PathoGFAIR: a collection of FAIR and adaptable (meta)genomics workflows for (foodborne) pathogens detection and tracking
PathoGFAIR is a collection of Galaxy-based FAIR workflows employing state-of-the-art tools to detect and track pathogens from metagenomic Nanopore sequencing. Although initially developed to detect pathogens in food datasets, the workflows can be applied to other metagenomic Nanopore pathogenic data. PathoGFAIR incorporates visualisations and reports for comprehensive results.
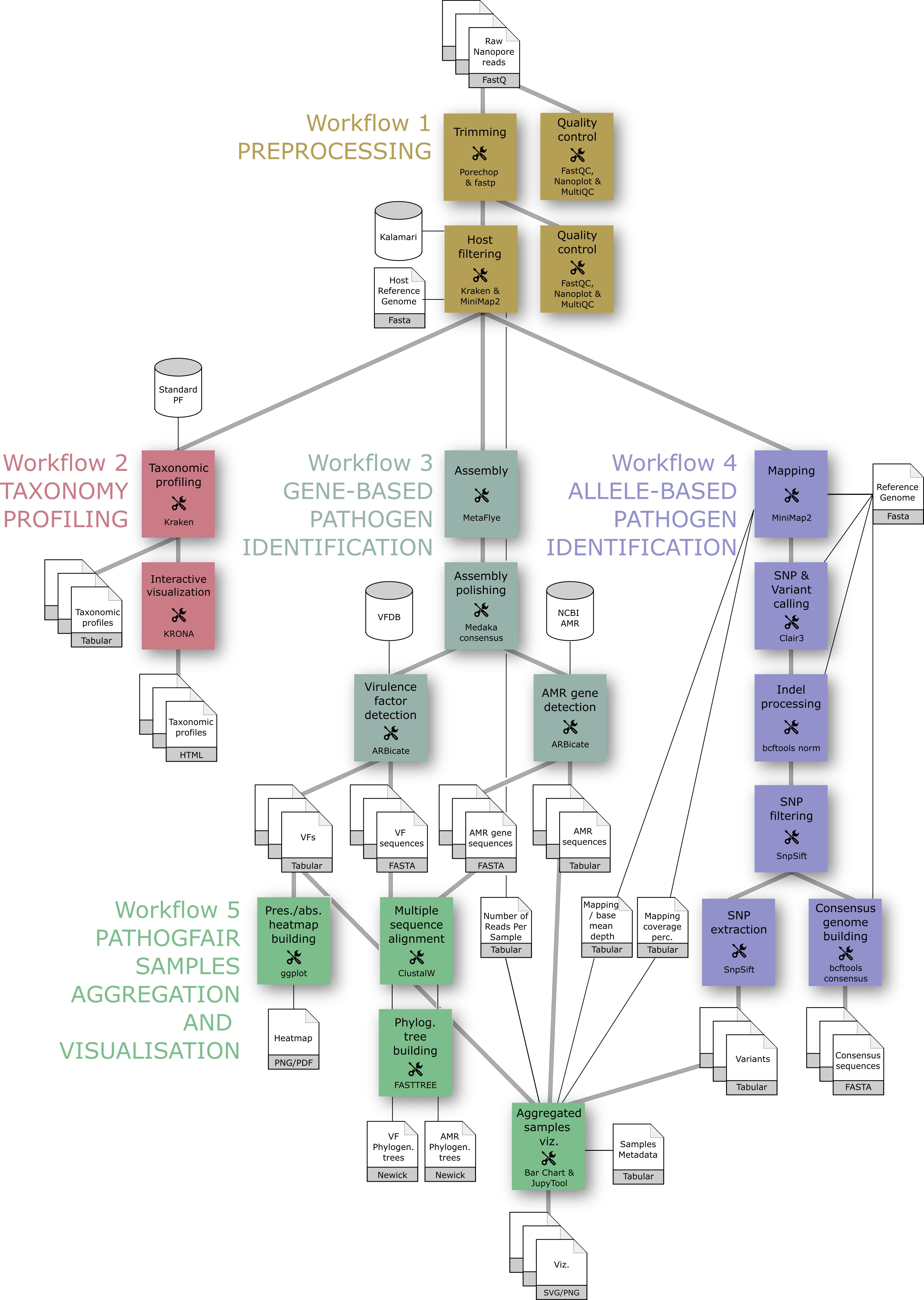
The core of PathoGFAIR project is a series of 5 Galaxy-based workflows designed to process Nanopore sequencing data, detect pathogens, and track their presence across samples:
- Preprocessing: where the quality controlling, reads trimming for quality retaining, host sequences removal and other contaminating sequences removal take place
- Taxonomy Profiling: where taxonomy profiling takes place identifying and visualizing our samples' community abundances down to the subspecies level
- Gene-based Pathogen Identification: where we identify all possible pathogens by identifying all the Virulence factors (VFs) genes and their specific locations, we also identify Antimicrobial resistance genes (AMRs) within the same workflow.
