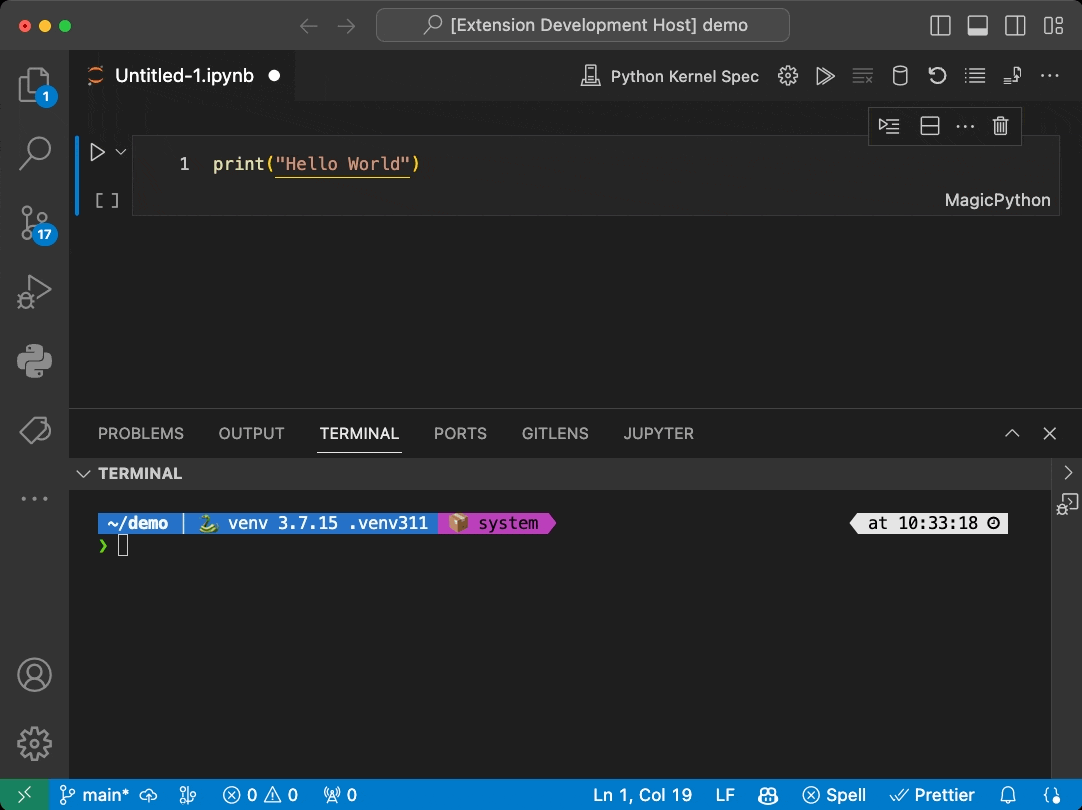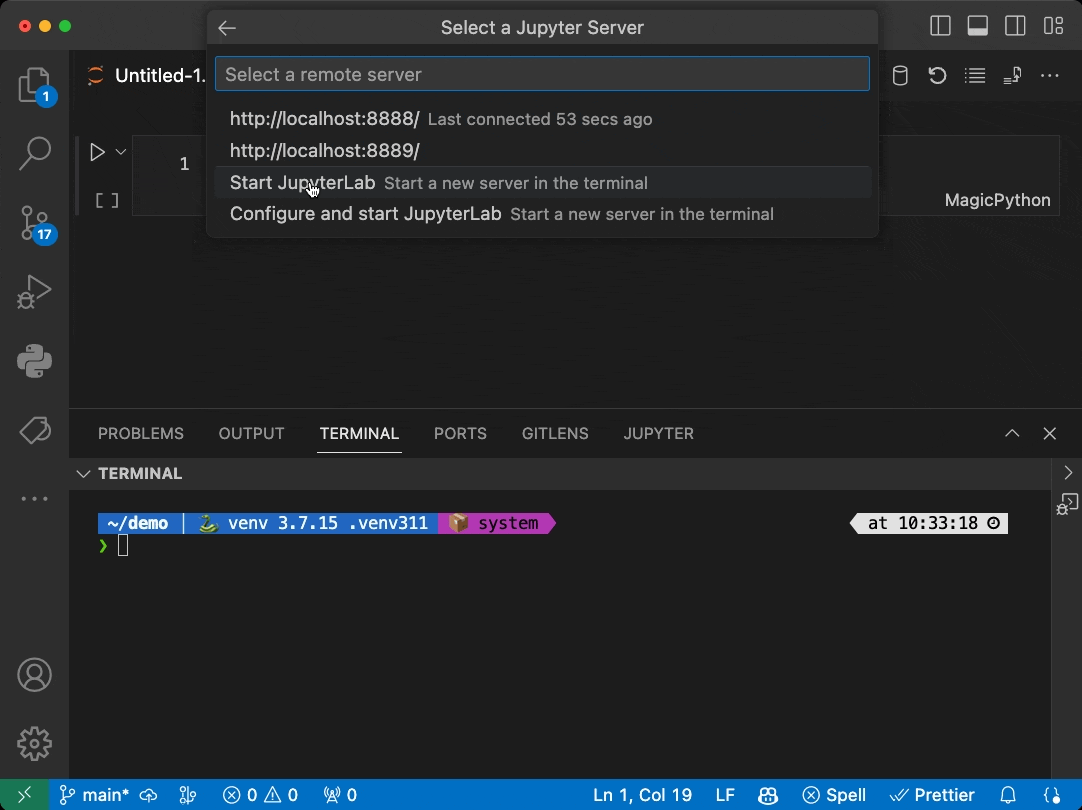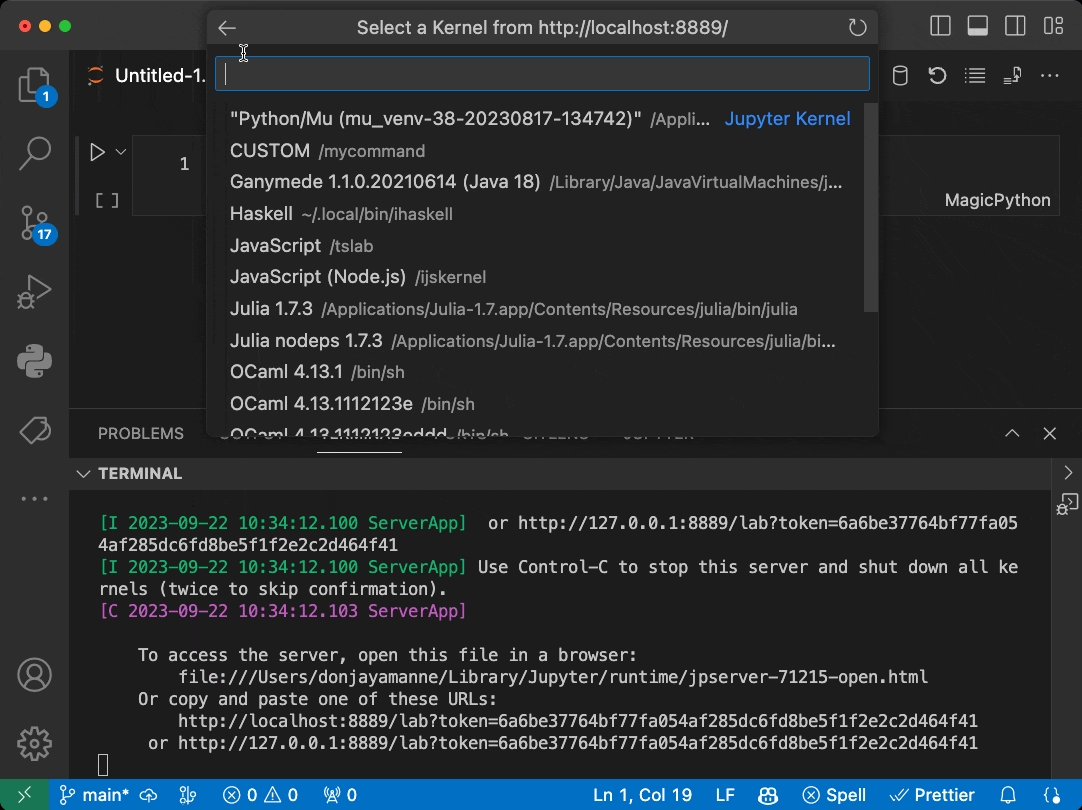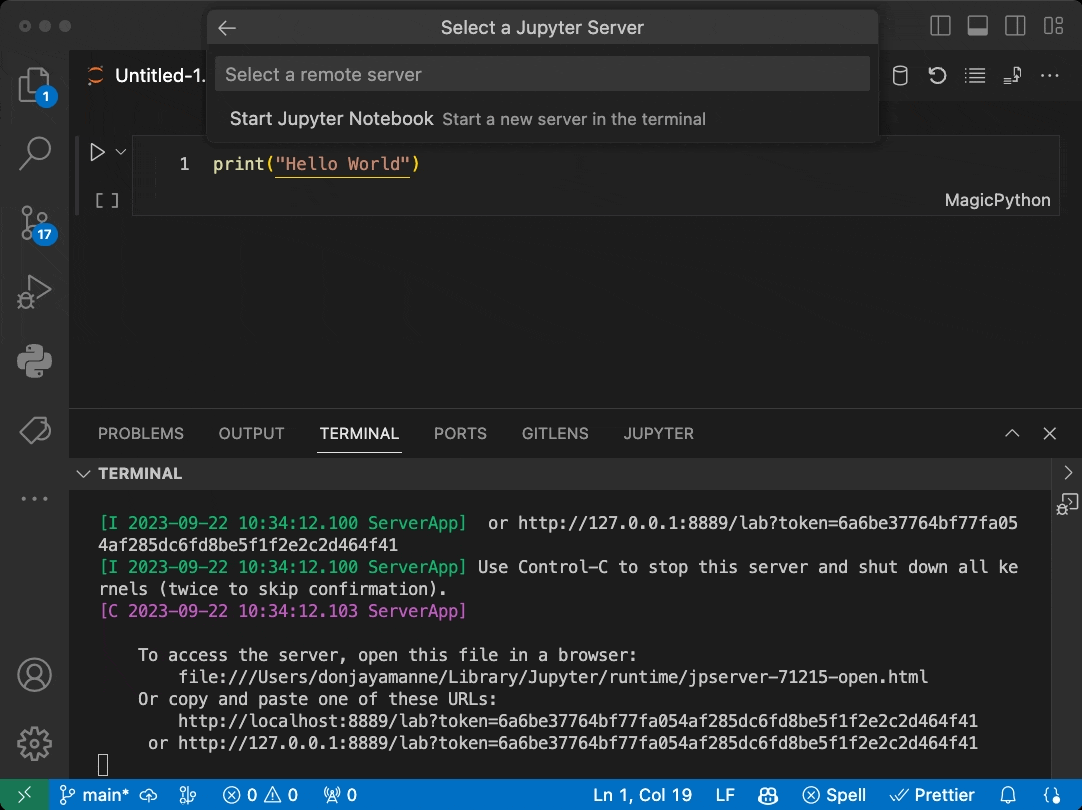
This is a very simple extension sample demonstrating the use of the Jupyter Extension API allowing other extensions to contribute Jupyter Servers via the Kernel Picker for Jupyter notebooks:
- The sample extension finds Jupyter Servers running locally on the current machine
- This list of servers is then provided to the Jupyter extension via the Jupyter Extension API
- Upon opening a notebook and selecting a kernel the option
Local JupyterLab Servers...will display the above servers. - From there, the user can select a kernel and run code in the notebook against one of the local kernels.
- Sample showcases the use of the
backbutton to allow the user to go back to the previous step. - Sample showcases the use of custom quick picks to get additional information from the user.
cd jupyter-server-provider-samplecode .: Open the folder in VS Code- Run
npm installin terminal to install dependencies - Run the
Run Extensiontarget in the Debug View. This will:- Start a task
npm: watchto compile the code - Run the extension in a new VS Code window
- Start a task
- Select the kernel Picker for a notebook and select the option
Local JupyterLab Servers... - To see servers show up in this list, start JupyterLab or Jupyter Notebook outside VS Code or from within the integrated terminal (e.g. jupyter lab)
- When displaying a custom UI in the kernel picker, please ensure to add a
backbutton to allow the user to go back to the previous step. The sample shows the use of thebackbutton and how throwingCancellationErrorvs returningundefinedhelps Jupyter extension distinguish betweencancelvsbackbehaviour. - Minimize creating multiple collections, as this will result in multiple steps to selecting a kernel.