We have three jigsaw puzzle solvers based on the following models which solve the left-right-adjacency-problem, namely
- AdjacencyClassifier_NoML
- FromScratch
- ResNetFT
To avoid introducing more terms, we call the jigsaw solvers by the names of the models they are based upon. We evaulate these solvers on 80 images from the CUB-200 test data set and compare their respective performances
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib_venn import venn3, venn3_unweighted
import matplotlib.ticker as plticker
import os
import sys
import pprint
import itertools
from collections import defaultdict
import copy
# generate random integer values
import random
from random import seed
from random import randint
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pylab import array
from random import sample
import math
import shelve
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader, IterableDataset
from torchvision import transforms, utils
from torch import nn, optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
#from torchvision.utils import make_grid
from Puzzle_generator import *
from Checking_adjacency_dataset import *
from FromScratch_CNN import *
from ResNetFT_Finetuning import *
from Training_template import *
from Adjacency_distance import *
from Search_template_gpu import *if torch.cuda.is_available():
GpuAvailable=True
my_device = torch.device("cuda:0")
print("Running on the GPU")
else:
GpuAvailable=False
my_device = torch.device("cpu")
print("Running on the CPU")
Running on the CPU
#Input global variables
my_test_dir = os.getenv("MY_TEST_DIR")
no_of_test_images = 80
my_puzzle_square_piece_dim = 75my_learning_rate = 0.001
my_momentum = 0.9model_names = ['AdjacencyClassifier_NoML', 'FromScratch', 'ResNetFT']
models = [AdjacencyClassifier_NoML()]
for i in [1,2]:
model_name=model_names[i]
model,loss_criterion,optimizer = make_model_lc_optimizer(model_name,
my_learning_rate,
my_momentum)
best_model_path=f"./best_model_for_{model_name}.pt"
model, optimizer, epochs_trained, min_val_loss = load_checkpoint_gpu(best_model_path,
model,
optimizer,
GpuAvailable)
model.eval()
models.append(model)
if 'GpuAvailable':
models[i].to(my_device)
Using FromScratch - Expect more number of parameters to learn!
bigunit.0.conv1.weight
bigunit.0.conv2.weight
bigunit.0.unit.2.weight
bigunit.0.unit.2.bias
bigunit.0.unit.5.weight
bigunit.0.unit.5.bias
bigunit.1.conv1.weight
bigunit.1.conv2.weight
bigunit.1.unit.2.weight
bigunit.1.unit.2.bias
bigunit.1.unit.5.weight
bigunit.1.unit.5.bias
bigunit.2.conv1.weight
bigunit.2.conv2.weight
bigunit.2.unit.2.weight
bigunit.2.unit.2.bias
bigunit.2.unit.5.weight
bigunit.2.unit.5.bias
bigunit.3.conv1.weight
bigunit.3.conv2.weight
bigunit.3.unit.2.weight
bigunit.3.unit.2.bias
bigunit.3.unit.5.weight
bigunit.3.unit.5.bias
bigunit.4.conv1.weight
bigunit.4.conv2.weight
bigunit.4.unit.2.weight
bigunit.4.unit.2.bias
bigunit.4.unit.5.weight
bigunit.4.unit.5.bias
bigunit.5.conv1.weight
bigunit.5.conv2.weight
bigunit.5.unit.2.weight
bigunit.5.unit.2.bias
bigunit.5.unit.5.weight
bigunit.5.unit.5.bias
fc1.weight
fc1.bias
bn1.weight
bn1.bias
fc2.weight
fc2.bias
bn2.weight
bn2.bias
No_of_parameters to learn : 44
Fine tuning ResNet - Expect more number of parameters to learn!
