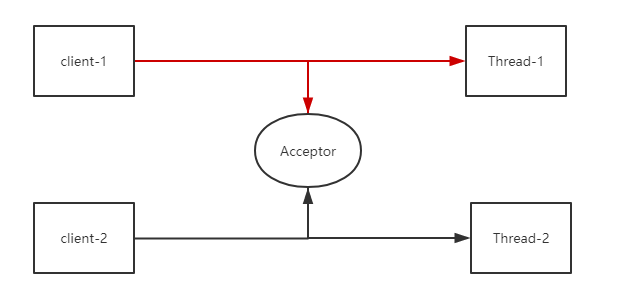
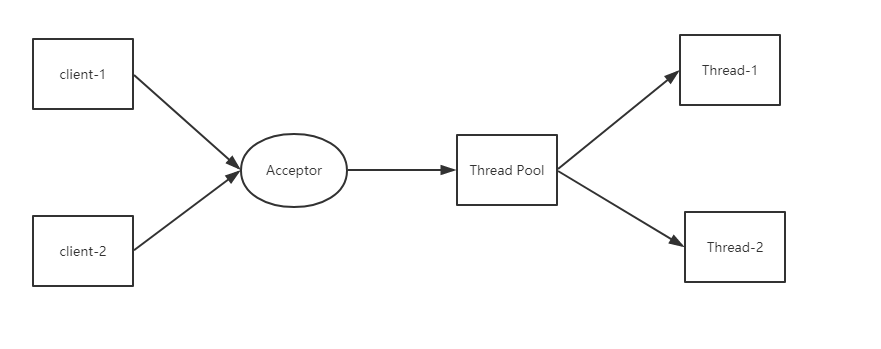
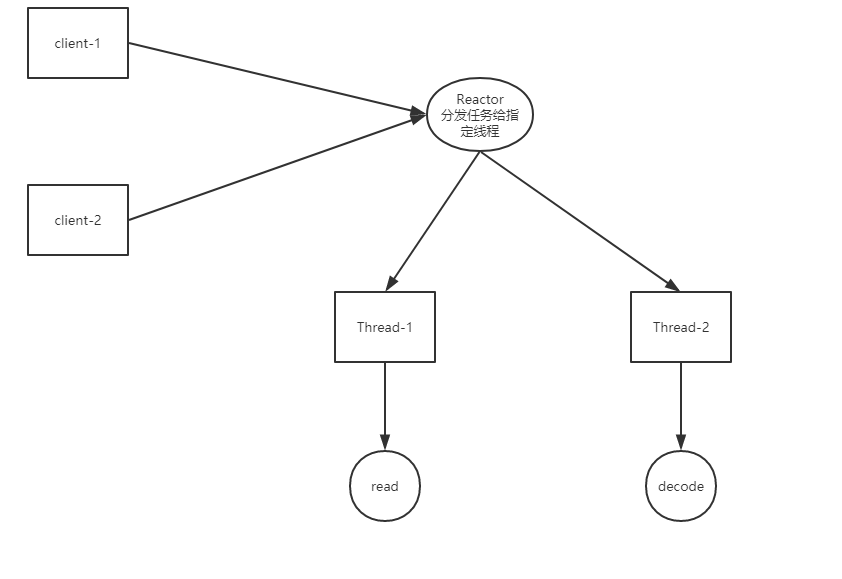
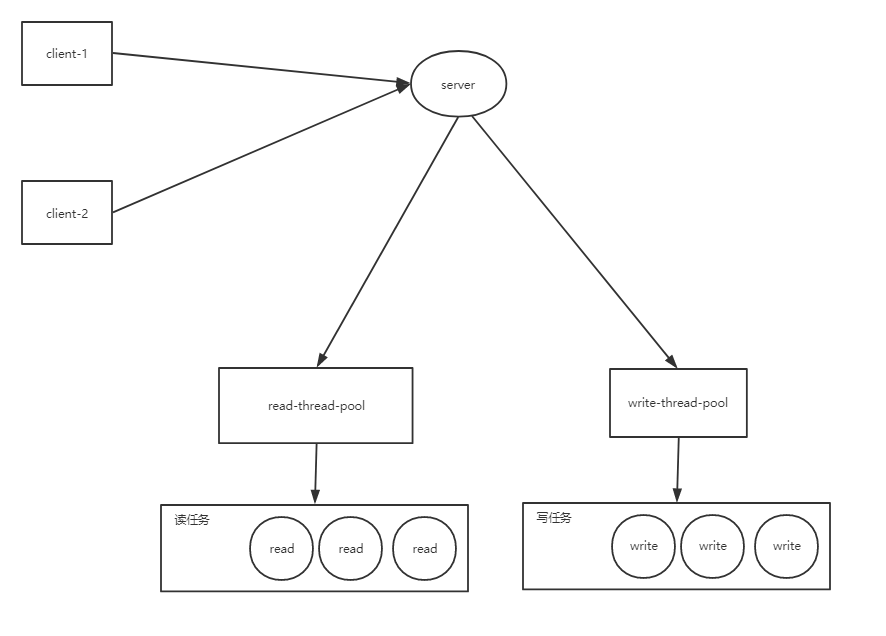
Netty is an asynchronous event-driven network application framework for rapid development of maintainable high performance protocol servers & clients.
