| title | description | services | ms.subservice | ms.date | ms.topic | ms.custom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Azure Automation Start/Stop VMs during off-hours overview |
This article describes the Start/Stop VMs during off-hours feature, which starts or stops VMs on a schedule and proactively monitor them from Azure Monitor Logs. |
automation |
process-automation |
02/04/2020 |
conceptual |
devx-track-azurepowershell |
The Start/Stop VMs during off-hours feature start or stops enabled Azure VMs. It starts or stops machines on user-defined schedules, provides insights through Azure Monitor logs, and sends optional emails by using action groups. The feature can be enabled on both Azure Resource Manager and classic VMs for most scenarios.
This feature uses Start-AzVm cmdlet to start VMs. It uses Stop-AzVM for stopping VMs.
Note
While the runbooks have been updated to use the new Azure Az module cmdlets, they use the AzureRM prefix alias.
Note
Start/Stop VMs during off-hours has been updated to support the newest versions of the Azure modules that are available. The updated version of this feature, available in the Marketplace, doesn’t support AzureRM modules because we have migrated from AzureRM to Az modules.
The feature provides a decentralized low-cost automation option for users who want to optimize their VM costs. You can use the feature to:
- Schedule VMs to start and stop.
- Schedule VMs to start and stop in ascending order by using Azure Tags. This activity is not supported for classic VMs.
- Autostop VMs based on low CPU usage.
The following are limitations with the current feature:
- It manages VMs in any region, but can only be used in the same subscription as your Azure Automation account.
- It is available in Azure and Azure Government for any region that supports a Log Analytics workspace, an Azure Automation account, and alerts. Azure Government regions currently don't support email functionality.
Note
Before you install this version, we would like you to know about the next version, which is in preview right now. This new version (V2) offers all the same functionality as this one, but is designed to take advantage of newer technology in Azure. It adds some of the commonly requested features from customers, such as multi-subscription support from a single Start/Stop instance.
-
The runbooks for the Start/Stop VMs during off hours feature work with an Azure Run As account. The Run As account is the preferred authentication method because it uses certificate authentication instead of a password that might expire or change frequently.
-
An Azure Monitor Log Analytics workspace that stores the runbook job logs and job stream results in a workspace to query and analyze. The Automation account can be linked to a new or existing Log Analytics workspace, and both resources need to be in the same resource group.
We recommend that you use a separate Automation account for working with VMs enabled for the Start/Stop VMs during off-hours feature. Azure module versions are frequently upgraded, and their parameters might change. The feature isn't upgraded on the same cadence and it might not work with newer versions of the cmdlets that it uses. Before importing the updated modules into your production Automation account(s), we recommend you import them into a test Automation account to verify there aren't any compatibility issues.
You must have certain permissions to enable VMs for the Start/Stop VMs during off-hours feature. The permissions are different depending on whether the feature uses a pre-created Automation account and Log Analytics workspace or creates a new account and workspace.
You don't need to configure permissions if you're a Contributor on the subscription and a Global Administrator in your Azure Active Directory (AD) tenant. If you don't have these rights or need to configure a custom role, make sure that you have the permissions described below.
To enable VMs for the Start/Stop VMs during off-hours feature using an existing Automation account and Log Analytics workspace, you need the following permissions on the Resource Group scope. To learn more about roles, see Azure custom roles.
| Permission | Scope |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/read | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/variables/write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/schedules/write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/runbooks/write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/connections/write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/certificates/write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/modules/write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/modules/read | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.automation/automationAccounts/jobSchedules/write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/read | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.OperationsManagement/solutions/write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/* | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Insights/diagnosticSettings/write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Insights/ActionGroups/Write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Insights/ActionGroups/read | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/read | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Resources/deployments/* | Resource Group |
You can enable VMs for the Start/Stop VMs during off-hours feature using a new Automation account and Log Analytics workspace. In this case, you need the permissions defined in the preceding section as well as the permissions defined in this section. You also require the following roles:
- Co-Administrator on subscription. This role is required to create the Classic Run As account if you are going to manage classic VMs. Classic Run As accounts are no longer created by default.
- Membership in the Azure AD Application Developer role. For more information on configuring Run As Accounts, see Permissions to configure Run As accounts.
