Audio Front-end Framework[中文]
Espressif Audio Front-end (AFE) algorithm framework is independently developed by ESPRESSIF AI Lab. Based on ESP32 series chips, the framework can provide high-quality and stable audio data to the host.
Espressif AFE provides the most convenient way to do audio front-end processing on ESP32 series chips. Espressif AFE framework stably transfers high-quality audio data to the host for further wake-up or speech recognition.
The functions supported in Espressif AFE are as follows:
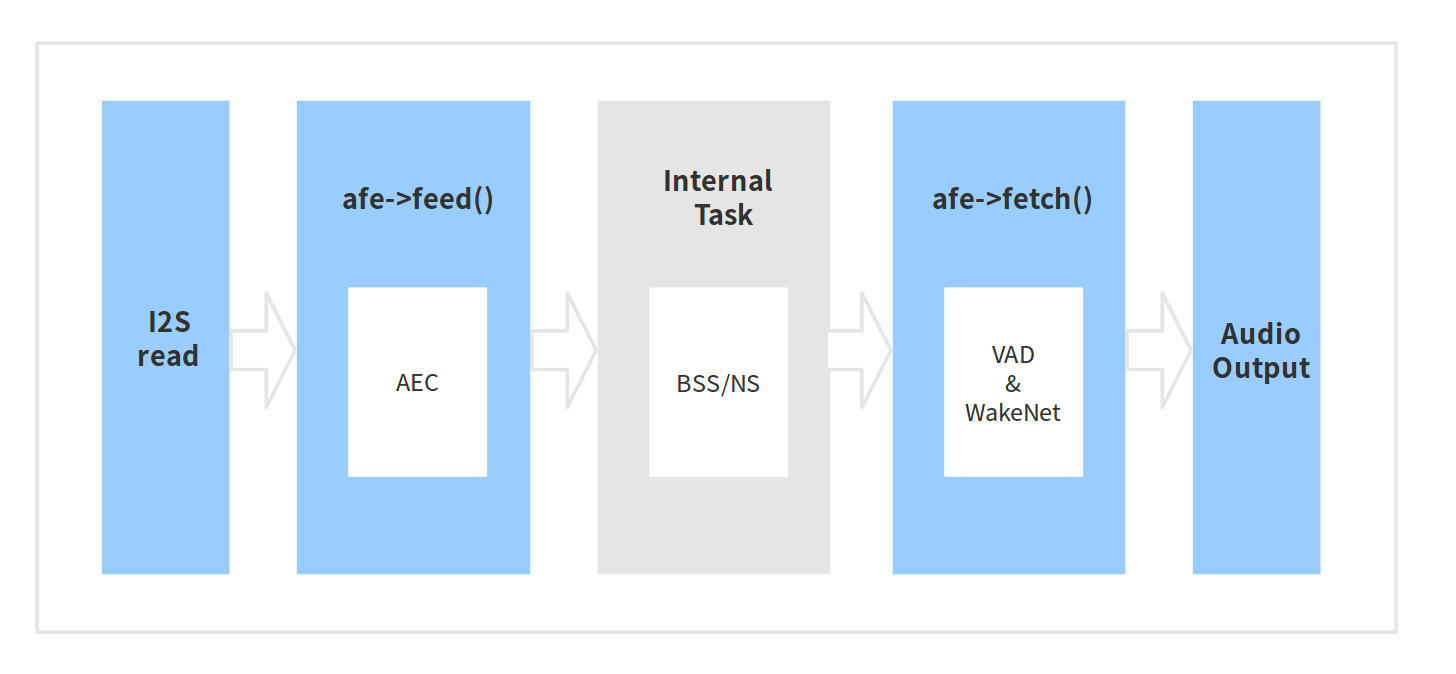
The workflow of Espressif AFE is as follows:
The workflow of Espressif AFE can be divided into four parts:
- AFE creation and initialization
- AFE feed: Input audio data and will run AEC in the feed function
- Internal BSS/NS algorithms
- AFE fetch: Return the audio data after processing and the output value. the AFE fetch will perform VAD internally. If you configure WakeNet to be 'enabled', WakeNet wil do wake-word detection
Note: afe->feed() and afe->fetch() are visible to users, while internal BSS/NS task is invisible to users.
