diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3618_split_array_by_prime_indices/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3618_split_array_by_prime_indices/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..100a396c5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3618_split_array_by_prime_indices/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3618_split_array_by_prime_indices;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Math #Number_Theory #Biweekly_Contest_161
+// #2025_07_22_Time_3_ms_(100.00%)_Space_62.61_MB_(10.13%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public long splitArray(int[] nums) {
+ int n = nums.length;
+ boolean[] isPrime = sieve(n);
+ long sumA = 0;
+ long sumB = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ if (isPrime[i]) {
+ sumA += nums[i];
+ } else {
+ sumB += nums[i];
+ }
+ }
+ return Math.abs(sumA - sumB);
+ }
+
+ // Sieve of Eratosthenes to find all prime indices up to n
+ private boolean[] sieve(int n) {
+ boolean[] isPrime = new boolean[n];
+ if (n > 2) {
+ isPrime[2] = true;
+ }
+ for (int i = 3; i < n; i += 2) {
+ isPrime[i] = true;
+ }
+ if (n > 2) {
+ isPrime[2] = true;
+ }
+ for (int i = 3; i * i < n; i += 2) {
+ if (isPrime[i]) {
+ for (int j = i * i; j < n; j += i * 2) {
+ isPrime[j] = false;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ isPrime[0] = false;
+ if (n > 1) {
+ isPrime[1] = false;
+ }
+ return isPrime;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3618_split_array_by_prime_indices/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3618_split_array_by_prime_indices/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e5c8cfdc9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3618_split_array_by_prime_indices/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+3618\. Split Array by Prime Indices
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums`.
+
+Split `nums` into two arrays `A` and `B` using the following rule:
+
+* Elements at **prime** indices in `nums` must go into array `A`.
+* All other elements must go into array `B`.
+
+Return the **absolute** difference between the sums of the two arrays: `|sum(A) - sum(B)|`.
+
+**Note:** An empty array has a sum of 0.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The only prime index in the array is 2, so `nums[2] = 4` is placed in array `A`.
+* The remaining elements, `nums[0] = 2` and `nums[1] = 3` are placed in array `B`.
+* `sum(A) = 4`, `sum(B) = 2 + 3 = 5`.
+* The absolute difference is `|4 - 5| = 1`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-1,5,7,0]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The prime indices in the array are 2 and 3, so `nums[2] = 7` and `nums[3] = 0` are placed in array `A`.
+* The remaining elements, `nums[0] = -1` and `nums[1] = 5` are placed in array `B`.
+* `sum(A) = 7 + 0 = 7`, `sum(B) = -1 + 5 = 4`.
+* The absolute difference is `|7 - 4| = 3`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3619_count_islands_with_total_value_divisible_by_k/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3619_count_islands_with_total_value_divisible_by_k/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ee2704f1b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3619_count_islands_with_total_value_divisible_by_k/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3619_count_islands_with_total_value_divisible_by_k;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Matrix #Union_Find #Biweekly_Contest_161 #Depth_First_Search
+// #Breadth_First_Search #2025_07_22_Time_16_ms_(96.65%)_Space_70.96_MB_(50.08%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ private int m;
+ private int n;
+
+ public int countIslands(int[][] grid, int k) {
+ int count = 0;
+ m = grid.length;
+ n = grid[0].length;
+ for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
+ if (grid[i][j] != 0) {
+ int curr = dfs(i, j, grid);
+ if (curr % k == 0) {
+ count++;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return count;
+ }
+
+ private int dfs(int i, int j, int[][] grid) {
+ if (i >= m || j >= n || i < 0 || j < 0 || grid[i][j] == 0) {
+ return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
+ }
+ int count = grid[i][j];
+ grid[i][j] = 0;
+ int x = dfs(i + 1, j, grid);
+ int y = dfs(i, j + 1, grid);
+ int a = dfs(i - 1, j, grid);
+ int b = dfs(i, j - 1, grid);
+ if (x != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
+ count += x;
+ }
+ if (y != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
+ count += y;
+ }
+ if (a != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
+ count += a;
+ }
+ if (b != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
+ count += b;
+ }
+ return count;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3619_count_islands_with_total_value_divisible_by_k/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3619_count_islands_with_total_value_divisible_by_k/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..841a4bc2c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3619_count_islands_with_total_value_divisible_by_k/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+3619\. Count Islands With Total Value Divisible by K
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an `m x n` matrix `grid` and a positive integer `k`. An **island** is a group of **positive** integers (representing land) that are **4-directionally** connected (horizontally or vertically).
+
+The **total value** of an island is the sum of the values of all cells in the island.
