A HEADER FILE project with macros that can change text color/style and move cursor in CONSOLE by ANSI Escape Codes, and some utility macros for CUDA and Qt.
Homepage: https://github.com/BH2WFR/ConsoleUtil
author: BH2WFR
LICENSE: MIT License
Reference of Ansi Escape Codes:
| name | author | link | path | license |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| scope_guard | ricab | https://github.com/ricab/scope_guard | include/scope_guard |
Unlicense |
| xorstr | JustasMasiulis | https://github.com/JustasMasiulis/xorstr | include/xorstr |
Apache 2.0 |
| yamc | yohhoy | https://github.com/yohhoy/yamc | include/LegacyUtil/yamc |
MIT |
| span | tcbrindle | https://github.com/tcbrindle/span | include/LegacyUtil/span |
BSL 1.0 |
-
features using Ansi Escape code (like color customizing, or cursor moving macros in this header file) DO NOT SUPPORT Windows version lower than Windows 10 1511, otherwise it can't display properly in windows cmd.
- If you are using these operating systems, pls
#define CONSOLE_UTIL_ANSI_ESCAPE_UNSUPPORTED 1before#include <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h>to disable features by printing Ansi Escape Code.
- If you are using these operating systems, pls
-
C language version
≥ C99, C++ language≥ C++98, with##__VA_ARGS__extension support.(MSVC supports
##__VA_ARGS__since VS2015 Update 3. if your MSVC or VS version is older, pls delete "##", MSVC eats trailing comma before__VA_ARGS__by default without/Zc::preprocessorcommand) -
Pls #include the header file <
ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h> after other header files, especially those from libraries such as Qt/fmtlib. DO NOT #include <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h> in header files. -
You can include <
ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> in header files. No need to include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> in source files if you already included <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h>, because it has been included in <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h>. -
DO NOT use macros with name starting with underscore
_externally, such as_CUTIL_EXPAND_MSVC().
#include <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h> // already wrapped in <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h>-
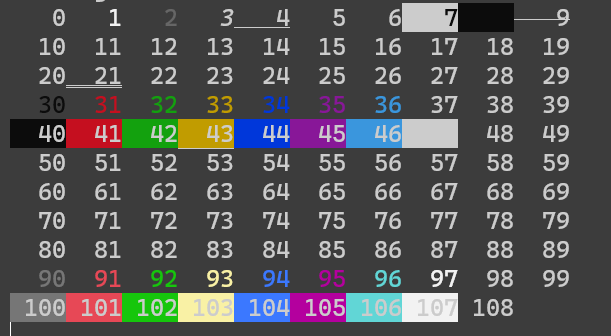
Set Front Color, Back Color, and font style for messages to print by printf/cout.
Forecolors:
FBlack,FRed,FGreen,FYellow,FBlue,FMagenta,FCyan,FWhite,FDefault,FRgb(66, 66, 66)Bright Forecolors:
FGray(=FGrey,FLBlack),FLRed,FLGreen,FLYellow,FLBlue,FLMagenta,FLCyan,FLWhite;Backcolors:
BBlack,BRed,BGreen,BYellow,BBlue,BMagenta,BCyan,BWhite,BDefault,BRgb(66, 66, 66);Bright Backcolors:
BGray(=BGrey,BLBlack),BLRed,BLGreen,BLYellow,BLBlue,BLMagenta,BLCyan,BLWhite;Font Styles:
CBold,CWeak,CItalic,CUnderLine,CFlash,CQFlash,CInvert(swap fg and bg colors),CHide;Reset to Default:
CRstorCReset, you must append this to the end of the string literal to revert console style back to default.printf(BRed FLGreen CQFlash "test" CReset "\n"); // Red Background, Light Green Text Forecolor, and flashing quickly std::cout << CCyan "test" CReset << "\n"; // Text forecolor: cyan fmt::println(CYellow "test" CReset); // Text forecolor: yellow
-
Control text cursor location in console, or erase text.
