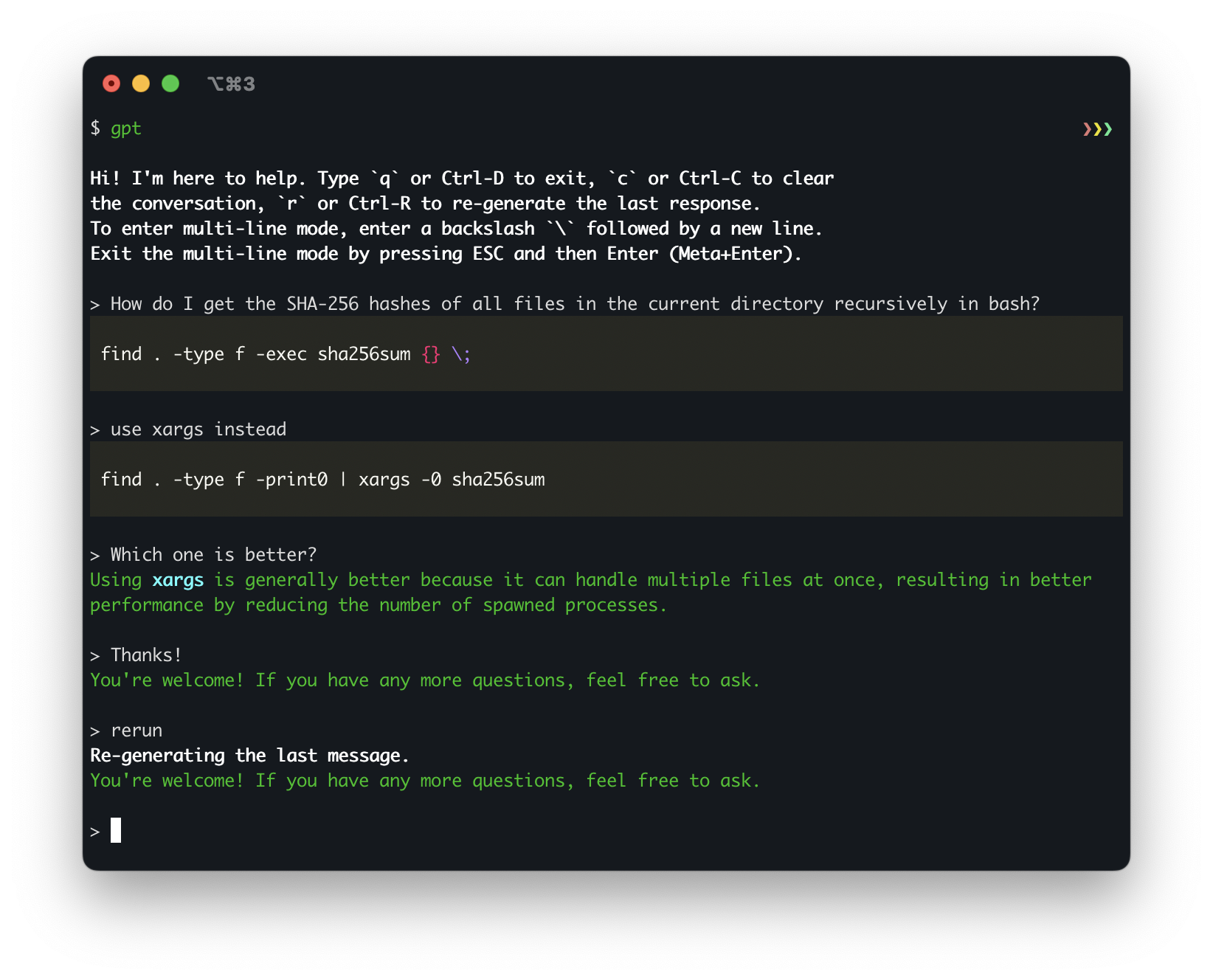
Command-line interface for ChatGPT.
- Command-Line Interface: Interact with ChatGPT directly from your terminal.
- Model Customization: Override the default model, temperature, and top_p values for each assistant, giving you fine-grained control over the AI's behavior.
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Use Ctrl-C, Ctrl-D, and Ctrl-R shortcuts for easier conversation management and input control.
- Multi-Line Input: Enter multi-line mode for more complex queries or conversations.
- Markdown Support: Enable or disable markdown formatting for chat sessions to tailor the output to your preferences.
