-blue.svg)

Tensorflow implementation of Densely Connected Bidirectional LSTM with Applications to Sentence Classification, [arXiv:1802.00889].
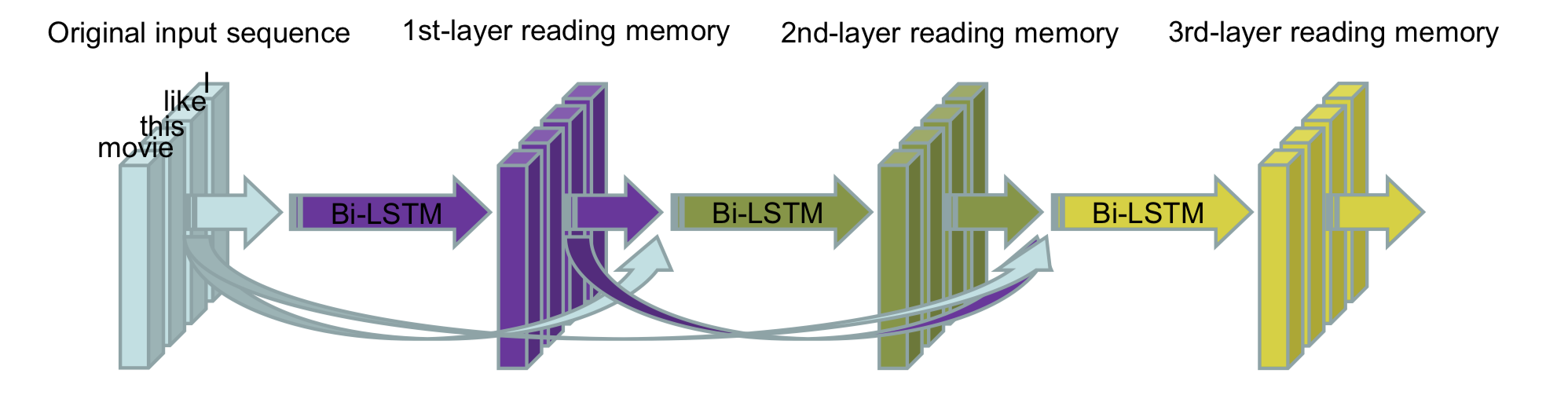
The architecture of DC-Bi-LSTM. The first-layer reading memory is obtained based on original input sequence, and second-layer reading memory based on the position-aligned concatenation of original input sequence and first-layer reading memory, and so on. Finally, get the n-th-layer reading memory and take it as the final feature representation for classification.
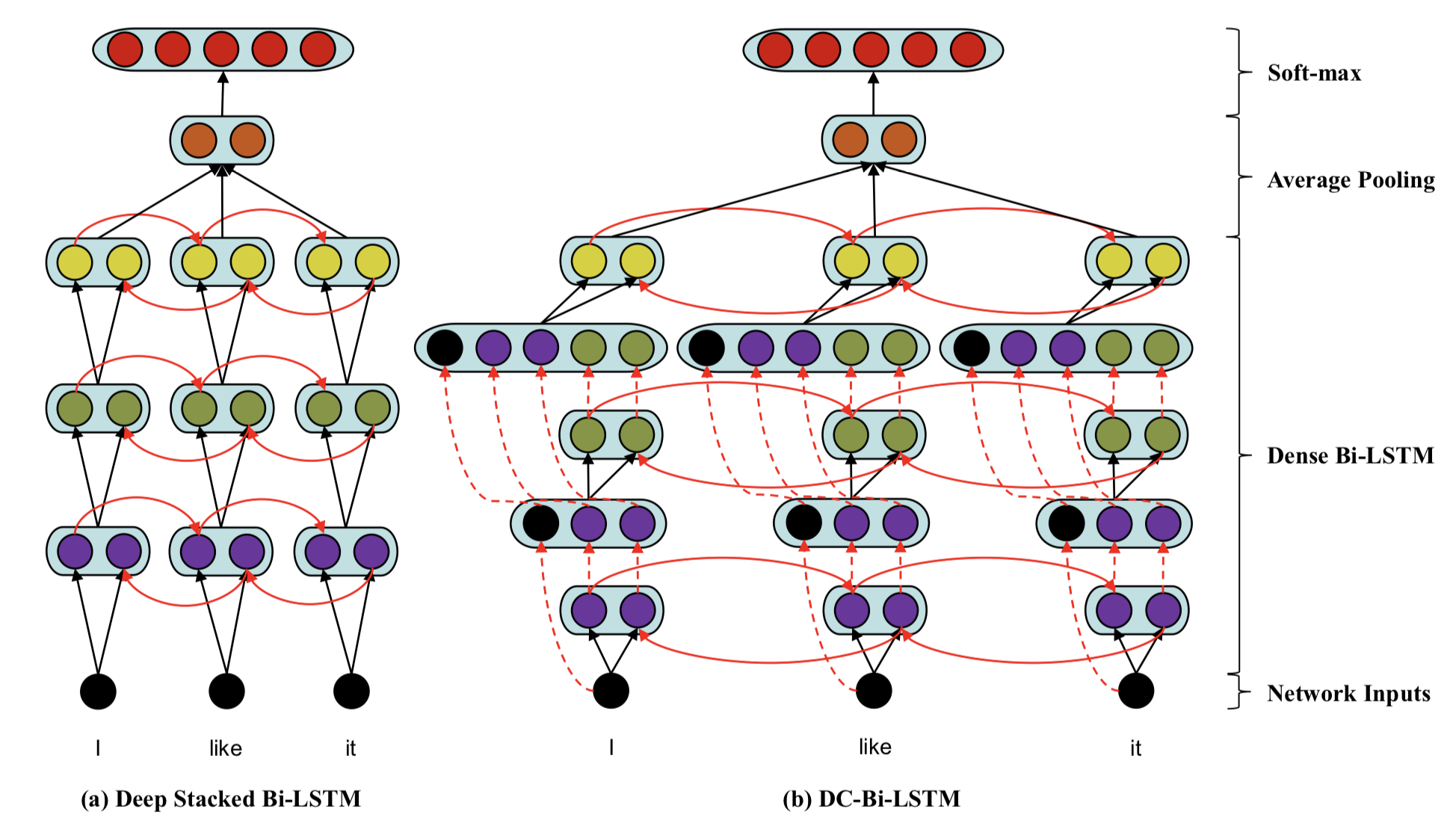
Illustration of (a) Deep Stacked Bi-LSTM and (b) DC-Bi-LSTM. Each black node denotes an input layer. Purple, green, and yellow nodes denote hidden layers. Orange nodes denote average pooling of forward or backward hidden layers. Each red node denotes a class. Ellipse represents the concatenation of its internal nodes. Solid lines denote the connections of two layers. Finally, dotted lines indicate the operation of copying.
More details of datasets are shown here: [dataset/raw/README.md]
| Dataset | Classes | Average sentence length | Dataset size | Vocab size | Number of words present in word2vec | Test size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR | 2 | 20 | 10662 | 18765 | 16448 | CV |
| SST1 | 5 | 18 | 11855 | 17836 | 16262 | 2210 |
| SST2 | 2 | 19 | 9613 | 16185 | 14838 | 1821 |
| Subj | 2 | 23 | 10000 | 21323 | 17913 | CV |
| TREC | 6 | 10 | 5952 | 9592 | 9125 | 500 |
| CR | 2 | 19 | 3775 | 5340 | 5046 | CV |
| MPQA | 2 | 3 | 10606 | 6246 | 6083 | CV |
CV means cross validation
Configuration: all parameters and configurations are stored in models/config.py.
The first step is to prepare the required data (pre-trained word embeddings and raw datasets). The raw datasets are already included in this repository, which are located at dataset/raw/, word embeddings used in the paper, the 300-dimensional Glove vectors that were trained on 42 billion words, can be obtained by
$ cd dataset
$ ./download_emb.shAfter downloading the pre-trained word embeddings, run following to build training, development and testing dataset among all raw datasets, the built datasets will be stored in dataset/data/ directory.
