数据结构+算法=程序
数据元素之间的关系
数据元素之间的关系[★★★★★]
数据的逻辑结构在计算机上存储形式,包括内存,硬盘,软盘,光盘等
-
顺序存储:数据元素存储在地址连续的存储单元里,其数据间的物理关系和逻辑关系是一致的.例如:【数组】的存储
-
链式存储:数据结构存储在任意的存储单元里,这组存储单元可以连续,也可以不连续,数据单元中还存放着指针,指向其关联元素的位置.由于数据之前的关系经常发生变化,所以链式结构这种存储结构更加灵活.
解决特定程序问题的技巧和方式.
针对某个特定问题,解决的算法不唯一,但是掌握一些好的算法很有帮助
-
输入
算法具有零个或多个输入
-
输出
算法至少有一个或多个输出
-
有穷
算法在执行完有限的步骤后自动结束而不会出现无限循环
-
确定性
算法的每一个步骤都具有确定的含义,不会出现二义性
-
可行性
算法的每一步都能必须是可行的,每一步执行有限次数完成
- 正确性
- 可读性
- 健壮性
- 时间效率高存储量低
-
事后统计法
不可取,因为要编写独立的测试方法,麻烦
不同的测试方法和环境也会导致统计结果的差异
-
事前统计法
研究算法随着输入规模的增大其增长量的抽象!
进行输入测试时,关注主要项,忽略次要项!
- 概念
研究规模n的增大,算法执行次数的增长率. 执行次数==时间
算法复杂度:O(n)
算法复杂度:O(n²)
- 常见时间复杂度举例
效率
元素按照逻辑上的先后关系依次存储
- 优点
- 无须为额外的逻辑关系而增加额外的存储空间.(物理结构和逻辑结构一致)
- 可以快速的存取表中任意位置的元素.(通过下标快速找到指定元素)
- 缺点
- 插入和删除元素需要移动大量元素.(需要对其他元素重新定义下标)
- 当线性表长度变化较大时,难以确定存储空间的容量.(每次分配连续的空间存储数据)
- 容易造成存储空间的碎片
每个节点及存储数据也存储下个元素的地址(指针),第一个节点称作头节点,第二个节点称为尾节点.
创建方式有头插法(插入顺序和输入顺序想法)和尾插法(插入顺序和插入顺序一致)
-
优点
无须预先分配空间,空间可以不连续
有效的利用存储空间,较少空间碎片化
-
缺点
元素没有下标,需要循环查找
-
分配方式
- 顺序结构需要一段连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的数据
- 链式结构用一组任意的存储单元存放线性表关系
-
时间性能
- 查找
- 顺序存储O(1)
- 链式存储O(n)
- 插入和删除
- 顺序存储O(n)
- 链式存储O(1)
- 查找
-
空间性能
- 顺序存储结构需要预分配存储空间,元素个数有限制
- 单链表不需要预分配空间,元素个数无限制
-
总结
频繁查找用顺序存储结构
频繁插入和删除用链表存储结构
Q: 快速查找未知长度单链表的中间节点
回答一:时间复杂度O(n+n/2)=O(3n/2)
1. 先遍历链表确定总长度L
2. 再从头节点遍历到L/2
回答二:时间复杂度O(n)
1. 设置快慢2个指针,快指针的速度是慢指针的2倍
2. 快指针和慢指针同时遍历链表
3. 当快指针指向尾节点的时候慢指针刚好指向中间节点
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("程序说明如下:");
System.out.println("由m个人围成一个首尾相连的圈报数。从第一个人开始,从1开始报数,报到n的人出圈,剩下的人继续从1开始报数,直到所有的人都出圈为止。对于给定的m和n,求出所有人的出圈顺序.");
//提示输入总人数
System.out.println("请输入做这个游戏的总人数:");
Scanner sca = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sca.nextInt();
//提示输入要出圈的数值
System.out.println("请输入要出圈的数值:");
int n = sca.nextInt();
System.out.println("按出圈的次序输出序号:");
//创建有m个值的数组
int[] a = new int[m];
//初始长度,以后出圈一个,长度就减一
int len = m;
//给数组赋值
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
a[i] = i + 1;
//i为元素下表,j代表当前要报的数
int i = 0;
int j = 1;
while (len > 0) { //如果数组长度减为0,结束游戏
if (j % n == 0) {//找到要出圈的人,并把圈中人数减一
System.out.print(a[i % m] + " ");
a[i % m] = -1;
j = 1;//有人出圈后开始从1接着报数
i++;
len--;
} else {//没人出圈,i++,位置往后移动,j++口号加一个,如刚才报的是1,下一个该报2,3,4直到n
i++;
j++;
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("经过了"+i+"次,游戏结束");
}- 初始化给定长度数组,数组元素为默认值0
int[] arr = new int[10];- 初始化数组时赋值
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,4,3,4,5};public class MyArray {
private long[] arr;
private int elements; //元素个数
public MyArray() {
arr = new long[50];
}
public MyArray(int len) {
arr = new long[len];
}
}- 末尾追加
public void insert(long value) {
arr[elements] = value;
elements++;
}- 有序追加
public void insert(long value) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < elements; i++) {
if (arr[i] > value) {
break;
}
}
//元素后移
for (int j = elements; j>i ; j--) {
arr[j]=arr[j-1];
}
arr[i]=value;
elements++;
}private void checkIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > elements - 1) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}public long get(int index) {
checkIndex(index);
return arr[index];
}public int search(long value) {
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < elements; i++) {
