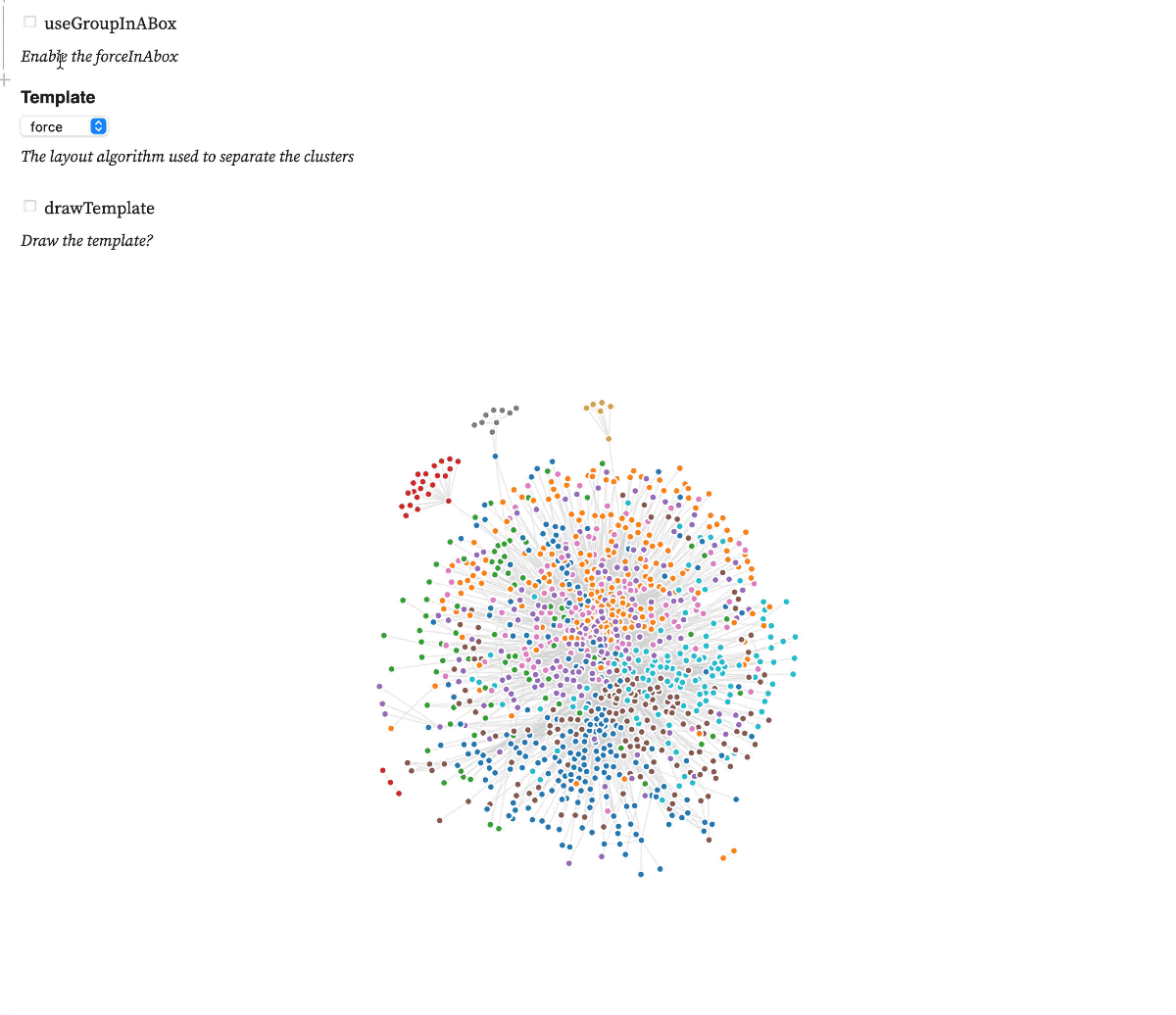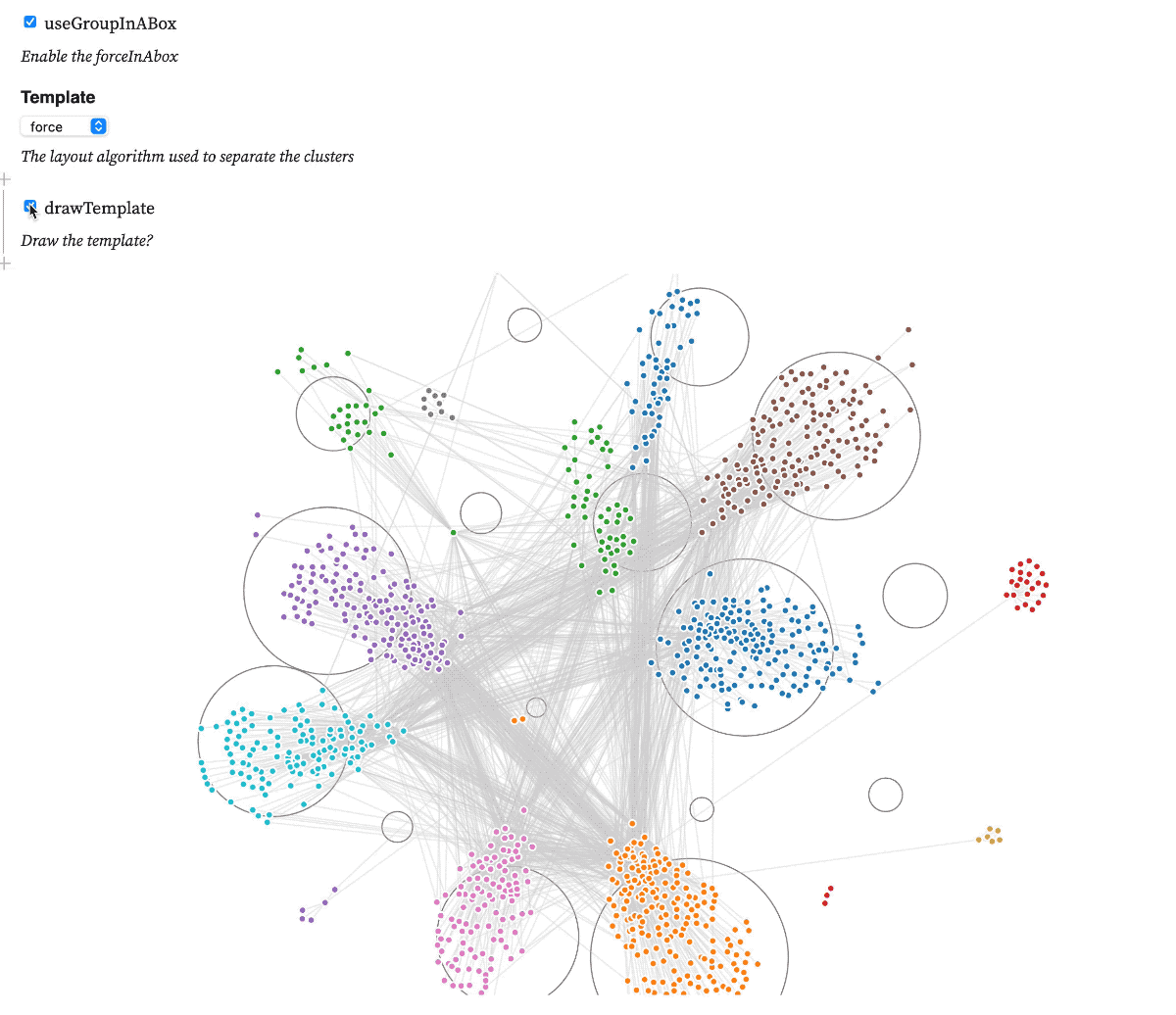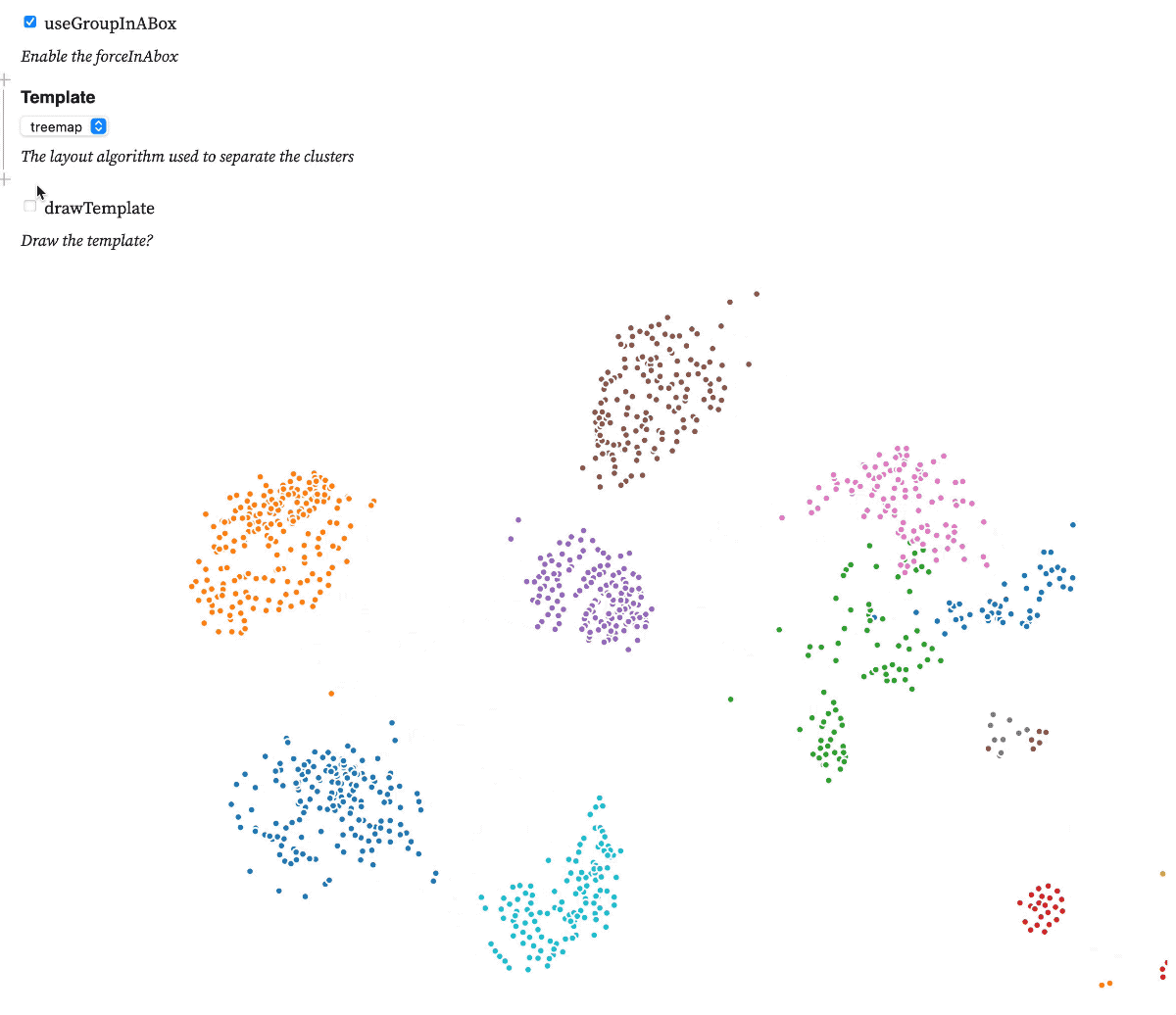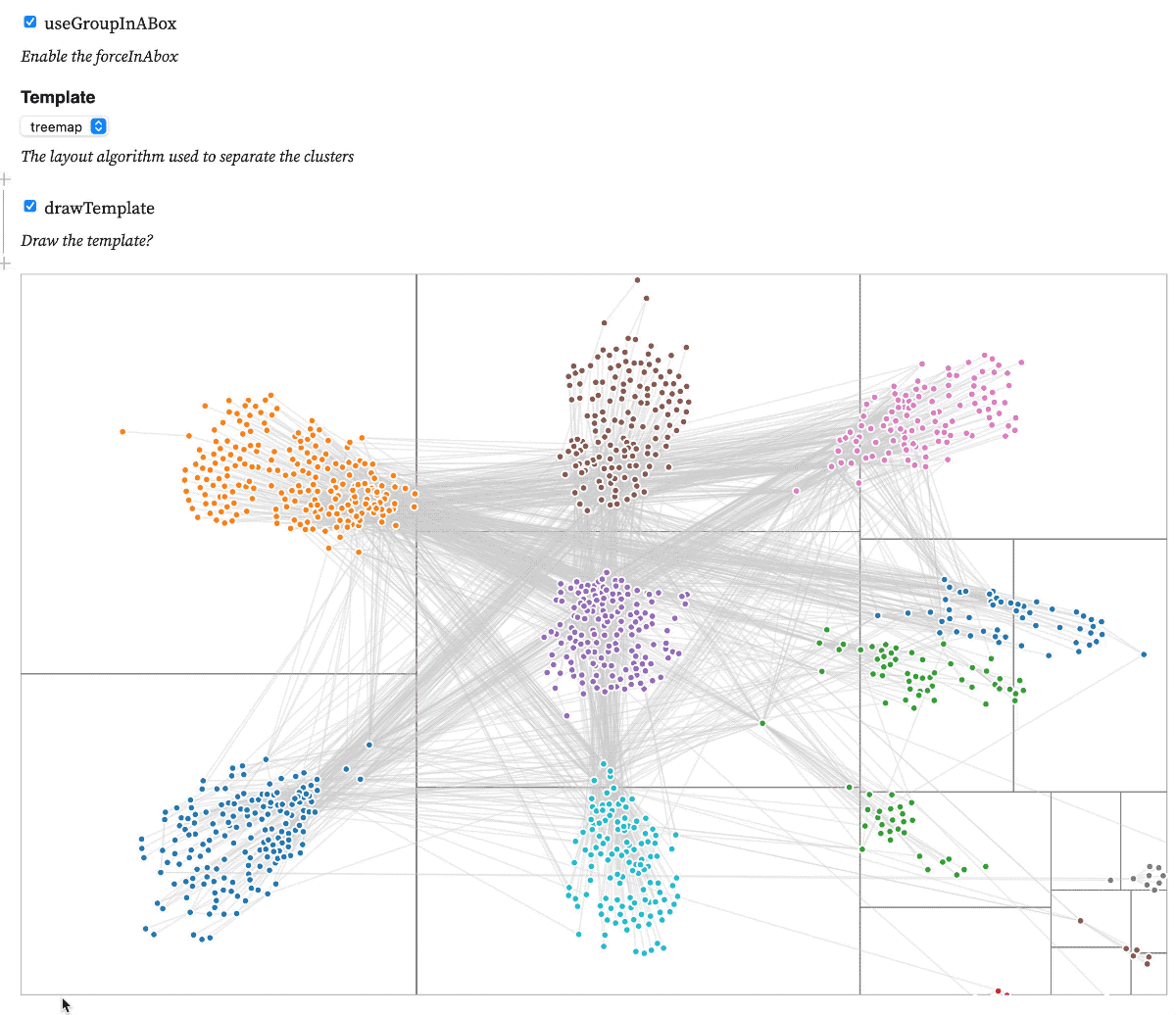
Test forceInABox on this observableNotebook
A d3.js v6 force that implements the Group-in-a-box layout algorithm to distribute nodes in a network according to their clusters. The algorithm uses a treemap or a force diagram to compute focis that are later used to distribute each cluster into it's own box.
