A distributed transaction solution with high performance and ease of use for microservices architecture.
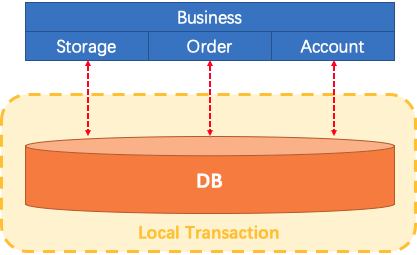
Let's imagine a traditional monolithic application. Its business is built up with 3 modules. They use a single local data source.
Naturally, data consistency will be guaranteed by the local transaction.
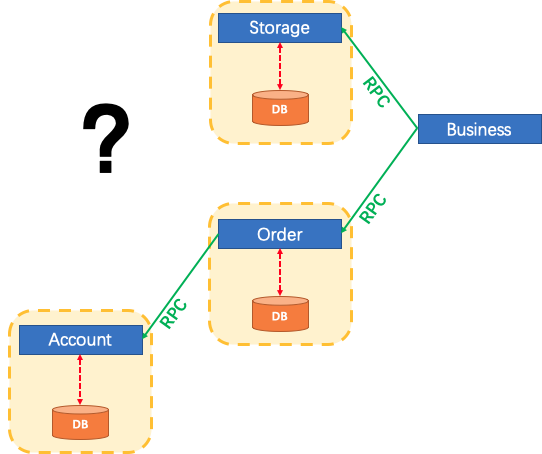
Things have changed in microservices architecture. The 3 modules mentioned above are designed to be 3 services on top of 3 different data sources (Pattern: Database per service). Data consistency within every single service is naturally guaranteed by the local transaction.
But how about the whole business logic scope?
Seata is just a solution to the problem mentioned above.
Firstly, how to define a Distributed Transaction?
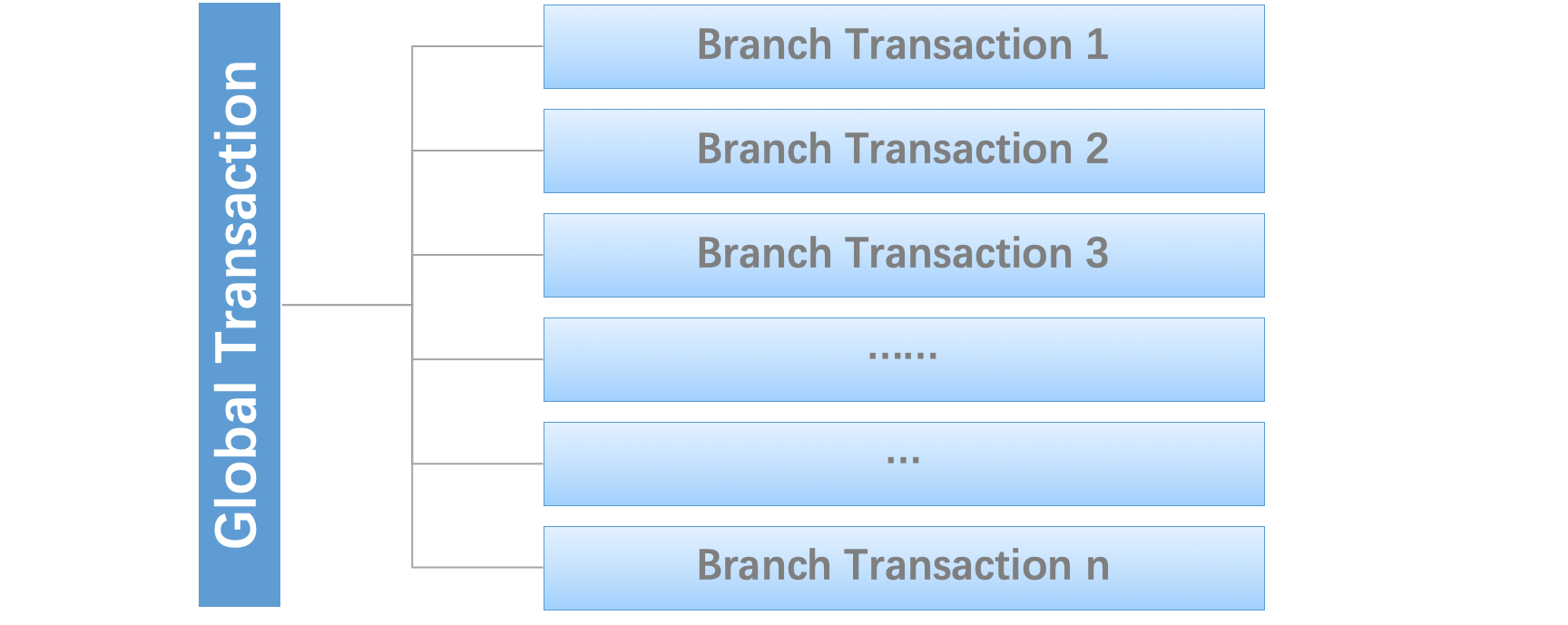
We say, a Distributed Transaction is a Global Transaction which is made up with a batch of Branch Transaction, and normally Branch Transaction is just Local Transaction.