Move cursor:
CUp(2),CDown(3),CFwd(4),CBack(5),CNextLn(1),CPrevLn(1),
CHorzPos(12)(column X, absolute),CPos(44, 55)(move the cursor to row 44, column 55)Just print them, use individual or append to string literals.
printf(CForward(2)); // move thr cursor 2 characters right, equals to `CRight(2)` or `CFwd(2)`. printf(CCursorPos(15, 20)); // move the text cursor to (15, 20) position CUTIL_CONSOLE_CURSOR_POS(15, 20); // equivalent, calls SetConsoleCursorPosition() in win32.
-
set console encoding, console window size (in windows), or console title, also with pause program and force abort the program.
CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_UTF8(); // switch console encoding to UTF-8 (windows) CUTIL_CONSOLE_TITLE("MyProject"); // set console window title (calls SetConsoleTitleA() or SetConsoleTitleW() for windows, and print ansi escape code "\033]0;%s\007" for linux) // CUTIL_CONSOLE_TITLE(_TEXT("MyProgram")); // CUTIL_CONSOLE_TITLE_A("MyProgram"); // CUTIL_CONSOLE_TITLE_W(L"MyProgram"); CUTIL_CONSOLE_SIZE(100, 30); // set console window size to with of 30 chars and height of 30 lines (only available in windows) CUTIL_CONSOLE_CLEAR(); // clear console (calls system("cls") ) printf("中文한글\n"); // you can correctly display this when the code saved in UTF-8 Encoding, especially in MSVC Compiler.
// available encodings: CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_UTF8(); CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_GB2312(); CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_BIG5(); CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_KOR(); CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_JIS(); CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_LATIN1(); CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_LATIN2(); CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_CYR(); CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_WIN1250(); CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_WIN1251(); CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_WIN1252();
- set program locale to
UTF-8
CUTIL_LOCALE_UTF8(); // setlocale(LC_ALL, ".UTF-8") CUTIL_LOCALE_DEFAULT() // setlocale(LC_ALL, "") CUTIL_LOCALE_UTF8_PRINT() // print if succeed or not
- set program locale to
-
Print Text only in Debug Build, and do Not Print in Release Build.
pls make sure that macro "
_DEBUG" is defined in Debug Build, or macro "NDEBUG" is defined in Release Build.int a{1}; CUTIL_DEBUG_PRINTLN("debug text {}", a); // calls fmt::println()(fmtlib) or std::println()(C++23) CUTIL_DEBUG_COUT("debug text " << a << '\n'); // calls std::cout << CUTIL_DEBUG_PRINTF("debug text %d", a); // calls printf() // these function-like macros will DO NOTHING IN RELEASE BUILD. CUTIL_DEBUG_PRINTLN_ERR("debug stderr text {}", a); // print to stderr CUTIL_DEBUG_CERR("debug stderr text " << a << '\n'); CUTIL_DEBUG_PRINTF_ERR("debug stderr text %d", a);
-
Flush the input buffer to ensure that subsequent "scanf()" or "cin" calls receive valid input.
(吸收输入缓存区内的其余字符, 以便下次 scanf 或 cin 时能够获取到正确的输入内容)
// #define CUTIL_FLUSH_INPUT_BUFFER() {char ch; while((ch = getchar()) != '\n') continue;} int num1, num2; scanf("%d", &num1); // you inputed "123ss", then still remains characters "ss" in the input buffer CUTIL_CONSOLE_FLUSH_INPUTBUFFER(); // flush input buffer (clear) scanf("%d", &num2); // you can normally input other contents.
