered into external browser windows (for use in multi-monitor setups) by configuring them with the enableFloat attribute. When this attribute is present an additional icon is shown in the tab header bar allowing the tab to be popped out into an external window.
For popouts to work there needs to be an additional html page 'popout.html' hosted at the same location as the main page (copy the one from examples/demo). The popout.html is the host page for the popped out tab, the styles from the main page will be copied into it at runtime.
Because popouts are rendering into a different document to the main layout any code in the popped out tab that uses the global document or window objects will not work correctly (for example custom popup menus), they need to instead use the document/window of the popout. To get the document/window of the popout use the following method on one of the elements rendered in the popout (for example a ref or target in an event handler):
const currentDocument = this.selfRef.current.ownerDocument;
const currentWindow = currentDocument.defaultView!;
In the above code selfRef is a React ref to the toplevel element in the tab being rendered.
Note: some libraries support popout windows by allowing you to specify the document to use, for example see the getDocument() callback in agGrid at https://www.ag-grid.com/javascript-grid-callbacks/
| Prop | Description |
|---|---|
| font | the tab font (overrides value in css). Example: font={{size:"12px", style:"italic"}} |
| icons | object mapping keys among close, maximize, restore, more, popout to React nodes to use in place of the default icons, can alternatively return functions for creating the React nodes |
| onAction | function called whenever the layout generates an action to update the model (allows for intercepting actions before they are dispatched to the model, for example, asking the user to confirm a tab close.) Returning undefined from the function will halt the action, otherwise return the action to continue |
| onRenderTab | function called when rendering a tab, allows leading (icon), content section, buttons and name used in overflow menu to be customized |
| onRenderTabSet | function called when rendering a tabset, allows header and buttons to be customized |
| onModelChange | function called when model has changed |
| onExternalDrag | function called when an external object (not a tab) gets dragged onto the layout, with a single dragenter argument. Should return either undefined to reject the drag/drop or an object with keys dragText, jsonDrop, to create a tab via drag (similar to a call to addTabToTabSet). Function onDropis passed the added tabNodeand thedrop DragEvent`, unless the drag was canceled. |
| classNameMapper | function called with default css class name, return value is class name that will be used. Mainly for use with css modules. |
| i18nMapper | function called for each I18nLabel to allow user translation, currently used for tab and tabset move messages, return undefined to use default values |
| supportsPopout | if left undefined will do simple check based on userAgent |
| popoutURL | URL of popout window relative to origin, defaults to popout.html |
| realtimeResize | boolean value, defaults to false, resize tabs as splitters are dragged. Warning: this can cause resizing to become choppy when tabs are slow to draw |
| onTabDrag | function called while dragging a tab, whether from the layout or using addTabWithDragAndDrop. Called with the TabNode being dragged / the tab json from addTabWithDragAndDrop, the TabNode being dragged over, the x and y coordinates relative to the dragged-over tab, and the DockLocation that would be used. Should return undefined for default behavior, or an object containing x, y, width, height, callback, cursor fields. Coordinates are in pixels relative to the dragged-over tab, and callback will be called with the same arguments if the tab is dropped. cursor is an optional string field that should contain a CSS cursor value, such as copy or row-resize. If callback is called, the layout does not perform its default behavior on drop. |
| onRenderDragRect | callback for rendering the drag rectangles |
| onRenderFloatingTabPlaceholder | callback for rendering the floating tab placeholder |
| onContextMenu | callback for handling context actions on tabs and tabsets |
| onAuxMouseClick | callback for handling mouse clicks on tabs and tabsets with alt, meta, shift keys, also handles center mouse clicks |
| onShowOverflowMenu | callback for handling the display of the tab overflow menu |
| onTabSetPlaceHolder | callback for rendering a placeholder when a tabset is empty |
| iconFactory | a factory function for creating icon components for tab bar buttons. NOTE: for greater customization of the tab use onRenderTab instead of this callback |
| titleFactory | a factory function for creating title components for tab bar buttons. NOTE: for greater customization of the tab use onRenderTab instead of this callback |