To use it just add the forceInABox as another force in your simulation and make sure your other forces don't overpower it.
a note on input data format: forceInABox expects a graph object, with a links array that contains link objects with source and target properties. the values of the source and target properties should refer to the index value of the source or target node. example of this node-index convention
<!-- Include d3.v6 or forceSimulation -->
<script
type="text/javascript"
src="https://unpkg.com/force-in-a-box/dist/forceInABox.js"
></script>// Create the simulation with a small forceX and Y towards the center
let simulation = d3
.forceSimulation()
.force("charge", d3.forceManyBody())
.force("x", d3.forceX(width / 2).strength(0.05))
.force("y", d3.forceY(height / 2).strength(0.05));
// Instantiate the forceInABox force
let groupingForce = forceInABox()
.strength(0.1) // Strength to foci
.template(template) // Either treemap or force
.groupBy("group") // Node attribute to group
.links(graph.links) // The graph links. Must be called after setting the grouping attribute
.size([width, height]); // Size of the chart
// Add your forceInABox to the simulation
simulation.nodes(graph.nodes).force("group", groupingForce).force(
"link",
d3.forceLink(graph.links).distance(50).strength(groupingForce.getLinkStrength) // default link force will try to join nodes in the same group stronger than if they are in different groups
);Here is a forceInABox demo