+
+Return the number of islands with a total value **divisible by** `k`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
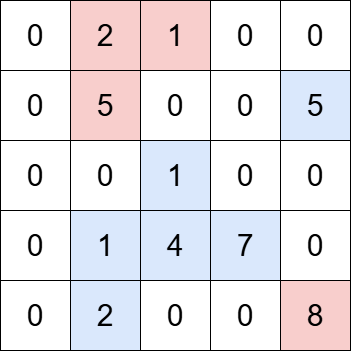
+
+
+**Input:** grid = [[0,2,1,0,0],[0,5,0,0,5],[0,0,1,0,0],[0,1,4,7,0],[0,2,0,0,8]], k = 5
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The grid contains four islands. The islands highlighted in blue have a total value that is divisible by 5, while the islands highlighted in red do not.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
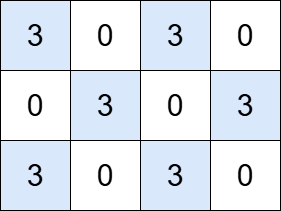
+
+
+**Input:** grid = [[3,0,3,0], [0,3,0,3], [3,0,3,0]], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The grid contains six islands, each with a total value that is divisible by 3.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* `1 <= m, n <= 1000`
+* 1 <= m * n <= 105
+* 0 <= grid[i][j] <= 106
+* 1 <= k <= 106
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3620_network_recovery_pathways/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3620_network_recovery_pathways/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..288799452
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3620_network_recovery_pathways/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3620_network_recovery_pathways;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Binary_Search #Heap_Priority_Queue #Graph #Topological_Sort
+// #Shortest_Path #Biweekly_Contest_161 #2025_07_22_Time_151_ms_(66.08%)_Space_108.87_MB_(63.77%)
+
+import java.util.ArrayList;
+import java.util.Arrays;
+import java.util.LinkedList;
+import java.util.List;
+import java.util.Queue;
+
+public class Solution {
+ private List topologicalSort(int n, List> g) {
+ int[] indeg = new int[n];
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ for (int adjNode : g.get(i)) {
+ indeg[adjNode]++;
+ }
+ }
+ Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
+ List ts = new ArrayList<>();
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
+ if (indeg[i] == 0) {
+ q.offer(i);
+ }
+ }
+ while (!q.isEmpty()) {
+ int u = q.poll();
+ ts.add(u);
+ for (int v : g.get(u)) {
+ indeg[v]--;
+ if (indeg[v] == 0) {
+ q.offer(v);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return ts;
+ }
+
+ private boolean check(
+ int x, int n, List> adj, List ts, boolean[] online, long k) {
+ long[] d = new long[n];
+ Arrays.fill(d, Long.MAX_VALUE);
+ d[0] = 0;
+ for (int u : ts) {
+ // If d[u] is reachable
+ if (d[u] != Long.MAX_VALUE) {
+ for (int[] p : adj.get(u)) {
+ int v = p[0];
+ int c = p[1];
+ if (c < x || !online[v]) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ if (d[u] + c < d[v]) {
+ d[v] = d[u] + c;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return d[n - 1] <= k;
+ }
+
+ public int findMaxPathScore(int[][] edges, boolean[] online, long k) {
+ int n = online.length;
+ // Adjacency list for graph with edge weights
+ List> adj = new ArrayList<>();
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
+ }
+ List> g = new ArrayList<>();
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ g.add(new ArrayList<>());
+ }
+ for (int[] e : edges) {
+ int u = e[0];
+ int v = e[1];
+ int c = e[2];
+ adj.get(u).add(new int[] {v, c});
+ g.get(u).add(v);
+ }
+ List ts = topologicalSort(n, g);
+ if (!check(0, n, adj, ts, online, k)) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ int l = 0;
+ int h = 0;
+ for (int[] e : edges) {
+ h = Math.max(h, e[2]);
+ }
+ while (l < h) {
+ int md = l + (h - l + 1) / 2;
+ if (check(md, n, adj, ts, online, k)) {
+ l = md;
+ } else {
+ h = md - 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return l;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3620_network_recovery_pathways/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3620_network_recovery_pathways/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d8aab05a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3620_network_recovery_pathways/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+3620\. Network Recovery Pathways
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a directed acyclic graph of `n` nodes numbered from 0 to `n − 1`. This is represented by a 2D array `edges` of length `m`, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, costi] indicates a one‑way communication from node ui to node vi with a recovery cost of costi.
+
+Some nodes may be offline. You are given a boolean array `online` where `online[i] = true` means node `i` is online. Nodes 0 and `n − 1` are always online.
+
+A path from 0 to `n − 1` is **valid** if:
+
+* All intermediate nodes on the path are online.
+* The total recovery cost of all edges on the path does not exceed `k`.
+
+For each valid path, define its **score** as the minimum edge‑cost along that path.
+
+Return the **maximum** path score (i.e., the largest **minimum**\-edge cost) among all valid paths. If no valid path exists, return -1.
+
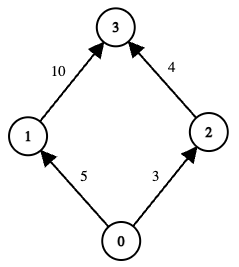
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** edges = [[0,1,5],[1,3,10],[0,2,3],[2,3,4]], online = [true,true,true,true], k = 10
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* The graph has two possible routes from node 0 to node 3:
+
+ 1. Path `0 → 1 → 3`
+
+ * Total cost = `5 + 10 = 15`, which exceeds k (`15 > 10`), so this path is invalid.
+
+ 2. Path `0 → 2 → 3`
+
+ * Total cost = `3 + 4 = 7 <= k`, so this path is valid.
+
+ * The minimum edge‐cost along this path is `min(3, 4) = 3`.
+
+* There are no other valid paths. Hence, the maximum among all valid path‐scores is 3.
+
+
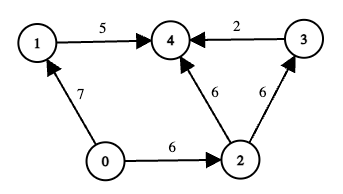
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** edges = [[0,1,7],[1,4,5],[0,2,6],[2,3,6],[3,4,2],[2,4,6]], online = [true,true,true,false,true], k = 12
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* Node 3 is offline, so any path passing through 3 is invalid.
+
+* Consider the remaining routes from 0 to 4:
+
+ 1. Path `0 → 1 → 4`
+
+ * Total cost = `7 + 5 = 12 <= k`, so this path is valid.
+
+ * The minimum edge‐cost along this path is `min(7, 5) = 5`.
+
+ 2. Path `0 → 2 → 3 → 4`
+
+ * Node 3 is offline, so this path is invalid regardless of cost.
+
+ 3. Path `0 → 2 → 4`
+
+ * Total cost = `6 + 6 = 12 <= k`, so this path is valid.
+
+ * The minimum edge‐cost along this path is `min(6, 6) = 6`.
+
+* Among the two valid paths, their scores are 5 and 6. Therefore, the answer is 6.
+
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == online.length`
+* 2 <= n <= 5 * 104
+* `0 <= m == edges.length <=` min(105, n * (n - 1) / 2)
+* edges[i] = [ui, vi, costi]
+* 0 <= ui, vi < n
+* ui != vi
+* 0 <= costi <= 109
+* 0 <= k <= 5 * 1013
+* `online[i]` is either `true` or `false`, and both `online[0]` and `online[n − 1]` are `true`.
