Yaetos is a framework to write data pipelines on top of Pandas and Spark, and deploy them to Amazon Web Services (AWS). It can run locally or on AWS (using S3 datasets and running the process on an AWS cluster). The focus is on making simple things easy and complex things possible (and as easy as can be). It's name stands for "Yet Another ETL Tool on Spark".
- In the simplest cases, pipelines consist of SQL files only. No need to know any programming. Suitable for business intelligence use cases.
- In more complex cases, pipelines consist of python files, giving access to Pandas, Spark dataframes, RDDs and any python library (scikit-learn, tensorflow, pytorch). Suitable for AI use cases.
It integrates several popular open source systems:
Some features:
- The ability to run jobs locally and on a cluster in the cloud without any changes.
- The support for dependencies across jobs
- The support for incremental jobs (inc. idempotency)
- The automatic creation of AWS clusters when needed.
- The support for git and unit-tests
- The ability to integrate any python library in the process (ex: machine learning libraries).
yaetos_cmdline_demo_jobs_v3.mp4
Run the commands from the "installation instructions" section below. Then run this sql example locally with:
yaetos run_dockerized jobs/generic/launcher.py --job_name=examples/ex1_sql_job.sql
It will open the manifesto file (jobs_metadata.yml), find the job called examples/ex1_sql_job.sql, i.e. these lines, get the job parameters from there (input paths, output path...), execute the transform defined in the job ex1_sql_job.sql using sparkSQL engine, and dump the output here. To run the same sql example on an AWS cluster, add --deploy=EMR to the same command line above. In that case, inputs and outputs will be taken from S3, as defined by the base_path param in the manifesto here. If you don't have a cluster available, it will create one and terminate it after the job is finished. You can see the status on the job process in the "steps" tab of your AWS EMR web page.
For the rest of the documentation, we will go in the docker environment with the following command, and will execute the commands from there.
yaetos launch_docker_bash
To run an ETL that showcases manipulation of a spark dataframes, more flexible than the sql example above, run this frameworked pyspark example ex1_frameworked_job.py with this:
python jobs/examples/ex1_frameworked_job.py
To try an example with job dependencies, run ex4_dependency4_job.py with this:
python jobs/examples/ex4_dependency4_job.py --dependencies
It will run all 3 dependencies defined in the jobs_metadata registry. There are other examples in jobs/examples/.
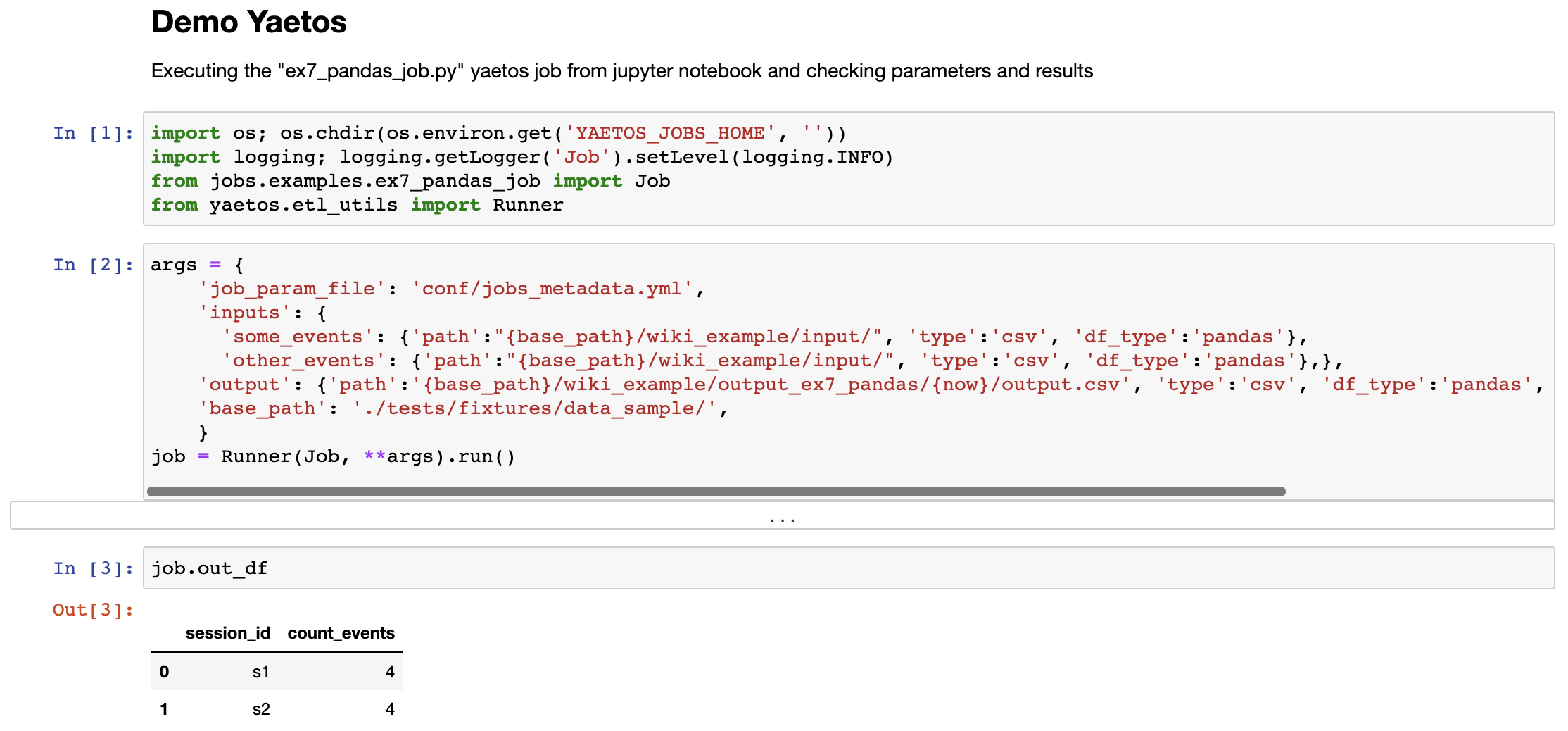
To explore jobs in jupyter notebooks, from the host OS:
yaetos launch_docker_jupyter
Then, open a browser, go to http://localhost:8888/tree/notebooks, open inspect_ex4_dependencies4_job.ipynb. It will look like this:
To create dashboards, Yaetos integrates "Panel" python library (https://panel.holoviz.org/). Dashboards can be defined in jupyter notebooks (see example in ./dashboards folder) and published using "Panel".