- Allele-based Pathogen Identification: where we identify all the SNPs and variants and create the consensus sequences of all samples
- Samples Aggregation and Visualisation: where we visualize the outputs of the pathogens drawing a heatmap of all the found pathogenic genes for all samples, phylogenetic trees relating samples together per common pathogenic genes found, and bar charts for important tabular outputs of previous workflows, e.g. number of identified SNPs and variants per sample, number of removed host reads and mapping depth and coverage.
Workflows are available on 2 workflows registries (Dockstore and WorkflowHub) and several Galaxy servers.
To assist in understanding and using the workflows, we provide extensive tutorial and recording available via the Galaxy Training Network GTN.
To demonstrate PathoGFAIR and its features, 130 samples from 2 studies (without or with prior pathogen isolation) were analysed.
All samples contained pathogens known beforehand and were sequenced using Oxford Nanopore technology.
Pathogens were deliberately spiked into 46 samples to mimic real-world scenarios given a protocol developed in the context of PathoGFAIR.
The full analysis can be found in a dedicated Galaxy history.
To further test PathoGFair, 84 public datasets were used. The full analysis can be found in a dedicated Galaxy history.
To evaluate the effectiveness of PathoGFAIR workflows, a benchmarking analysis was performed comparing PathoGFAIR's pathogen detection capabilities with the systems and pipelines.
This section provides detailed instructions to replicate the PathoGFAIR benchmarking process, as outlined in our dedicated protocol on protocols.io. The focus here is on running the selected systems/pipelines used in our benchmarking.
-
Setup: Import the Galaxy history, which contains the benchmarking results of PathoGFAIR
-
Results:
- View the results directly.
- Rerun PathoGFAIR workflows on the same 46 samples, available under dataset number
47:biolytix_classified_samples.
-
Setup:
-
Create an Account on CZID: We used credentials from Engy Nasr, University of Freiburg.
-
Create a public or private Project with the following details:
- Name
- Description
- Analysis Type: Metagenomics
- Sequencing Type: Nanopore
-
Upload Datasets: Upload the 46 samples (total size: 7GB) either locally or from a public repository:
- Local upload (our recommendation): Download the samples from our published Galaxy history and upload them.
- Online upload: Use the NCBI repository PRJNA982679.
-
Upload or Enter Metadata: Metadata fields we included are: host [Chicken], Ct value, sampling date, location, and nucleotide type [DNA], which are available in our metadata table in
data/benchmark.For a full list of possible fields to include, see: CZID Metadata Dictionary.
-
-
Execution: Sample uploads started on Tuesday, October 15th, at 9 AM. Dataset upload finished at 9:58 AM. Analysis was fully completed for all samples after: 1hour and 30 mins of the datasets finished upload.
-
Results: View the analysis results: CZID Results, use the drop down menu on the top left to switch between samples.
-
Setup:
- Create an Account on BugSeq: We used credentials from Engy Nasr, University of Freiburg.
- Upload datasets: Upload the 46 samples (total size: 7GB) either locally or via their BaseSpace, that you have to contact them for. We uploaded them from local directory, same as explained for CZID(IDseq)
- Set up parameters
- Platform: Nanopore
- Device & Chemistry: MinION/GridION/Flongle - R9.4.1
- Metagenomic Database: NCBI nt (BugSeq recommendation for metagenomics samples)
- Sample Type: Generic (BugSeq recommendation)
- Sequenced Material: DNA
- Outbreak Analysis (Genomic Relatedness Visualization): yes
-
Execution: Sample uploads started on Tuesday, October 15th, at 11:30 AM. Dataset upload finished at 12:30 PM. Analysis was fully completed for all samples after: 1hour and 30 mins of the datasets finished upload.