if (arr[i] == value) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
return index;
} public int binarySearch(long value) {
int middle = 0;
int begin = 0;
int last = elements;
int index = -1;
while (true) {
//计算中间索引
middle = (begin + last) / 2;
//如果中间值刚好等于value,则返回middle
if (arr[middle] == value) {
index = middle;
return index;
} else if (begin > last) { //退出条件
break;
} else { //如果中间值大于value,重新查找前半段
if (arr[middle] > value) {
last = middle - 1;
} else { //如果中间值小于value,重新查找前半段
begin = middle + 1;
}
}
}
return index;
}注意二分查找的元素必须有序
public void display() {
System.out.print("[ ");
for (int i = 0; i < elements; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.print("]");
}public void update(int index, long value) {
checkIndex(index);
arr[index] = value;
} public void delelteByIndex(int index) {
checkIndex(index);
//从index开始遍历
for (int j = index; j < elements; j++) {
//将index后的值往前移动
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
}
//arr的数据总数-1
elements--;
}public void deleteByValue(long value) {
//获得value的索引
int index = search(value);
//删除index对应的值
delelteByIndex(index);
}public void bubbleSort(long[] arr) {
//控制比较次数
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
//比较值大小
for (int j = arr.length - 1; j > i; j--) {
//如果j小于j-1,向前冒泡
if (arr[j] < arr[j - 1]) {
long temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
arr[j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}public void selectionSort(long[] arr) {
//k永远指向最小数
int k = 0;
//交换的变量
long temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
//从第一位开始比较
k = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
//如果k位置的值大于j的值,k指向j
if (arr[j] < arr[k]) {
k = j;
}
//经过循环k永远指向最小值
}
//交换k和i的值
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[k];
arr[k] = temp;
}
}public void insertSort(long[] arr) {
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
long temp = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > temp) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}相比插入排序,希尔排序在移动元素的次数更少
public void shellSort(long[] arr) {
//初始化一个间隔
int h = 1;
while (h < arr.length / 3) {
h = h * 3 + 1;
}
while (h > 0) {
long temp = 0;
for (int i = h; i < arr.length; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
int j = i;
while (j > h - 1 && arr[j - h] >= temp) {
arr[j] = arr[j - h];
j -= h;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
h = (h - 1) / 3;
}
}/**
* 划分数组
*/
public int partition(long[] arr, int left, int right, long point) {
int leftPtr = left - 1;
int rightPtr = right;
while (true) {
while (leftPtr < rightPtr && arr[++leftPtr] < point) ;
while (rightPtr > leftPtr && arr[--rightPtr] > point) ;
if (leftPtr >= rightPtr) {
break;
} else {
long temp = arr[leftPtr];
arr[leftPtr] = arr[rightPtr];
arr[rightPtr] = temp;
}
}
long temp = arr[leftPtr];
arr[leftPtr] = arr[right];
arr[right] = temp;
return leftPtr;
}
/**
* 快速排序
*
* @param arr
* @param left
* @param right
*/
public void quickSort(long[] arr, int left, int right) {
if (right - left <= 0) {
return;
} else {
//设置比较关键字
long point = arr[right];
//获得切入点,同时对数组进行划分
int partition = partition(arr, left, right, point);
//对左边的子数组进行快速排序
quickSort(arr, left, partition - 1);