-
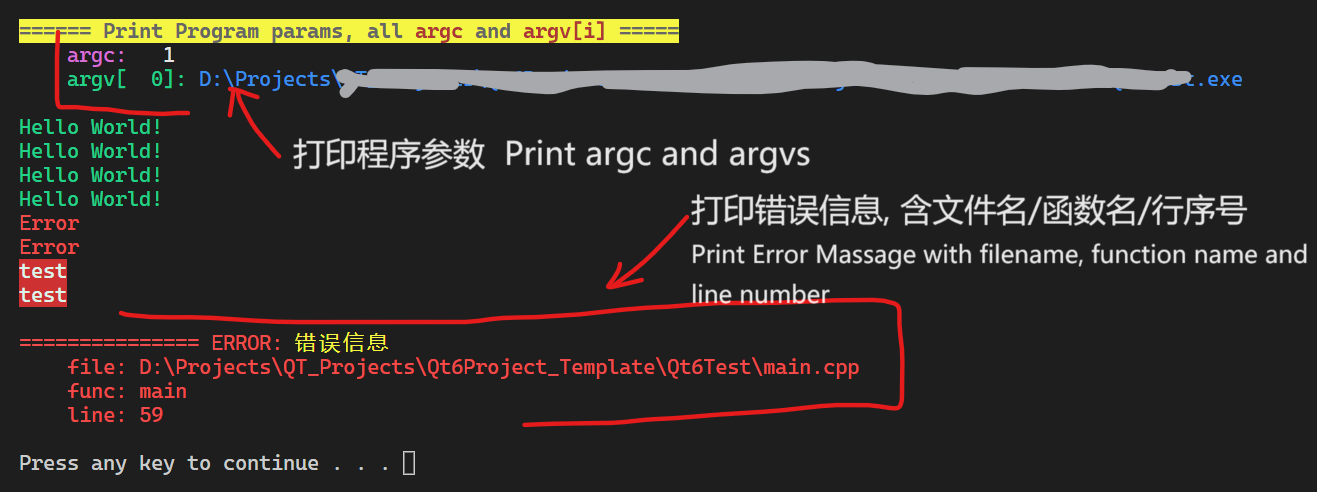
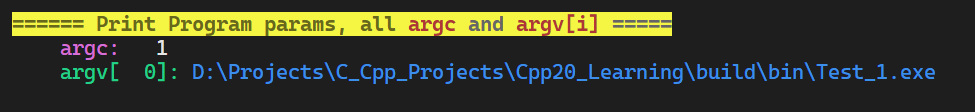
print argc and argv arguments of main(int argc, char* argv[]) function in sequence.
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ CUTIL_PRINT_ARGV(argc, argv);// print all argc and argv[n] of main() function return 0; }
-
Print custom Error Message with filename, line number and function name
打印错误信息,并输出当前文件名、行号、函数名
-
Other useful C/C++ Macros
#include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> // already wrapped in <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h>, you can include the latter instead in source files. // <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> can be included in header files.
-
decide if the project is under debug build or Release build mode.
in MSVC, macro
_DEBUGis defined under debug build; in GCC, macroNDEBUGis defined under release build.you can add
add_compile_definitions("$<IF:$<CONFIG:Debug>,_DEBUG,NDEBUG>")in CMake.#include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> #if CUTIL_DEBUG_BUILD // Debug //... #else // Release RelWithDebInfo MinSizeRel //... #endif
-
set bit to a unsigned integer variable in some hardware projects; rotate bits
use
std::bitset<>in C++.#include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> uint16_t num {0b00000000'00000001}; // C++14 // operate bit by index, starts at 0. use them in a seperate line, and returns nothing CUTIL_BIT_SET_IDX(num, 0); // equals to {num |= (1u << 0));} CUTIL_BIT_CLEAR_IDX(num, 2); // equals to {num &= ~(1u << 2));} CUTIL_BIT_FLIP_IDX(num, 3); // equals to {num ^= (1u << 3));} if(CUTIL_BIT_GET_IDX(num, 0) != 0){ // reading bit, if bit is 1, returns `(1<<BIT_IDX)`, NOT 1 printf("%x\n", num); } if(CUTIL_BIT_CHECK_IDX(num, 0) == 1){ // reading bit, if bit is 1, returns `1`, `!= CUTIL_BIT_GET_IDX()` printf("%x\n", num); } // operate bit by mask CUTIL_BIT_SET_MASK(num, 0x2B00); // equals to {num |= 0x2B00;} CUTIL_BIT_CLEAR_MASK(num, 0x2B00); // equals to {num &= ~0x2B00;} CUTIL_BIT_FLIP_MASK(num, 0x1100); // equals to {num ^= 0x1100;} if(CUTIL_BIT_GET_MASK(num, 0x0022) != 0){ // returns (num & 0x0022) printf("%x\n", num); } // rotate bits. use them in a seperate line, and returns nothing uint16_t var{0x1234}; CUTIL_BIT_ROTATE_LEFT_SIZE(8*sizeof(uint16_t), var, 1); // rotate bits of `var` by 1 bit step CUTIL_BIT_ROTATE_RIGHT_SIZE(8*sizeof(uint16_t), var, 1); CUTIL_BIT_ROTATE_LEFT_TYPE(std::decay<decltype(var)>::type, var, 1); // equivelent, also `typeof` for GNU C or C23 CUTIL_BIT_ROTATE_RIGHT_TYPE(std::decay<decltype(var)>::type, var, 1); CUTIL_BIT_ROTATE_LEFT(var, 1); // equivelent, C++, GNU C, C23 only CUTIL_BIT_ROTATE_RIGHT(var, 1);
- get high or low byte (uint8_t) of a word (uint16_t)
uint16_t v {0x1234}; printf("%x \n", v); // -> 1234 printf("%x %x \n", CUTIL_GET_WORD_HIGH(v), CUTIL_GET_WORD_LOW(v)); // -> 12 34 printf("%x %x \n", CUTIL_SET_WORD_HIGH(v, 0xFE), CUTIL_SET_WORD_LOW(v, 0xBA)); // -> FE BA printf("%x \n", v); // -> FEBA
-
convert variable to another type bitwise
use
std::bit_cast<NewType>after C++20.