- Contributor on the subscription or the following permissions.
| Permission | Scope |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Authorization/Operations/read | Subscription |
| Microsoft.Authorization/permissions/read | Subscription |
| Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/read | Subscription |
| Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/write | Subscription |
| Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/delete | Subscription |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/connections/read | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/certificates/read | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/write | Resource Group |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write | Resource Group |
The Start/Stop VMs during off-hours feature include preconfigured runbooks, schedules, and integration with Azure Monitor logs. You can use these elements to tailor the startup and shutdown of your VMs to suit your business needs.
The following table lists the runbooks that the feature deploys to your Automation account. Do NOT make changes to the runbook code. Instead, write your own runbook for new functionality.
Important
Don't directly run any runbook with child appended to its name.
All parent runbooks include the WhatIf parameter. When set to True, the parameter supports detailing the exact behavior the runbook takes when run without the parameter and validates that the correct VMs are targeted. A runbook only performs its defined actions when the WhatIf parameter is set to False.
| Runbook | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AutoStop_CreateAlert_Child | VMObject AlertAction WebHookURI |
Called from the parent runbook. This runbook creates alerts on a per-resource basis for the Auto-Stop scenario. |
| AutoStop_CreateAlert_Parent | VMList WhatIf: True or False |
Creates or updates Azure alert rules on VMs in the targeted subscription or resource groups. VMList is a comma-separated list of VMs (with no whitespaces), for example, vm1,vm2,vm3.WhatIf enables validation of runbook logic without executing. |
| AutoStop_Disable | None | Disables Auto-Stop alerts and default schedule. |
| AutoStop_VM_Child | WebHookData | Called from the parent runbook. Alert rules call this runbook to stop a classic VM. |
| AutoStop_VM_Child_ARM | WebHookData | Called from the parent runbook. Alert rules call this runbook to stop a VM. |
| ScheduledStartStop_Base_Classic | CloudServiceName Action: Start or Stop VMList |
Performs action start or stop in classic VM group by Cloud Services. |
| ScheduledStartStop_Child | VMName Action: Start or Stop ResourceGroupName |
Called from the parent runbook. Executes a start or stop action for the scheduled stop. |
| ScheduledStartStop_Child_Classic | VMName Action: Start or Stop ResourceGroupName |
Called from the parent runbook. Executes a start or stop action for the scheduled stop for classic VMs. |
| ScheduledStartStop_Parent | Action: Start or Stop VMList WhatIf: True or False |
Starts or stops all VMs in the subscription. Edit the variables External_Start_ResourceGroupNames and External_Stop_ResourceGroupNames to only execute on these targeted resource groups. You can also exclude specific VMs by updating the External_ExcludeVMNames variable. |
| SequencedStartStop_Parent | Action: Start or Stop WhatIf: True or False VMList |
Creates tags named sequencestart and sequencestop on each VM for which you want to sequence start/stop activity. These tag names are case-sensitive. The value of the tag should be a list of positive integers, for example, 1,2,3, that corresponds to the order in which you want to start or stop. Note: VMs must be within resource groups defined in External_Start_ResourceGroupNames, External_Stop_ResourceGroupNames, and External_ExcludeVMNames variables. They must have the appropriate tags for actions to take effect. |
The following table lists the variables created in your Automation account. Only modify variables prefixed with External. Modifying variables prefixed with Internal causes undesirable effects.