+* The given graph is a directed acyclic graph.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3621_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_i/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3621_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_i/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6a49b7154
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3621_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_i/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3621_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_i;
+
+// #Hard #Dynamic_Programming #Math #Combinatorics #Biweekly_Contest_161
+// #2025_07_22_Time_9_ms_(70.67%)_Space_44.76_MB_(55.42%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ private static final int MX_LN = 61;
+ private final long[][] slct = new long[MX_LN][MX_LN];
+ private final int[] popHeight = new int[MX_LN];
+
+ public Solution() {
+ for (int i = 0; i < MX_LN; i++) {
+ slct[i][0] = slct[i][i] = 1;
+ for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
+ slct[i][j] = slct[i - 1][j - 1] + slct[i - 1][j];
+ }
+ }
+ popHeight[1] = 0;
+ for (int v = 2; v < MX_LN; v++) {
+ popHeight[v] = 1 + popHeight[Long.bitCount(v)];
+ }
+ }
+
+ private long countNumbers(long upperLimit, int setBits) {
+ if (setBits == 0) {
+ return 1;
+ }
+ long count = 0;
+ int used = 0;
+ int len = 0;
+ for (long x = upperLimit; x > 0; x >>= 1) {
+ len++;
+ }
+ for (int pos = len - 1; pos >= 0; pos--) {
+ if (((upperLimit >> pos) & 1) == 1) {
+ if (setBits - used <= pos) {
+ count += slct[pos][setBits - used];
+ }
+ used++;
+ if (used > setBits) {
+ break;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if (Long.bitCount(upperLimit) == setBits) {
+ count++;
+ }
+ return count;
+ }
+
+ public long popcountDepth(long tillNumber, int depthQuery) {
+ if (depthQuery == 0) {
+ return tillNumber >= 1 ? 1 : 0;
+ }
+ long total = 0;
+ for (int ones = 1; ones < MX_LN; ones++) {
+ if (popHeight[ones] == depthQuery - 1) {
+ total += countNumbers(tillNumber, ones);
+ }
+ }
+ if (depthQuery == 1) {
+ total -= 1;
+ }
+ return total;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3621_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_i/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3621_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..bc2f988ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3621_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+3621\. Number of Integers With Popcount-Depth Equal to K I
+
+Hard
+
+You are given two integers `n` and `k`.
+
+For any positive integer `x`, define the following sequence:
+
+* p0 = x
+* pi+1 = popcount(pi) for all `i >= 0`, where `popcount(y)` is the number of set bits (1's) in the binary representation of `y`.
+
+This sequence will eventually reach the value 1.
+
+The **popcount-depth** of `x` is defined as the **smallest** integer `d >= 0` such that pd = 1.
+
+For example, if `x = 7` (binary representation `"111"`). Then, the sequence is: `7 → 3 → 2 → 1`, so the popcount-depth of 7 is 3.
+
+Your task is to determine the number of integers in the range `[1, n]` whose popcount-depth is **exactly** equal to `k`.
+
+Return the number of such integers.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, k = 1
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The following integers in the range `[1, 4]` have popcount-depth exactly equal to 1:
+
+| x | Binary | Sequence |
+|---|--------|------------|
+| 2 | `"10"` | `2 → 1` |
+| 4 | `"100"`| `4 → 1` |
+
+Thus, the answer is 2.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 7, k = 2
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The following integers in the range `[1, 7]` have popcount-depth exactly equal to 2:
+
+| x | Binary | Sequence |
+|---|---------|----------------|
+| 3 | `"11"` | `3 → 2 → 1` |
+| 5 | `"101"` | `5 → 2 → 1` |
+| 6 | `"110"` | `6 → 2 → 1` |
+
+Thus, the answer is 3.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 1015
+* `0 <= k <= 5`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3622_check_divisibility_by_digit_sum_and_product/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3622_check_divisibility_by_digit_sum_and_product/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2d7025f46
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3622_check_divisibility_by_digit_sum_and_product/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3622_check_divisibility_by_digit_sum_and_product;
+
+// #Easy #Math #Weekly_Contest_459 #2025_07_22_Time_0_ms_(100.00%)_Space_40.91_MB_(44.64%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public boolean checkDivisibility(int n) {
+ int x = n;
+ int sum = 0;
+ int mul = 1;
+ while (x != 0) {
+ sum += x % 10;
+ mul *= x % 10;
+ x = x / 10;
+ }
+ return n % (sum + mul) == 0;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3622_check_divisibility_by_digit_sum_and_product/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3622_check_divisibility_by_digit_sum_and_product/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c033e3f13
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3622_check_divisibility_by_digit_sum_and_product/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+3622\. Check Divisibility by Digit Sum and Product
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a positive integer `n`. Determine whether `n` is divisible by the **sum** of the following two values:
+
+* The **digit sum** of `n` (the sum of its digits).
+
+* The **digit** **product** of `n` (the product of its digits).
+
+
+Return `true` if `n` is divisible by this sum; otherwise, return `false`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 99
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Since 99 is divisible by the sum (9 + 9 = 18) plus product (9 \* 9 = 81) of its digits (total 99), the output is true.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 23
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Since 23 is not divisible by the sum (2 + 3 = 5) plus product (2 \* 3 = 6) of its digits (total 11), the output is false.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 106
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3623_count_number_of_trapezoids_i/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3623_count_number_of_trapezoids_i/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..37f4bc048
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3623_count_number_of_trapezoids_i/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3623_count_number_of_trapezoids_i;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Hash_Table #Math #Geometry #Weekly_Contest_459
+// #2025_07_22_Time_30_ms_(99.92%)_Space_100.93_MB_(64.40%)
+
+import java.util.HashMap;
+import java.util.Map;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int countTrapezoids(int[][] points) {
+ int mod = 1_000_000_007;
+ long inv = 500_000_004L;
+ Map map = new HashMap<>(points.length);
+ for (int[] p : points) {
+ map.merge(p[1], 1, Integer::sum);
+ }
+ long sum = 0L;
+ long sumPairs = 0L;
+ for (Integer num : map.values()) {
+ if (num > 1) {
+ long pairs = ((long) num * (num - 1) / 2) % mod;
+ sum = (sum + pairs) % mod;
+ sumPairs = (sumPairs + pairs * pairs % mod) % mod;
+ }
+ }
+ long res = (sum * sum % mod - sumPairs + mod) % mod;
+ res = (res * inv) % mod;
+ return (int) res;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3623_count_number_of_trapezoids_i/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3623_count_number_of_trapezoids_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2debd6da0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3623_count_number_of_trapezoids_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+3623\. Count Number of Trapezoids I
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a 2D integer array `points`, where points[i] = [xi, yi] represents the coordinates of the ith point on the Cartesian plane.
