Spring security
1. 认证 Authentication
1.1. 整体流程
1.2. 基于session认证
2. 授权 Authorization
2.1. 基于注解
2.2. 使用配置添加权限
2.3. 总结
3. Session 与 Cookies 认证
3.1. 认证过程
3.2. Cookie 无法防止CSRF攻击
4. Spring Security 对于CSRF攻击的解决方案
5. 基于token认证 JWT (Bearer Authentication)
5.1. Session认证暴露的缺点
5.2. 基于token 认证流程
5.3. jwt 组成
5.4. 总结
6. spring security + JWT
6.1. 继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
6.2. 基于AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
6.2.1. WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的配置demo
6.2.2. JWTAuthenticationFilter
6.2.3.
6.3. 基于OncePerRequestFilter
6.3.1. WebSecurityConfigurer
6.3.2. JwtTokenAuthenticationFilter
6.4. 登陆接口:验证用户名密码签发token
6.5. 权限问题
7. JWT token 常见问题
7.1. 注销登录等场景下 token 处理
7.2. 过期token 的续签问题
8. 跨源资源共享(CORS)
9. 相关资料
[Spring Security官网][https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.4.2/reference/html5/#servlet-architecture]
几个登陆认证重要的组件:
SecurityContextHolder:Spring Security存储安全身份验证者详细信息的位置。
使用ThreadLocal实现
SecurityContext:从SecurityContextHolder获得,并包含当前经过身份验证的用户的身份验证。
Authentication:是AuthenticationManager的输入,以提供用户提供的用于身份验证的凭据。
GrantedAuthority:授予身份验证主体的权限(即角色,作用域等)
AuthenticationManager:定义Spring Security的过滤器如何执行身份验证的API。
ProviderManager:AuthenticationManager的最常见实现,委托给一个 AuthenticationProviders 列表,每个AuthenticationProviders都可以验证登陆成功或者失败,如果没有一个 AuthenticationProvider验证通过, 那么会抛出ProviderNotFoundException。
AuthenticationProvider:可以通过supportType指定不同类型的认证的,比如账号密码的认证、token的认证等等。
AuthenticationEntryPoint:用于返回从客户端请求的 HTTP 响应(比如未认证的请求自动跳转、或者自己实现重定向到登录页面,发送WWW身份验证响应等)
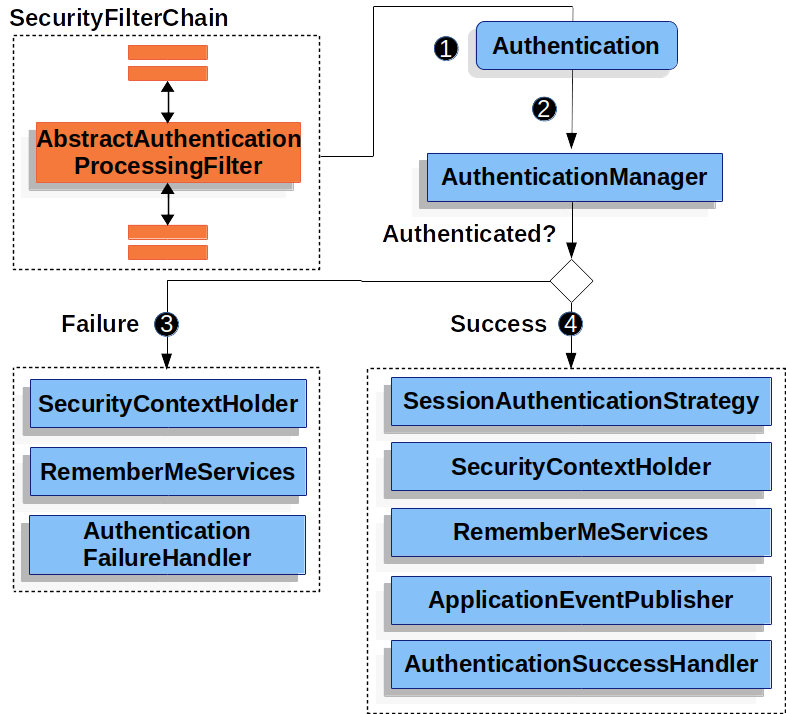
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter:用作验证用户凭据的基本过滤器。 在验证前,Spring Security 通常使用 AuthenticationEntryPoint 请求凭据。
UserDetailsService: spring security 默认提供的用户密码登陆接口。
-
When the user submits their credentials, the AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter creates an Authentication from the HttpServletRequest to be authenticated. The type of Authentication created depends on the subclass of AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter. For example, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter creates a UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken from a username and password that are submitted in the HttpServletRequest.
