Use the Rerun SDK (available for C++, Python and Rust) to log data like images, tensors, point clouds, and text. Logs are streamed to the Rerun Viewer for live visualization or to file for later use.
import rerun as rr # pip install rerun-sdk
rr.init("rerun_example_app")
rr.connect() # Connect to a remote viewer
# rr.spawn() # Spawn a child process with a viewer and connect
# rr.save("recording.rrd") # Stream all logs to disk
# Associate subsequent data with 42 on the “frame” timeline
rr.set_time_sequence("frame", 42))
# Log colored 3D points to the entity at `path/to/points`
rr.log("path/to/points", rr.Points3D(positions, colors=colors))
…
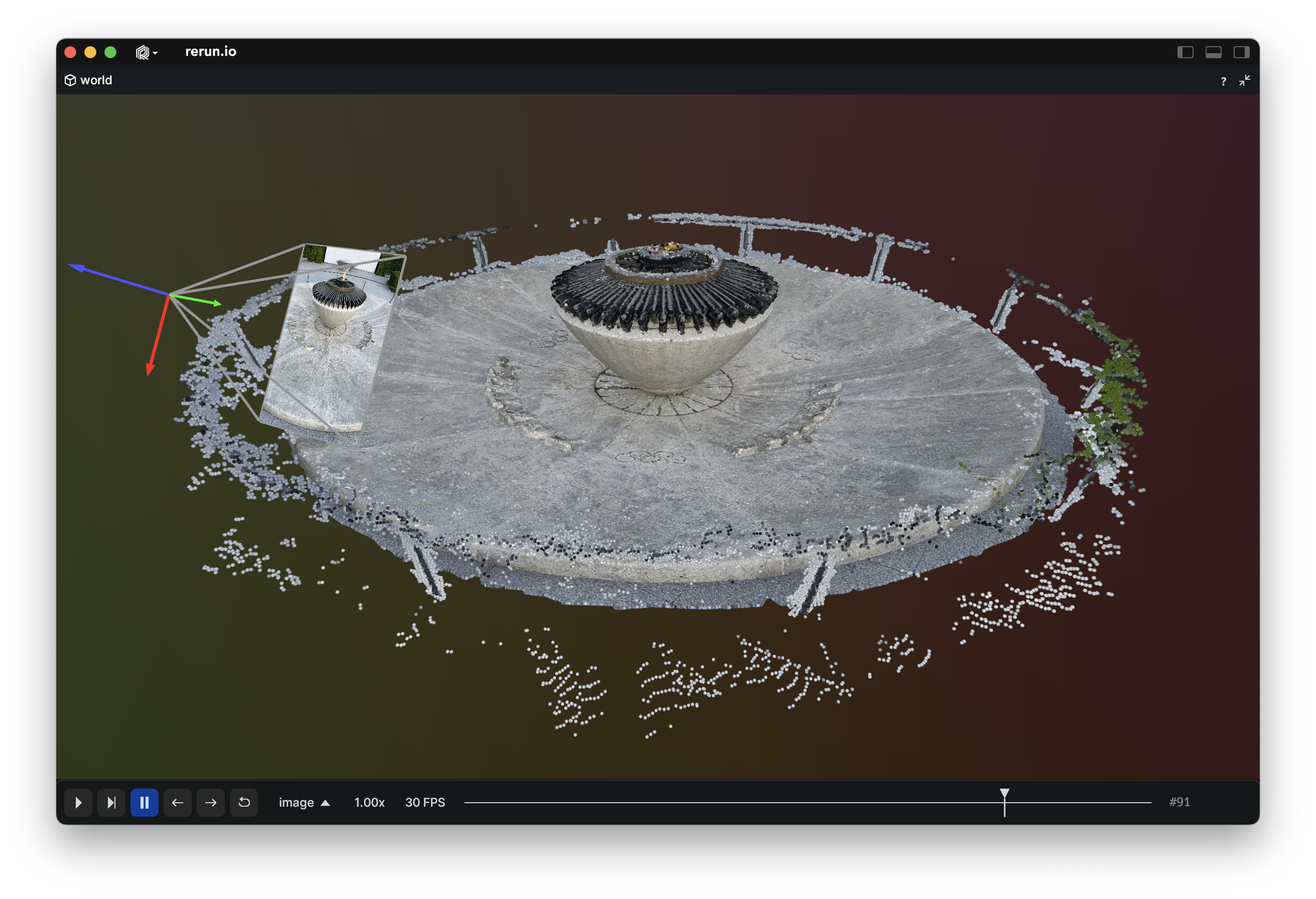
Both the Python and Rust library can start the Rerun Viewer, but to stream log data over the network or load our .rrd data files you also need the rerun binary.
It can be installed with pip install rerun-sdk or with cargo install rerun-cli.
You should now be able to run rerun --help in any terminal.
- 📚 High-level docs
- ⏃ Loggable Types
- ⚙️ Examples
- 🌊 C++ API docs
- 🐍 Python API docs
- 🦀 Rust API docs
⁉️ Troubleshooting
We are in active development. There are many features we want to add, and the API is still evolving. Expect breaking changes!
Some shortcomings:
- Time-scalar plots and text logs are currently very slow.
- Points cloud sizes are limited, and big point clouds are slow.
- The data you want to visualize must fit in RAM.
- See https://www.rerun.io/docs/howto/limit-ram for how to bound memory use.
- We plan on having a disk-based data store some time in the future.
Rerun uses an open-core model. Everything in this repository will stay open source and free (both as in beer and as in freedom). In the future, Rerun will offer a commercial product that builds on top of the core free project.
The Rerun open source project targets the needs of individual developers. The commercial product targets the needs specific to teams that build and run computer vision and robotics products.
ARCHITECTURE.mdBUILD.mdrerun_py/README.md- build instructions for Python SDKCODE_OF_CONDUCT.mdCODE_STYLE.mdCONTRIBUTING.mdRELEASES.md
- Download the correct
.whlfrom GitHub Releases - Run
pip install rerun_sdk<…>.whl(replace<…>with the actual filename) - Test it:
rerun --version