+
+A **horizontal** **trapezoid** is a convex quadrilateral with **at least one pair** of horizontal sides (i.e. parallel to the x-axis). Two lines are parallel if and only if they have the same slope.
+
+Return the _number of unique_ **_horizontal_ _trapezoids_** that can be formed by choosing any four distinct points from `points`.
+
+Since the answer may be very large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** points = [[1,0],[2,0],[3,0],[2,2],[3,2]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
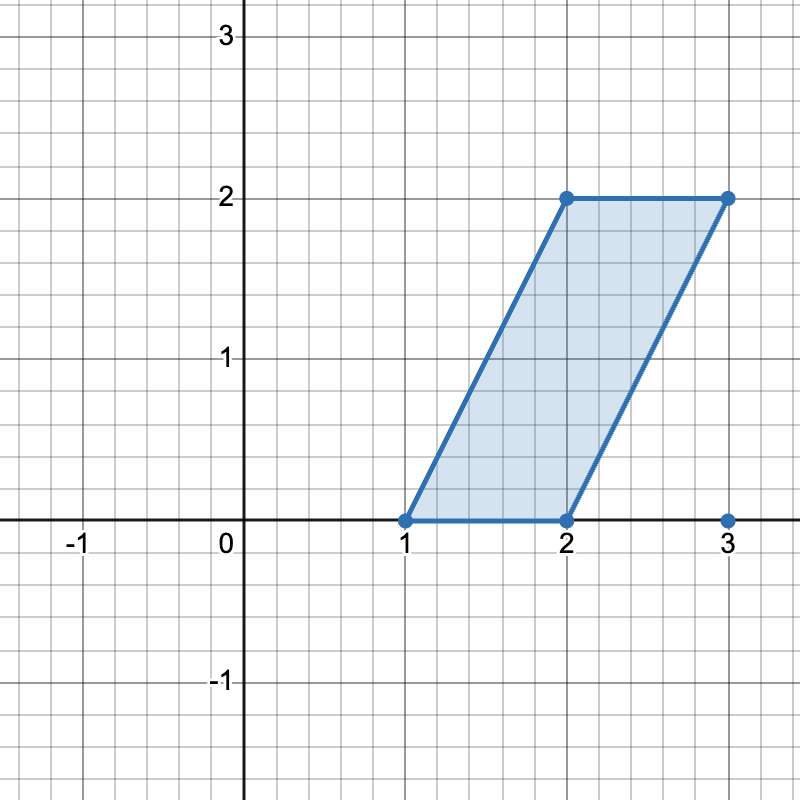
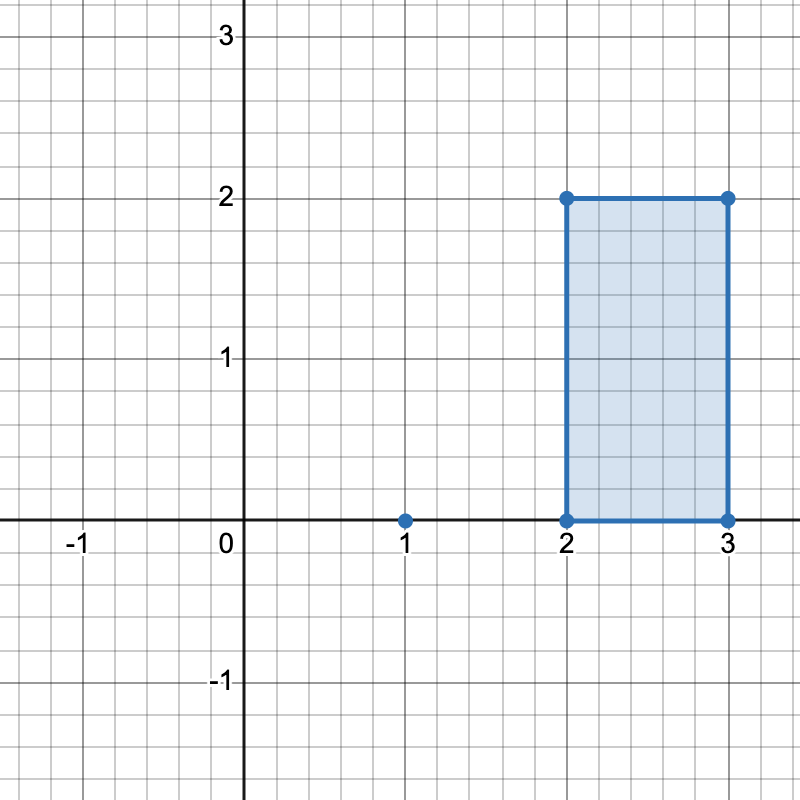
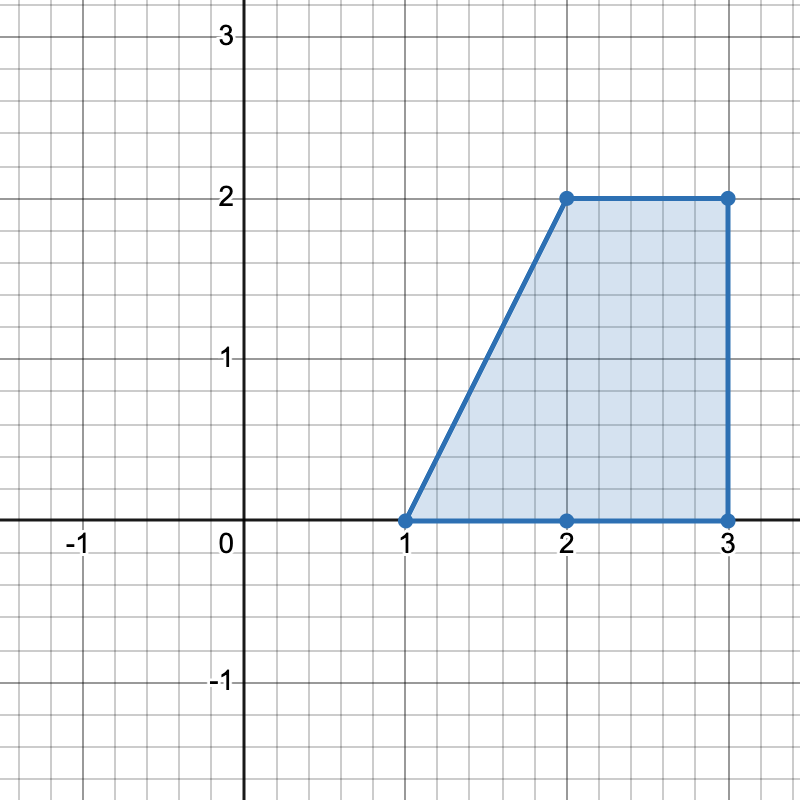
+  
+
+There are three distinct ways to pick four points that form a horizontal trapezoid:
+
+* Using points `[1,0]`, `[2,0]`, `[3,2]`, and `[2,2]`.
