Nikhila Ravi, Valentin Gabeur, Yuan-Ting Hu, Ronghang Hu, Chaitanya Ryali, Tengyu Ma, Haitham Khedr, Roman Rädle, Chloe Rolland, Laura Gustafson, Eric Mintun, Junting Pan, Kalyan Vasudev Alwala, Nicolas Carion, Chao-Yuan Wu, Ross Girshick, Piotr Dollár, Christoph Feichtenhofer
[Paper] [Project] [Demo] [Dataset] [Blog] [BibTeX]
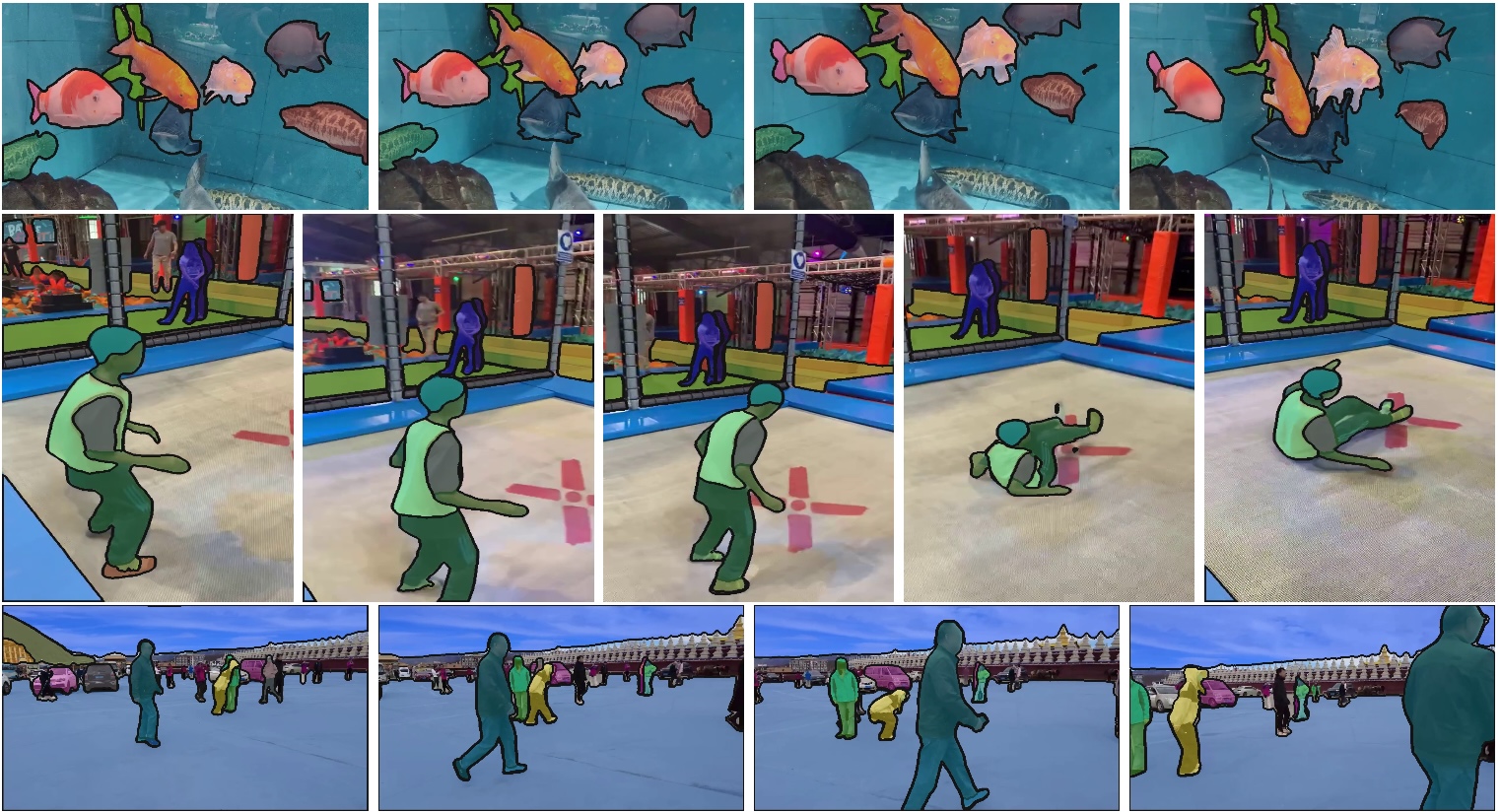
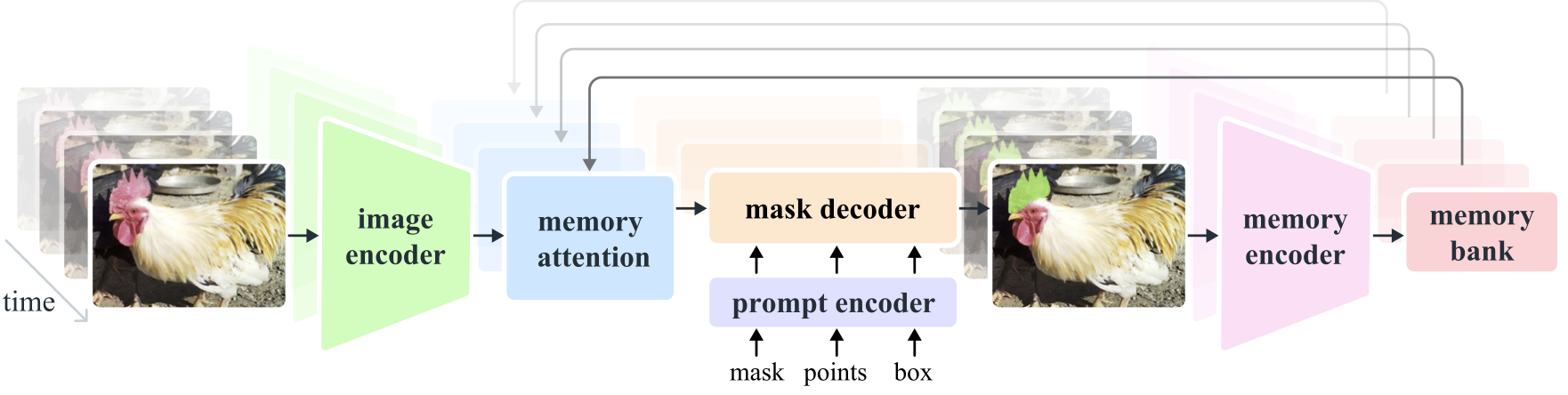
Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2) is a foundation model towards solving promptable visual segmentation in images and videos. We extend SAM to video by considering images as a video with a single frame. The model design is a simple transformer architecture with streaming memory for real-time video processing. We build a model-in-the-loop data engine, which improves model and data via user interaction, to collect our SA-V dataset, the largest video segmentation dataset to date. SAM 2 trained on our data provides strong performance across a wide range of tasks and visual domains.
SAM 2 needs to be installed first before use. The code requires python>=3.10, as well as torch>=2.3.1 and torchvision>=0.18.1. Please follow the instructions here to install both PyTorch and TorchVision dependencies. You can install SAM 2 on a GPU machine using:
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything-2.git
cd segment-anything-2; pip install -e .To use the SAM 2 predictor and run the example notebooks, jupyter and matplotlib are required and can be installed by:
pip install -e ".[demo]"Note:
- It's recommended to create a new Python environment for this installation and install PyTorch 2.3.1 (or higher) via