//对右边的子数组进行快速排序
quickSort(arr, partition + 1, right);
}
}public class MyStack {
/**
* 底层是数组实现
*/
private long[] arr;
/**
* 指向栈顶的指针
*/
private int top;
public MyStack() {
arr = new long[10];
top = -1;
}
public MyStack(int length) {
arr = new long[length];
top = -1;
}
}public void push(long value) {
arr[++top] = value;
}public long pop() {
return arr[top--];
}public long peek() {
return arr[top];
}public boolean isEmpty(){
return top==-1;
}public boolean isFull(){
return top==arr.length-1;
}public class MyQueue {
/**
* 底层使用数组实现
*/
private long[] arr;
/**
* 元素数量
*/
private int elements;
/**
* 队头
*/
private int front;
/**
* 队尾
*/
private int end;
public MyQueue() {
arr = new long[10];
elements = 0;
front = 0;
end = -1;
}
public MyQueue(int maxSize) {
arr = new long[maxSize];
elements = 0;
front = 0;
end = -1;
}
}- 非循环添加
public void insert(long value) {
arr[++end] = value;
elements++;
}- 循环添加
public void insert(long value) {
if (end>=arr.length-1) {
end=-1;
}else{
elements++;
}
arr[++end] = value;
}- 非循环移除
public long remove() {
elements--;
return arr[front++];
}- 循环移除
public long remove() {
long value = arr[front++];
if(front == arr.length) {
front = 0;
}
elements--;
return value;
}public long peek() {
return arr[front];
}public boolean isEmpty() {
return elements == 0;
}public boolean isFull() {
return elements == arr.length;
}public class Node {
public long value;
public Node next;
public Node(long value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void display() {
System.out.print(value+" ");
}
}public class LinkList {
private Node first;
public LinkList() {
first = null;
}
}public void insertFirst(long value) {
Node node = new Node(value);
node.next = first;
first = node;
}public Node deleteFirst() {
Node tmp = first;
first = tmp.next;
return tmp;
}public void display() {
Node current = first;
while (current != null) {
current.display();
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}public Node find(long value) {
Node current = first;
if (current == null) {
return null;
}
while (current.value != value) {
if (current == null) {
return null;
}
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}public Node delete(long value) {
Node current = first;
Node previous = first;
//找到值为value的节点
while (current.value != value) {
if (current.next == null) {
return null;
}
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
if (current == first) {
first = first.next;
} else {
previous.next = current.next;
}
return current;
}public class FirstLastLinkList {
/**
* 头结点
*/
private Node first;
/**
* 尾节点
*/
private Node last;
public FirstLastLinkList() {
this.first = null;
this.last = null;
}
}public void insertFirst(long value) {
Node node = new Node(value);
if (isEmpty()) {
last = node;
}
node.next = first;
first = node;
}public void insertLast(long value) {
Node node = new Node(value);
if (isEmpty()) {
first = node;
} else {
last.next = node;
}
last = node;
}public Node deleteFirst() {
Node temp = first;
if (first.next == null) {
last = null;
}
first = temp.next;
return temp;
}public void display() {
Node current = first;
while (current != null) {
current.display();