+* Using points `[2,0]`, `[3,0]`, `[3,2]`, and `[2,2]`.
+* Using points `[1,0]`, `[3,0]`, `[3,2]`, and `[2,2]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
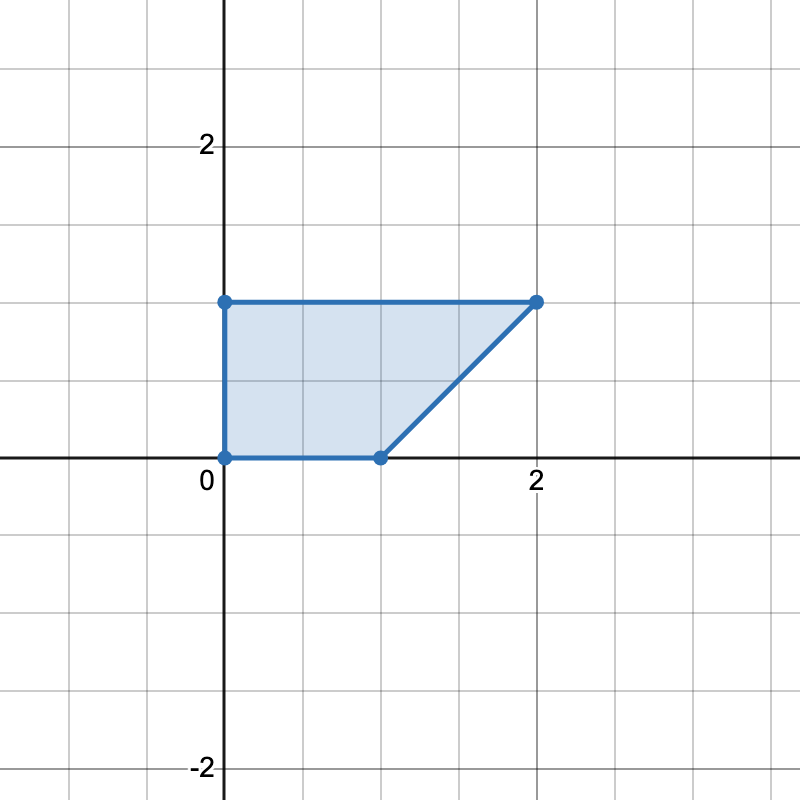
+**Input:** points = [[0,0],[1,0],[0,1],[2,1]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+There is only one horizontal trapezoid that can be formed.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 4 <= points.length <= 105
+* –108 <= xi, yi <= 108
+* All points are pairwise distinct.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3624_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_ii/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3624_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_ii/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..aa6b25e77
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3624_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_ii/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3624_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_ii;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Segment_Tree #Weekly_Contest_459
+// #2025_07_22_Time_27_ms_(96.44%)_Space_125.92_MB_(24.76%)
+
+import java.util.ArrayList;
+
+public class Solution {
+ private static final int[] DEPTH_TABLE = new int[65];
+
+ static {
+ DEPTH_TABLE[1] = 0;
+ for (int i = 2; i <= 64; ++i) {
+ DEPTH_TABLE[i] = 1 + DEPTH_TABLE[Integer.bitCount(i)];
+ }
+ }
+
+ private int computeDepth(long number) {
+ if (number == 1) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ return 1 + DEPTH_TABLE[Long.bitCount(number)];
+ }
+
+ public int[] popcountDepth(long[] nums, long[][] queries) {
+ int len = nums.length;
+ int maxDepth = 6;
+ FenwickTree[] trees = new FenwickTree[maxDepth];
+ for (int d = 0; d < maxDepth; ++d) {
+ trees[d] = new FenwickTree();
+ trees[d].build(len);
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
+ int depth = computeDepth(nums[i]);
+ if (depth < maxDepth) {
+ trees[depth].update(i + 1, 1);
+ }
+ }
+ ArrayList ansList = new ArrayList<>();
+ for (long[] query : queries) {
+ int type = (int) query[0];
+ if (type == 1) {
+ int left = (int) query[1];
+ int right = (int) query[2];
+ int depth = (int) query[3];
+ if (depth >= 0 && depth < maxDepth) {
+ ansList.add(trees[depth].queryRange(left + 1, right + 1));
+ } else {
+ ansList.add(0);
+ }
+ } else if (type == 2) {
+ int index = (int) query[1];
+ long newVal = query[2];
+ int oldDepth = computeDepth(nums[index]);
+ if (oldDepth < maxDepth) {
+ trees[oldDepth].update(index + 1, -1);
+ }
+ nums[index] = newVal;
+ int newDepth = computeDepth(newVal);
+ if (newDepth < maxDepth) {
+ trees[newDepth].update(index + 1, 1);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ int[] ansArray = new int[ansList.size()];
+ for (int i = 0; i < ansList.size(); i++) {
+ ansArray[i] = ansList.get(i);
+ }
+ return ansArray;
+ }
+
+ private static class FenwickTree {
+ private int[] tree;
+ private int size;
+
+ public FenwickTree() {
+ this.size = 0;
+ }
+
+ public void build(int n) {
+ this.size = n;
+ this.tree = new int[size + 1];
+ }
+
+ public void update(int index, int value) {
+ while (index <= size) {
+ tree[index] += value;
+ index += index & (-index);
+ }
+ }
+
+ public int query(int index) {
+ int result = 0;
+ while (index > 0) {
+ result += tree[index];
+ index -= index & (-index);
+ }
+ return result;
+ }
+
+ public int queryRange(int left, int right) {
+ if (left > right) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ return query(right) - query(left - 1);
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3624_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_ii/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3624_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..50904c084
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3624_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+3624\. Number of Integers With Popcount-Depth Equal to K II
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an integer array `nums`.