pipfollowing https://pytorch.org/. If you have a PyTorch version lower than 2.3.1 in your current environment, the installation command above will try to upgrade it to the latest PyTorch version usingpip. - The step above requires compiling a custom CUDA kernel with the
nvcccompiler. If it isn't already available on your machine, please install the CUDA toolkits with a version that matches your PyTorch CUDA version.
Please see INSTALL.md for FAQs on potential issues and solutions.
First, we need to download a model checkpoint. All the model checkpoints can be downloaded by running:
cd checkpoints
./download_ckpts.shor individually from:
Then SAM 2 can be used in a few lines as follows for image and video prediction.
SAM 2 has all the capabilities of SAM on static images, and we provide image prediction APIs that closely resemble SAM for image use cases. The SAM2ImagePredictor class has an easy interface for image prompting.
import torch
from sam2.build_sam import build_sam2
from sam2.sam2_image_predictor import SAM2ImagePredictor
checkpoint = "./checkpoints/sam2_hiera_large.pt"
model_cfg = "sam2_hiera_l.yaml"
predictor = SAM2ImagePredictor(build_sam2(model_cfg, checkpoint))
with torch.inference_mode(), torch.autocast("cuda", dtype=torch.bfloat16):
predictor.set_image(<your_image>)
masks, _, _ = predictor.predict(<input_prompts>)Please refer to the examples in image_predictor_example.ipynb for static image use cases.
SAM 2 also supports automatic mask generation on images just like SAM. Please see automatic_mask_generator_example.ipynb for automatic mask generation in images.