AEC runs in
afe->feed()function;
BSS is an independent task in AFE;
The results of VAD and WakeNet are obtained byafe->fetch()function.
Espressif AFE supports both single MIC and dual MIC scenarios. The internal task of single MIC applications is processed by NS, and the internal task of dual MIC applications is processed by BSS.
-
Single MIC
esp_afe_sr_iface_t *afe_handle = &esp_afe_sr_1mic; -
Dual MIC
esp_afe_sr_iface_t *afe_handle = &esp_afe_sr_2mic;
-
AFE single MIC
- Input audio data format: 16KHz, 16bit, two channels (one is mic data, another is reference data)
- The data frame length is 32ms. Users can use
afe->get_feed_chunksize()to get the number of sampling points needed (the data type of sampling points is int16).
The input data is arranged as follows:
-
AFE dual MIC
- Input audio data format: 16KHz, 16bit, three channels (two are mic data, another is reference data)
- The data frame length is 32ms. Users can use
afe->get_feed_chunksize()to get the number of sampling points needed (the data type of sampling points is int16).
The input data is arranged as follows:
Note: the converted data size is: afe->get_feed_chunksize * channel number * sizeof(short)
The AEC (Acoustic Echo Cancellation) algorithm supports maximum two-mic processing, which can effectively remove the echo in the mic input signal, and help with further speech recognition.
NS algorithm supports single-channel processing and can suppress the non-human noise in single-channel audio, especially for steady noise.
BSS algorithm supports dual-channel processing, which can well separate the target sound source from the rest of the interference sound, so as to extract the useful audio signal and ensure the quality of the subsequent speech.
VAD algorithm supports real-time output of the voice activity state of the current frame.
Users can choose whether to detect wake words in AFE. When calling afe->disable_wakenet(afe_data), it will enter bypass mode, and the WakeNet will not run.
The output audio of AFE is single-channel data. When WakeNet is enabled, AFE will output single-channel data with human voice.
afe_handle is the function handle that the user calls the AFE interface. Users need to select the corresponding AFE handle according to the single MIC and dual MIC applications.
-
Single MIC
esp_afe_sr_iface_t *afe_handle = &esp_afe_sr_1mic; -
Dual MIC
esp_afe_sr_iface_t *afe_handle = &esp_afe_sr_2mic;
Get the configuration of AFE:
afe_config_t afe_config = AFE_CONFIG_DEFAULT();
Users can adjust the switch of each algorithm module and its corresponding parameters in macros AFE_ CONFIG_ DEFAULT ():
#define AFE_CONFIG_DEFAULT() { \
.aec_init = true, \
.se_init = true, \
.vad_init = true, \
.wakenet_init = true, \
.vad_mode = 3, \
.wakenet_model = &WAKENET_MODEL, \
.wakenet_coeff = &WAKENET_COEFF, \
.wakenet_mode = DET_MODE_2CH_90, \
.afe_mode = SR_MODE_HIGH_PERF, \
.afe_perferred_core = 0, \
.afe_perferred_priority = 5, \
.afe_ringbuf_size = 50, \
.alloc_from_psram = 1, \
.agc_mode = 2, \
}
-
aec_init: Whether the AEC algorithm is enabled.
-
se_init: Whether the BSS/NS algorithm is enabled.
-
vad_init: Whether the VAD algorithm is enabled.
-
wakenet_init: Whether the wake algorithm is enabled.
-
vad_mode: The VAD operating mode. A more aggressive (higher mode) VAD is more.
-
wakenet_model/wakenet_coeff/wakenet_mode: Use
make menuconfigto choose WakeNet model. Please refer to:WakeNet -
afe_mode: Espressif AFE supports two working modes: SR_MODE_LOW_COST, SR_MODE_HIGH_PERF. See the afe_sr_mode_t enumeration for details.
-
SR_MODE_LOW_COST: The quantified version occupies less resources.
-
SR_MODE_HIGH_PERF: The non-quantified version occupies more resources.