+
+For any positive integer `x`, define the following sequence:
+
+* p0 = x
+* pi+1 = popcount(pi) for all `i >= 0`, where `popcount(y)` is the number of set bits (1's) in the binary representation of `y`.
+
+This sequence will eventually reach the value 1.
+
+The **popcount-depth** of `x` is defined as the **smallest** integer `d >= 0` such that pd = 1.
+
+For example, if `x = 7` (binary representation `"111"`). Then, the sequence is: `7 → 3 → 2 → 1`, so the popcount-depth of 7 is 3.
+
+You are also given a 2D integer array `queries`, where each `queries[i]` is either:
+
+* `[1, l, r, k]` - **Determine** the number of indices `j` such that `l <= j <= r` and the **popcount-depth** of `nums[j]` is equal to `k`.
+* `[2, idx, val]` - **Update** `nums[idx]` to `val`.
+
+Return an integer array `answer`, where `answer[i]` is the number of indices for the ith query of type `[1, l, r, k]`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,4], queries = [[1,0,1,1],[2,1,1],[1,0,1,0]]
+
+**Output:** [2,1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+| `i` | `queries[i]` | `nums` | binary(`nums`) | popcount-
depth | `[l, r]` | `k` | Valid
`nums[j]` | updated
`nums` | Answer |
+|-----|--------------|----------|----------------|---------------------|----------|-----|---------------------|--------------------|---------|
+| 0 | [1,0,1,1] | [2,4] | [10, 100] | [1, 1] | [0, 1] | 1 | [0, 1] | — | 2 |
+| 1 | [2,1,1] | [2,4] | [10, 100] | [1, 1] | — | — | — | [2,1] | — |
+| 2 | [1,0,1,0] | [2,1] | [10, 1] | [1, 0] | [0, 1] | 0 | [1] | — | 1 |
+
+Thus, the final `answer` is `[2, 1]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,5,6], queries = [[1,0,2,2],[2,1,4],[1,1,2,1],[1,0,1,0]]
+
+**Output:** [3,1,0]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+| `i` | `queries[i]` | `nums` | binary(`nums`) | popcount-
depth | `[l, r]` | `k` | Valid
`nums[j]` | updated
`nums` | Answer |
+|-----|----------------|----------------|-----------------------|---------------------|----------|-----|---------------------|--------------------|---------|
+| 0 | [1,0,2,2] | [3, 5, 6] | [11, 101, 110] | [2, 2, 2] | [0, 2] | 2 | [0, 1, 2] | — | 3 |
+| 1 | [2,1,4] | [3, 5, 6] | [11, 101, 110] | [2, 2, 2] | — | — | — | [3, 4, 6] | — |
+| 2 | [1,1,2,1] | [3, 4, 6] | [11, 100, 110] | [2, 1, 2] | [1, 2] | 1 | [1] | — | 1 |
+| 3 | [1,0,1,0] | [3, 4, 6] | [11, 100, 110] | [2, 1, 2] | [0, 1] | 0 | [] | — | 0 |
+
+Thus, the final `answer` is `[3, 1, 0]`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2], queries = [[1,0,1,1],[2,0,3],[1,0,0,1],[1,0,0,2]]
+
+**Output:** [1,0,1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+| `i` | `queries[i]` | `nums` | binary(`nums`) | popcount-
depth | `[l, r]` | `k` | Valid
`nums[j]` | updated
`nums` | Answer |
+|-----|----------------|------------|----------------|---------------------|----------|-----|--------------------|--------------------|---------|
+| 0 | [1,0,1,1] | [1, 2] | [1, 10] | [0, 1] | [0, 1] | 1 | [1] | — | 1 |
+| 1 | [2,0,3] | [1, 2] | [1, 10] | [0, 1] | — | — | — | [3, 2] | |
+| 2 | [1,0,0,1] | [3, 2] | [11, 10] | [2, 1] | [0, 0] | 1 | [] | — | 0 |
+| 3 | [1,0,0,2] | [3, 2] | [11, 10] | [2, 1] | [0, 0] | 2 | [0] | — | 1 |
+
+Thus, the final `answer` is `[1, 0, 1]`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n == nums.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 1015
+* 1 <= queries.length <= 105
+* `queries[i].length == 3` or `4`
+ * `queries[i] == [1, l, r, k]` or,
+ * `queries[i] == [2, idx, val]`
+ * `0 <= l <= r <= n - 1`
+ * `0 <= k <= 5`
+ * `0 <= idx <= n - 1`
+ * 1 <= val <= 1015
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3625_count_number_of_trapezoids_ii/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3625_count_number_of_trapezoids_ii/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1fb61b968
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3625_count_number_of_trapezoids_ii/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3625_count_number_of_trapezoids_ii;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Hash_Table #Math #Geometry #Weekly_Contest_459
+// #2025_07_22_Time_347_ms_(99.10%)_Space_131.20_MB_(46.85%)