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}public Node find(long value) {
Node current = first;
while (current.value != value) {
if (current.next == null) {
return null;
}
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}public Node delete(long value) {
Node current = first;
Node previous = first;
while (current.value != value) {
if (current.next == null) {
return null;
}
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
if (current == first) {
first = first.next;
} else {
previous.next = current.next;
}
return current;
}public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
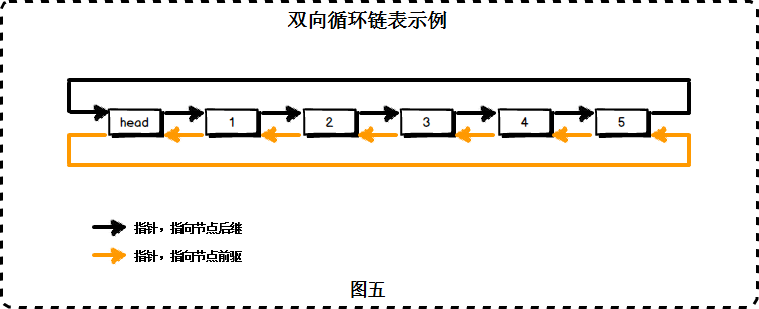
}public class DoubleNode {
public long value;
public DoubleNode next;
public DoubleNode previous;
public DoubleNode(long value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void display() {
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
}public class DoubleLinkList {
/**
* 头结点
*/
private DoubleNode first;
/**
* 尾节点
*/
private DoubleNode last;
public DoubleLinkList() {
first = null;
last = null;
}
}public void insertFirst(long value) {
DoubleNode node = new DoubleNode(value);
if (isEmpty()) {
last = node;
} else {
first.previous = node;
}
node.next = first;
first = node;
}public void insertLast(long value) {
DoubleNode node = new DoubleNode(value);
if (isEmpty()) {
first = node;
} else {
last.next = node;
node.previous = last;
}
last = node;
}public DoubleNode deleteFirst() {
DoubleNode temp = first;
if (first.next == null) {
last = null;
} else {
first.next.previous = null;
}
first = temp.next;
return temp;
}public DoubleNode deleteLast() {
if (first.next == null) {
first = null;
} else {
last.previous.next = null;
}
last = last.previous;
return last;
}public void display() {
DoubleNode current = first;
while (current != null) {
current.display();
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}public DoubleNode delete(long value) {
DoubleNode current = first;
while (current.value != value) {
if (current.next == null) {
return null;
}
current = current.next;
}
if (current == first) {
first = first.next;
} else {
current.previous.next = current.next;
}
return current;
}public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}规则:第n项的值=n-1项的值+n
项数: 1,2,3,4,5,6
值: 1,3,6,10,15,21
public int getNumber(int n) {
int total = 0;
while (n > 0) {
total = total + n;
n--;
}
return total;
}public int getNumberByRecursion(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return n + getNumberByRecursion(n - 1);
}
}规则:第1项为0,第2项为1,第3项为1...第n项为(n-1)+(n-2)
项数: 1,2,3,4,5,6
值: 0,1,1,2,3,5
public int getNumber(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 0;
} else if (n == 2) {
return 1;
} else {
return getNumber(n - 1) + getNumber(n - 2);
}
}思路分析:
1. 将TopN-1个盘子从A移动到B
2. 将TopN的盘子从A移动到C
3. 将TopN-1个盘子从B移动到C
public void doTower(int topN, char from, char inter, char to) {
if (topN == 1) {
System.out.println("盘子1,从" + from + "塔座到" + to + "塔座");
} else {
//1.将topN-1的盘子从from移动到inter
doTower(topN - 1, from, to, inter);
//2.将topN的盘子从from移动到to
System.out.println("盘子" + topN + ",从" + from + "塔座到" + to + "塔座");
//3.将topN-1的盘子从inter移动到to
doTower(topN - 1, inter, from, to);
}
}概念:树一种抽象数据类型,用来模拟具有树状结构性质的数据集合.
