A No-code workflow executor
Dagu executes DAGs (Directed acyclic graph) from declarative YAML definitions. Dagu also comes with a web UI for visualizing workflow.
- Dagu
Airflow or Prefect requires us to write Python code for workflow definitions. For my specific situation, there were hundreds of thousands of existing Perl or ShellScript codes. Adding another layer of Python would add too much complexity for us. We needed more light-weight solution. So, we developed a No-code workflow executor that doesn't require writing code. We hope that this tool will help other people in the same situation.
- Dagu is a single command and it uses the file system to stores data in JSON format. Therefore, no DBMS or cloud service is required.
- Dagu executes DAGs defined in declarative YAML format. Existing programs can be used without any modification.
Download the latest binary from the Releases page and place it in your $PATH. For example, you can download it in /usr/local/bin.
Download this example YAML and place it in the current directory with extension *.yaml.
Start the server with dagu server and browse to http://localhost:8000 to explore the Web UI.
You can start the example by pressing Start on the UI.
dagu start [--params=<params>] <file>- start a workflowdagu status <file>- display the current status of a workflowdagu retry --req=<request-id> <file>- retry the failed/canceled workflowdagu stop <file>- stop a workflow execution by sending a TERM signaldagu dry [--params=<params>] <file>- dry-run a workflowdagu server- start a web server for web UI
You can launch web UI by dagu server command. Default URL is http://localhost:8000.
-
DAGs: Overview of all DAGs (workflows).
-
Detail: Realtime status of the workflow.
-
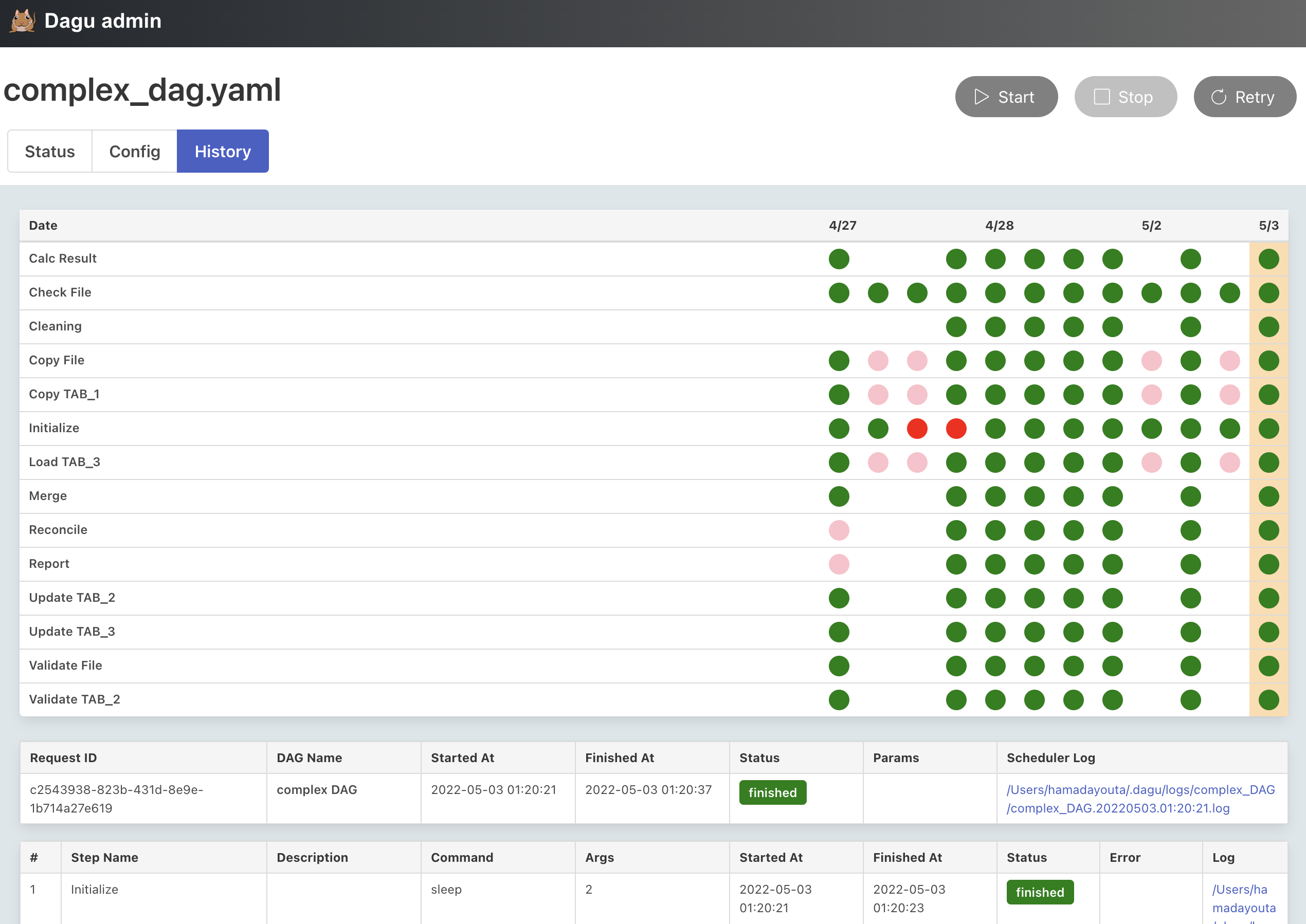
History: History of the execution of the workflow.