- Predefined Messages: Set up predefined messages for your custom assistants to establish context or role-play scenarios.
- Multiple Assistants: Easily switch between different assistants, including general, dev, and custom assistants defined in the config file.
- Flexible Configuration: Define your assistants, model parameters, and API key in a YAML configuration file, allowing for easy customization and management.
At present, the simplest way is to clone the repository to your machine and then install the tool as described below.
This install assumes a Linux/OSX machine with python and pip available.
git clone https://github.com/kharvd/gpt-cli
cd gpt-cli
pip install -r requirements.txtAdd the OpenAI API token to your .bashrc file (in the root of your home folder).
In this example we use nano, you can use any text editor.
nano ~/.bashrc
export OPENAI_API_TOKEN=<your_token_here>
Run the tool
python gpt.py
You can also use a .gptrc file for configuration. See the Configuration section below.
Make sure to set the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable to your OpenAI API key (or put it in the ~/.gptrc file as described below).
usage: gpt.py [-h] [--no_markdown] [--model MODEL] [--temperature TEMPERATURE] [--top_p TOP_P]
[--prompt PROMPT] [--execute EXECUTE] [--no_stream]
[{dev,general,bash}]
Run a chat session with ChatGPT. See https://github.com/kharvd/gpt-cli for more information.
positional arguments:
{dev,general,bash} The name of assistant to use. `general` (default) is a generally helpful
assistant, `dev` is a software development assistant with shorter
responses. You can specify your own assistants in the config file
~/.gptrc. See the README for more information.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--no_markdown Disable markdown formatting in the chat session.
--model MODEL The model to use for the chat session. Overrides the default model defined
for the assistant.
--temperature TEMPERATURE
The temperature to use for the chat session. Overrides the default
temperature defined for the assistant.
--top_p TOP_P The top_p to use for the chat session. Overrides the default top_p defined
for the assistant.
--prompt PROMPT, -p PROMPT
If specified, will not start an interactive chat session and instead will
print the response to standard output and exit. Use `-` to read the prompt
from standard input.
--execute EXECUTE, -e EXECUTE
If specified, passes the prompt to the assistant and allows the user to
edit the produced shell command before executing it. Implies --no_stream.
Use `-` to read the prompt from standard input.
--no_stream If specified, will not stream the response to standard output. This is
useful if you want to use the response in a script. Ignored when the
--prompt option is not specified.
Type q or Ctrl-D to exit, c or Ctrl-C to clear the conversation, r or Ctrl-R to re-generate the last response.
To enter multi-line mode, enter a backslash \ followed by a new line. Exit the multi-line mode by pressing ESC and then Enter.
You can override the model parameters using --model, --temperature and --top_p arguments at the end of your prompt. For example:
> What is the meaning of life? --model gpt-4 --temperature 2.0
The meaning of life is subjective and can be different for diverse human beings and unique-phil ethics.org/cultuties-/ it that reson/bdstals89im3_jrf334;mvs-bread99ef=g22me
The dev assistant is instructed to be an expert in software development and provide short responses.
$ ./gpt.py devThe bash assistant is instructed to be an expert in bash scripting and provide only bash commands. Use the --execute option to execute the commands. It works best with the gpt-4 model.
./gpt.py bash -e "How do I list files in a directory?"This will prompt you to edit the command in your $EDITOR it before executing it.
You can configure the assistants in the config file ~/.gptrc. The file is a YAML file with the following structure:
default_assistant: <assistant_name>
markdown: False
api_key: <openai_api_key>
assistants:
<assistant_name>:
model: <model_name>
temperature: <temperature>
top_p: <top_p>
messages:
- { role: <role>, content: <message> }
- ...
<assistant_name>:
...You can override the parameters for the pre-defined assistants as well.
You can specify the default assistant to use by setting the default_assistant field. If you don't specify it, the default assistant is general. You can also specify the model, temperature and top_p to use for the assistant. If you don't specify them, the default values are used. These parameters can also be overridden by the command-line arguments.
Example:
default_assistant: dev
markdown: True
api_key: <openai_api_key>
assistants:
pirate:
model: gpt-4
temperature: 1.0
messages:
- { role: system, content: "You are a pirate." }$ ./gpt.py pirate
> Arrrr
Ahoy, matey! What be bringing ye to these here waters? Be it treasure or adventure ye seek, we be sailing the high seas together. Ready yer map and compass, for we have a long voyage ahead!