-
Next, the Authentication is passed into the AuthenticationManager to be authenticated.
-
If authentication fails, then Failure
The SecurityContextHolder is cleared out. RememberMeServices.loginFail is invoked. If remember me is not configured, this is a no-op.
AuthenticationFailureHandler is invoked. -
If authentication is successful, then Success.
SessionAuthenticationStrategy is notified of a new log in.
The Authentication is set on the SecurityContextHolder. Later the SecurityContextPersistenceFilter saves the SecurityContext to the HttpSession.
RememberMeServices.loginSuccess is invoked. If remember me is not configured, this is a no-op.
ApplicationEventPublisher publishes an InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent.
AuthenticationSuccessHandler is invoked.
大流程:
- AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 过滤器从HttpServletRequest获取认证的标识,根据标识创建Authentication。具体创建何种类型的Authentication,自己通过继承AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter去实现
-
比如UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 创建的Authentication类型是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
-
- Authentication传递到AuthenticationManager进行认证,ProviderManager会通过委托到支持具体该类型Authentication的AuthenticationProvider
- AuthenticationProvider进行认证,认证成功
默认的security认证是基于username的session认证
第一次访问:
- 首先进入应用页面 SecurityContextPersistenceFilter会获取HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository#loadContext 获取cookies中的session,第一次进入jsessionId未空
- AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter.requiresAuthentication 判读是否需要验证,第一次进入页面为GET方法,而认证仅支持POST方式。
- DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter跳转登陆页面。我们cookies中增加了JsessionID
第二次访问
- 登陆页面输入账号密码 SecurityContextPersistenceFilter会获取HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository#loadContext 获取cookies中的session,第一次进入jsessionId未空
- AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter.requiresAuthentication 判读是否需要验证,调用UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter的attemptAuthentication
- AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 进行账户密码认证,将认证成功的加入到sessionContext中
第三次访问
- SecurityContextPersistenceFilter根据JSESSIONID会获取HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository,发现该sessionId已认证pass
使用注解标注方法是否有权限
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('USER')")
@PostFilter("hasPermission(filterObject, 'read') or hasPermission(filterObject, 'admin')")
public List<Contact> getAll();
另一种做法是在继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter时,将url及对应的权限全部load进 httpSecurity中
ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer<HttpSecurity>.ExpressionInterceptUrlRegistry urlRegistry = http.authorizeRequests();
Map<String, String> resourcePermissions = permissionService.getResourcePermissions();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : resourcePermissions.entrySet()) {
urlRegistry = urlRegistry.antMatchers(entry.getKey()).hasAnyAuthority(entry.getValue());
}
使用配置添加权限,相当于需要一大部分的工作量配置角色对应的权限。
- 好处:数据库显示前台表统一管理。
- 坏处:配置工作量大,每个角色均需要配置。新增加接口需要新增加数据库记录。
基于注解配置权限
- 好处:开发人员即可配置权限,配置简单。
- 缺点:权限散落在各个接口中,不利于统一管理。
很多时候我们都是通过 SessionID 来实现特定的用户,SessionID 一般会选择存放在 Redis 中。举个例子:用户成功登陆系统,然后返回给客户端具有 SessionID 的 Cookie,当用户向后端发起请求的时候会把 SessionID 带上,这样后端就知道你的身份状态了。关于这种认证方式更详细的过程如下:
- 用户向服务器发送用户名和密码用于登陆系统。
- 服务器验证通过后,服务器为用户创建一个 Session,并将 Session信息存储 起来。
- 服务器向用户返回一个 SessionID,写入用户的 Cookie。
- 当用户保持登录状态时,Cookie 将与每个后续请求一起被发送出去。