- 异步,事件驱动框架
同步并阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个连接一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程进行处理,如果这个连接不做任何事情会造成不必要的线程开销,当然可以通过线程池机制改善。
- 应用场景:适用于连接数目比较小且固定的架构,这种方式对服务器资源要求比较高,并发局限于应用中
同步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个请求一个线程,即客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到多路复用器上,多路复用器轮询到连接有I/O请求时才启动一个线程进行处理。
- 应用场景:适用于连接数目多且连接比较短(轻操作)的架构,比如聊天服务器,并发局限于应用中,编程比较复杂
异步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个有效请求一个线程,客户端的I/O请求都是由OS先完成了再通知服务器应用去启动线程进行处理,
- 应用场景:适用于连接数目多且连接比较长(重操作)的架构,比如相册服务器,充分调用OS参与并发操作,编程比较复杂
Java NIO FileChannel是连接文件的通道。使用FileChannel,您可以从文件中读取数据和将数据写入文件。Java NIO FileChannel类是NIO用于替代使用标准Java IO API读取文件的方法。
- 开启
- 不能直接开启,需要通过
InputStream,OutputStream获取 java.io.FileOutputStream#getChannel
- 不能直接开启,需要通过
- 读取
java.nio.channels.FileChannel#read(java.nio.ByteBuffer)
- 写入
java.nio.channels.FileChannel#write(java.nio.ByteBuffer)
- 关闭
java.nio.channels.spi.AbstractInterruptibleChannel#close
- 大小
- 返回通道连接到的文件的文件大小。
java.nio.channels.FileChannel#size
- 位置
- 对
FileChannel进行读取或写入时,你会在特定的位置上这样做。您可以通过调用FileChannel#position()方法来获取对象的当前位置。还可以通过调用FileChannel的position(long pos)方法设置位置。 java.nio.channels.FileChannel#position()
- 对
- 截断
- 可以通过调用该
FileChannel的truncate()方法来截断文件。当您截断文件时,您可以在给定的长度上将其截断。 java.nio.channels.FileChannel#truncate
- 可以通过调用该
public class FileChannelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("E:\\mck\\javaBook-src\\netty\\src\\main\\resources\\data.data");
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
FileChannel fc = fos.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
byteBuffer.put("hello , fileChannel\n".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
byteBuffer.flip();
fc.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
byteBuffer.clear();
fos.close();
fc.close();
}
} Selector 一般称 为选择器 (或 多路复用器) 。它是Java NIO核心组件中的一个,用于检查一个或多个NIO Channel(通道)的状态是否处于可读、可写。可以实现单线程管理多个channels,也就是说可以管理多个网络连接。
-
开启
java.nio.channels.Selector#open
-
channel 注册
-
channel.configureBlocking(false); SelectionKey key = channel.register(selector, Selectionkey.OP_READ);
channel必须是非阻塞的
-
-
java.nio.channels.SelectionKeyjava.nio.channels.SelectionKey#OP_READ读事件java.nio.channels.SelectionKey#OP_WRITE写事件java.nio.channels.SelectionKey#OP_CONNECT连接事件java.nio.channels.SelectionKey#OP_ACCEPT确认事件
-
停止选择
-
java.nio.channels.Selector#wakeup通过调用Selector对象的wakeup()方法让处在阻塞状态的select()方法立刻返回 该方法使得选择器上的第一个还没有返回的选择操作立即返回。如果当前没有进行中的选择操作,那么下一次对select()方法的一次调用将立即返回。
-
java.nio.channels.Selector#close该方法使得任何一个在选择操作中阻塞的线程都被唤醒(类似
wakeup()),同时使得注册到该Selector的所有Channel被注销,所有的键将被取消,但是Channel本身并不会关闭。
-
Channel 是Netty 网络操作的接口,它除了包括基本I/O操作、bind、connect、read、write ,还包括了Netty 的相关操作
Netty 基于事件驱动模型,使用不同的事件来通知我们状态的改变或者操作状态的改变。
EventLoop定义了在整个连接的生命周期里当有事件发生的时候处理的核心抽象。
EventLoopGroup可以包含一个或多个EventLoop- 一个
EventLoop在它的生命周期内只能与一个Thread绑定。 - 所有有
EnventLoop处理的 I/O 事件都将在它专有的 Thread 上被处理。 - 一个
Channel在它的生命周期内只能注册与一个EventLoop。 - 一个
EventLoop可被分配至一个或多个Channel。 - 当一个连接到达时,Netty 就会注册一个 Channel,然后从 EventLoopGroup 中分配一个 EventLoop 绑定到这个Channel上,在该Channel的整个生命周期中都是有这个绑定的 EventLoop 来服务的。
通过该接口的
addListener()方法注册一个ChannelFutureListener,当操作执行成功或者失败时,监听就会自动触发返回结果
ChannelHandler它充当了所有处理入站和出站数据的应用程序逻辑的容器。ChannelHandler 有两个核心子类ChannelInboundHandler和ChannelOutboundHandler,其中ChannelInboundHandler用于接收、处理入站数据和事件,而ChannelOutboundHandler则相反。
ChannelPipeline为ChannelHandler链提供了一个容器并定义了用于沿着链传播入站和出站事件流的 API。一个数据或者事件可能会被多个 Handler 处理,在这个过程中,数据或者事件经流ChannelPipeline,由ChannelHandler处理。在这个处理过程中,一个ChannelHandler接收数据后处理完成后交给下一个ChannelHandler,或者什么都不做直接交给下一个ChannelHandler。
package com.huifer.netty.hello;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
/**
* <p>Title : NettyServer </p>
* <p>Description : </p>
*
* @author huifer
* @date 2019-06-24
*/
public class NettyServer {
public static final String IP = "127.0.0.1";
public static final int PORT = 9999;
/**
* 最大线程数
*/
public static final int BIG_GROUP_SIZE = 2 * Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
public static final int BIG_THREAD_SIZE = 100;
public static final EventLoopGroup WORK_GROUP = new NioEventLoopGroup(BIG_THREAD_SIZE);
private static final EventLoopGroup BOOS_GROUP = new NioEventLoopGroup(BIG_GROUP_SIZE);
public static void start() throws Exception {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
// 设置boos group 和 work group
serverBootstrap.group(BOOS_GROUP, WORK_GROUP)