uint32_t i = 0x12345678; float f; CUTIL_BITWISE_MEMCPY(float, &f, &i); // assign `i` to `f` bitwise // -> memcpy(&f, &i, sizeof(float)) f = CUTIL_BITWISE_CAST_UNSAFE(float, &f) // UB, unrecommended // -> f = (* (volatile float*) (volatile void*) &i); // auto f = std::bit_cast<float>(i) // C++20
-
swap variables in C
WARNING: DO NOT use for C arrays!
types of
_VAR1and_VAR2should be strictly equaldo not use in C++, pls replace with
std::swap()#include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> uint32_t a = 1, b = 2; // type of `a` and `b` must be strictly equal. CUTIL_SWAP(a, b); // in C++(std::decay<decltype(var)>::type), GNU C(typeof), or C23(typeof) CUTIL_SWAP_TYPE(uint32_t, a, b); // equivelent, specify the type. CUTIL_SWAP_TYPE(typeof(a), a, b); // equivelent, in GNU C or C23 CUTIL_SWAP_TYPE(std::decay<decltype(var)>::type, a, b); // equivelent in C++, but prefer to use `std::swap()`
-
get the bigger or smaller item between two numeric variables.
use
std::min()andstd::maxin C++.
uint32_t a = 1, b = 2; // type of `a` and `b` must be strictly equal. int max_ab = CUTIL_MAX(a, b); // bigger number between a and b int min_ab = CUTIL_MIN(a, b); // smaller number between a and b max_ab = std::max(a, b); // equivalent to above in C++
-
limit the numeric variable in range, and get if the value of variable is within the range
recommended to use
var = std::clamp(var, min, max)after C++17.
int a = 35, b = 26, c = 19, d = 35; CUTIL_LIMIT(a, 20, 30); // a: 35 -> 30 CUTIL_LIMIT(b, 20, 30); // b: 26 CUTIL_LIMIT(c, 20, 30); // c: 19 -> 20 d = CUTIL_CLAMP(d, 20, 30); // d: 35 -> 30, only returns value d = std::clamp(d, 20, 30); // C++17, equivalent to above printf("%d %d %d\n", a, b, c); // output: 30 26 20 printf("%d %d", CUTIL_IN_RANGE(a, 20, 40), CUTIL_IN_OPEN_RANGE(c, 20, 30)); // output: 1 0
- increase or decrease the value of numeric variable within the range [_min, _max]
- increase or decrease the value of numeric variable, and rolling within the range [_min, _max]
- increase or decrease the value, and prevent overflowing, only for GNU C, C23, C++11
int num = 0; for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++){ printf("%d ", CUTIL_INCREASE_LIMIT(num, 1, 5)); // 1 2 3 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 } for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++){ printf("%d ", CUTIL_DECREASE_LIMIT(num, 1, 0)); // 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 } for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++){ printf("%d ", CUTIL_INCREASE_ROLL(num, 1, 0, 5)); // 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 } for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++){ printf("%d ", CUTIL_DECREASE_ROLL(num, 1, 0, 5)); // 5 4 3 2 1 0 5 4 3 2 1 0 } int8_t num = -125; for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++){ CUTIL_DECREASE(num, 1u); printf("%d ", num); // -> -126 -127 -128 -128 -128 -128 } num = 124; for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++){ CUTIL_INCREASE(num, 1u); printf("%d ", num); // -> 125 126 127 127 127 127 }
-
check if two floating-point numbers are equal (float, double, long double) by checking diff of two numbers is within epsilon limit.