Note
Limitations on VM name and resource group are largely a result of variable size. See Variable assets in Azure Automation.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| External_AutoStop_Condition | The conditional operator required for configuring the condition before triggering an alert. Acceptable values are GreaterThan, GreaterThanOrEqual, LessThan, and LessThanOrEqual. |
| External_AutoStop_Description | The alert to stop the VM if the CPU percentage exceeds the threshold. |
| External_AutoStop_Frequency | The evaluation frequency for rule. This parameter accepts input in timespan format. Possible values are from 5 minutes to 6 hours. |
| External_AutoStop_MetricName | The name of the performance metric for which the Azure Alert rule is to be configured. |
| External_AutoStop_Severity | Severity of the metric alert, which can range from 0 to 4. |
| External_AutoStop_Threshold | The threshold for the Azure Alert rule specified in the variable External_AutoStop_MetricName. Percentage values range from 1 to 100. |
| External_AutoStop_TimeAggregationOperator | The time aggregation operator applied to the selected window size to evaluate the condition. Acceptable values are Average, Minimum, Maximum, Total, and Last. |
| External_AutoStop_TimeWindow | The size of the window during which Azure analyzes selected metrics for triggering an alert. This parameter accepts input in timespan format. Possible values are from 5 minutes to 6 hours. |
| External_EnableClassicVMs | Value specifying if classic VMs are targeted by the feature. The default value is True. Set this variable to False for Azure Cloud Solution Provider (CSP) subscriptions. Classic VMs require a Classic Run As account. |
| External_ExcludeVMNames | Comma-separated list of VM names to exclude, limited to 140 VMs. If you add more than 140 VMs to the list, VMs specified for exclusion might be inadvertently started or stopped. |
| External_Start_ResourceGroupNames | Comma-separated list of one or more resource groups that are targeted for start actions. |
| External_Stop_ResourceGroupNames | Comma-separated list of one or more resource groups that are targeted for stop actions. |
| External_WaitTimeForVMRetrySeconds | The wait time in seconds for the actions to be performed on the VMs for the SequencedStartStop_Parent runbook. This variable allows the runbook to wait for child operations for a specified number of seconds before proceeding with the next action. The maximum wait time is 10800, or three hours. The default value is 2100 seconds. |
| Internal_AutomationAccountName | Specifies the name of the Automation account. |
| Internal_AutoSnooze_ARM_WebhookURI | The webhook URI called for the AutoStop scenario for VMs. |
| Internal_AutoSnooze_WebhookUri | The webhook URI called for the AutoStop scenario for classic VMs. |
| Internal_AzureSubscriptionId | The Azure subscription ID. |
| Internal_ResourceGroupName | The Automation account resource group name. |
Note
For the variable External_WaitTimeForVMRetryInSeconds, the default value has been updated from 600 to 2100.
Across all scenarios, the variables External_Start_ResourceGroupNames, External_Stop_ResourceGroupNames, and External_ExcludeVMNames are necessary for targeting VMs, except for the comma-separated VM lists for the AutoStop_CreateAlert_Parent, SequencedStartStop_Parent, and ScheduledStartStop_Parent runbooks. That is, your VMs must belong to target resource groups for start and stop actions to occur. The logic works similar to Azure Policy, in that you can target the subscription or resource group and have actions inherited by newly created VMs. This approach avoids having to maintain a separate schedule for every VM and manage starts and stops in scale.
The following table lists each of the default schedules created in your Automation account. You can modify them or create your own custom schedules. By default, all schedules are disabled except for the Scheduled_StartVM and Scheduled_StopVM schedules.
Don't enable all schedules, because doing so might create overlapping schedule actions. It's best to determine which optimizations you want to do and modify them accordingly. See the example scenarios in the overview section for further explanation.
| Schedule name | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Schedule_AutoStop_CreateAlert_Parent | Every 8 hours | Runs the AutoStop_CreateAlert_Parent runbook every 8 hours, which in turn stops the VM-based values in External_Start_ResourceGroupNames, External_Stop_ResourceGroupNames, and External_ExcludeVMNames variables. Alternatively, you can specify a comma-separated list of VMs by using the VMList parameter. |
| Scheduled_StopVM | User-defined, daily | Runs the ScheduledStopStart_Parent runbook with a parameter of Stop every day at the specified time. Automatically stops all VMs that meet the rules defined by variable assets. Enable the related schedule Scheduled-StartVM. |
| Scheduled_StartVM | User-defined, daily | Runs the ScheduledStopStart_Parent runbook with a parameter value of Start every day at the specified time. Automatically starts all VMs that meet the rules defined by variable assets. Enable the related schedule Scheduled-StopVM. |
| Sequenced-StopVM | 1:00 AM (UTC), every Friday | Runs the Sequenced_StopStop_Parent runbook with a parameter value of Stop every Friday at the specified time. Sequentially (ascending) stops all VMs with a tag of SequenceStop defined by the appropriate variables. For more information on tag values and asset variables, see Runbooks. Enable the related schedule, Sequenced-StartVM. |
| Sequenced-StartVM | 1:00 PM (UTC), every Monday | Runs the SequencedStopStart_Parent runbook with a parameter value of Start every Monday at the specified time. Sequentially (descending) starts all VMs with a tag of SequenceStart defined by the appropriate variables. For more information on tag values and variable assets, see Runbooks. Enable the related schedule, Sequenced-StopVM. |
If you are using the Start/Stop VMs during off-hours feature for classic VMs, Automation processes all your VMs sequentially per cloud service. VMs are still processed in parallel across different cloud services.
