This project maps tree extent at the ten-meter scale using open source artificial intelligence and satellite imagery. The data enables accurate reporting of tree cover in urban areas, tree cover on agricultural lands, and tree cover in open canopy and dry forest ecosystems.
This repository contains the source code for the project. A full description of the methodology can be found on arXiv. The data product specifications can be accessed on the wiki page.
- Background
- Data Extent
- Methodology
- Validation and Analysis | Jupyter Notebook
- Definitions
- Limitations
John Brandt & Fred Stolle (2021) A global method to identify trees outside of closed-canopy forests with medium-resolution satellite imagery, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 42:5, 1713-1737, DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2020.1841324
Utilizing this repository to generate your own data requires:
- Sentinel-Hub API key, see Sentinel-hub
- Amazon Web Services API key (optional) with s3 read/write privileges
The API keys should be stored as config.yaml in the base directory with the structure:
key: "YOUR-SENTINEL-HUB-API-KEY"
awskey: "YOUR-AWS-API-KEY"
awssecret: "YOUR-AWS-API-SECRET"
The code can be utilized without AWS by setting --ul_flag False in download_and_predict_job.py. By default, the pipeline will output satellite imagery and predictions in 6 x 6 km tiles to the --s3_bucket bucket.
git clone https://github.com/wri/sentinel-tree-cover
cd sentinel-tree-cover/
touch config.yaml
vim config.yaml # insert your API keys here
docker build -t sentinel_tree_cover .
docker run -it --entrypoint /bin/bash sentinel_tree_cover:latest
cd src
python3 download_and_predict_job.py --country "country" --year year
- Clone repository
- Install dependencies
pip3 install -r requirements.txt - Install GDAL (different process for different operating systems, see https://gdal.org)
- Download model
python3 src/models/download_model.py - Start Jupyter notebook and navigate to
notebooks/folder
The notebooks/ folder contains ordered notebooks for downloading training and testing data and training the model, as follows:
- 1a-download-sentinel-2: downloads monthly mosaic 10 and 20 meter bands for training / testing plots
- 1b-download-sentinel-1: downloads monthly VV-VH db sigma Sentinel-1 imagery for training / testing plots
- 2-data-preprocessing: Combines satellite imagery for training / testing plots with labelled data from Collect Earth Online
- 3-feature-selection: Feature selection for remote sensing indices utilizing random forests
- 4-model: Trains and deploys tree cover model