- 服务器可以将存储在 Cookie 上的 Session ID 与存储在内存中或者数据库中的 Session 信息进行比较,以验证用户的身份,返回给用户客户端响应信息的时候会附带用户当前的状态。
另外,Spring Session提供了一种跨多个应用程序或实例管理用户会话信息的机制。
在登陆了网银后,点击误导的超链接,导致跨服务请求成功。
<a src=http://www.mybank.com/Transfer?bankId=11&money=10000>科学理财,年盈利率过万</>
进行Session 认证的时候,我们一般使用 Cookie 来存储 SessionId,当我们登陆后后端生成一个SessionId放在Cookie中返回给客户端,服务端通过Redis或者其他存储工具记录保存着这个Sessionid,客户端登录以后每次请求都会带上这个SessionId,服务端通过这个SessionId来标示你这个人。如果别人通过 cookie拿到了 SessionId 后就可以代替你的身份访问系统了。
可以使用token认证的方式避免误点攻击链接导致的跨服务请求问题。
基于token 认证经常将认证凭证存储在local storage中,在请求的时候前端再动态添加凭证到请求中。因此误点的外部链接无法添加token到转发的请求中。
spring Security对于CSRF攻击的解决方案就是CsrfFilter。
- 开启spring security的防csrf功能之后,对于访问后端的请求,若发现cookies中无
XSRF-TOKEN的cookie,便会使用UUID生成一个tokenset cookie。\ - 在
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的配置中,可设置Matcher对URL或只对HTTP-METHOD中POST、PATCH、DELETE等请求,进行CSRF拦截\ - 假设对POST请求进行拦截,CsrfFilter会对校验cookies中的
XSRF-TOKEN。校验的方式为与请求头X-XSRF-TOKEN或参数中_csrf的值进行验证,如果不一致,则为CSRF攻击。 因此前端对于后端的请求均要把cookie中的XSRF-TOKEN设置到请求头或者参数中,才能通过后端的校验。
以上就防止的cooies认证中,对于超链接跳转的CSRF攻击。
以下spring 官方提到了,使用了CORS同源策略的时候,CsrfFilter的重要性。
It is important to keep the CsrfToken a secret from other domains. This means if you are using Cross Origin Sharing (CORS), you should NOT expose the CsrfToken to any external domains.
** 核心逻辑可以见CsrfFilter **
Json web token (JWT), 是为了在网络应用环境间传递声明而执行的一种基于JSON的开放标准((RFC 7519).该token被设计为紧凑且安全的,特别适用于分布式站点的单点登录(SSO)场景。JWT的声明一般被用来在身份提供者和服务提供者间传递被认证的用户身份信息,以便于从资源服务器获取资源,也可以增加一些额外的其它业务逻辑所必须的声明信息,该token也可直接被用于认证,也可被加密。
内存开销大: 每个用户经过我们的应用认证之后,我们的应用都要在服务端做一次记录,以方便用户下次请求的鉴别,通常而言session都是保存在内存中,而随着认证用户的增多,服务端的开销会明显增大。
分布式场景限制:在分布式的应用上,相应的限制了负载均衡器的能力。这也意味着限制了应用的扩展能力。
CSRF跨服务请求问题: 因为是基于cookie来进行用户识别的, cookie如果被截获,用户就会很容易受到跨站请求伪造的攻击。
基于token的鉴权机制类似于http协议也是无状态的,它不需要在服务端去保留用户的认证信息或者会话信息。这就意味着基于token认证机制的应用不需要去考虑用户在哪一台服务器登录了,这就为应用的扩展提供了便利。
流程上是这样的:
- 用户使用用户名密码来请求服务器
- 服务器进行验证用户的信息
- 服务器通过验证发送给用户一个token
- 客户端存储token,并在每次请求时附送上这个token值
- 服务端验证token值,并返回数据 这个token必须要在每次请求时传递给服务端,它应该保存在请求头里, 另外,服务端要支持CORS(跨来源资源共享)策略,一般我们在服务端这么做就可以了Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *。
JWT 由 3 部分构成:
- Header :描述 JWT 的元数据。定义了生成签名的算法以及 Token 的类型。
- Payload(负载):用来存放实际需要传递的数据
- Signature(签名):服务器通过Payload、Header和一个密钥(secret)使用 Header 里面指定的签名算法(默认是 HMAC SHA256)生成。
secret是保存在服务器端的,jwt的签发生成也是在服务器端的,secret就是用来进行jwt的签发和jwt的验证,所以,它就是你服务端的私钥,在任何场景都不应该流露出去。一旦客户端得知这个secret, 那就意味着客户端是可以自我签发jwt了。
public String generateToken(String subject) {
return Jwts.builder()
// 设置发行人即 签发的 APP
.setIssuer( APP_NAME )
// 存放实际传递数据
.setSubject(subject)
// token 生成时间
.setIssuedAt(new Date())
// 过期时间
.setExpiration(generateExpirationDate())
// SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM加密算法 SECRET加盐字段 进行组合加密
.signWith( SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM, SECRET )
// 生成token
.compact();
}
优点
- 因为json的通用性,所以JWT是可以进行跨语言支持的,像JAVA,JavaScript,NodeJS,PHP等很多语言都可以使用。
- 因为有了payload部分,所以JWT可以在自身存储一些其他业务逻辑所必要的非敏感信息。
- 便于传输,jwt的构成非常简单,字节占用很小,所以它是非常便于传输的。
- 它不需要在服务端保存会话信息, 所以它易于应用的扩展
- 安全相关
- 不应该在jwt的payload部分存放敏感信息,因为该部分是客户端可解密的部分。
- 保护好secret私钥,该私钥非常重要。
- 如果可以,请使用https协议
继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类,重写config 方法,定制一些httpSecurity的规则。
对于前后端分离的开发模式,需开放一个签发认证的url接口,而其他url接口根据业务要求,可以直接屏蔽返回未认证。
对应JWT的集成目前主要有两种方式:
- 继承
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter,使用认证章节中的流程。通过filter返回具体的Authentication对象,由有Provider进行认证逻辑处理 - 继承
OncePerRequestFilter,进行认证逻辑完成后,手工设置SpringSecurityHolder中的认证为成功
参考资料:
@EnableWebSecurity
@Slf4j