FLT_EPSILONDBL_EPSILONin<float.h>, orstd::numeric_limits<double>::epsilon()in<limits>float.hmust be included.
#include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> float a = -1.00000f, b = -0.99999f; // they can regarded as equal double c = 1.000000000, d = 1.0000000001; bool isEqual1 = CUTIL_EQUAL_F(a, b); // fabs(a-b) within (-epsilon, +epsilon), epsilon == FLT_EPSILON in <float.h> bool isEqual2 = CUTIL_EQUAL_D(c, d); // epsilon == DBL_EPSILON in <float.h> bool isEqual3 = CUTIL_EQUAL(c, d, 0.0001); // custom epsilon value
-
-
input a comma
,to argument of functional macro#define MY_MACRO(_x, _y) _x // extract first param MY_MACRO(a CUTIL_COMMA b, c); // expands to `a, b` // CUTIL_COMMA inserts a comma `,` to an argument, and avoid being regarded as seperator of arguments
-
C character conversion & assertion (
charonly, notwchar_t)-
is in uppercase/lowercase
-
is an alphabet/number/punctuation
-
is in range of ASCII/ASCII symbol/ASCII control characters
-
get or convert
charto lowercase/uppercase
-
```c++ #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_UPPER(_ch) ((_ch) >= 'A' && (_ch) <= 'Z') #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_LOWER(_ch) ((_ch) >= 'a' && (_ch) <= 'z') #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_ALPHABET(_ch) (CUTIL_CHAR_IS_UPPER(_ch) || CUTIL_CHAR_IS_LOWER(_ch)) #define CUTIL_CHAR_GET_UPPER(_ch) ((char)(CUTIL_CHAR_IS_LOWER(_ch) ? ((_ch) - 0x20) : (_ch))) #define CUTIL_CHAR_GET_LOWER(_ch) ((char)(CUTIL_CHAR_IS_UPPER(_ch) ? ((_ch) + 0x20) : (_ch))) #define CUTIL_CHAR_SET_UPPER(_ch) (_ch = CUTIL_CHAR_GET_UPPER(_ch), _ch) #define CUTIL_CHAR_SET_LOWER(_ch) (_ch = CUTIL_CHAR_GET_LOWER(_ch), _ch) #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_NUMBER(_ch) ((_ch) >= '0' && (_ch) <= '9') // #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_DIGIT(_ch) CUTIL_CHAR_IS_DEC(_ch) #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_DEC(_ch) CUTIL_CHAR_IS_NUMBER(_ch) #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_HEX(_ch) (CUTIL_CHAR_IS_NUMBER(_ch) || ((_ch) >= 'A' && (_ch) <= 'F') || ((_ch) >= 'a' && (_ch) <= 'f')) #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_ALPHANUMERIC(_ch) (CUTIL_CHAR_IS_ALPHABET(_ch) || CUTIL_CHAR_IS_NUMBER(_ch)) #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_PUNCT(_ch) (((_ch) >= '!' && (_ch) <= '/') || ((_ch) >= ':' && (_ch) <= '@') || ((_ch) >= '[' && (_ch) <= '`') || ((_ch) >= '{' && (_ch) <= '~')) #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_CONTROL(_ch) ((_ch) <= 0x1F && (_ch) >= 