$ cd dataset
$ python3 prepro.pyThen training model on a specific dataset via
$ python3 train_model.py --task <str> --resume_training <bool> --has_devset <bool>
# eg:
$ python3 train_model.py --task subj --resume_training True --has_devset FalseIf everything goes properly, then the training process will be launched
...
word embedding shape: [None, None, 350]
dense bi-lstm outputs shape: [None, None, 200]
average pooling outputs shape: [None, 200]
logits shape: [None, 2]
params number: 1443400
No checkpoint found in directory ./ckpt/subj/, cannot resume training. Do you want to start a new training session?
(y)es | (n)o: y
Start training...
Epoch 1/30:
45/45 [==============================] - 567s - train loss: 0.5043
Testing model over TEST dataset: accuracy - 91.100
-- new BEST score on TEST dataset: 91.100
...
Epoch 4/30:
45/45 [==============================] - 519s - train loss: 0.1998
Testing model over TEST dataset: accuracy - 94.200
-- new BEST score on TEST dataset: 94.200
Epoch 6/30:
45/45 [==============================] - 505s - train loss: 0.1534
Testing model over TEST dataset: accuracy - 94.500
-- new BEST score on TEST dataset: 94.500
Epoch 7/30:
45/45 [==============================] - 530s - train loss: 0.1415
Testing model over TEST dataset: accuracy - 94.000
...Here only test the model on several datasets with some epochs to validate if the model works properly.
experiments on MacBook Pro (13-inch, 2017) with 3.1GHz Intel Core i5 CPU and 16GB 2133MHz LPDDR3 RAM
| Dataset | Train Epochs | Batch Size | Dev | Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR | 11 (w/o cross-validation) | 200 | N.A. | 82.4 |
| SST1 | 20 | 200 | 50.9 | 51.2 |
| SST2 | 13 | 200 | 84.7 | 88.1 |
| Subj | 6 (w/o cross-validation) | 200 | N.A. | 94.5 |
| TREC | 15 | 128 | N.A. | 94.7 |
| CR | 10 (w/o cross-validation) | 64 | N.A. | 82.9 |
| MPQA | 5 (w/o cross-validation) | 64 | N.A. | 87.3 |
the evaluation results on some datasets are slightly lower than those proposed in the paper may caused by data processing, different parameter settings (like, batch size, learning rate, learning rate decay, grad clip, char emb and etc.) or without applying cross-validation.