public class WebSecurityConfigurer extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
// 设置从不创建session,正常基于jwt认证才会如此设置
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy( SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS ).and()
// 设置异常处理返回
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint( restAuthenticationEntryPoint ).and()
// 设置不拦截的url请求
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/v1/admin/login/**").permitAll();
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated().and()
// 添加拦截器
.addFilterBefore(tokenAuthenticationFilter, BasicAuthenticationFilter.class);
// 禁止跨服务请求
http.csrf().disable();
}
}@Slf4j
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class UserWebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private JwtAuthenticationProvider jwtAuthenticationProvider;
@Autowired
private JwtRefreshAuthenticationProvider jwtRefreshAuthenticationProvider;
@Autowired
private PermissionProperty PermissionProperty;
@Autowired
private IJwtTokenService jwtTokenService;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// 设置从不创建session,正常基于jwt认证才会如此设置
http.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS).and();
// 设置读取配置的permitAll 以及允许所有接口使用OPTIONS
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers(resolvePermitAll()).permitAll()
.and().authorizeRequests().antMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS).permitAll()
// 添加自定义的Authentication过滤器
.and().addFilterAt(jwtAuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
// 设置异常处理返回,主要用于处理AccessDeny的异常
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint( restAuthenticationEntryPoint );
// 开启同源认证CORS过滤器
String contentSecurityPolicyStyleSrc = "style-src 'self' " + String.join(" ", securityProperty.getCsp().getStyleSrc());
String contentSecurityPolicyScriptSrc = "script-src 'self' "+ String.join(" ", securityProperty.getCsp().getScriptSrc());
http.cors().configurationSource(corsConfigurationSource())
.and().headers()
.frameOptions().deny()
.contentTypeOptions()
.and().xssProtection()
.and().cacheControl()
.and().httpStrictTransportSecurity()
.and().addHeaderWriter(new StaticHeadersWriter("Content-Security-Policy", contentSecurityPolicyStyleSrc, contentSecurityPolicyScriptSrc));
http.csrf().csrfTokenRepository(cookieCsrfTokenRepository)
.requireCsrfProtectionMatcher(createRequireCsrfProtectionMatcher());
}
/**
* 基于认证的provider
* @param auth
*/
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) {
auth.authenticationProvider(jwtAuthenticationProvider);
auth.authenticationProvider(jwtRefreshAuthenticationProvider);
}
/**
* 设置自己自定义的JwtAuthenticationFilter
* 注意要再matcher中指定拦截的范围
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private JwtAuthenticationFilter jwtAuthenticationFilter() throws Exception {
List<RequestMatcher> matchers = Lists.newArrayList();
for (String pattern : resolvePermitAll()) {
matchers.add(new AntPathRequestMatcher(pattern, null));
}
JwtAuthenticationFilter jwtAuthenticationFilter = new JwtAuthenticationFilter(
request -> matchers.stream().noneMatch(matcher -> matcher.matches(request))
);
jwtAuthenticationFilter.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager());
// 认证失败及成功处理器
jwtAuthenticationFilter.setAuthenticationFailureHandler(createAuthenticationFailureHandler());
jwtAuthenticationFilter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(createAuthenticationSuccessHandler());
return jwtAuthenticationFilter;
}
/**
* 同源处理器,自定义设置允许传输的请求头字段