For promptable segmentation and tracking in videos, we provide a video predictor with APIs for example to add prompts and propagate masklets throughout a video. SAM 2 supports video inference on multiple objects and uses an inference state to keep track of the interactions in each video.
import torch
from sam2.build_sam import build_sam2_video_predictor
checkpoint = "./checkpoints/sam2_hiera_large.pt"
model_cfg = "sam2_hiera_l.yaml"
predictor = build_sam2_video_predictor(model_cfg, checkpoint)
with torch.inference_mode(), torch.autocast("cuda", dtype=torch.bfloat16):
state = predictor.init_state(<your_video>)
# add new prompts and instantly get the output on the same frame
frame_idx, object_ids, masks = predictor.add_new_points(state, <your_prompts>):
# propagate the prompts to get masklets throughout the video
for frame_idx, object_ids, masks in predictor.propagate_in_video(state):
...Please refer to the examples in video_predictor_example.ipynb for details on how to add prompts, make refinements, and track multiple objects in videos.
Alternatively, models can also be loaded from Hugging Face (requires pip install huggingface_hub).
For image prediction:
import torch
from sam2.sam2_image_predictor import SAM2ImagePredictor
predictor = SAM2ImagePredictor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam2-hiera-large")
with torch.inference_mode(), torch.autocast("cuda", dtype=torch.bfloat16):
predictor.set_image(<your_image>)
masks, _, _ = predictor.predict(<input_prompts>)For video prediction:
import torch
from sam2.sam2_video_predictor import SAM2VideoPredictor
predictor = SAM2VideoPredictor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam2-hiera-large")
with torch.inference_mode(), torch.autocast("cuda", dtype=torch.bfloat16):
predictor.set_image(<your_image>)
masks, _, _ = predictor.predict(<input_prompts>)| Model | Size (M) | Speed (FPS) | SA-V test (J&F) | MOSE val (J&F) | LVOS v2 (J&F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sam2_hiera_tiny | 38.9 | 47.2 | 75.0 | 70.9 | 75.3 |
| sam2_hiera_small | 46 | 43.3 (53.0 compiled*) | 74.9 | 71.5 | 76.4 |
| sam2_hiera_base_plus | 80.8 | 34.8 (43.8 compiled*) | 74.7 | 72.8 | 75.8 |
| sam2_hiera_large | 224.4 | 24.2 (30.2 compiled*) | 76.0 | 74.6 | 79.8 |
* Compile the model by setting compile_image_encoder: True in the config.
See sav_dataset/README.md for details.
The models are licensed under the Apache 2.0 license. Please refer to our research paper for more details on the models.
See contributing and the code of conduct.
The SAM 2 project was made possible with the help of many contributors (alphabetical):
Karen Bergan, Daniel Bolya, Alex Bosenberg, Kai Brown, Vispi Cassod, Christopher Chedeau, Ida Cheng, Luc Dahlin, Shoubhik Debnath, Rene Martinez Doehner, Grant Gardner, Sahir Gomez, Rishi Godugu, Baishan Guo, Caleb Ho, Andrew Huang, Somya Jain, Bob Kamma, Amanda Kallet, Jake Kinney, Alexander Kirillov, Shiva Koduvayur, Devansh Kukreja, Robert Kuo, Aohan Lin, Parth Malani, Jitendra Malik, Mallika Malhotra, Miguel Martin, Alexander Miller, Sasha Mitts, William Ngan, George Orlin, Joelle Pineau, Kate Saenko, Rodrick Shepard, Azita Shokrpour, David Soofian, Jonathan Torres, Jenny Truong, Sagar Vaze, Meng Wang, Claudette Ward, Pengchuan Zhang.
Third-party code: we use a GPU-based connected component algorithm adapted from cc_torch (with its license in LICENSE_cctorch) as an optional post-processing step for the mask predictions.
If you use SAM 2 or the SA-V dataset in your research, please use the following BibTeX entry.
@article{ravi2024sam2,
title={SAM 2: Segment Anything in Images and Videos},
author={Ravi, Nikhila and Gabeur, Valentin and Hu, Yuan-Ting and Hu, Ronghang and Ryali, Chaitanya and Ma, Tengyu and Khedr, Haitham and R{\"a}dle, Roman and Rolland, Chloe and Gustafson, Laura and Mintun, Eric and Pan, Junting and Alwala, Kalyan Vasudev and Carion, Nicolas and Wu, Chao-Yuan and Girshick, Ross and Doll{\'a}r, Piotr and Feichtenhofer, Christoph},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.00714},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.00714},
year={2024}
}