Drug Repurposing Knowledge Graph (DRKG) is a comprehensive biological knowledge graph relating genes, compounds, diseases, biological processes, side effects and symptoms. DRKG includes information from six existing databases including DrugBank, Hetionet, GNBR, String, IntAct and DGIdb, and data collected from recent publications particularly related to Covid19. It includes 97,055 entities belonging to 13 entity-types; and 5,869,294 triplets belonging to 106 edge-types. These 106 edge-types show a type of interaction between one of the 17 entity-type pairs (multiple types of interactions are possible between the same entity-pair), as depicted in the figure below. It also includes a bunch of notebooks about how to explore and analysis the DRKG using statistical methodologies or using machine learning methodologies such as knowledge graph embedding.
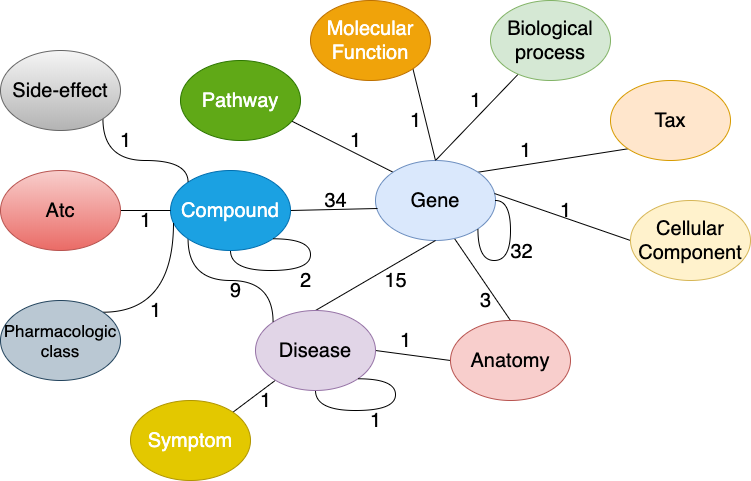
Figure: Interactions in the DRKG. The number next to an edge indicates the number of relation-types for that entity-pair in DRKG.
You can directly download drkg by following commands:
wget https://dgl-data.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/dataset/DRKG/drkg.tar.gz
The whole dataset contains three part:
- drkg.tsv, a tsv file containg the original drkg in the format of (h, r, t) triplets.
- embed, a folder containing the pretrained Knowledge Graph Embedding using the entire drkg.tsv as the training set.
- entity2src.tsv, a directory mapping entities in drkg to their original sources.
The DRKG mebedding is trained using TransE_l2 model with dimention size of 400, there are four files:
- DRKG_TransE_l2_entity.npy, NumPy binary data, storing the entity embedding
- DRKG_TransE_l2_relation.npy, NumPy binary data, storing the relation embedding
- entities.tsv, mapping from entity_name to tentity_id.
- relations.tsv, mapping from relation_name to relation_id
To use the pretrained embedding, one can use np.load to load the entity embeddings and relation embeddings separately:
import numpy as np
entity_emb = np.load('./embed/DRKG_TransE_l2_entity.npy')
rel_emb = np.load('./embed/DRKG_TransE_l2_relation.npy')
The type-wise distribution of the entities in DRKG and their original data-source(s) is shown in following table.
| Entity type | Drugbank | GNBR | Hetionet | STRING | IntAct | DGIdb | Bibliography | Total Entities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomy | - | - | 400 | - | - | - | - | 400 |
| Atc | 4048 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4048 |
| Biological Process | - | - | 11381 | - | - | - | - | 11381 |
| Cellular Component | - | - | 1391 | - | - | - | - | 1391 |
| Compound | 9708 | 11961 | 1538 | - | 153 | 6348 | 6250 | 24313 |
| Disease | - | 4747 | 257 | - | - | - | 33 | 4920 |
| Gene | 4973 | 27111 | 19145 | 18316 | 16321 | 2551 | 3181 | 39220 |
| Molecular Function | - | - | 2884 | - | - | - | - | 2884 |
| Pathway | - | - | 1822 | - | - | - | - | 1822 |
| Pharmacologic Class | - | - | 345 | - | - | - | - | 345 |
| Side Effect | - | - | 5701 | - | - | - | - | 5701 |
| Symptom | - | - | 415 | - | - | - | - | 415 |
| Tax | - | 215 | - | - | - | - | - | 215 |
| Total | 18729 | 44034 | 45279 | 18316 | 16474 | 8899 | 9464 | 97055 |
The following table shows the number of triplets between different entity-type pairs in DRKG for DRKG and various datasources.