* 允许跨域的地址等等
*/
private CorsConfigurationSource corsConfigurationSource() {
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
config.setAllowCredentials(true);
config.setAllowedHeaders(Lists.newArrayList("Origin", "Content-Type", "Accept", "X-Flow-Id"));
config.setExposedHeaders(Lists.newArrayList("Content-Type", "X-TenantID", "X-Track-Id"));
config.setAllowedOrigins(Lists.newArrayList(securityProperty.getCors().getAllowOrigins()));
config.setAllowedMethods(Lists.newArrayList(HttpMethod.OPTIONS.name(), HttpMethod.GET.name(), HttpMethod.POST.name()));
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", config);
return source;
}
/**
* 从配置中读取
* @return
*/
private String[] resolvePermitAll() {
return securityJwtProperty.getPermitAll();
}
/**
* 设置csrftoken的过滤
* @return
*/
private RequestMatcher createRequireCsrfProtectionMatcher() {
return new RequestMatcher() {
private final AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
private final HashSet<String> allowedMethods = new HashSet<>(
Arrays.asList("GET", "HEAD", "TRACE", "OPTIONS"));
public boolean matches(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (this.allowedMethods.contains(request.getMethod())) {
log.debug("CSRF disabled of methods {} match", request.getRequestURI());
return false;
}
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(request.getHeader("Authorization"))) {
log.debug("CSRF disabled matched header Authorization, requestURI: {}", request.getRequestURI());
return false;
}
return Stream.concat(Stream.of(securityJwtProperty.getPermitAll()), Stream.of(securityJwtProperty.getSwaggerPermitAll()))
.noneMatch(pattern -> this.antPathMatcher.match(pattern, request.getRequestURI()));
}
};
}
}@Slf4j
public class JwtAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
private IJwtTokenService jwtTokenService;
/**
* 拦截对应的的JWTHeader 递交给对应的Providr
* @param request
* @param response
* @return
*/
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
String authorization = request.getHeader(AuthorizationHeader);
if (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(authorization) && authorization.startsWith("bearer ")) {
return attemptHeaderAuthentication(request, authorization);
}
if (request.getCookies() == null) {
throw new JwtAuthenticationException(String.format("Jwt cookies are absent, request api is [%s]", request.getServletPath()));
}
String jwt = authorization.substring(7);
String[] jwtSplits = jwt.split("\\.");
if (jwtSplits.length != 3) {
log.error("Jwt is in wrong format, request api is {}", request.getServletPath());
throw new JwtAuthenticationException(String.format("Jwt is in wrong format, request api is [%s]", request.getServletPath()));
}
JwtAuthenticationToken jwtToken = jwtTokenService.digestJwtToken(jwt);
jwtToken.setAgentContext(agentContext);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(jwtToken);
}
@Override
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException {
super.successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}@Slf4j
@Component
public class JwtAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Autowired
private BlacklistService blacklistService;
@Autowired
private UserPermissionClient userPermissionClient;
/**
* 执行认证逻辑
* @param authentication
* @return
* @throws AuthenticationException
*/
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
JwtAuthenticationToken jwtToken = (JwtAuthenticationToken) authentication;
// ....