The src/ folder contains the source code for the project, as well as the primary entrypoint for the Docker container, download_and_predict_job.py
download_and_predict_job.py can be used as follows, with additional optional arguments listed in the file: python3 download_and_predict_job.py --country $COUNTRY --year $YEAR
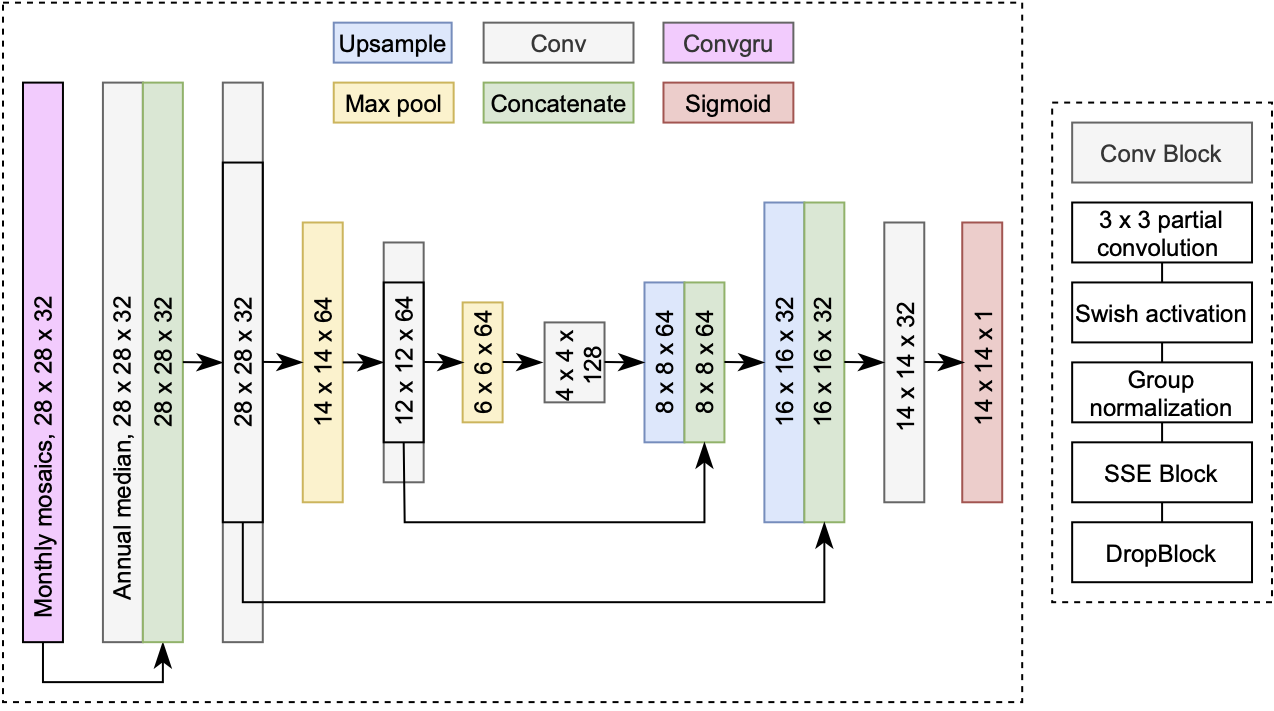
This model uses a U-Net architecture with the following modifications:
- Convolutional GRU encoder with group normalization to develop temporal features of monthly cloud-free mosaics
- Concurrent spatial and channel squeeze excitation in both the encoder and decoder (https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.02579)
- DropBlock and Zoneout for generalization in both the encoder and decoder
- Group normalization and Swish activation in both the encoder and decoder
- AdaBound optimizer with Stochastic Weight Averaging and Sharpness Aware Minimization
- Binary cross entropy and boundary loss
- Smoothed image predictions across moving windows with Gaussian filters
- A much larger input (28x28) than output (14x14) at training time, with 182x182 and 168x168 input and output size in production, respectively
This project uses Sentinel 1 and Sentinel 2 imagery. Monthly composites of Sentinel 1 VV-VH imagery are fused with the nearest Sentinel 2 10- and 20-meter bands. These images are preprocessed by:
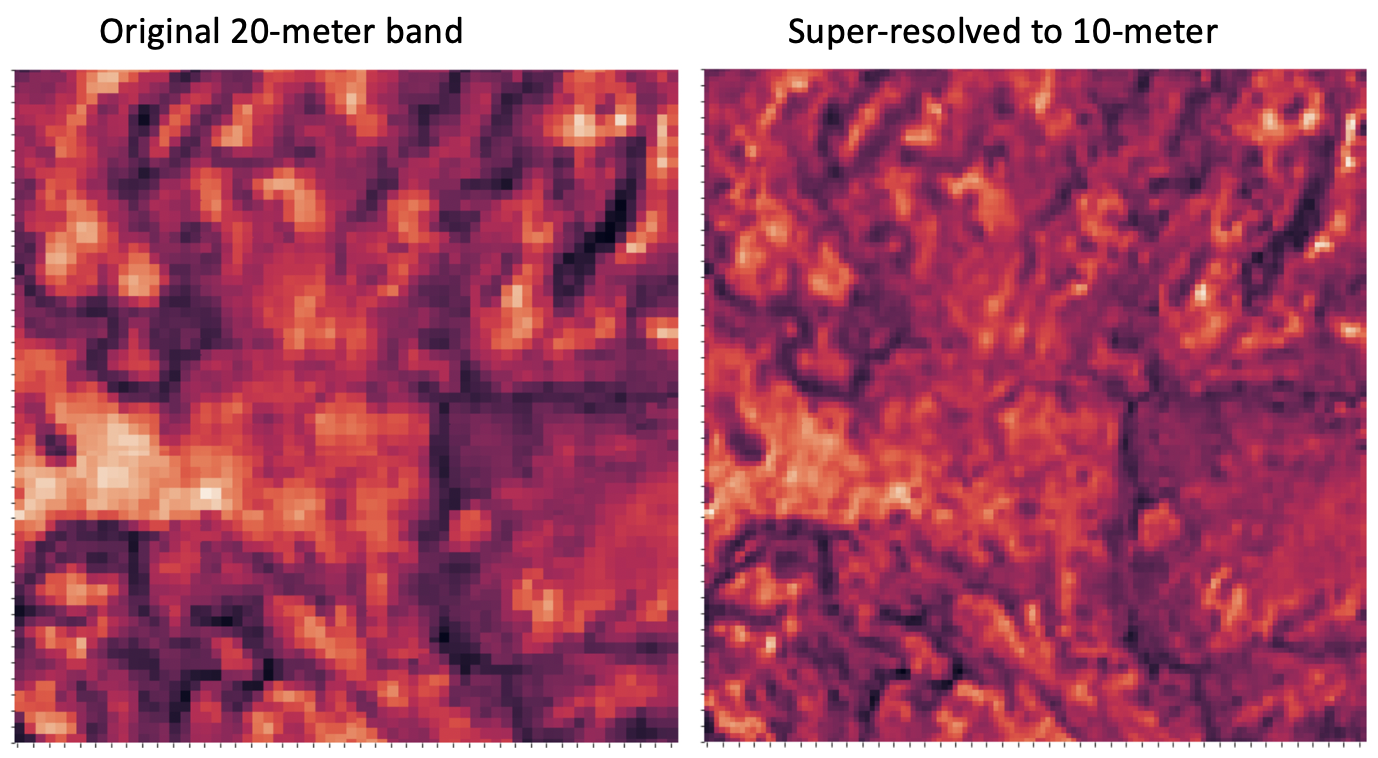
- Super-resolving 20m bands to 10m with DSen2
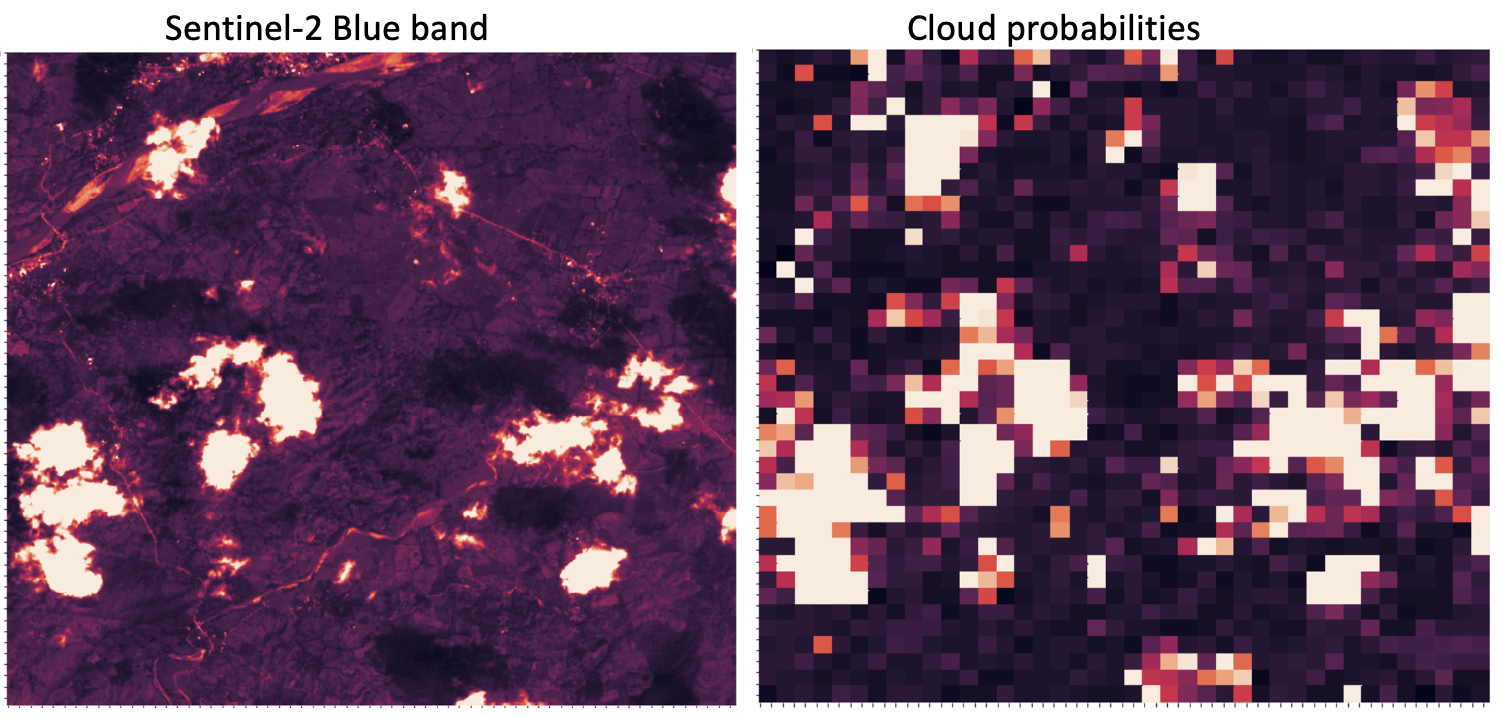
- Calculating cloud cover and cloud shadow masks
- Removing steps with >20% cloud cover, and linearly interpolating to remove clouds and shadows from <20% cloud cover images
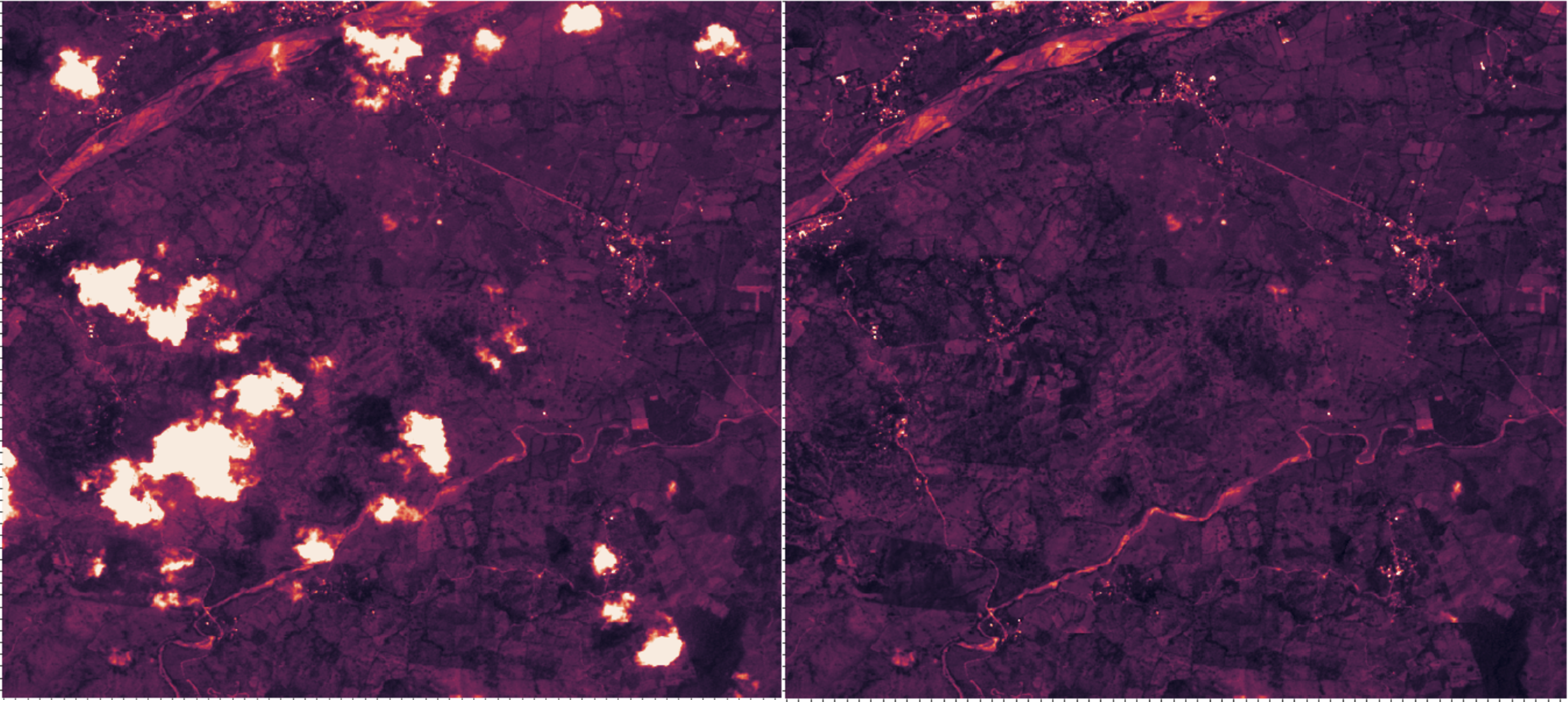
- Applying Whittaker smoothing (lambda = 800) to each time series for each pixel for each band to reduce noise
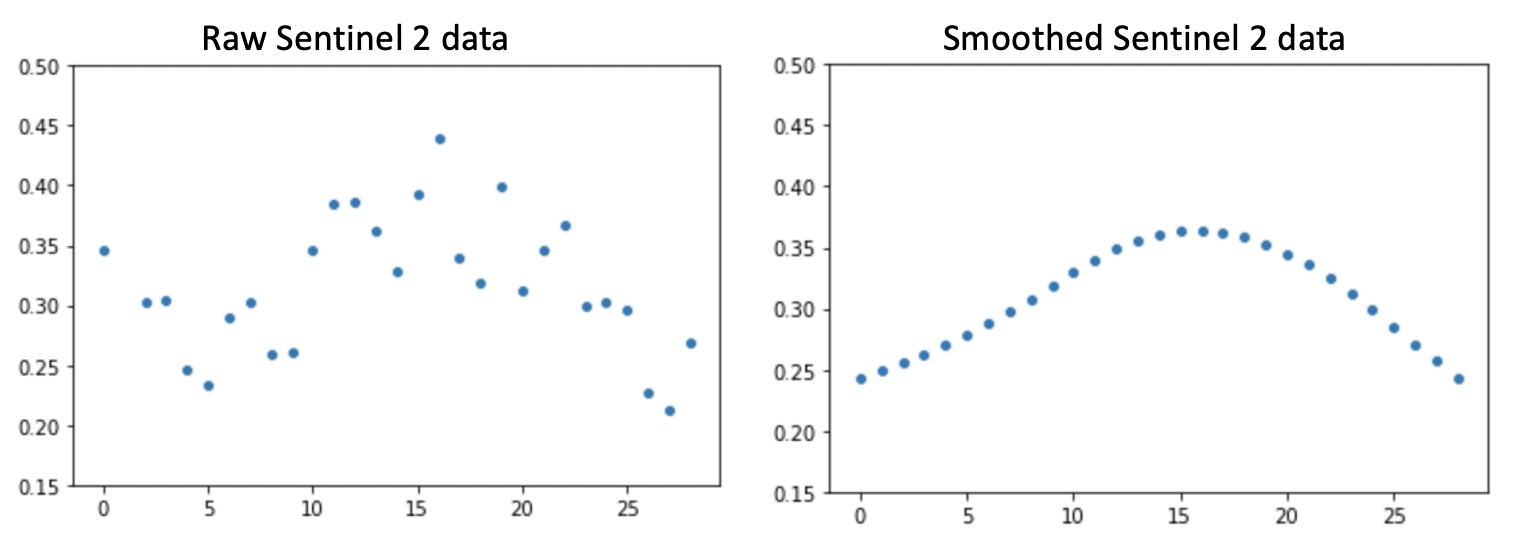
- Calculating vegetation indices, including EVI, BI, and MSAVI2
The cloud / shadow removal and temporal mosaicing algorithm is summarized below:
- Select all images with <30% cloud cover
- Select up to two images per month with <30% cloud cover, closest to beginning and middle of month
- Select least cloudy image if max CC > 15%, otherwise select the image closest to the middle of the month
- Linearly interpolate clouds and cloud shadows with a rolling median
- Smooth time series data with a rolling median
- Linearly interpolate image stack to a 5 day timestep
- Smooth time stack with Whittaker smoother
- Go back through and remove clouds, cloud shadows one final time
The code is released under the GNU General Public License v3.0.
├── LICENSE