// 设置channel
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
// 设置 channel handler 处理 ,childHandler 针对连接进行处理
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
// 编解码器添加
pipeline.addLast(
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, 100, 0,
100));
pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(IP, PORT).sync();
// 关闭时的监听器
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
System.out.println(" 服务启动 ");
}
protected static void shutdown() {
WORK_GROUP.shutdownGracefully();
BOOS_GROUP.shutdownGracefully();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
NettyServer.start();
}
}-
io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap-
io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap#group(io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup, io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup)该方法将BOOS_GROUP,WORK_GROUP保存到变量中 -
io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#channelpublic B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass) { if (channelClass == null) { throw new NullPointerException("channelClass"); } return channelFactory(new ReflectiveChannelFactory<C>(channelClass)); } public ReflectiveChannelFactory(Class<? extends T> clazz) { ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(clazz, "clazz"); try { this.constructor = clazz.getConstructor(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Class " + StringUtil.simpleClassName(clazz) + " does not have a public non-arg constructor", e); } }
- 通过
io.netty.channel.ReflectiveChannelFactory#ReflectiveChannelFactory将.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)保存到io.netty.channel.ReflectiveChannelFactory#constructor变量中,在需要时调用io.netty.channel.ReflectiveChannelFactory#newChannel进行初始化
- 通过
-
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(IP, PORT).sync();-
io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#bind(java.net.SocketAddress)-
io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#doBindprivate ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) { final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister(); final Channel channel = regFuture.channel(); if (regFuture.cause() != null) { return regFuture; } if (regFuture.isDone()) { // At this point we know that the registration was complete and successful. ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise(); doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise); return promise; } else { // Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not. final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel); regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { Throwable cause = future.cause(); if (cause != null) { // Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an // IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel. promise.setFailure(cause); } else { // Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use. // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586 promise.registered(); doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise); } } }); return promise; } }
io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#initAndRegister
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() { Channel channel = null; try { channel = channelFactory.newChannel(); // NioServerSocketChannel 初始化 init(channel); } catch (Throwable t) { if (channel != null) { // channel can be null if newChannel crashed (eg SocketException("too many open files")) channel.unsafe().closeForcibly(); // as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t); } // as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t); } ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel); if (regFuture.cause() != null) { if (channel.isRegistered()) { channel.close(); } else { channel.unsafe().closeForcibly(); } } // If we are here and the promise is not failed, it's one of the following cases: // 1) If we attempted registration from the event loop, the registration has been completed at this point. // i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now because the channel has been registered. // 2) If we attempted registration from the other thread, the registration request has been successfully // added to the event loop's task queue for later execution. // i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now: // because bind() or connect() will be executed *after* the scheduled registration task is executed // because register(), bind(), and connect() are all bound to the same thread. return regFuture; }