Attributes allowed in the 'global' element
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| splitterSize | 8 | width in pixels of all splitters between tabsets/borders |
| splitterExtra | 0 | additional width in pixels of the splitter hit test area |
| legacyOverflowMenu | false | use the legacy text only overflow menu |
| enableEdgeDock | true | |
| tabEnableClose | true | allow user to close all tabs via close button |
| tabCloseType | 1 | see values in ICloseType |
| tabEnableDrag | true | allow user to drag all tabs to new location |
| tabEnableRename | true | allow user to rename all tabs by double clicking |
| tabEnableFloat | false | enable popouts in all tabs (in popout capable browser) |
| tabClassName | null | |
| tabIcon | null | |
| tabEnableRenderOnDemand | true | whether to avoid rendering component until tab is visible |
| tabDragSpeed | 0.3 | CSS transition speed of drag outlines (in seconds) |
| tabBorderWidth | -1 | width when added to border, -1 will use border size |
| tabBorderHeight | -1 | height when added to border, -1 will use border size |
| tabSetEnableDeleteWhenEmpty | true | |
| tabSetEnableDrop | true | allow user to drag tabs into all tabsets |
| tabSetEnableDrag | true | allow user to drag tabs out of all tabsets |
| tabSetEnableDivide | true | allow user to drag tabs to region of all tabsets, splitting into new tabset |
| tabSetEnableMaximize | true | allow user to maximize all tabsets to fill view via maximize button |
| tabSetEnableClose | false | allow user to close all tabsets via close button |
| tabSetAutoSelectTab | true | whether to select new/moved tabs in all tabsets |
| tabSetClassNameTabStrip | null | height in pixels of tab strips in all tabsets |
| tabSetClassNameHeader | null | |
| tabSetEnableTabStrip | true | enable tab strip and allow multiple tabs in all tabsets |
| tabSetHeaderHeight | 0 | height of tabset header in pixels; if left as 0 then the value will be calculated from the current fontSize |
| tabSetTabStripHeight | 0 | height of tabset tab bar in pixels; if left as 0 then the value will be calculated from the current fontSize |
| borderBarSize | 0 | size of the border bars in pixels; if left as 0 then the value will be calculated from the current fontSize |
| borderEnableAutoHide | false | hide border if it has zero tabs |
| borderEnableDrop | true | allow user to drag tabs into this border |
| borderAutoSelectTabWhenOpen | true | whether to select new/moved tabs in border when the border is already open |
| borderAutoSelectTabWhenClosed | false | whether to select new/moved tabs in border when the border is curently closed |
| borderClassName | null | |
| borderSize | 200 | initial width in pixels for left/right borders, height for top/bottom borders |
| borderMinSize | 0 | minimum width in pixels for left/right borders, height for top/bottom borders |
| tabSetMinHeight | 0 | minimum width (in px) for all tabsets |
| tabSetMinWidth | 0 | minimum height (in px) for all tabsets |
| tabSetTabLocation | top | show tabs in location top or bottom |
| rootOrientationVertical | false | the top level 'row' will layout horizontally by default, set this option true to make it layout vertically |
Attributes allowed in nodes of type 'row'.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | row | |
| weight | 100 | |
| width | null | preferred pixel width |
| height | null | preferred pixel height |
| children | required | a list of row and tabset nodes |
Attributes allowed in nodes of type 'tab'.
Inherited defaults will take their value from the associated global attributes (see above).
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | tab | |
| name | required | name of tab to be displayed in the tab button |
| altName | optional | if there is no name specifed then this value will be used in the overflow menu |
| component | required | string identifying which component to run (for factory) |
| config | null | a place to hold json config for the hosted component |
| id | auto generated | |
| helpText | optional | An optional help text for the tab to be displayed upon tab hover. |
| enableClose | inherited | allow user to close tab via close button |
| closeType | inherited | see values in ICloseType |
| enableDrag | inherited | allow user to drag tab to new location |
| enableRename | inherited | allow user to rename tabs by double clicking |
| enableFloat | inherited | enable popout (in popout capable browser) |
| floating | false | |
| className | inherited | |
| icon | inherited | |
| enableRenderOnDemand | inherited | whether to avoid rendering component until tab is visible |
| borderWidth | inherited | width when added to border, -1 will use border size |
| borderHeight | inherited | height when added to border, -1 will use border size |
Tab nodes have a getExtraData() method that initially returns an empty object, this is the place to add extra data to a tab node that will not be saved.