conv1.weight
bn1.weight
bn1.bias
layer1.0.conv1.weight
layer1.0.bn1.weight
layer1.0.bn1.bias
layer1.0.conv2.weight
layer1.0.bn2.weight
layer1.0.bn2.bias
layer1.1.conv1.weight
layer1.1.bn1.weight
layer1.1.bn1.bias
layer1.1.conv2.weight
layer1.1.bn2.weight
layer1.1.bn2.bias
layer2.0.conv1.weight
layer2.0.bn1.weight
layer2.0.bn1.bias
layer2.0.conv2.weight
layer2.0.bn2.weight
layer2.0.bn2.bias
layer2.0.downsample.0.weight
layer2.0.downsample.1.weight
layer2.0.downsample.1.bias
layer2.1.conv1.weight
layer2.1.bn1.weight
layer2.1.bn1.bias
layer2.1.conv2.weight
layer2.1.bn2.weight
layer2.1.bn2.bias
layer3.0.conv1.weight
layer3.0.bn1.weight
layer3.0.bn1.bias
layer3.0.conv2.weight
layer3.0.bn2.weight
layer3.0.bn2.bias
layer3.0.downsample.0.weight
layer3.0.downsample.1.weight
layer3.0.downsample.1.bias
layer3.1.conv1.weight
layer3.1.bn1.weight
layer3.1.bn1.bias
layer3.1.conv2.weight
layer3.1.bn2.weight
layer3.1.bn2.bias
layer4.0.conv1.weight
layer4.0.bn1.weight
layer4.0.bn1.bias
layer4.0.conv2.weight
layer4.0.bn2.weight
layer4.0.bn2.bias
layer4.0.downsample.0.weight
layer4.0.downsample.1.weight
layer4.0.downsample.1.bias
layer4.1.conv1.weight
layer4.1.bn1.weight
layer4.1.bn1.bias
layer4.1.conv2.weight
layer4.1.bn2.weight
layer4.1.bn2.bias
fc.weight
fc.bias
No_of_parameters to learn : 62
def calculate_example_metric(file_name, puzzle_square_piece_dim,model_name, model, puzzle_input,device, show_solving_progress=False,input_display=False):
if show_solving_progress:
print(f"Solving {file_name}...")
rows = puzzle_input[0]
cols = puzzle_input[1]
no_of_pieces = rows*cols
top_left_piece_new_label = puzzle_input[2]
top_left_piece_orientation = puzzle_input[3]
new_to_old_label_dict = puzzle_input[4]
shuffled_puzzle_pieces_np = puzzle_input[5]
board = solve_puzzle(rows, cols,top_left_piece_new_label,top_left_piece_orientation,
shuffled_puzzle_pieces_np, puzzle_square_piece_dim,model_name, model,device,show_solving_progress)
if show_solving_progress:
print("*****************")
print(f"Solved puzzle using {model_name} solver")
board.display(puzzle_square_piece_dim)
information_dict = board.information_dict
predicted_new_to_old_dict = board.predicted_new_to_old_dict
correct_position = 0
correct_position_and_rotation = 0
for k in new_to_old_label_dict:
if new_to_old_label_dict[k][:2] == predicted_new_to_old_dict[k][:2]:
correct_position += 1
if new_to_old_label_dict[k][2] == predicted_new_to_old_dict[k][2]:
correct_position_and_rotation += 1
if show_solving_progress:
print("*******************")
print(f"In correct position: {correct_position}")
print(f"In correct position and rotation: {correct_position_and_rotation}")
return(no_of_pieces, correct_position, correct_position_and_rotation)
import time
def run_solver(image_name,i,eval_df,count,row_number):
my_model_name = model_names[i]
my_model = models[i]
start_time = time.time()
my_input = get_puzzle_pieces(image_name,my_puzzle_square_piece_dim, display=False)
pieces,correct_pos,correct_pos_and_rotation = calculate_example_metric(image_name,my_puzzle_square_piece_dim,
my_model_name, my_model,my_input,my_device,
show_solving_progress=False,
input_display=False)
time_taken = round(time.time()-start_time,2)
results_dict = {"model" : my_model_name,
"image_name": image_name,
"image_index" : count,
"no_of_pieces": pieces,
"correct_pos": correct_pos,
"correct_pos_and_orientation": correct_pos_and_rotation,
"time_taken": time_taken}
eval_df.loc[row_number] = pd.Series(results_dict)
column_names = ["model","image_name", "image_index" , "no_of_pieces", "correct_pos", "correct_pos_and_orientation", "time_taken"]
eval_results_df = pd.DataFrame(columns = column_names, index = list(range(1,no_of_test_images +1)))count = 0
row_number = 0
done = False
for folder in sample(os.listdir(my_test_dir), len(os.listdir(my_test_dir))):
folder_path = os.path.join(my_test_dir,folder)
images_from_this_folder=0
for image_name in sample(os.listdir(folder_path), len(os.listdir(folder_path))):
count += 1
images_from_this_folder += 1
image_name = os.path.join(folder_path, image_name)
for i in range(1,4):
row_number += 1
run_solver(image_name,i,eval_results_df,count,row_number)
eval_results_df.to_csv('eval_results.csv')
print(f"Processed Image #{count} with model {model_names[i]}")
if count >= no_of_test_images:
done = True
break
if images_from_this_folder >= 2:
break
if done:
break
The evaluation was run on Google Colabs so as to use GPU services and the dataframe was stored as a csv file called eval_results_final.csv
#Read csv data and put it into a dataframe
eval_results_df= pd.read_csv('eval_results_final.csv')#Get dataframe columns
eval_results_df.columnsIndex(['Unnamed: 0', 'model', 'image_name', 'image_index', 'no_of_pieces',
'correct_pos', 'correct_pos_and_orientation', 'time_taken'],
dtype='object')
#Drop unnecessary column
del eval_results_df['Unnamed: 0']#Add a new column called solved (1 if the model solves the puzzle completely correctly, 0 otherwise)
eval_results_df['solved'] = eval_results_df.apply(lambda row: 1 if row.no_of_pieces == row.correct_pos_and_orientation else 0, axis=1)eval_results_df.head(6).dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| model | image_name | image_index | no_of_pieces | correct_pos | correct_pos_and_orientation | time_taken | solved | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | AdjacencyClassifier_NoML | CUB_200_test/172.Nashville_Warbler/Nashville_W... | 1 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 13.46 | 1 |
| 1 | FromScratch | CUB_200_test/172.Nashville_Warbler/Nashville_W... | 1 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 21.28 | 1 |
| 2 | ResNetFT | CUB_200_test/172.Nashville_Warbler/Nashville_W... | 1 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 25.64 | 1 |
| 3 | AdjacencyClassifier_NoML | CUB_200_test/172.Nashville_Warbler/Nashville_W... | 2 | 36 | 17 | 17 | 13.31 | 0 |
| 4 | FromScratch | CUB_200_test/172.Nashville_Warbler/Nashville_W... | 2 | 36 | 1 | 1 | 21.95 | 0 |
| 5 | ResNetFT | CUB_200_test/172.Nashville_Warbler/Nashville_W... | 2 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 23.83 | 1 |
#creating dataframes for individual models
model_names = ['AdjacencyClassifier_NoML', 'FromScratch', 'ResNetFT']
models_stats_dict= {}
for model_name in model_names:
models_stats_dict[model_name]=eval_results_df[eval_results_df.model==model_name].reset_index(drop=True)sizes_of_puzzles = list(eval_results_df.no_of_pieces.unique())puzzle_size_freq = eval_results_df['no_of_pieces'].value_counts()//3puzzle_size_freq = puzzle_size_freq.rename_axis('puzzle_sizes').reset_index(name='no_of_puzzles')puzzle_size_freq.dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| puzzle_sizes | no_of_puzzles | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 36 | 67 |
| 1 | 25 | 11 |
| 2 | 16 | 2 |
eval_stats_df = pd.DataFrame(columns=model_names, index=['avg_time_taken','percentage_solved'])#average time taken
avg_time_taken = {}
for model_name in model_names:
avg_time_taken[model_name] =models_stats_dict[model_name]["time_taken"].mean()
eval_stats_df.loc['avg_time_taken'] = pd.Series(avg_time_taken)#percentage solved
percentage_solved = {}
for model_name in model_names:
percentage_solved[model_name] = models_stats_dict[model_name]["solved"].sum()/no_of_test_images
eval_stats_df.loc['percentage_solved'] = pd.Series(percentage_solved)#average puzzle size
avg_puzzle_sizes = {}
for model_name in model_names:
avg_puzzle_sizes[model_name] =models_stats_dict[model_name]["no_of_pieces"].mean()
eval_stats_df.loc['avg_puzzle_sizes'] = pd.Series(avg_puzzle_sizes)eval_stats_df.dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| AdjacencyClassifier_NoML | FromScratch | ResNetFT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| avg_time_taken | 11.2126 | 18.9795 | 23.0482 |
| percentage_solved | 0.875 | 0.375 | 0.875 |
| avg_puzzle_sizes | 33.9875 | 33.9875 | 33.9875 |
#examples' solved statuses vs models
comparison_df = pd.DataFrame(columns=model_names, index=list(range(no_of_test_images)))
for model_name in model_names:
comparison_df[model_name]= models_stats_dict[model_name]["solved"]#comparing the symmetric difference of two models at a time
model_name_pairs = []
for i,j in [(0,1), (0,2), (1,2)]:
models_in_comparison = model_names[i]+"/"+model_names[j]
model_name_pairs.append(models_in_comparison)
comparison_df[models_in_comparison] = comparison_df.apply(lambda row: row[model_names[i]] ^ row[model_names[j]], axis=1)for model_name_pair in model_name_pairs:
first_model = model_name_pair.split("/")[0]
second_model = model_name_pair.split("/")[1]
a = eval_stats_df.loc['percentage_solved'][first_model]*no_of_test_images