+
+import java.util.HashMap;
+import java.util.Map;
+
+public class Solution {
+ private static class Slope {
+ int dx;
+ int dy;
+
+ Slope(int dx, int dy) {
+ this.dx = dx;
+ this.dy = dy;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public boolean equals(Object o) {
+ if (this == o) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ if (!(o instanceof Slope)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ Slope s = (Slope) o;
+ return dx == s.dx && dy == s.dy;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public int hashCode() {
+ return dx * 1000003 ^ dy;
+ }
+ }
+
+ private static class Pair {
+ int a;
+ int b;
+
+ Pair(int a, int b) {
+ this.a = a;
+ this.b = b;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public boolean equals(Object o) {
+ if (this == o) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ if (!(o instanceof Pair)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ Pair p = (Pair) o;
+ return a == p.a && b == p.b;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public int hashCode() {
+ return a * 1000003 ^ b;
+ }
+ }
+
+ public int countTrapezoids(int[][] points) {
+ int n = points.length;
+ Map> slopeLines = new HashMap<>();
+ Map> midpointSlopes = new HashMap<>();
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ int x1 = points[i][0];
+ int y1 = points[i][1];
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
+ int x2 = points[j][0];
+ int y2 = points[j][1];
+ int dx = x2 - x1;
+ int dy = y2 - y1;
+ int g = gcd(Math.abs(dx), Math.abs(dy));
+ dx /= g;
+ dy /= g;
+ if (dx < 0 || (dx == 0 && dy < 0)) {
+ dx = -dx;
+ dy = -dy;
+ }
+ int nx = -dy;
+ int ny = dx;
+ long lineId = (long) nx * x1 + (long) ny * y1;
+ Slope slopeKey = new Slope(dx, dy);
+ slopeLines
+ .computeIfAbsent(slopeKey, k -> new HashMap<>())
+ .merge(lineId, 1, Integer::sum);
+ int mx = x1 + x2;
+ int my = y1 + y2;
+ Pair mid = new Pair(mx, my);
+ midpointSlopes
+ .computeIfAbsent(mid, k -> new HashMap<>())
+ .merge(slopeKey, 1, Integer::sum);
+ }
+ }
+ long trapezoidsRaw = 0;
+ for (Map lines : slopeLines.values()) {
+ if (lines.size() < 2) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ long s = 0;
+ long s2 = 0;
+ for (Integer line : lines.values()) {
+ s += line;
+ s2 += (long) line * line;
+ }
+ trapezoidsRaw += (s * s - s2) / 2;
+ }
+ long parallelograms = 0;
+ for (Map mp : midpointSlopes.values()) {
+ if (mp.size() < 2) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ long s = 0;
+ long s2 = 0;
+ for (Integer num : mp.values()) {
+ s += num;
+ s2 += (long) num * num;
+ }
+ parallelograms += (s * s - s2) / 2;
+ }
+ long res = trapezoidsRaw - parallelograms;
+ return res > Integer.MAX_VALUE ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : (int) res;
+ }
+
+ private int gcd(int a, int b) {
+ while (b != 0) {
+ int t = a % b;
+ a = b;
+ b = t;
+ }
+ return a == 0 ? 1 : a;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3625_count_number_of_trapezoids_ii/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3625_count_number_of_trapezoids_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..bda582e70
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3601_3700/s3625_count_number_of_trapezoids_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+3625\. Count Number of Trapezoids II
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a 2D integer array `points` where points[i] = [xi, yi] represents the coordinates of the ith point on the Cartesian plane.
+
+Return _the number of unique_ _trapezoids_ that can be formed by choosing any four distinct points from `points`.
+
+A **trapezoid** is a convex quadrilateral with **at least one pair** of parallel sides. Two lines are parallel if and only if they have the same slope.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** points = [[-3,2],[3,0],[2,3],[3,2],[2,-3]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
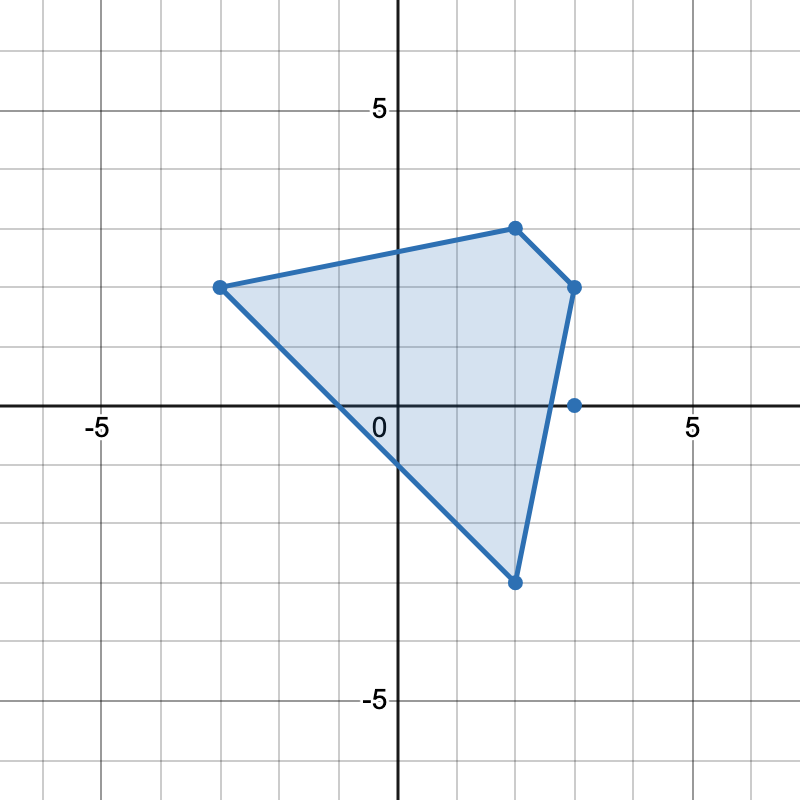
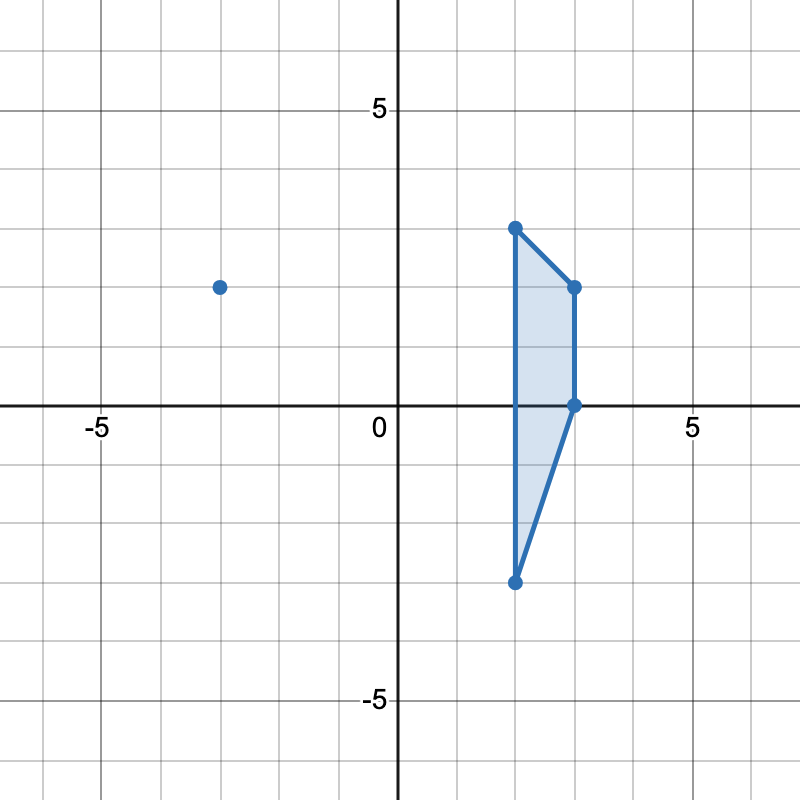
+ 
+
+There are two distinct ways to pick four points that form a trapezoid:
+
+* The points `[-3,2], [2,3], [3,2], [2,-3]` form one trapezoid.