| Entity-type pair | Drugbank | GNBR | Hetionet | STRING | IntAct | DGIdb | Bibliography | Total interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Gene, Gene) | - | 66722 | 474526 | 1496708 | 254346 | - | 58629 | 2350931 |
| (Compound, Gene) | 24801 | 80803 | 51429 | - | 1805 | 26290 | 25666 | 210794 |
| (Disease, Gene) | - | 95400 | 27977 | - | - | - | 461 | 123838 |
| (Atc, Compound) | 15750 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 15750 |
| (Compound, Compound) | 1379271 | - | 6486 | - | - | - | - | 1385757 |
| (Compound, Disease) | - | 77782 | 1145 | - | - | - | - | 78927 |
| (Gene, Tax) | - | 14663 | - | - | - | - | - | 14663 |
| (Biological Process, Gene) | - | - | 559504 | - | - | - | - | 559504 |
| (Disease, Symptom) | - | - | 3357 | - | - | - | - | 3357 |
| (Anatomy, Disease) | - | - | 3602 | - | - | - | - | 3602 |
| (Disease, Disease) | - | - | 543 | - | - | - | - | 543 |
| (Anatomy, Gene) | - | - | 726495 | - | - | - | - | 726495 |
| (Gene, Molecular Function) | - | - | 97222 | - | - | - | - | 97222 |
| (Compound, Pharmacologic Class) | - | - | 1029 | - | - | - | - | 1029 |
| (Cellular Component, Gene) | - | - | 73566 | - | - | - | - | 73566 |
| (Gene, Pathway) | - | - | 84372 | - | - | - | - | 84372 |
| (Compound, Side Effect) | - | - | 138944 | - | - | - | - | 138944 |
| Total | 1419822 | 335370 | 2250197 | 1496708 | 256151 | 26290 | 84756 | 5869294 |
Before using notebooks here, you need to install some dependencies:
Currently all notebooks use PyTorch as Deep Learning backend. For install other version of pytorch please goto Install PyTorch
sudo pip3 install torch==1.5.0+cu101 torchvision==0.6.0+cu101 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
If you want to analyze DRKG with DGL with notebooks at [drkg-with-dgl], you need to install DGL package. Currently we use the newest stable version of DGL. For install other version of DGL please goto Install DGL
sudo pip3 install dgl-cu101
If you want to training the model with notebooks (e.g., using Train_embeddings.ipynb or Edge_score_analysis.ipynb) at [knowledge-graph-embedding-based-analysis-of-drkg], you need to install DGL as in [install-dgl-optional] and install DGL-KE package here. Currently we use the newest stable version of DGL-KE. DGL-KE can work with DGL > 0.4.3 (either CPU or GPU)
sudo pip3 install dglke
We provide a notebook, with example of using DRKG with Deep Graph Library (DGL). The following notebook provides an example of building a heterograph from DRKG in DGL; and some examples of queries on the DGL heterograph:
We analyzed directly the structure of the extracted DRKG. Since the datasources may contain related information, we want to verify that combining the edge information from different sources is meaningful.
To evaluate the structural similarity among a pair of relation types we compute their Jaccard similarity coefficient and the overlap among the two edge types via the overlap coeffcient:
We analyze the extracted DRKG by learning a TransE KGE model that utilizes the
We split the edge triplets in training, validation and test sets as follows
Finally, we obtain the entity and relation embeddings for the DRKG. We can do various embedding based analysis as provided in the following notebooks:
- Relation_similarity_analysis.ipynb, analyzing the generate relation embedding similarity.
- Entity_similarity_analysis.ipynb, analyzing the generate entity embedding similarity.
- Edge_score_analysis.ipynb, evaluating whether the learned KGE model can predict the edges of DRGK
- Edge_similarity_based_on_link_recommendation_results.ipynb, evaluating how similar are the predicted links among different relation types.
We present an example of using pretrained DRKG model for drug repurposing for COVID-19. In the example, we directly use the pretrined model provided at DRKG dataset and proposed 100 drugs for COVID-19. The following notebook provides the details:
This project is licensed under the Apache-2.0 License. However, the DRKG integrates data from many resources and users should consider the licensing of each source (see this table) . We apply a license attribute on a per node and per edge basis for sources with defined licenses.