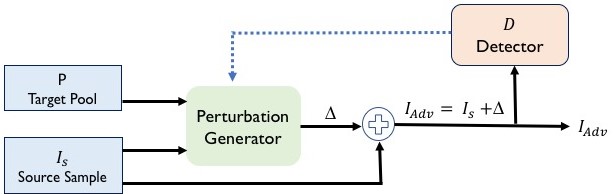
This repository contains code and data of the paper Mockingbird: Defending Against Deep-Learning-Based Website Fingerprinting Attacks with Adversarial Traces, published in IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security (TIFS). Read the paper at IEEE Xplore. Mockingbird is designed to work against deep-learning-based website fingerprinting attacks. Extensive evaluation shows that Mockingbird is effective against both white-box and black-box attacks including a more advanced intersection attacks.
@article{rahman2021mockingbird,
title={{Mockingbird:Defending Against Deep-Learning-Based Website Fingerprinting Attacks
with Adversarial Traces}},
author={M. S. {Rahman} and M. {Imani} and N. {Mathews} and M. {Wright}},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security},
year={2021},
volume={16},
pages={1594-1609},
doi={10.1109/TIFS.2020.3039691}
}
Ensuring all the depencies is critical. It is hard to keep all the packages updated at once. Some versions might be relaitvely old.
So we suggest the users to create a python virtual environment or conda environment and install the required packages.
Please make sure you have all the dependencies available and installed.
- NVIDIA GPU should be installed in the machine, running on CPU will significantly increase time complexity.
- Ubuntu 16.04.5/ CentOS Linux 7
- Python3-venv/ conda
- Keras version: 2.2.4
- TensorFlow version: 1.15.0
- Numpy: 1.16.6
- Matplotlib: 2.2.5
- CUDA Version: 10.2
- CuDNN Version: 7
- Python Version: 2.7.5
-- Please install the required packages using the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txt
We have shared the processed data using a Google Drive. Please download the processed data from this Google Drive URL.
After downloading, please put the data into the dataset directory.
Arguments:
- `--data_dir` : dataset directory.
- `--data_type` : choices= ['full_duplex', 'half_duplex']
- `--detector` : choices = ['DF', 'AWF']\
detector model. DF as a detector will enable white-box attack\
and AWF as a detector will enable black-box attack.
- `--case` : choices=[1,2]\
number of cases to run.
- `--target_pool` : number of samples in the target pool.
- `--num_iteration` : number of iterations to generate the adversarial trace.
Example of Usage:
python mockingbird.py --data_dir dataset --data_type full_duplex --detector DF --case 1 --target_pool 1 --num_iteration 1
Arguments:
- `--data_dir` : dataset directory.
- `--data_type` : choices= ['full_duplex', 'half_duplex']
- `--detector` : choices = ['DF', 'AWF']\
detector model. DF as a detector will enable white-box attack\
and AWF as a detector will enable black-box attack.
- `--case` : choices=[1,2]\
number of cases to run.
- `--target_pool` : number of samples in the target pool.
- `--num_iteration` : number of iterations to generate the adversarial trace.
- `--exp_type` : choices = ['Undefended', 'Defended']\
Select Experiment Type to run: defended/undefended.
- `--intersection_attack` : choices= [True, False]
- `--multi_gpu` : choices= [True, False]
- `--num_gpu` : number of gpus.
- `--optimizer` : choices = ['Adam', 'Adamax']\
The optimizer for the experiment.
- `--batch_size` : choices = [32, 50, 64, 128, 256]\
The batch size for the experiment.
- `--verbose` : choices = [0, 1, 2]
- `--learning_rate` : learning rate of the optimizer.
Example of Usage:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python run_attack.py --data_dir dataset --data_type full_duplex --detector DF --case 1 --target_pool 1 --num_iteration 1 --exp_type Defended --intersection_attack False --attack_model DF --optimizer Adamax --epoch 2 --batch_size 128 --verbose 1 --learning_rate 0.001
Plesae refer to this repository for the code of the information leakage analysis.
Please, address any questions, comments, or feedback to the authors of the paper. The main developers of this code are:
- Mohammad Saidur Rahman ([email protected])
- Mohsen Imani ([email protected])
- Nate Mathews ([email protected])
- Matthew Wright ([email protected])
This material is based upon work supported in part by the National Science Foundation (NSF) under Grants No. 1423163, 1722743, 1816851, and 1433736.