Attributes allowed in nodes of type 'tabset'.
Inherited defaults will take their value from the associated global attributes (see above).
Note: tabsets can be dynamically created as tabs are moved and deleted when all their tabs are removed (unless enableDeleteWhenEmpty is false).
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | tabset | |
| weight | 100 | relative weight for sizing of this tabset in parent row |
| width | null | preferred pixel width |
| height | null | preferred pixel height |
| name | null | named tabsets will show a header bar above the tabs |
| config | null | a place to hold json config used in your own code |
| selected | 0 | index of selected/visible tab in tabset |
| maximized | false | whether tabset is currently maximized to fill view |
| enableClose | false | allow user to close tabset via a close button |
| id | auto generated | |
| children | required | a list of tab nodes |
| enableDeleteWhenEmpty | inherited | |
| enableDrop | inherited | allow user to drag tabs into this tabset |
| enableDrag | inherited | allow user to drag tabs out this tabset |
| enableDivide | inherited | allow user to drag tabs to region of this tabset, splitting into new tabset |
| enableMaximize | inherited | allow user to maximize tabset to fill view via maximize button |
| autoSelectTab | inherited | whether to select new/moved tabs in tabset |
| classNameTabStrip | inherited | |
| classNameHeader | inherited | |
| enableTabStrip | inherited | enable tab strip and allow multiple tabs in this tabset |
| headerHeight | inherited | |
| tabStripHeight | inherited | height in pixels of tab strip |
| tabLocation | inherited | show tabs in location top or bottom |
| minHeight | inherited | minimum height (in px) for this tabset |
| minWidth | inherited | minimum width (in px) for this tabset |
Attributes allowed in nodes of type 'border'.
Inherited defaults will take their value from the associated global attributes (see above).
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | border | |
| size | inherited | size of the tab body when selected |
| minSize | inherited | |
| selected | -1 | index of selected/visible tab in border; -1 means no tab unselected / border closed |
| id | auto generated | border_ + border name e.g. border_left |
| config | null | a place to hold json config used in your own code |
| show | true | show/hide this border |
| enableAutoHide | false | hide border if it has zero tabs |
| children | required | a list of tab nodes |
| barSize | inherited | size of this border's bar in pixels; if left as 0 then the value will be calculated from the current fontSize |
| enableDrop | inherited | |
| autoSelectTabWhenOpen | inherited | whether to select new/moved tabs in border when the border is already open |
| autoSelectTabWhenClosed | inherited | whether to select new/moved tabs in border when the border is currently closed |
| className | inherited |
All changes to the model are applied through actions.
You can intercept actions resulting from GUI changes before they are applied by
implementing the onAction callback property of the Layout.
You can also apply actions directly using the Model.doAction() method.