jwtToken.setAuthenticated(true);
return jwtToken;
}
/**
* 设置支持认证何种类型的Authentication
* @param authentication
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return authentication.isAssignableFrom(JwtAuthenticationToken.class);
}
}@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfigurer extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private RestAuthenticationEntryPoint restAuthenticationEntryPoint;
@Autowired
private TokenAuthenticationFilter tokenAuthenticationFilter;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy( SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS ).and()
.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint( restAuthenticationEntryPoint ).and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/v1/admin/login/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/upload/**").permitAll();
// API权限控制
ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer<HttpSecurity>.ExpressionInterceptUrlRegistry urlRegistry = http.authorizeRequests();
Map<String, String> resourcePermissions = new HashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : resourcePermissions.entrySet()) {
urlRegistry = urlRegistry.antMatchers(entry.getKey()).hasAnyAuthority(entry.getValue());
}
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated().and()
// 在默认的BasicAuthenticationFilter前添加自定义的过滤器
.addFilterBefore(tokenAuthenticationFilter, BasicAuthenticationFilter.class);
http.csrf().disable();
}
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) {
web.ignoring().antMatchers(
HttpMethod.POST,
"/api/v1/admin/login/toLogin"
).antMatchers(
HttpMethod.POST,
"/api/v1/front/wxAuthor/**"
).antMatchers(
HttpMethod.POST,
"/api/v1/admin/wxAuthor/**"
).antMatchers(
HttpMethod.POST,
"/api/v1/front/wxMessage/**"
).antMatchers(
HttpMethod.GET,
"/static/**"
).antMatchers(
HttpMethod.GET,
"/upload/**"
);
}
}注意在SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication); 设置认证成功的authentication,Spring security就会认为已经认证成功
@Component
public class TokenAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Autowired
private TokenHelper tokenHelper;
@Override
public void doFilterInternal(
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain
) throws IOException, ServletException {
String userInfo;
String authToken = tokenHelper.getToken(request);
if (authToken != null) {
// get username from token
userInfo = tokenHelper.getUserInfoFromToken(authToken);
System.out.println(userInfo);
if (userInfo != null) {
if (tokenHelper.validateToken(authToken)) {
String[] userInfos = userInfo.split("~");
String userName = userInfos[0];
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = buildAuthorities(userName);
TokenBasedAuthentication authentication = new TokenBasedAuthentication(new AccountCredentials(userName, authorities));
authentication.setToken(authToken);
authentication.setAuthenticated(true);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
}
}
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
private List<GrantedAuthority> buildAuthorities(String userName) {
List<String> permissionNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
for (String permissionName : permissionNames) {
GrantedAuthority authority = new PermissionGrantedAuthority(permissionName);
authorities.add(authority);
}
return authorities;
}
}@GetMapping
private String toLogin(HttpServletRequest request, String username, String password) {
// 登录成功