To write a new ETL, create a new file in the jobs/ folder or any subfolders, either a .sql file or a .py file, following the examples from that same folder, and register that job, its inputs and output path locations in conf/jobs_metadata.yml. To run the jobs, execute the command lines following the same patterns as above:
python jobs/generic/launcher.py --job_name=examples/some_sql_file.sql
# or
python jobs/examples/some_python_file.py
Extra arguments:
- To run the job with its dependencies: add
--dependencies - To run the job in the cloud: add
--deploy=EMR - To run the job in the cloud on a schedule: add
--deploy=airflow
Jobs can be unit-tested using py.test. For a given job, create a corresponding job in tests/jobs/ folder and add tests that relate to the specific business logic in this job. See tests/jobs/ex1_frameworked_job_test.pyfor an example.
Depending on the parameters chosen to load the inputs ('df_type':'pandas' in conf/jobs_metadata.yml), the job will use:
- Spark: for big-data use cases in SQL and python
- DuckDB and Pandas: for normal-data use cases in SQL
- Pandas: for normal-data use cases in python
... is done using py.test. Run them with:
yaetos launch_docker_bash
# From inside the docker container
pytest tests/*
yaetos_cmdline_demo_install_v1.mp4
To install the library and create a folder with all necessary files and folders:
pip install yaetos
cd /path/to/an/empty/folder/that/will/contain/pipeline/code
yaetos setup # to create sub-folders and setup framework files.
An example of the folder structure is available at github.com/arthurprevot/yaetos_jobs with more sample jobs. The tool can also be used by cloning this repository, mostly for people interested in contributing to the framework itself. Feel free to contact the author if you need more details on setting it up that way.
The setup comes with a docker environment with all libraries necessary (python and spark). It also comes with sample jobs pulling public data. To test running one of the sample job locally, in docker:
yaetos run_dockerized jobs/examples/ex1_frameworked_job.py --dependencies
The docker container is setup to share the current folder with the host, so ETL jobs can be written from your host machine, using any IDE, and run from the container directly.
To get jobs executed and/or scheduled in AWS, You need to:
- fill AWS parameters in
conf/config.cfg. - have
~/.aws/folder setup to give access to AWS secret keys. If not, runpip install awscli, andaws configure.
To check running the same job in the cloud works:
yaetos run_dockerized jobs/examples/ex1_frameworked_job.py --dependencies --deploy=EMR
The status of the job can be monitored in AWS in the EMR section.
This repository includes few jobs or data pipelines to demonstrate Yaetos core functionalities. More "businessy" use cases are available in a separate repository at github.com/arthurprevot/yaetos_jobs. They include:
- Data pipelines to pull information out of ChatGPT programmatically, to feed into datasets.
- Data pipelines to fine tune a "small" open source LLM (aka generative AI), called Albert, for classification, and to run inferences. The model is small enough to run from a laptop (no need for GPU).
- Data pipelines to pull employee contact information out of Apollo.io for a set of companies.
- Data pipelines to process images (could be satellite, medical, etc) to find contours (@ scale, using Spark).
- Data pipelines to process carbon emissions data from climate-trace (https://climatetrace.org/).
- Data pipelines to pull information from Github contributors using Github API.
- more unit-testing
- integration with other resource provisioning tools (kubernetes...)
- integration with complementary open source data tools (great expectations, airbyte...)
- adding type annotations to code and type checks to CI
- automatic pulling/pushing data from s3 to local (sampled) for local development
- easier dataset reconciliation
- ...
Lots of room for improvement. Contributions welcome. Feel free to reach out at [email protected]