b = eval_stats_df.loc['percentage_solved'][second_model]*no_of_test_images
#a+b-2x = comparison_df[model_name_pair].sum()
#solved_jointly = x
solved_jointly = int((a+b-comparison_df[model_name_pair].sum())/2)
solved_by_first_model_alone = int(a - solved_jointly)
solved_by_second_model_alone = int(b - solved_jointly)
unsolved_jointly = int(no_of_test_images - (a+b-solved_jointly))
print("")
print(f"Comparing {first_model} and {second_model}")
print("")
print(f"Solved jointly = {solved_jointly}")
print(f"Unsolved jointly = {unsolved_jointly}")
print(f"Solved by {first_model} alone = {solved_by_first_model_alone}")
print(f"Solved by {second_model} alone = {solved_by_second_model_alone}")
print("")
print("********************************")
Comparing AdjacencyClassifier_NoML and FromScratch
Solved jointly = 30
Unsolved jointly = 10
Solved by AdjacencyClassifier_NoML alone = 40
Solved by FromScratch alone = 0
********************************
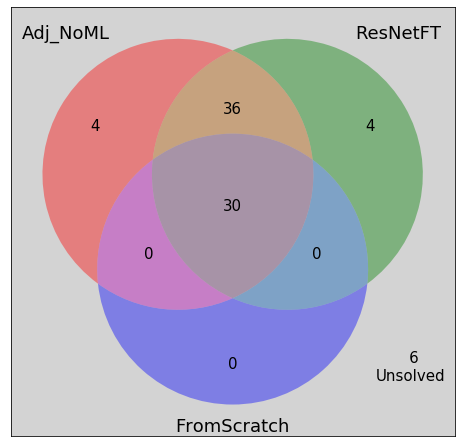
Comparing AdjacencyClassifier_NoML and ResNetFT
Solved jointly = 66
Unsolved jointly = 6
Solved by AdjacencyClassifier_NoML alone = 4
Solved by ResNetFT alone = 4
********************************
Comparing FromScratch and ResNetFT
Solved jointly = 30
Unsolved jointly = 10
Solved by FromScratch alone = 0
Solved by ResNetFT alone = 40
********************************
#Examples solved by all three models
comparison_df["solved_by_all_three"] = comparison_df.apply(lambda row: 1 if row[model_names[0]]==1 and row[model_names[1]] == 1 and row[model_names[2]]==1 else 0, axis=1)solved_by_all_three = comparison_df["solved_by_all_three"].sum()#Examples solved by at least one of the three models
comparison_df["solved_by_atleast_one"] = comparison_df.apply(lambda row: row[model_names[0]] + row[model_names[1]] + row[model_names[2]], axis=1)solved_by_atleast_one = len(comparison_df[comparison_df["solved_by_atleast_one"]>0])solved_by_none = len(comparison_df[comparison_df["solved_by_atleast_one"]<=0])print(f'Solved by all the three models = {solved_by_all_three}')
print(f'Solved by at least one model = {solved_by_atleast_one}')
print(f'Solved by none of the models = {solved_by_none}')Solved by all the three models = 30
Solved by at least one model = 74
Solved by none of the models = 6
unsolved_indices_dict = {}
unsolved_indices_dict["All"]= list(comparison_df[comparison_df["solved_by_atleast_one"]<=0].index)
for model_name in model_names:
unsolved_indices_dict[model_name] = list(models_stats_dict[model_name][models_stats_dict[model_name]["solved"]==0].index)unsolved_images_dict = {}
for key in unsolved_indices_dict:
unsolved_images_dict[key] = set()
for i in unsolved_indices_dict[key]:
unsolved_images_dict[key].add(models_stats_dict["AdjacencyClassifier_NoML"].loc[i]["image_name"])shelfFile = shelve.open('mydata')
shelfFile["unsolved_indices_dict"] = unsolved_indices_dict
shelfFile["unsolved_images_dict"] = unsolved_images_dict
shelfFile.close()There were 67 six-by-six puzzles, 11 five-by-five puzzles and 2 four-by-four puzzles in the evaluation set
puzzle_size_freq.dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| puzzle_sizes | no_of_puzzles | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 36 | 67 |
| 1 | 25 | 11 |
| 2 | 16 | 2 |
Both the AdjacencyClassifier_NoML and the ResNetFT solved 87.5 % of the puzzles completely correctly. FromScratch underperformed by solving only 37.5 % of the puzzles completely correctly.
eval_stats_df.dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| AdjacencyClassifier_NoML | FromScratch | ResNetFT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| avg_time_taken (sec) | 11.2126 | 18.9795 | 23.0482 |
| percentage_solved | 0.875 | 0.375 | 0.875 |
| avg_puzzle_sizes | 33.9875 | 33.9875 | 33.9875 |
fig = plt.figure()
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size':15})
v = venn3_unweighted(subsets = (4, 4, 36, 0,0,0,30), set_labels=('Adj_NoML', 'ResNetFT', 'FromScratch'))
plt.axis("on")
plt.text(0.45, -0.55, ' 6\nUnsolved')
plt.gca().set_facecolor('lightgray')
fig.tight_layout(pad=-5);The current evaluation classifies a puzzle as unsolved even if the models got a major chunk right but placed it incorrectly on the board. So we will further visually investigate what the models did on puzzles they did not solve completey correctly.