0x00) #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_ASCII(_ch) ((_ch) >= 0x01 && (_ch) <= 0x7E) #define CUTIL_CHAR_IS_SYMBOL(_ch) ((_ch) >= 0x20 && (_ch) <= 0x7E) ``` ``` #define TEST(_x) fmt::println("{}: {}", _x, CUTIL_CHAR_IS_UPPER(_x)) CUTIL_SEQ_FOREACH(TEST, '`', 'a', 'b', 'z', '{', '0', '9', '@', 'A', 'B', 'Z', '['); // fmt::println("{}: {}", '`', CUTIL_CHAR_IS_UPPER('`')); // fmt::println("{}: {}", '`', CUTIL_CHAR_IS_UPPER('`')); // ... // fmt::println("{}: {}", '[', CUTIL_CHAR_IS_UPPER('[')); // case conversion char b = 'a'; auto c = CUTIL_CHAR_SET_UPPER(b); fmt::println("{} {}", b, c); ```
-
operate value of specific memory location
-
get pointer (in specific type) which points to the address of specific variable
-
get value from the memory address in the specific type
-
set memory at the specific location in the specific type
-
```c++ #define CUTIL_GET_PTR_TYPE(_type, _var) ((_type *) (void*) &(_var)) #define CUTIL_GET_MEM_TYPE(_type, _ptr) (*((volatile _type *) (_ptr))) #define CUTIL_SET_MEM_TYPE(_type, _ptr, _val) (*((volatile _type *) _ptr) = _val, _val) uint32_t a = 0x12345678; uint32_t b = 0xFEDCBA98; printf("%x, %x \n", CUTIL_GET_MEM_U32(&a), CUTIL_GET_MEM_U32(&b)); // get content as type `uint32_t` at the location `&a and `&b`, it prints the value of `a` and `b` printf("%p, %p \n", CUTIL_GET_PTR_U32(a), CUTIL_GET_PTR_U32(b)); // get address as type `uint32_t*` of the variable `a` and `b` printf("%p\n", CUTIL_GET_PTR_TYPE(uint32_t, a)); // equivelent CUTIL_SET_MEM_U32(&a, 0x66666666); // set content of address `&b` as `0x66666666`, in the type of `uint32_t` CUTIL_SET_MEM_TYPE(uint32_t, &b, 0x77777777); // set content of address `&b` as `0x77777777`, in the type of `uint32_t` printf("%x, %x \n", CUTIL_GET_MEM_U32(&a), CUTIL_GET_MEM_U32(&b));
// output: // 12345678, fedcba98 // 000000C48D7BFB04, 000000C48D7BFB24 // 000000C48D7BFB04 // 66666666, fedcba98 ```
-
count amount of arguments (up to 35 params)
CUTIL_VA_CNT(...)(also compatible for compiler that do not support##__VA_ARGS__, to eliminate a leading comma if__VA_ARGS__is empty)
#include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> int a = CUTIL_VA_CNT(); // -> 0 int b = CUTIL_VA_CNT(b1); // -> 1 int c = CUTIL_VA_CNT(c1, c2); // -> 2 int d = CUTIL_VA_CNT(c1, c2, c3); // -> 3
CUTIL_VA_EXISTS(...)get if arguments exists
int a = CUTIL_VA_EXISTS(); // -> 0 int b = CUTIL_VA_EXISTS(b1); // -> 1 int c = CUTIL_VA_EXISTS(c1, c2); // -> 1 int d = CUTIL_VA_EXISTS(c1, c2, c3);// -> 1
-
match C++ language version, especially if you want to let the project build both by MSVC and G++.