-
io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap#init@Override void init(Channel channel) throws Exception { final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = options0(); synchronized (options) { setChannelOptions(channel, options, logger); } final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> attrs = attrs0(); synchronized (attrs) { for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: attrs.entrySet()) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") AttributeKey<Object> key = (AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey(); channel.attr(key).set(e.getValue()); } } ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline(); final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = childGroup; final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = childHandler; final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] currentChildOptions; final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] currentChildAttrs; synchronized (childOptions) { currentChildOptions = childOptions.entrySet().toArray(newOptionArray(0)); } synchronized (childAttrs) { currentChildAttrs = childAttrs.entrySet().toArray(newAttrArray(0)); } p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() { @Override public void initChannel(final Channel ch) throws Exception { final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); ChannelHandler handler = config.handler(); if (handler != null) { pipeline.addLast(handler); } ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor( ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs)); } }); } }); }
-
io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#setChannelOptions(io.netty.channel.Channel, java.util.Map.Entry<io.netty.channel.ChannelOption<?>,java.lang.Object>[], io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLogger)static void setChannelOptions( Channel channel, Map.Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] options, InternalLogger logger) { for (Map.Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object> e: options) { setChannelOption(channel, e.getKey(), e.getValue(), logger); } }
-
io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#setChannelOptionprivate static void setChannelOption( Channel channel, ChannelOption<?> option, Object value, InternalLogger logger) { try { if (!channel.config().setOption((ChannelOption<Object>) option, value)) { logger.warn("Unknown channel option '{}' for channel '{}'", option, channel); } } catch (Throwable t) { logger.warn( "Failed to set channel option '{}' with value '{}' for channel '{}'", option, value, channel, t); } }
-
channel 配置
-
io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel#configprivate final ServerSocketChannelConfig config;
-
-
NioServerSocketChannel初始化public NioServerSocketChannel() { this(newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER)); } public NioServerSocketChannel(ServerSocketChannel channel) { super(null, channel, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); config = new NioServerSocketChannelConfig(this, javaChannel().socket()); } private static ServerSocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) { try { /** * Use the {@link SelectorProvider} to open {@link SocketChannel} and so remove condition in * {@link SelectorProvider#provider()} which is called by each ServerSocketChannel.open() otherwise. * * See <a href="https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2308">#2308</a>. */ return provider.openServerSocketChannel(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new ChannelException( "Failed to open a server socket.", e); } }
provider.openServerSocketChannel();private static final SelectorProvider DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER = SelectorProvider.provider();
sun.nio.ch.SelectorProviderImpl#openServerSocketChannelJDK所提供
-
-
public class TcpHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("channel active。。。。。。。。。。。。。");
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务端接到: " + msg.toString());
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("服务端返回信息: 你好");
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务端异常" + cause.getLocalizedMessage());
}
}