This method takes a single argument, created by one of the following action
generators (typically accessed as FlexLayout.Actions.<actionName>):
| Action Creator | Description |
|---|---|
| Actions.addNode(newNodeJson, toNodeId, location, index, select?) | add a new tab node to the given tabset node; select specifies whether to select new tab, defaulting to autoSelectTab attribute; returns the created Node |
| Actions.moveNode(fromNodeId, toNodeId, location, index, select?) | move a tab node from its current location to the new node and location; select specifies whether to select tab, defaulting to new tabset's autoSelectTab attribute |
| Actions.deleteTab(tabNodeId) | delete the given tab |
| Actions.renameTab(tabNodeId, newName) | rename the given tab |
| Actions.selectTab(tabNodeId) | select the given tab |
| Actions.setActiveTabset(tabsetNodeId) | set the tabset as the active tabset |
| Actions.adjustSplit(splitterNodeId, value) | adjust the size of the given splitter |
| Actions.adjustBorderSplit(borderNodeId, pos) | updates the size of the given border node |
| Actions.maximizeToggle(tabsetNodeId) | toggles whether the given tabset node is maximized |
| Actions.updateModelAttributes(attributes) | updates the global attributes |
| Actions.updateNodeAttributes(nodeId, attributes) | updates the attributes of the given node |
| Actions.floatTab(nodeId) | popout the tab into a floating browser window |
| Actions.unFloatTab(nodeId) | restore a popped out tab to the main layout |
model.doAction(FlexLayout.Actions.updateModelAttributes({
splitterSize:40,
tabSetHeaderHeight:40,
tabSetTabStripHeight:40
}));The above example would increase the size of the splitters, tabset headers and tabs, this could be used to make adjusting the layout easier on a small device.
model.doAction(FlexLayout.Actions.addNode(
{type:"tab", component:"grid", name:"a grid", id:"5"},
"1", FlexLayout.DockLocation.CENTER, 0));This example adds a new grid component to the center of tabset with id "1" and at the 0'th tab position (use value -1 to add to the end of the tabs).
Note: you can get the id of a node (e.g., the node returned by the addNode
action) using the method node.getId().
If an id wasn't assigned when the node was created, then one will be created for you of the form #<uuid> (e.g. #0c459064-8dee-444e-8636-eb9ab910fb27).
Methods on the Layout Component for adding tabs, the tabs are specified by their layout json.
Example:
this.layoutRef.current.addTabToTabSet("NAVIGATION", {type:"tab", component:"grid", name:"a grid"});
This would add a new grid component to the tabset with id "NAVIGATION" (where this.layoutRef is a ref to the Layout element, see https://reactjs.org/docs/refs-and-the-dom.html ).
| Layout Method | Description |
|---|---|
| addTabToTabSet(tabsetId, json) | adds a new tab to the tabset with the given Id |
| addTabToActiveTabSet(json) | adds a new tab to the active tabset |
| addTabWithDragAndDrop(dragText, json, onDrop) | adds a new tab by dragging a marker to the required location, with the drag starting immediately; on success, onDrop is passed the created tab Node; on cancel, no arguments are passed |
| addTabWithDragAndDropIndirect(dragText, json, onDrop) | adds a new tab by dragging a marker to the required location, the marker is shown and must be clicked on to start dragging |
| moveTabWithDragAndDrop( node, dragText) | Move a tab/tabset using drag and drop triggered from a custom event |
You can handle events on nodes by adding a listener, this would typically be done in the components constructor() method.
Example:
constructor(props) {
super(props);
let config = this.props.node.getConfig();
// save state in flexlayout node tree
this.props.node.setEventListener("save", (p) => {
config.subject = this.subject;
};
}
| Event | parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| resize | called when tab is resized during layout, called before it is rendered with the new size | |
| close | called when a tab is closed | |
| visibility | called when the visibility of a tab changes | |
| save | called before a tabnode is serialized to json, use to save node config by adding data to the object returned by node.getConfig() |
First install dependencies:
yarn install
Compile the project and run the examples:
yarn start
Open your browser at http://localhost:8080/examples/ to show the examples directory, click on the examples to run them.
The 'yarn start' command will watch for changes to flexlayout and example source, so you can make changes to the code and then refresh the browser to see the result.
To run the tests in the Cypress interactive runner use:
yarn cypress
To build the npm distribution run 'yarn build', this will create the artifacts in the dist dir.
| Name | Repository |
|---|---|
| rc-dock | https://github.com/ticlo/rc-dock |
| Dockview | https://dockview.dev/ |
| lumino | https://github.com/jupyterlab/lumino |
| golden-layout | https://github.com/golden-layout/golden-layout |
| react-mosaic | https://github.com/nomcopter/react-mosaic |