-
Results: On Tuesday, October 15th, at 15:21 PM, we received that the analysis had failed, as we have insufficient sample credits. We sent to their support for help directly after receiving their email. They replied back that we can only analyse 10 samples not 46, so BugSeq will be removed from the benchmark.
GitHub Repository
In the GitHub repository, you'll find sources (Jupyter notebooks) to replicate figures in the manuscript.
The notebooks are also designed to run on any Galaxy instance using Jupytool.
-
data: folder with 2 subfolders (1 per use case:samples_without_prior_pathogen_isolationandsamples_with_prior_pathogen_isolation), each containing metadata and Galaxy-generated outputs of the workflows on samples from each use cases -
bin: folder with two Jupyter notebooks (1 per use case) for- importing all tables from the
datafolder - generating all figures to the
resultsfolder.
- importing all tables from the
-
results: folder with results after running the Jupyter notebooks on the workflows output datasets. -
docs: folder with figures (docs/figures) and tables (docs/tables) mentioned in the paper.
To reproduce the figures in results, we need to run the notebooks bin and then needs the following:
- jupyter
- openpyxl
- matplotlib
- numpy
- pandas
- python=3.13.1
- requests
- seaborn
- scikit-learn
- scipy
- upsetplot
- clustergrammer2
This can be installed with a conda environment:
$ conda env create -f environment.yml
-
Activate conda environment
$ conda activate pathogfair -
Launch Jupyter
$ jupyter notebook -
Go to http://localhost:8888 (a page should open automatically in your browser)
-
Navigate to
bin -
Open the notebooks and run them
Feel free to contribute, open issues, or provide feedback.
If you use or refer to this project in your research, please cite the associated paper:
PathoGFAIR: a collection of FAIR and adaptable (meta)genomics workflows for (foodborne) pathogens detection and tracking Engy Nasr, Anna Henger, Björn Grüning, Paul Zierep, Bérénice Batut bioRxiv 2024.06.26.600753; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.26.600753
All sources for the figures and tables in the paper can be found in this GitHub repository
- Figure 1 created using Inkscape (SVG in
docs/figures/Figure_1.svg) - Figure 2
- Panels (A), (B), (D), (E), (F) generated by
bin/samples_without_prior_pathogen_isolation.ipynb - Panel (C) corresponds to a phylogenetic tree generated using Galaxy and available in this Galaxy history (step 11427)
- Panels arranged and colored using Inkscape (SVG in
docs/figures/Figure_2.svg)
- Panels (A), (B), (D), (E), (F) generated by
- Figure 3
- Panels generated by
bin/samples_without_prior_pathogen_isolation.ipynb - Panels arranged and colored by Inkscape (SVG in
docs/figures/Figure_3.svg)
- Panels generated by
- Supplementary Figure S1 generated by
bin/samples_without_prior_pathogen_isolation.ipynb - Supplementary online Figure S2
- Supplementary Figure S3 generated by
bin/samples_without_prior_pathogen_isolation.ipynb - Supplementary Figure S4
- Phylogenetic tree generated using Galaxy and available in this Galaxy history (step 11425)
- Colors added using Inkscape (SVG in
docs/figures/Supplementary_Figure_S4.svg)
- Supplementary Figure S5 generated by
bin/samples_with_prior_pathogen_isolation.ipynb - Supplementary online Figure S6
- Supplementary Figure S7
- Panels generated by
bin/samples_with_prior_pathogen_isolation.ipynb - Panels arranged using Inkscape (SVG in
docs/figures/Supplementary_Figure_S7.svg)
- Panels generated by
- Supplementary Figure S8
- Phylogenetic tree generated using Galaxy and available in this Galaxy history (step 2742)
- Colors added using Inkscape (SVG in
docs/figures/Supplementary_Figure_S8.svg)
- Supplementary Figure S9
- Heatmap generated by
bin/samples_without_prior_pathogen_isolation.ipynb - Labels added using Inkscape (SVG in
docs/figures/Supplementary_Figure_S9.svg)
- Heatmap generated by
- Table 1: Comparison of features between PathoGFAIR and other similar pipelines or systems
- Supplemantary Table T1: source in
docs/tables/Supplementary_Table_T1.tsv - Supplemantary Table T2: source in
docs/tables/Supplementary_Table_T2.tsv - Supplemantary Table T3: source in
docs/tables/Supplementary_Table_T3.tsv - Supplemantary Table T4: source in
docs/tables/Supplementary_Table_T4.tsv