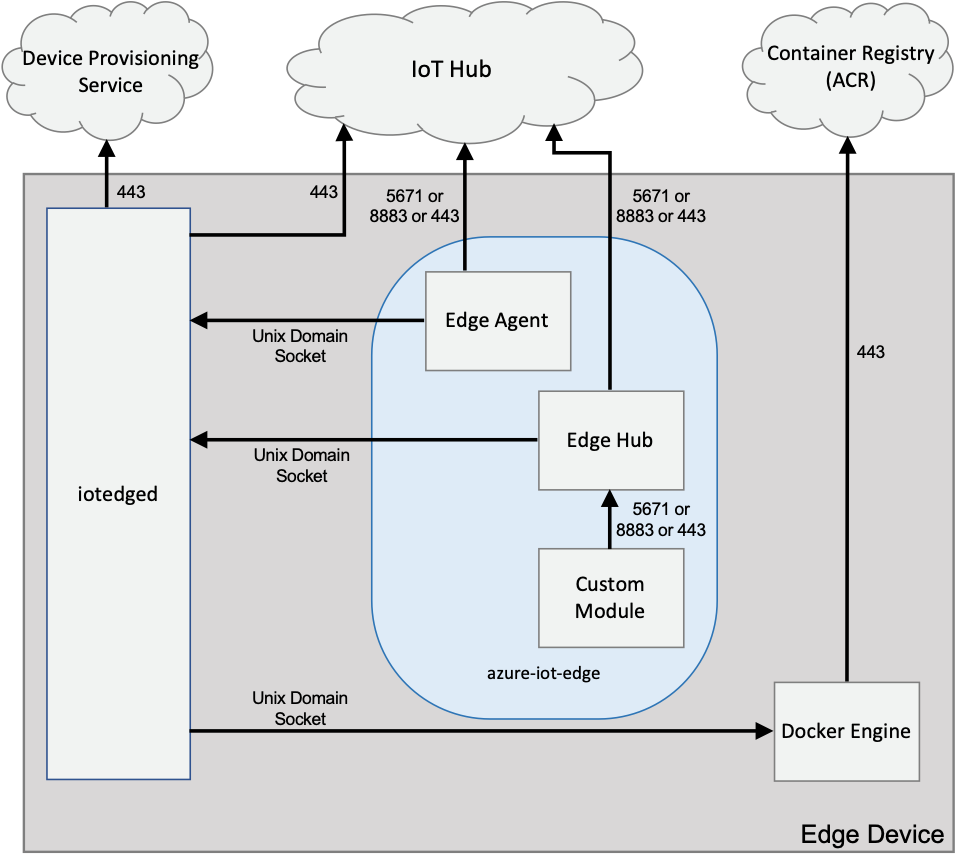
IoT Edge uses the networking capabilities of the Moby runtime to connect to IoT Hub and provide connectivity between modules. In a basic IoT Edge setup, the default configuration should be sufficient. However, if there are additional requirements for firewalls or network topology, it is helpful to understand IoT Edge's network setup and dependencies.
By default, IoT Edge places modules on a Docker network rather than the host network. This allows an additional form of isolation between the host network and application containers.
On Windows, all containers are started on the Moby nat network. The only requirement for IoT Edge is that this nat network has outbound internet connectivity to IoT Hub, a container registry, and optionally the Device Provisioning Service.
On Linux, aziot-edged creates a user-defined network named azure-iot-edge when it boots for the first time.
It also starts the Edge Agent and places it on the azure-iot-edge network.
All other modules (containers), including the Edge Hub, are started by the Edge Agent and placed on the azure-iot-edge network.
Edge Agent and Edge Hub require outbound internet connectivity to IoT Hub to function properly.
This means that a route from the azure-iot-edge subnet to the internet must exist and no firewall rules are set up to block traffic.
This network is configured via the moby_runtime section of the aziot-edged's config file (`/etc/aziot/edged/config.yaml):
moby_runtime:
uri: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
network: "azure-iot-edge"In version 1.0.9 and later additional container network configuration such as enabling IPv6 networking and providing the IPAM settings can be achieved by specifying the relevant configuration in the network settings.
moby_runtime:
uri: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
network:
name: "azure-iot-edge"
ipv6: true
ipam:
config:
- gateway: '172.18.0.1'
subnet: '172.18.0.0/16'
ip_range: '172.18.0.0/16'
- gateway: '2021:ffff:e0:3b1:1::1'
subnet: '2021:ffff:e0:3b1:1::/80'
ip_range: '2021:ffff:e0:3b1:1::/80'Any changes to other specific settings of this network must be made out of band, via the Moby Engine. Read the Docker networking guide for more information.
For more details on how to configure IoT edge to work on IPv6 networks, please refer to the IPv6 networking guide on Linux devices guide.
This network can be configured before starting IoT Edge, as the aziot-edged does a "get or create" operation on the network when starting.
Pre-configuring a network and updating the network in the config.yaml allows complete control over its settings.
IoT Edge does not require any inbound ports to be open for proper operation.
Depending on the scenario, IoT Edge does require several ports to be open for outbound connectivity. The following table describes these requirements:
| Protocol | Port | Inbound | Outbound |
|---|---|---|---|
| MQTT | 8883 | OPTIONAL (For gateway scenario) | OPEN* |
| MQTT+WS | 443 | OPTIONAL (For gateway scenario) | OPEN* |
| AMQP | 5671 | OPTIONAL (For gateway scenario) | OPEN* |
| AMQP+WS | 443 | OPTIONAL (For gateway scenario) | OPEN* |
| HTTPS | 443 | OPTIONAL (For gateway scenario) | OPEN |
In the gateway scenario, at least one of the Edge Hub's supported protocols must be open for downstream devices to connect. This means that one of 8883, 5671, and 443 must be open to inbound access. If no downstream devices are to connect to the edge device as a gateway, then all inbound connectivity can be disabled.
*The Edge Agent and Edge Hub require one of ports 5671, 8883, or 443 open for outbound connectivity to IoT Hub.
The aziot-edged requires outbound connectivity on port 443 to IoT Hub, and optionally to the Device Provisioning Service (DPS), if DPS is used for provisioning.
The Moby Engine requires outbound connectivity on port 443 to a container registry.
The protocol (and thus the port used) for the upstream communication to IoT Hub can be configured for the Edge Agent and Edge Hub by setting the UpstreamProtocol environment variable on both the Edge Agent and Edge Hub via a deployment.
The valid values are:
MqttAmqpMqttWsAmqpWs