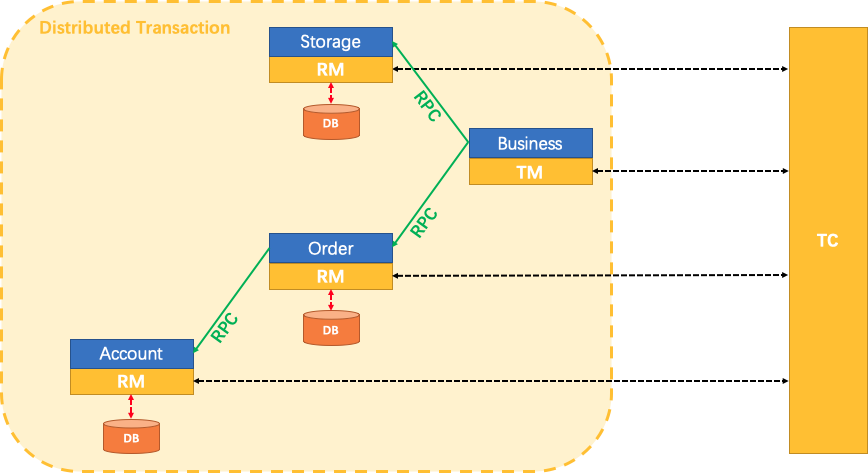
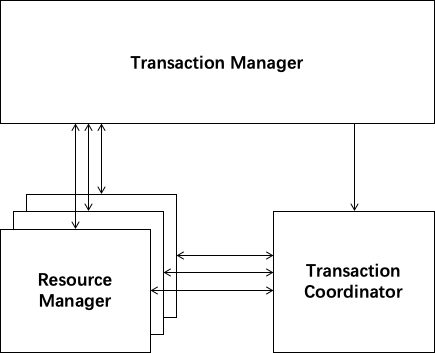
There are 3 basic components in Seata:
- Transaction Coordinator(TC): Maintain status of global and branch transactions, drive the global commit or rollback.
- Transaction Manager(TM): Define the scope of global transaction: begin a global transaction, commit or rollback a global transaction.
- Resource Manager(RM): Manage resources that branch transactions working on, talk to TC for registering branch transactions and reporting status of branch transactions, and drive the branch transaction commit or rollback.
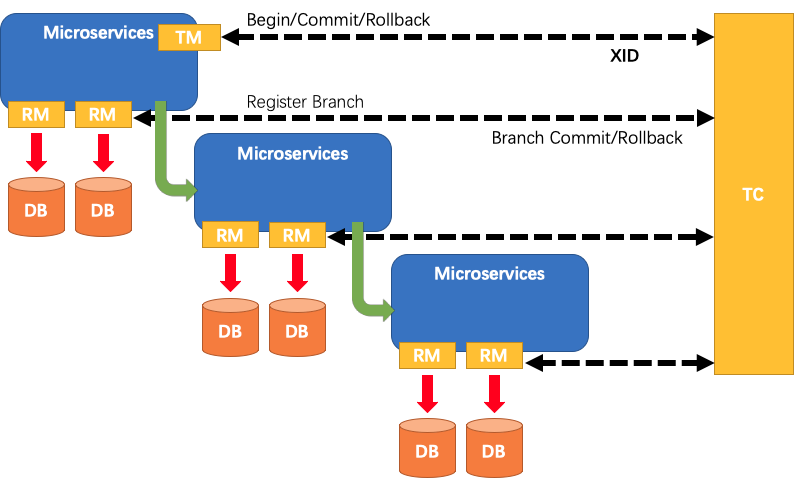
A typical lifecycle of Seata managed distributed transaction:
- TM asks TC to begin a new global transaction. TC generates an XID representing the global transaction.
- XID is propagated through microservices' invoke chain.
- RM register local transaction as a branch of the corresponding global transaction of XID to TC.
- TM asks TC for committing or rollbacking the corresponding global transaction of XID.
- TC drives all branch transactions under the corresponding global transaction of XID to finish branch committing or rollbacking.
For more details about principle and design, please go to Seata wiki page.
-
XTS: Extended Transaction Service. Ant Financial middleware team developed the distributed transaction middleware since 2007, which is widely used in Ant Financial and solves the problems of data consistency across databases and services.
-
DTX: Distributed Transaction Extended. Since 2013, XTS has been published on the Ant Financial Cloud, with the name of DTX .
- TXC: Taobao Transaction Constructor. Alibaba middleware team start this project since 2014 to meet distributed transaction problem caused by application architecture change from monolithic to microservices.
- GTS: Global Transaction Service. TXC as an Aliyun middleware product with new name GTS was published since 2016.
- Fescar: we start the open source project Fescar based on TXC/GTS since 2019 to work closely with the community in the future.
- Seata :Simple Extensible Autonomous Transaction Architecture. Ant Financial joins Fescar, which make it to be a more neutral and open community for distributed transaction,and Fescar be renamed to Seata.
<seata.version>0.8.1</seata.version>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-all</artifactId>
<version>${seata.version}</version>
</dependency>
You can view the full documentation from the wiki: Seata wiki page.
Please follow the template for reporting any issues.
Contributors are welcomed to join the Seata project. Please check CONTRIBUTING about how to contribute to this project.
-
Twitter: Follow along for latest Seata news on Twitter.
-
Mailing list:
- [email protected] , for dev/user discussion. subscribe, unsubscribe, archive
Dingtalk
- Seata Ecosystem Entry - A GitHub group
seatato gather all Seata relevant projects - Seata Samples - Samples for Seata
- Seata Docker - Seata integration with docker
- Seata K8s - Seata integration with k8s
- Awesome Seata - Description of Seata related projects
- Seata Website - Seata official website
This project exists thanks to all the people who contribute. [Contributors].
Seata is under the Apache 2.0 license. See the LICENSE file for details.