CUTIL_CPP_LANGequals to "_MSVC_LANG" for MSVC, and "__cplusplus" for other compilers.#include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> #if CUTIL_CPP_LANG >= 199711L // C++98 #if CUTIL_CPP_LANG >= 201103L // C++11 #if CUTIL_CPP_LANG >= 201402L // C++14 #if CUTIL_CPP_LANG >= 201703L // C++17 #if CUTIL_CPP_LANG >= 202002L // C++20 #if CUTIL_CPP_LANG >= 202302L // C++23 (temporary unsupported)
-
set C++11 class constructor/moving/copying to disabled/default
#include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> class MyClass{ public: CUTIL_CLASS_DEFAULT_CONSTRUCTOR(MyClass) // generates MyClass(), ~MyClass() = default; CUTIL_CLASS_DISABLE_COPY_MOVE(MyClass) // cannot move or copy this class // =delete: MyClass(const MyClass&), operator=(const MyClass&), MyClass(MyClass&&), operator=(MyClass&&), } class MyClass{ public: CUTIL_CLASS_DEFAULT_FUNCTIONS(MyClass) // generates 6 functions =default: MyClass(), ~MyClass(), MyClass(const MyClass&), // operator=(const MyClass&), MyClass(MyClass&&), operator=(MyClass&&) } /* available macros: #define CUTIL_CLASS_DEFAULT_CONSTRUCTOR(_CLASS_NAME) #define CUTIL_CLASS_DISABLE_COPY(_CLASS_NAME) #define CUTIL_CLASS_DEFAULT_COPY(_CLASS_NAME) #define CUTIL_CLASS_DISABLE_MOVE(_CLASS_NAME) #define CUTIL_CLASS_DEFAULT_MOVE(_CLASS_NAME) #define CUTIL_CLASS_DISABLE_COPY_MOVE(_CLASS_NAME) #define CUTIL_CLASS_DEFAULT_COPY_MOVE(_CLASS_NAME) #define CUTIL_CLASS_DEFAULT_FUNCTIONS(_CLASS_NAME) */
-
memory allocation and operations for C (wrapped
malloc()free()memset()memcpy()with typename to macros. use AMOUNT of variables to substitute length in bytes.)CUTIL_TYPE_FREE()macro also sets pointer tonullptr.use
std::allocator()in C++11 to replace mallocuse
std::uninitialized_copystd::uninitialized_fillstd::uninitialized_movein C++#include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> const size_t amount = 20; // amount of variables ( length in bytes! ) uint32_t* aD1 = CUTIL_TYPE_MALLOC(uint32_t, amount); // std::vector<uint32_t> v1(20); -> elements == 0xCDCDCDCD in heap uint32_t* aD2 = CUTIL_TYPE_CALLOC(uint32_t, amount); // std::vector<uint32_t> v1(20, 0x00000000); uint32_t aD3[amount]; // C99 VLA, unsupported in C++, -> elements == 0xCCCCCCCC in stack uint32_t* aD3 = CUTIL_TYPE_MEMSET(uint32_t, aD1, 0x66, amount); // set all elements of aD1 to 0x66666666, returns aD3 == aD1 uint32_t* aD4 = CUTIL_TYPE_MEMMOVE(uint32_t, aD2, aD1, amount); // copy aD1 elements to aD2, returns aD4==aD2 uint32_t* aD5 = CUTIL_TYPE_MEMCPY(uint32_t, aD2, aD1, amount); // equivalents to above. int compResult = CUTIL_TYPE_MEMCMP(uint32_t, aD1, aD2, amount); // returns 0, contents of mem blocks equal. CUTIL_TYPE_FREE(aD1); // element values -> 0xDDDDDDDD (deleted heap); then set `aD1` to `nullptr` CUTIL_TYPE_FREE(aD2); // set `aD2` to `nullptr` // you need't add `aD1 = NULL`.
-
deleteordelete[]pointer to heap created bynewornew[], then set tonullptr.#include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> uint32_t* p1 = new uint32_t(123); uint32_t* p2 = new uint32_t[50]; CUTIL_DELETE(p1); // do {delete p; p = NULL;} while(0) CUTIL_DELETE_ARRAY(p2); // do {delete[] p; p = NULL;} while(0) // you need't add `p1 = nullptr`.
