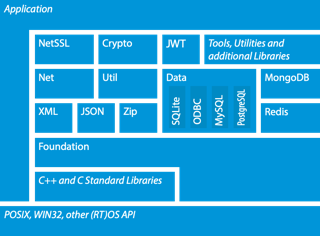
- A collection of C++ class libraries, conceptually similar to the Java Class Library or the .NET Framework.
- Focused on solutions to frequently-encountered practical problems.
- Focused on "internet-age" network-centric applications.
- Written in efficient, modern, 100% ANSI/ISO Standard C++.
- Based on and complementing the C++ Standard Library/STL.
- Highly portable and available on many different platforms, from embedded to server.
- Open Source, licensed under the Boost Software License.
To start using POCO, see the Guided Tour and Getting Started documents.
- CMake 3.5 or newer
- A C++17 compiler (Visual C++ 2017, GCC 8.0, Clang 5, or newer)
- OpenSSL headers and libraries (optional, but recommended)
- MySQL, PostgreSQL and ODBC client libraries (optional)
Most Unix/Linux systems already have OpenSSL preinstalled. If your system does not have OpenSSL, please get it from https://www.openssl.org or another source. You do not have to build OpenSSL yourself - a binary distribution is fine. For example, via Debian APT:
$ apt-get install openssl libssl-dev
On macOS, the easiest way to install OpenSSL is via Homebrew:
$ brew install openssl
The easiest way to install OpenSSL on Windows is to use a binary
(prebuild) release, for example the one from Shining Light
Productions that comes with a
Windows installer.
OpenSSL can also be installed via the vcpkg package manager.
On Windows, POCO can also use the native Windows TLS APIs (SChannel).
All dependencies can be installed with the following commands:
$ sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get -y install git g++ make cmake libssl-dev libmysqlclient-dev libpq-dev
$ sudo yum install -y git gcc-c++ make cmake3 openssl-devel mysql-devel postgresql-devel
$ brew install cmake openssl mysql-client libpq
CMake (version 3.5 or newer) is the recommended build system for building the POCO C++ Libraries.
$ git clone -b main https://github.com/pocoproject/poco.git
$ cd poco
$ mkdir cmake-build
$ cd cmake-build
$ cmake ..
$ cmake --build . --config Release
On macOS, it's necessary to tell CMake where to find the OpenSSL headers
and libraries by setting the OPENSSL_ROOT_DIR CMake variable.
For example, if OpenSSL has been installed with Homebrew,
the cmake invocation becomes:
$ cmake .. -DOPENSSL_ROOT_DIR=/opt/homebrew/opt/openssl@3
Similarly, the locations of other external libraries can be specified:
$ cmake .. -DOPENSSL_ROOT_DIR=/opt/homebrew/opt/openssl@3 -DMYSQL_ROOT_DIR=/opt/homebrew/opt/mysql-client -DPostgreSQL_ROOT_DIR=/opt/homebrew/opt/libpq
Other common ways of building with CMake (e.g., cmake-gui) will also work.
There are also a number of project-specific CMake variables that can be changed.
With a proper CMake toolchain file (specified via the CMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE CMake variable),
the POCO C++ Libraries can be cross-compiled for embedded Linux systems:
$ cmake .. -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=/path/to/mytoolchain.cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/path/to/target
The POCO C++ Libraries headers and libraries can be optionally be installed by building the install target.
$ sudo cmake --build . --target install
The default install location is /usr/local/ on Linux and macOS and
C:\Program Files (x64)\ on Windows and can be overridden by setting
the CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX CMake variable.
You can download and install poco using the vcpkg dependency manager:
$ git clone https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg.git
$ cd vcpkg
$ ./bootstrap-vcpkg.sh
$ ./vcpkg integrate install
$ ./vcpkg install poco
The poco port in vcpkg is kept up to date by Microsoft team members and community contributors. If the version is out of date, please create an issue or pull request on the vcpkg repository.
You can download and install poco using the Conan(https://github.com/conan-io/conan) package manager. It needed to be installed first(https://conan.io/downloads.html):
You can install Poco libraries from Conan Center(https://conan.io/center.html):
$ conan install -r conancenter poco/1.12.0@
Or, you can download Poco recipe and build locally:
$ conan install -r conancenter poco/1.12.0@ --build=poco
The Poco recipe and packages in Conan Center are kept up to date by Conan team members and community contributors. If the version is out of date, or you detect any wrong behavior, please create an issue or pull request(https://github.com/conan-io/conan-center-index) on the Conan Center Index repository.
If you do not want to or cannot use CMake, POCO can also be built with Visual Studio (project and solution files included) or GNU Make (Linux, macOS and other supported Unix platforms).
Please refer to the documentation for more information.
POCO can also be obtained via different package managers.
POCO has an active user and contributing community, please visit our website and blog. Answers to POCO-related questions can also be found on Stack Overflow.
Please see CONTRIBUTING for submitting contributions, bugs reports, feature requests or security issues.
In regards to Boost, in spite of some functional overlapping, POCO is best thought of as a Boost complement (rather than replacement). Side-by-side use of Boost and POCO is a very common occurrence.