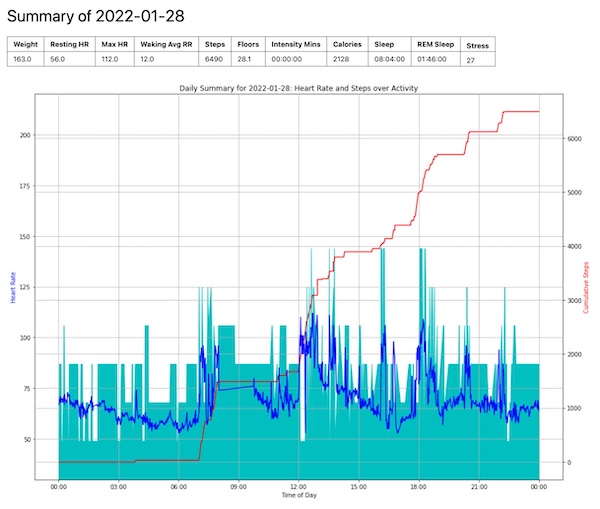
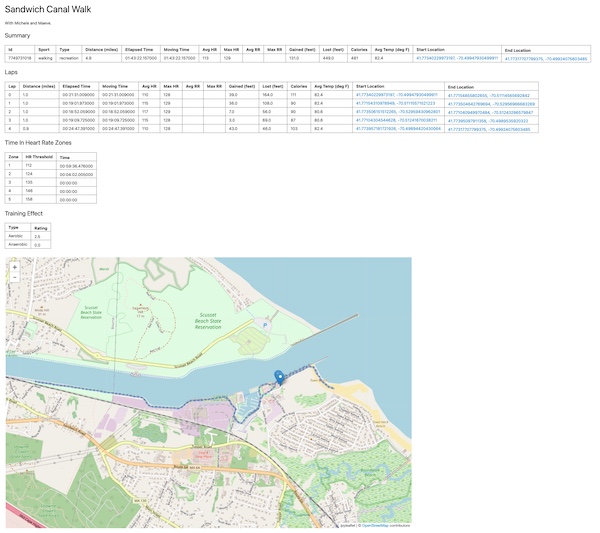
Python scripts for parsing health data into and manipulating data in a SQLite database. SQLite is a light weight database that doesn't require a server.
What they can do:
- Automatically download and import Garmin daily monitoring files (all day heart rate, activity, climb/descend, stress, and intensity minutes) from the user's Garmin Connect "Daily Summary" page.
- Extract sleep, weight, and resting heart rate data from Garmin Connect, store it as JSON files, and import it into the DB.
- Download and import activity files from Garmin Connect. A summary table for all activities and more detailed data for some activity types. Lap and record entries for activities.
- Summarizing data into a DB with tables containing daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly summaries.
- Graph your data from the commandline or with Jupyter notebooks.
- Retain downloaded JSON and FIT files so that the DB can be regenerated without connecting to or redownloading data from Garmin Connect.
- Export activities as TCX files.
Once you have your data in the DB, I recommend using a supplied Jupyter notebooks, third party Jupyter notebooks, and/or SQLite browser like SQLite Studio or DB Browser for SQLite for browsing and working with the data. The scripts create some default views in the DBs that make browsing the data easier.
GarminDb releases are hosted on PyPI. GarminDb requires Python 3.x. With Python installed, install the latest release with pip by running pip install garmindb in a terminal.
- Copy
GarminConnectConfig.json.exampleto~/.GarminDb/GarminConnectConfig.json, edit it, and add your Garmin Connect username and password and adjust the start dates to match the dats of your data in Garmin Connect. - Starting out: download all of your data and create your db by running
garmindb_cli.py --all --download --import --analyzein a terminal. - Incrementally update your db by downloading the latest data and importing it by running
garmindb_cli.py --all --download --import --analyze --latestin a terminal. - Ocassionally run
garmin_cli.py --backupto backup your DB files.
Update to the latest release with pip install --upgrade garmindb.
The scripts are automated with Make. Run the Make commands in a terminal window.
- Git clone GarminDB repo using the SSH clone method. The submodules require you to use SSH and not HTTPS. Get the command from the green button on the project home page.
- Run
make setupin the cloned tree to get the scripts ready to process data. - Copy
GarminConnectConfig.json.exampleto~/.GarminDb/GarminConnectConfig.json, edit it, and add your Garmin Connect username and password and adjust the start dates to match the dats of your data in Garmin Connect. - Run
make create_dbsonce to fetch and process for you data. - Keep all of your local data up to date by periodically running only one command:
make.
There is more help on using the program in the wiki.
Jupyter notebooks for analzing data from the database can be found in the 'Jupyter' directory in the source tree. Links to user submitted notebooks can be found in the wiki.
Plugins allow the user to expand the types of data that are processed and stored in the database. GarminDb already has a number of plugins for handling data from third-party Connect IQ apps and data fields. Read more about plugins here.
Find out who's using GarminDb on what platforms, OSes, and python versions here. If you're using GarminDB and your scenario isn't listed send me a message or file an issue with your success case.
- You may get a DB version exception after updating the code, this means that the DB schema was updated and you need to rebuild your DBs by running
garmindb_cli.py --rebuild_db. Your DBs will be regenerated from the previously downloaded data files. All of your data will not be redownloaded from Garmin. - The scripts were developed on MacOS. Information or patches on using these scripts on other platforms are welcome.
- When a database update finishes, a summary of the data in the DB will be saved to stats.txt. The output includes the date ranges included in the downloaded daily monitoring files and activities. It includes the number of records for daily monitoring, activities, sleep, resting heart rate, weight, etc. Use the summary information to determine if all of your data has been downloaded from Garmin Connect. If not, adjust the dates in GarminConnectConfig.json and runt he download again.
- In
GarminConnectConfig.jsonthe "steps" element of the "course_views" is list of course ids that per course database views will be generated for. The database view allows you to compare all activities from that course.
- If you have issues, file a bug here on the project. See the Issues tab at the top of the project page. Run
make bugreportorgarmindb_bug_report.pyand include bugreport.txt in your bug report. - Besides errors that appear on the screen, one of the first places to look for more information is the log files (garmin.log, graphs.log).
- If your having issues with a particular data files, please considering sharing so I can debug it and add support.
Please submit a pull request targeting the develop branch and add your self to the contributors file. Run make flake8 at the top level and fix all errors before submitting your pull request.