├── Makefile <- Makefile with commands like `make data` or `make train`
├── README.md <- The top-level README for developers using this project.
├── docs <- A default Sphinx project; see sphinx-doc.org for details
│
├── models <- Trained and serialized models, model predictions, or model summaries
│
├── notebooks <- Jupyter notebooks
│ └── baseline
│ └── replicate-paper
│ └── visualization
│
├── references <- Data dictionaries, manuals, and all other explanatory materials.
│
├── requirements.txt <- The requirements file for reproducing the analysis environment, e.g.
│ generated with `pip freeze > requirements.txt`
│
├── setup.py <- makes project pip installable (pip install -e .) so src can be imported
├── src <- Source code for use in this project.
│ ├── __init__.py <- Makes src a Python module
│ │
│ ├── data <- Scripts to download or generate data
│ │ └── make_dataset.py
│ │
│ ├── features <- Scripts to turn raw data into features for modeling
│ │ └── build_features.py
│ │
│ ├── models <- Scripts to train models and then use trained models to make
│ │ │ predictions
│ │ ├── predict_model.py
│ │ └── train_model.py
│ │
│ └── visualization <- Scripts to create exploratory and results oriented visualizations
│ └── visualize.py
│
└── tox.ini <- tox file with settings for running tox; see tox.testrun.org