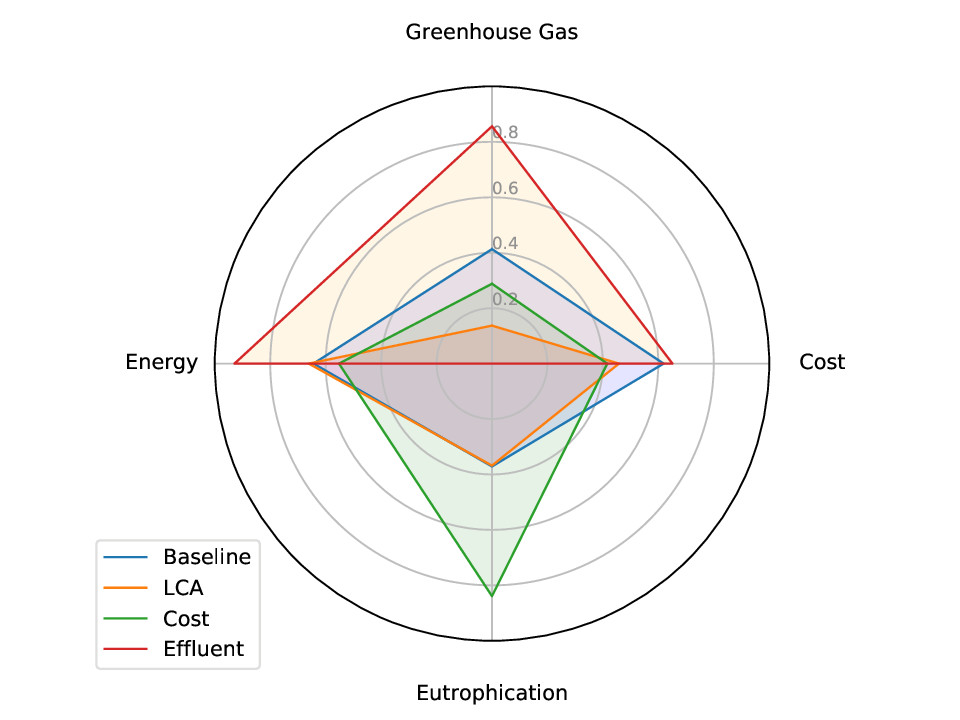
This study used a novel technique, Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning (MADRL), to optimize dissolved oxygen (DO) and dosage in a hypothetical WWTP. The reward function is specially designed as LCA-based form to achieve sustainability optimization. Four scenarios: baseline, LCA-oriented, cost-oriented and effluent-oriented are considered.
The MADDPG learning process mainly follows the original paper and is introduced in this section.
Different from the original paper, Gaussian noise
The result shows that optimization based on LCA has lowest environmental impacts. The comparison of different SRT indicates that a proper SRT can reduce negative impacts greatly. It is worth mentioning that the retrofitting of WWTPs should be implemented with the consideration of other environmental impacts except cost. Moreover, the comparison between DRL and genetic algorithm (GA) indicates that DRL can solve optimization problems effectively and has great extendibility.
@article{
}