if (password.equals("112233")) {
String token = tokenHelper.generateToken(username+"~role");
// 登陆成功
return token;
}
return "认证失败";
}
一、使用默认的spring security 需要继承GrantedAuthority,返回用于认证的getAuthority()
public class PermissionGrantedAuthority implements GrantedAuthority {
private final String permission;
public PermissionGrantedAuthority(String permission) {
Assert.hasText(permission, "A granted authority textual representation is required");
this.permission = permission;
}
@Override
public String getAuthority() {
return permission;
}
}二、 在用户成功认证完成之后,需要将用户对应的权限赋予用户
@Component
public class TokenAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Autowired
private ITokenAuthenticationService tokenAuthenticationService;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
BaseTokenAuthentication baseTokenAuthentication = (BaseTokenAuthentication)authentication;
String token = baseTokenAuthentication.getToken();
String userInfoFromToken = jwtTokenHelper.getUserInfoFromToken(token);
log.info("authenticate success userInfo:{}", userInfoFromToken);
BaseTokenAuthentication authentication = new BaseTokenAuthentication(token, createRole());
authentication.setAuthenticated(true);
return authentication;
}
// 此处只是简单的模拟该用户有 ADMIN权限
private List<? extends GrantedAuthority> createRole() {
return Arrays.asList(new PermissionGrantedAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN"));
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return authentication.isAssignableFrom(BaseTokenAuthentication.class);
}
}三、 配置url对应的权限
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class BaseWebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private PermissionProperty permissionProperty;
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
super.configure(web);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS).and()
// ...
// application中配置 url跟role的键值对,设置到authorize中
http.authorizeRequests(authorize -> {
permissionProperty.getPermissionList().forEach(model -> {
authorize.mvcMatchers(model.getUrl()).hasAnyRole(model.getRole());
});
authorize.anyRequest().denyAll();
});
}
}需要处理token的场景:
- 退出登录;
- 修改密码;
- 服务端修改了某个用户具有的权限或者角色;
- 用户的帐户被删除/暂停。
- 用户由管理员注销;
解决方案:
- 存储黑名单token,如redis + token过期时间存储黑名单。
- redis的数据结构可以使用string + 过期时间,把token 当key,value使用状态表示。
- redis 使用zset,使用过期时间当score,value为jwt token, 使用zrangeByscore 过滤是否还存在过期key, zrank key member 获取元素是否存在。
- 设置较短的token过期时间,但是会导致用户频繁登陆,体验不好。
- token有效期延长。适合安全度不高的系统。
- 用户登录返回两个 token。一个用于登陆一个用于续签。
- 一个是 accessToken ,它的过期时间 token 本身的过期时间比如半个小时
- 一个是 refreshToken 它的过期时间更长一点比如为1天。
该方案的不足是:
- 需要客户端来配合;
- 用户注销的时候需要同时保证两个 token 都无效;
- 重新请求获取 token 的过程中会有短暂 token 不可用的情况(可以通过在客户端设置定时器,当accessToken 快过期的时候,提前去通过 refreshToken 获取新的accessToken)。
跨源资源共享 (CORS) (或通俗地译为跨域资源共享)是一种基于HTTP 头的机制,该机制通过允许服务器标示除了它自己以外的其它origin(域,协议和端口),这样浏览器可以访问加载这些资源。
跨源域资源共享( CORS )机制允许 Web 应用服务器进行跨源访问控制,从而使跨源数据传输得以安全进行。作用与JSONP类似
具体Spring security中的配置可以见下文
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
// by default uses a Bean by the name of corsConfigurationSource
.cors(withDefaults());
// ...
}
@Bean
CorsConfigurationSource corsConfigurationSource() {
CorsConfiguration configuration = new CorsConfiguration();
configuration.setAllowedOrigins(Arrays.asList("https://example.com"));
configuration.setAllowedMethods(Arrays.asList("GET","POST"));
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", configuration);
return source;
}
}