A minimal definition is as follows:
name: minimal configuration # DAG's name
steps: # Steps inside the DAG
- name: step 1 # Step's name (should be unique within the file)
command: python main_1.py # Command and arguments to execute
- name: step 2
command: python main_2.py
depends:
- step 1 # [optional] Name of the step to depend onEnvironment variables can be defined and used using env field.
name: example
env:
SOME_DIR: ${HOME}/batch
steps:
- name: some task in some dir
dir: ${SOME_DIR}
command: python main.pyParameters can be defined using params field. Each parameter can be referenced as $1, $2, etc. Parameters can also be command substitutions or environment variables. You can override the parameters with the --params= parameter for start command.
name: example
params: param1 param2
steps:
- name: some task with parameters
command: python main.py $1 $2You can use command substitution in field values. A string enclosed in backquotes (`) is evaluated as a command and replaced with the result of standard output.
name: minimal configuration
env:
TODAY: "`date '+%Y%m%d'`"
steps:
- name: hello
command: "echo hello, today is ${TODAY}"By combining these settings, you have granular control over how the workflow runs.
name: all configuration # DAG's name
description: run a DAG # DAG's description
env: # Environment variables
LOG_DIR: ${HOME}/logs
PATH: /usr/local/bin:${PATH}
logDir: ${LOG_DIR} # Log directory to write standard output
histRetentionDays: 3 # Execution history retention days (not for log files)
delaySec: 1 # Interval seconds between steps
maxActiveRuns: 1 # Max parallel number of running step
params: param1 param2 # Default parameters for the DAG that can be referred to by $1, $2, and so on
preconditions: # Precondisions for whether the DAG is allowed to run
- condition: "`echo 1`" # Command or variables to evaluate
expected: "1" # Expected value for the condition
mailOn:
failure: true # Send a mail when the DAG failed
success: true # Send a mail when the DAG finished
MaxCleanUpTimeSec: 300 # The maximum amount of time to wait after sending a TERM signal to running steps before killing them
handlerOn: # Handler on Success, Failure, Cancel, Exit
success:
command: "echo succeed" # Command to execute when the DAG execution succeed
failure:
command: "echo failed" # Command to execute when the DAG execution failed
cancel:
command: "echo canceled" # Command to execute when the DAG execution canceled
exit:
command: "echo finished" # Command to execute when the DAG execution finished
steps:
- name: som task # Step's name
description: some task # Step's description
dir: ${HOME}/logs # Working directory
command: python main.py $1 # Command and parameters
mailOn:
failure: true # Send a mail when the step failed
success: true # Send a mail when the step finished
continueOn:
failed: true # Continue to the next regardless of the step failed or not
skipped: true # Continue to the next regardless the preconditions are met or not
retryPolicy: # Retry policy for the step
limit: 2 # Retry up to 2 times when the step failed
repeatPolicy: # Repeat policy for the step
repeat: true # Boolean whether to repeat this step
intervalSec: 60 # Interval time to repeat the step in seconds
preconditions: # Precondisions for whether the step is allowed to run
- condition: "`echo 1`" # Command or variables to evaluate
expected: "1" # Expected Value for the conditionThe global configuration file ~/.dagu/config.yaml is useful to gather common settings, such as the directory to write log files.
DAGU__DATA- path to directory for internal use by dagu (default :~/.dagu/data)DAGU__LOGS- path to directory for logging (default :~/.dagu/logs)
Please create ~/.dagu/admin.yaml.
host: <hostname for web UI address> # default value is 127.0.0.1
port: <port number for web UI address> # default value is 8080
dags: <the location of DAG configuration files> # default value is current working directory
command: <Absolute path to the dagu binary> # [optional] required if the dagu command not in $PATH
isBasicAuth: <true|false> # [optional] basic auth config
basicAuthUsername: <username for basic auth of web UI> # [optional] basic auth config
basicAuthPassword: <password for basic auth of web UI> # [optional] basic auth configCreating a global configuration ~/.dagu/config.yaml is a convenient way to organize common settings.
logDir: <path-to-write-log> # log directory to write standard output
histRetentionDays: 3 # history retention days
smtp: # [optional] mail server configuration to send notifications
host: <smtp server host>
port: <stmp server port>
errorMail: # [optional] mail configuration for error-level
from: <from address>
to: <to address>
prefix: <prefix of mail subject>
infoMail:
from: <from address> # [optional] mail configuration for info-level
to: <to address>
prefix: <prefix of mail subject>Feel free to contribute in any way you want. Share ideas, questions, submit issues, and create pull requests. Thank you!
Dagu's history data will be stored in the path of DAGU__DATA environment variable. The default location is $HOME/.dagu/data.
Log files are stored in the path of the DAGU__LOGS environment variable. The default location is $HOME/.dagu/logs. You can override this setting by logDir option in a YAML file.
The default retention period for execution history is 7 days. This setting can be changed with histRetentionDays option in a YAML file.
You can change the status of any task to a failed status. Then, when the job is retried, the tasks after the failed node will be executed.
No, there is no scheduler functionality so far. It is intended to be used with cron.
Dagu uses unix sockets to communicate with running processes.
https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/yohamta/dagu
This project is licensed under the GNU GPLv3 - see the LICENSE.md file for details