- 每个节点有零个或多个子节点
- 没有父节点的称为根节点
- 每个非跟节点有且只有一个父节点
- 除了根节点外,每个子节点可以分为多个不相交的子树
概念:每个节点最多只有2个子节点,分别为左子节点和右子节点
特点:
- 左子树上的所有节点的值均小于根节点的值
- 右子书上的所有节点的值均大于根节点的值
- 任意节点的左,右子树也分别为二叉树
- 没有键值相等的节点
public class Node {
/**
* 数据项
*/
public long data;
/**
* 数据项
*/
public String sDate;
/**
* 左节点
*/
public Node leftChild;
/**
* 右节点
*/
public Node rightChild;
/**
* 构造方法
*
* @param data
* @param sDate
*/
public Node(long data, String sDate) {
this.data = data;
this.sDate = sDate;
}
}public class OrderedBinaryTree {
/**
* 根节点
*/
private Node root;
}public void insert(long value, String sValue) {
//封装节点
Node newNode = new Node(value, sValue);
//引用当前节点
Node current = root;
//应用父节点
Node parent;
//如果root为null,第一次插入的时候
if (root == null) {
root = newNode;
return;
} else { //非第一次插入
//遍历树
while (true) {
//父节点指向当前节点
parent = current;
if (current.data > value) {
//如果当前指向的节点数据比插入的数据大,则走向左子树
current = current.leftChild;
if (current == null) {
parent.leftChild = newNode;
return;
}
} else {
//如果当前指向的节点的数据比插入数据小,则走向右子树
current = current.rightChild;
if (current == null) {
parent.rightChild = newNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}public Node find(long value) {
//应用当前节点,从根节点开始
Node current = root;
//循环,只要查找值不等于当前节点的数据项就一致查找
while (current.data != value) {
//进行比较,如果当前节点的值大于查找值,则走向左子树
if (current.data > value) {
current = current.leftChild;
} else { //如果当前节点的值小于查找值,则走向右子树
current = current.rightChild;
}
//如果查不到,返回null
if (current == null) {
return null;
}
}
return current;
}- 前序遍历
/**
* 前序遍历:
* (1)访问根节点
* (2)先序遍历左子树
* (3)先序遍历右子树
*
* @param localNode
*/
public void frontOrder(Node localNode) {
if (localNode != null) {
//访问根节点
System.out.println(localNode.data + "," + localNode.sData);
//前序遍历左子树
frontOrder(localNode.leftChild);
//前序遍历右子树
frontOrder(localNode.rightChild);
}
}- 中序遍历
/**
* 中序遍历
* (1)中序遍历左子树
* (2)访问根节点
* (3)中序遍历右子树
*
* @param localNode
*/
public void inOrder(Node localNode) {
if (localNode != null) {
//中序遍历左子树
inOrder(localNode.leftChild);
//访问根节点
System.out.println(localNode.data + "," + localNode.sData);
//中序遍历右子树
inOrder(localNode.rightChild);
}
}- 后续遍历
/**
* 后续遍历
* (1)后序遍历左子树
* (2)后序遍历右子树
* (3)访问根节点
*
* @param localNode
*/
public void afterOrder(Node localNode) {
if (localNode != null) {
//后续遍历左子树
afterOrder(localNode.leftChild);
//后续遍历右子树
afterOrder(localNode.rightChild);
//访问根节点
System.out.println(localNode.data + "," + localNode.sData);
}
}-
删除叶子节点:直接删除该节点,再修改其父节点的指针(注意分是根节点和不是根节点)
eg:删除72
-
删除单支节点:让p的子树与p的父亲节点相连,再删除p即可;(注意分是根节点和不是根节点两种情况)
eg:删除79
-
删除双支节点:首先找到p的后继y,因为y一定没有左子树,所以可以删除y,并让y的父亲节点成为y的右子树的父亲节点,并用y的值代替p的值
eg:删除9