For use of the feature with classic VMs, you need a Classic Run As account, which is not created by default. For instructions on creating a Classic Run As account, see Create a Classic Run As account.
If you have more than 20 VMs per cloud service, here are some recommendations:
- Create multiple schedules with the parent runbook ScheduledStartStop_Parent and specifying 20 VMs per schedule.
- In the schedule properties, use the
VMListparameter to specify VM names as a comma-separated list (no whitespaces).
Otherwise, if the Automation job for this feature runs more than three hours, it's temporarily unloaded or stopped per the fair share limit.
Azure CSP subscriptions support only the Azure Resource Manager model. Non-Azure Resource Manager services are not available in the program. When the Start/Stop VMs during off-hours feature runs, you might receive errors since it has cmdlets to manage classic resources. To learn more about CSP, see Available services in CSP subscriptions. If you use a CSP subscription, you should set the External_EnableClassicVMs variable to False after deployment.
[!INCLUDE azure-monitor-log-analytics-rebrand]
Use one of the following mechanisms to access the enabled feature:
-
From your Automation account, select Start/Stop VM under Related Resources. On the Start/Stop VM page, select Manage the solution under Manage Start/Stop VM Solutions.
-
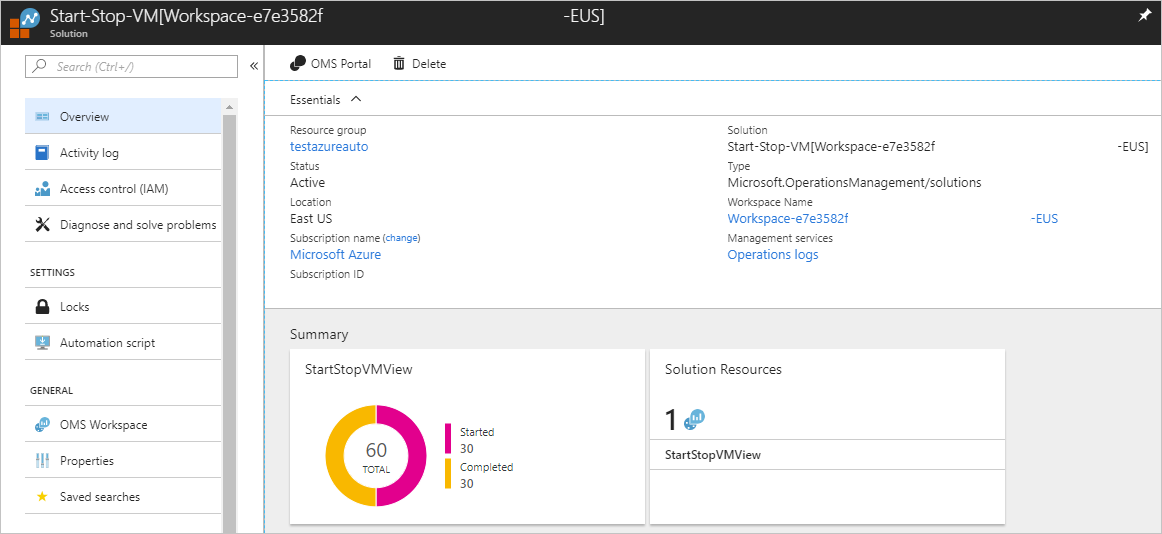
Navigate to the Log Analytics workspace linked to your Automation account. After after selecting the workspace, choose Solutions from the left pane. On the Solutions page, select Start-Stop-VM[workspace] from the list.
Selecting the feature displays the Start-Stop-VM[workspace] page. Here you can review important details, such as the information in the StartStopVM tile. As in your Log Analytics workspace, this tile displays a count and a graphical representation of the runbook jobs for the feature that have started and have finished successfully.
You can perform further analysis of the job records by clicking the donut tile. The dashboard shows job history and predefined log search queries. Switch to the log analytics advanced portal to search based on your search queries.
If you've deployed a previous version of Start/Stop VMs during off-hours, delete it from your account before deploying an updated release. Follow the steps to remove the feature and then follow the steps to enable it.
To enable the feature on VMs in your environment, see Enable Start/Stop VMs during off-hours.