**ESP32 only supports SR_MODE_HIGH_PERF;
And ESP32S3 supports both of the modes **
-
-
afe_perferred_core: The internal BSS/NS algorithm of AFE will be running on which CPU core.
-
afe_ringbuf_size: The configuration of the internal ringbuf size.
-
alloc_from_psram: Whether to allocate memory from external psram first. Three values can be configured:
-
0: Allocated from internal ram.
-
1: Part of memory is allocated from external psram.
-
2: Most of memory is allocated from external psram.
-
-
agc_mode: Configuration for linear audio amplification.
The user uses the afe_handle->create_from_config(&afe_config) function to obtain the data handle, which will be used internally in afe, and the parameters passed in are the configurations obtained in step 2 above.
/**
* @brief Function to initialze a AFE_SR instance
*
* @param afe_config The config of AFE_SR
* @returns Handle to the AFE_SR data
*/
typedef esp_afe_sr_data_t* (*esp_afe_sr_iface_op_create_from_config_t)(afe_config_t *afe_config);
After initializing AFE and WakeNet, users need to input audio data into AFE by afe_handle->feed() function for processing.
The input audio size and layout format can refer to the step Input Audio data.
/**
* @brief Feed samples of an audio stream to the AFE_SR
*
*
* @param afe The AFE_SR data handle
*
* @param in The input microphone signal, only support signed 16-bit @ 16 KHZ. The frame size can be queried by the
* `get_samp_chunksize`. The channel number can be queried `get_channel_num`.
* @return The size of input
*/
typedef int (*esp_afe_sr_iface_op_feed_t)(esp_afe_sr_data_t *afe, const int16_t* in);
Get the number of audio channels:
afe_handle->get_channel_num() function can provide the number of MIC data channels that need to be put into afe_handle->feed() function( Without reference channel).
/**
* @brief Get the channel number of samples that need to be passed to the fetch function
*
* @param afe The AFE_SR object to query
* @return The amount of channel number
*/
typedef int (*esp_afe_sr_iface_op_get_channel_num_t)(esp_afe_sr_data_t *afe);
Users can get the processed single-channel audio by afe_handle->fetch() function.
The number of data sampling points of fetch (the data type of sampling point is int16) can be got by afe_handle->get_fetch_chunksize.
/**
* @brief Get the amount of each channel samples per frame that need to be passed to the function
*
* Every speech enhancement AFE_SR processes a certain number of samples at the same time. This function
* can be used to query that amount. Note that the returned amount is in 16-bit samples, not in bytes.
*
* @param afe The AFE_SR object to query
* @return The amount of samples to feed the fetch function
*/
typedef int (*esp_afe_sr_iface_op_get_samp_chunksize_t)(esp_afe_sr_data_t *afe);
Please pay attention to the return value of afe_handle->fetch():
- AFE_FETCH_CHANNEL_VERIFIED: Audio channel confirmation (This value is not returned while single microphone wakes up.)
- AFE_FETCH_NOISE: Noise detected
- AFE_FETCH_SPEECH: Speech detected
- AFE_FETCH_WWE_DETECTED: Wakeup detected
- ...
/**
* @brief fetch enhanced samples of an audio stream from the AFE_SR
*
* @Warning The output is single channel data, no matter how many channels the input is.
*
* @param afe The AFE_SR object to query
* @param out The output enhanced signal. The frame size can be queried by the `get_samp_chunksize`.
* @return The state of output, please refer to the definition of `afe_fetch_mode_t`
*/
typedef afe_fetch_mode_t (*esp_afe_sr_iface_op_fetch_t)(esp_afe_sr_data_t *afe, int16_t* out);
When users need to perform other operations after wake-up, such as offline or online speech recognitioafe_handlen, they can pause the operation of WakeNet to reduce the CPU resource consumption.
Users can call afe_handle->disable_wakenet(afe_data) to stop WakeNet, or call afe_handle->enable_wakenet(afe_data) to enable WakeNet.
The usage of AEC is similar to that of WakeNet. Users can disable or enable AEC according to requirements.
-
Disable AEC
afe->disable_aec(afe_data);
-
Enable AEC
afe->enable_aec(afe_data);