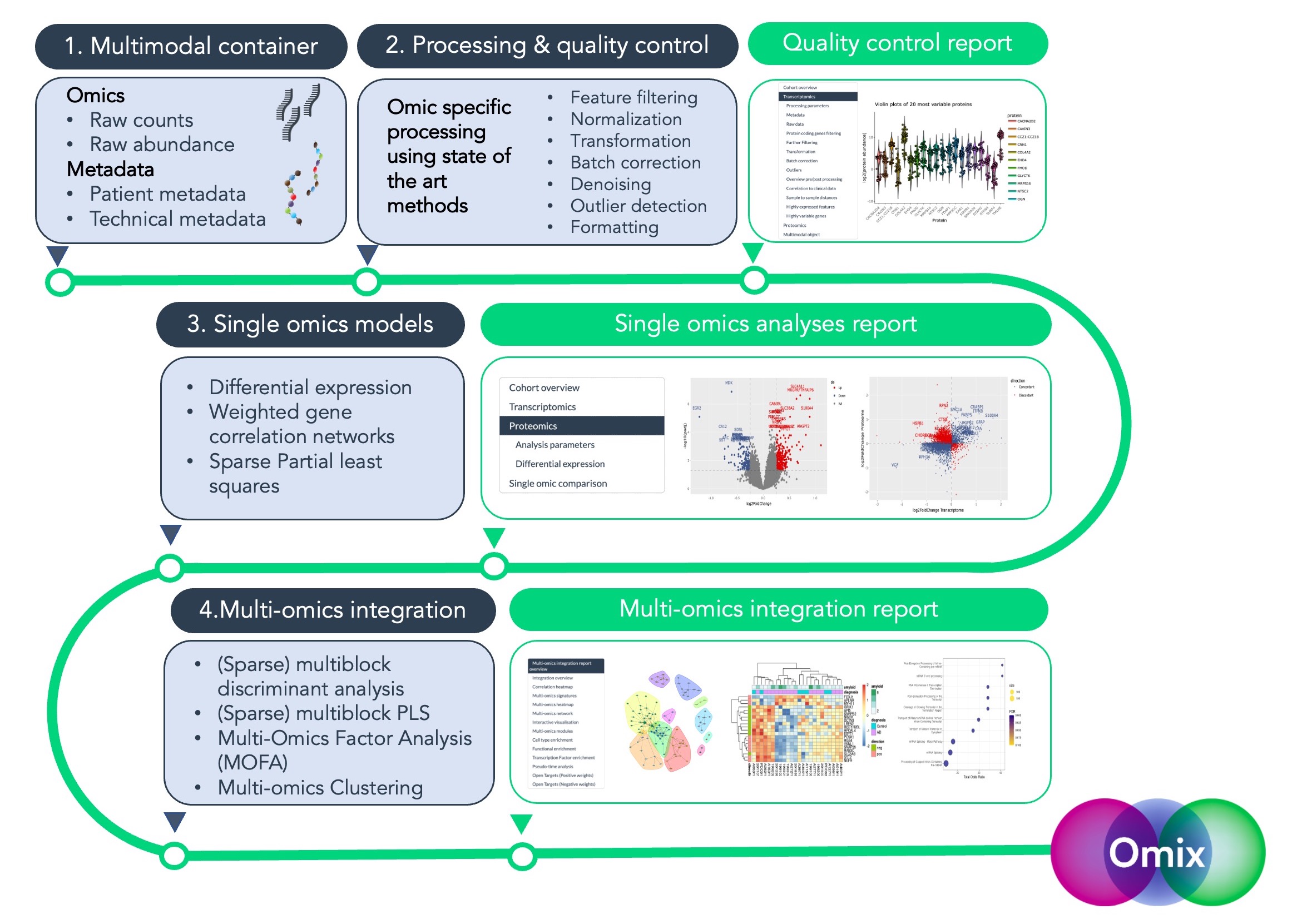
The Omix pipeline offers an integration and analysis framework for
multi-omics intended to pre-process, analyse, and v isualise multimodal
data flexibly to address research questions. Omix is built on four
consecutive blocks, (1) preparation of the multimodal container, (2)
processing and quality control, (3) single omic analyses, and (4)
multi-omics vertical integration
Pipeline outputs are standardised and include publication-quality plots, tables, and interactive reports.
