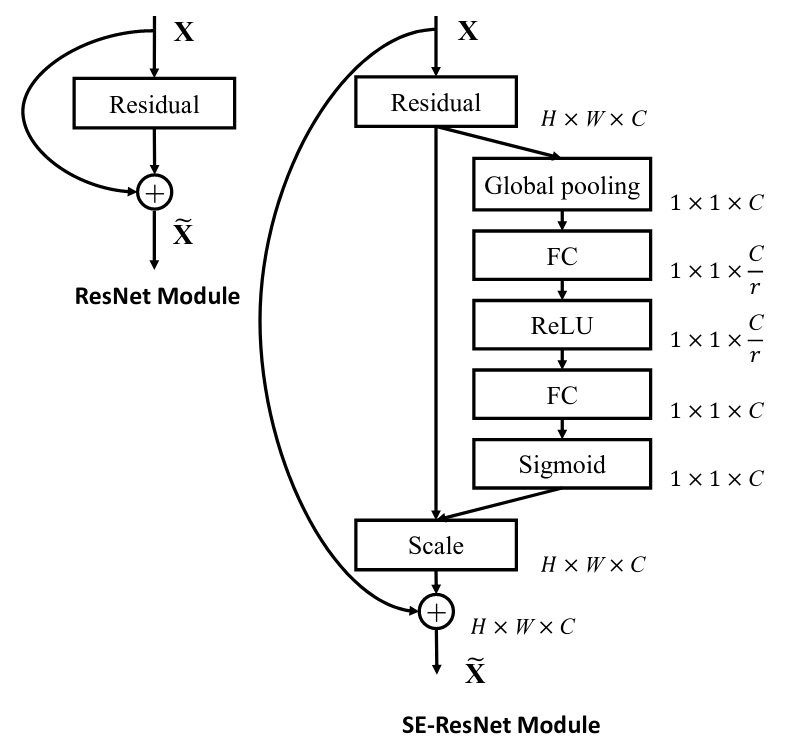
The central building block of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) is the convolution operator, which enables networks to construct informative features by fusing both spatial and channel-wise information within local receptive fields at each layer. A broad range of prior research has investigated the spatial component of this relationship, seeking to strengthen the representational power of a CNN by enhancing the quality of spatial encodings throughout its feature hierarchy. In this work, we focus instead on the channel relationship and propose a novel architectural unit, which we term the "Squeeze-and-Excitation" (SE) block, that adaptively recalibrates channel-wise feature responses by explicitly modelling interdependencies between channels. We show that these blocks can be stacked together to form SENet architectures that generalise extremely effectively across different datasets. We further demonstrate that SE blocks bring significant improvements in performance for existing state-of-the-art CNNs at slight additional computational cost. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks formed the foundation of our ILSVRC 2017 classification submission which won first place and reduced the top-5 error to 2.251%, surpassing the winning entry of 2016 by a relative improvement of ~25%.
| Model | Params(M) | Flops(G) | Top-1 (%) | Top-5 (%) | Config | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE-ResNet-50 | 28.09 | 4.13 | 77.74 | 93.84 | config | model | log |
| SE-ResNet-101 | 49.33 | 7.86 | 78.26 | 94.07 | config | model | log |
@inproceedings{hu2018squeeze,
title={Squeeze-and-excitation networks},
author={Hu, Jie and Shen, Li and Sun, Gang},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition},
pages={7132--7141},
year={2018}
}