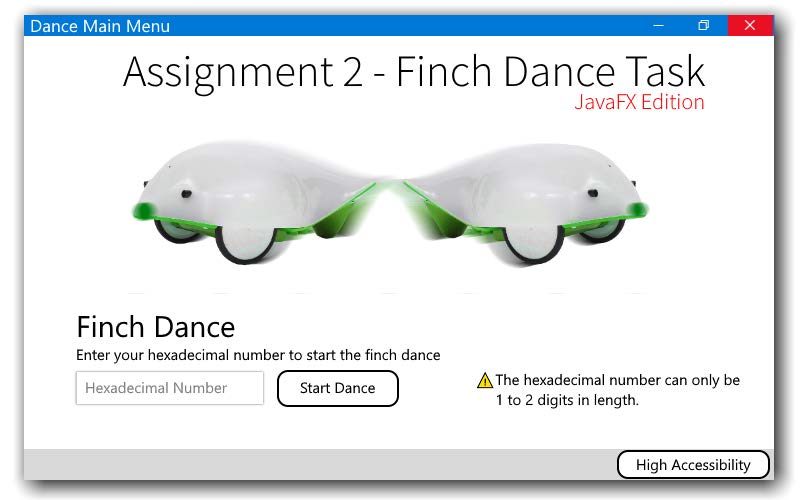
This program creates a dance pattern for the BirdBrain Finch 1.0 to dance based on a set of rules involving a hexadecimal conversion.
The dance is determined by the user input. However, we will make this problem slightly more interesting by using different number systems. We will be using binary, decimal, octal and hexadecimal number systems. So, your program should also serve as a number converter.
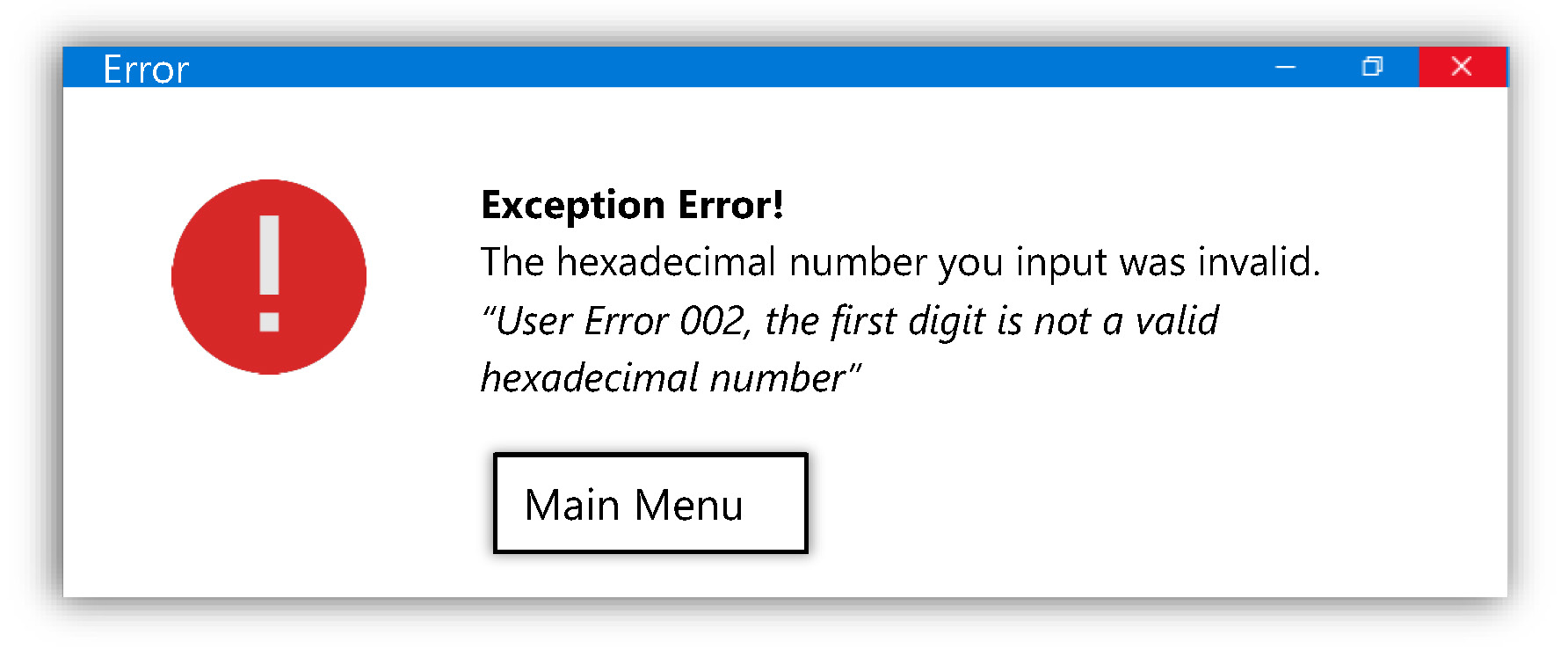
The program should ask the user to enter a hexadecimal number of either 1 or 2 digits (e.g., F or 1F).
Then the program should convert this hexadecimal number into the octal, decimal and binary equivalents. For example, if the user enters 5A, the octal equivalent is 132, the decimal equivalent is 90 and the binary equivalent is 1011010.
Once the conversion is done, these numbers will be used for creating the dance routine.
The speed of the finch is determined by the octal equivalent of the given hexadecimal number. However, if the octal number is smaller than 60 then the speed should be set to that octal number + 50. If the octal number exceeds the speed limit of the wheels of the finch, the speed should be set to the limit.
The colour of the LED of the finch’s beak is created by mixing different values of red, green, and blue. The red value should be the decimal equivalent of the given hexadecimal number; the green value should be equal to the remainder of the decimal equivalent when divided by 80, multiplied by 3; the blue value should be equal to the greater of the two (red or green) values.
The movements of the robot (forward or backwards) are determined by the binary equivalent of the given hexadecimal number. Specifically, the movements should be as follows: reading the binary number from right to left one digit at a time, the finch should move forward when the digit is equal to 1, and backwards when the digit is equal to zero. So, for example, 1011010 should cause the robot to move backwards, forward, backwards, forward, forward, backwards and finally forward. If the hexadecimal is one digit long, the duration of each movement (forward or backward) should be 1 second. If the hexadecimal is two digits long, the duration of each movement should be 0.5 seconds.