Omix offers a range of state-of-the-art processing functions and integrative models, equipped with versatile parameters and quality control features. This empowers researchers to explore different integration strategies easily, enhancing the speed, scalability, and flexibility of multi-omics analyses.
While the current version focuses on bulk transcriptomics and proteomics, future iterations aim to encompass a broader range of omics types, expanding the software’s applicability and usefulness.
You can install the development version of Omix from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("eleonore-schneeg/Omix")- Multi-omics data container
- The Omix multimodal container harmonises data management of multiple omics datasets. It enables the storage of raw and processed omics data slots, along with patient metadata, technical metadata, analysis parameters and outputs. The object structure relies on the MultiAssayExperiment library
- Data processing & Quality Control
- Each omics layer is processed separately according to best practices. Given the wide range of processing functionalities, users decide which parameters and steps of the modular sequence are performed, which involves all or a combination of the folllowing steps:
- Feature filtering
- Normalisation/ transformation
- Batch correction & denoising
- Sample outlier removal
- Formatting
- Single platform models
- Omix provides a suite of analysis options including differential analysis (DE), a standard method to identify genes that are differentially expressed between certain disease states; Weighted Gene correlation Network (WGCNA), to identify modules of genes that associate to certain disease covariates; sparse Partial Least Square (sPLS) to define a sparse set of omics features, or molecular signature, that explains the response variable.
- Vertical integration for joint analysis
- Omix provides a series of state-of-the-art integration models to perform patient-specific multi-omic integration, including:
- MOFA
- MEIFESTO
- Sparse Multi-Block PLS (sMB-PLS)
- DIABLO
- Multi-omics clustering models such as iCluster
- Downstream analyses
- Multi-omics integration is followed by a series of downstream analyses, including:
- Multi-omics networks with iGraph
- Community detection with the Louvain or Leiden clustering algorithms
- Pseudotime inference with Slingshot
- Functional enrichment with EnrichR
- Cell-type enrichment with EWCE
- Target validation based on the OpenTargets database
- Publication quality plots and analysis reports
Omix implements these modular steps and displays results in an interactive reports.
library(knitr)
kable(head(comparison_table))| …1 | Supported omics | Pre-processing | Single omic analysis | Integrative models | Use case | Downstream analyses | Interactive visualisations | Language | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miodin | SNP, RNA, methylation, Proteins, | + | - | MOFA | BM | - | - | R | Ulfenborg, B. (2019). |
| MiBiOmics | miRNA, RNA, Proteins | - | - | Co-inertia analysis | BD | Multi-omics networks | + | Web | (Zoppi et al., 2021) |
| Muon | Single cell omics | - | - | MOFA, WNN | NA | - | - | Python | (Bredikhin et al., 2022) |
| Movics | SNP, RNA, methylation, Proteins | - | - | Range of clustering algorithm | STR | Survival analysis, enrichment | - | R | (Lu, 2020) |
| Omix | RNA, Proteins | + | + | MOFA,MEIFESTO, sMBPLS, MBPLS, DIABLO, iCluster | BD, BM, STR | Multi-omics signatures, networks, modules, functional/ cell type/ TF enrichment, pseudotime, etc | + | R | NA |
Biomarker Discovery (BD), Biological Mechanisms (BM), Sample stratification (STR)
The Getting Started section of the documentation contains downloadable examples on how to use Omix.
The experiments described in our vignettes rely on in house data from the Multi-Omics Atlas Project, which may be obtained from the synapse portal for registered users.
- Project SynID: syn36812517
- Get started data: syn51533729
- Pseudo-temporal multi-omics integration: syn51516099
For reproducibility purposes, we provide a Docker container here.
After installing Docker you can first pull the container via:
docker pull eleonoreschneeg/omix:latestand then run the container:
docker run --rm -d -v $HOME:/home/rstudio/home -e ROOT=true -e PASSWORD=password -p 8787:8787 eleonoreschneeg/omix:1.0.0An RStudio server session can be accessed via a browser at localhost:8787 using Username: rstudio and Password: password Navigate to Omix and open the Omix.Rproj file.
Please cite Omix as:
Eléonore Schneegans, Nurun Fancy, Michael Thomas, Nanet Willumsen, Paul M Matthews, Johanna Jackson (2023) Omix: A Multi-Omics Integration Pipeline
For feature requests, please open an issue here.
Alternatively, you can fork the repository, add your change and issue a pull request.