+* The points `[2,3], [3,2], [3,0], [2,-3]` form another trapezoid.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** points = [[0,0],[1,0],[0,1],[2,1]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+There is only one trapezoid which can be formed.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `4 <= points.length <= 500`
+* –1000 <= xi, yi <= 1000
+* All points are pairwise distinct.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3618_split_array_by_prime_indices/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3618_split_array_by_prime_indices/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b7d9b890f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3618_split_array_by_prime_indices/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3618_split_array_by_prime_indices;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void splitArray() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().splitArray(new int[] {2, 3, 4}), equalTo(1L));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void splitArray2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().splitArray(new int[] {-1, 5, 7, 0}), equalTo(3L));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void splitArray3() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .splitArray(
+ new int[] {
+ -54818575,
+ 801071518,
+ 745054848,
+ -415289833,
+ 161564441,
+ 706292027,
+ 306478283,
+ 943480367,
+ 222076810,
+ 992619933
+ }),
+ equalTo(449455001L));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3619_count_islands_with_total_value_divisible_by_k/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3619_count_islands_with_total_value_divisible_by_k/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..40c0caaff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3619_count_islands_with_total_value_divisible_by_k/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3619_count_islands_with_total_value_divisible_by_k;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void countIslands() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .countIslands(
+ new int[][] {
+ {0, 2, 1, 0, 0},
+ {0, 5, 0, 0, 5},
+ {0, 0, 1, 0, 0},
+ {0, 1, 4, 7, 0},
+ {0, 2, 0, 0, 8}
+ },
+ 5),
+ equalTo(2));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void countIslands2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .countIslands(new int[][] {{3, 0, 3, 0}, {0, 3, 0, 3}, {3, 0, 3, 0}}, 3),
+ equalTo(6));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3620_network_recovery_pathways/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3620_network_recovery_pathways/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..42327109b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3620_network_recovery_pathways/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3620_network_recovery_pathways;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void findMaxPathScore() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .findMaxPathScore(
+ new int[][] {{0, 1, 5}, {1, 3, 10}, {0, 2, 3}, {2, 3, 4}},
+ new boolean[] {true, true, true, true},
+ 10L),
+ equalTo(3));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void findMaxPathScore2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .findMaxPathScore(
+ new int[][] {
+ {0, 1, 7}, {1, 4, 5}, {0, 2, 6}, {2, 3, 6}, {3, 4, 2}, {2, 4, 6}
+ },
+ new boolean[] {true, true, true, false, true},
+ 12L),
+ equalTo(6));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3621_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_i/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3621_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_i/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..417af8b56
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3621_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_i/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3621_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_i;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void popcountDepth() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().popcountDepth(4L, 1), equalTo(2L));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void popcountDepth2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().popcountDepth(7L, 2), equalTo(3L));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3622_check_divisibility_by_digit_sum_and_product/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3622_check_divisibility_by_digit_sum_and_product/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2deacc56e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3622_check_divisibility_by_digit_sum_and_product/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3622_check_divisibility_by_digit_sum_and_product;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void checkDivisibility() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().checkDivisibility(99), equalTo(true));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void checkDivisibility2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().checkDivisibility(23), equalTo(false));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3623_count_number_of_trapezoids_i/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3623_count_number_of_trapezoids_i/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..7543d19b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3623_count_number_of_trapezoids_i/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3623_count_number_of_trapezoids_i;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void countTrapezoids() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .countTrapezoids(new int[][] {{1, 0}, {2, 0}, {3, 0}, {2, 2}, {3, 2}}),
+ equalTo(3));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void countTrapezoids2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().countTrapezoids(new int[][] {{0, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {2, 1}}),
+ equalTo(1));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3624_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_ii/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3624_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_ii/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..50226360b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3624_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_ii/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3624_number_of_integers_with_popcount_depth_equal_to_k_ii;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void popcountDepth() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .popcountDepth(
+ new long[] {2, 4},
+ new long[][] {{1, 0, 1, 1}, {2, 1, 1}, {1, 0, 1, 0}}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {2, 1}));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void popcountDepth2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .popcountDepth(
+ new long[] {3, 5, 6},
+ new long[][] {{1, 0, 2, 2}, {2, 1, 4}, {1, 1, 2, 1}, {1, 0, 1, 0}}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {3, 1, 0}));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void popcountDepth3() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .popcountDepth(
+ new long[] {1, 2},
+ new long[][] {{1, 0, 1, 1}, {2, 0, 3}, {1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 0, 0, 2}}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {1, 0, 1}));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3625_count_number_of_trapezoids_ii/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3625_count_number_of_trapezoids_ii/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0dafdbff6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3601_3700/s3625_count_number_of_trapezoids_ii/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+package g3601_3700.s3625_count_number_of_trapezoids_ii;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void countTrapezoids() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .countTrapezoids(new int[][] {{-3, 2}, {3, 0}, {2, 3}, {3, 2}, {2, -3}}),
+ equalTo(2));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void countTrapezoids2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().countTrapezoids(new int[][] {{0, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {2, 1}}),
+ equalTo(1));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void countTrapezoids3() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .countTrapezoids(
+ new int[][] {
+ {71, -89},
+ {-75, -89},
+ {-9, 11},
+ {-24, -89},
+ {-51, -89},
+ {-77, -89},
+ {42, 11}
+ }),
+ equalTo(10));
+ }
+}