-
convert to string
#define CUTIL_STR(_1) #_1 #define CUTIL_LSTR(_1) CUTIL_CAT_TOKENS(L, #_1) // wchar_t #define CUTIL_U8STR(_1) CUTIL_CAT_TOKENS(u8, #_1) // C++17, char8_t #define CUTIL_U16STR(_1) CUTIL_CAT_TOKENS(u, #_1) // C++11, char16_t #define CUTIL_U32STR(_1) CUTIL_CAT_TOKENS(U, #_1) // C++11, char32_t
-
concatenate tokens without spaces or commas, up to 25 tokens
int a1 = CUTIL_CAT(11, 22); // a1 = 1122 int a2 = CUTIL_CAT(10, 11, 12, 13); // a2 = 10111213 std::cout << CUTIL_CAT(a, 1) << "\n"; // print variable `a1`
-
generate the code like
(var == 1 || var == 2 || var == 3 || ...)or(var != 1 && var != 2 && var != 3 && ...), up to 25 compared paramsWARNING: you can't compare some return value of functions like
getchar(), or++--operators. if you useif(CUTIL_EQUAL_OR(getchar(), 'a', 'b'))it will expand asif(getchar() == 'a' || getchar() == 'b')int var = 10; if(CUTIL_EQUAL_OR(var, 5, 10)){ // equivalent to `if(var == 5 || var == 10)` // equivalent to `if(! CUTIL_UNEQUAL_AND(var, 5, 10))` } if(CUTIL_EQUAL_OR(var, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10)){ // equivalent to `if(var == 2 || var == 4 || var == 6 || var == 8 || var == 10)` // equivalent to `if(! CUTIL_UNEQUAL_AND(var, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10))` } if(CUTIL_UNEQUAL_AND(var, 5, 10)){ // equivalent to `if(var != 5 && var != 10)` // equivalent to `if(! CUTIL_EQUAL_OR(var, 5, 10))` } if(CUTIL_UNEQUAL_AND(var, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10)){ // equivalent to `if(var != 2 && var != 4 && var != 6 && var != 8 && var != 10)` // equivalent to `if(! CUTIL_EQUAL_OR(var, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10))` }
-
get if variables in parameters mutually different
WARNING: you can't compare some return value of functions like
getchar(), or++--operators.if(CUTIL_UNEQUAL_ALL(a1, a2, a3, a4)){ // is `a1`, `a2`, `a3`, `a4` mutually different? // ( ((a1) != (a2) && (a1) != (a3) && (a1) != (a4)) // && ((a2) != (a3) && (a2) != (a4)) // && ((a3) != (a4)) ) } if(CUTIL_UNEQUAL_ALL(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5)){ // ( ((a1) != (a2) && (a1) != (a3) && (a1) != (a4) && (a1) != (a5)) // && ((a2) != (a3) && (a2) != (a4) && (a2) != (a5)) // && ((a3) != (a4) && (a3) != (a5)) // && ((a4) != (a5)) ) }
-
Implement function overloading based on the number of parameters and the trailing digit by token concatenation.
CUTIL_OVERLOAD_IDX(MyFunc, 2)(); // MyFunc2(); CUTIL_OVERLOAD_IDX(var_, 3) = 10; // var_3 = 10; // Deduce suffix by amount of arguments within the macro CUTIL_OVERLOAD_AMOUNT(MyFunc, 2, 4, 6)(2, 4, 6); // MyFunc3(2, 4, 6);
-
call a single-argument function/macro for each parameter, simillar to
BOOST_PP_SEQ_FOR_EACH, up to 25 iterations#define TEST_PRINT(x) fmt::println("{}", x) //* Must take exactly 1 argument CUTIL_SEQ_FOREACH(TEST_PRINT, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7); // -> {fmt::println("{}", 1); fmt::println("{}", 2); ...}
-
repeat function or macro calling, similar to
BOOST_PP_REPEAT, up to 25 loops#define TEST_PRINT(x) fmt::println("{}", x) #define TEST_1(x, y) fmt::println("{} {}", x, y) #define TEST_2(x, ...) printf("%d", x); CUTIL_SEQ_FOREACH(TEST_PRINT, __VA_ARGS__) CUTIL_REPEAT(3, TEST_1, 22, 44); // repeat `fmt::println("{} {}", 22, 44)` for 3 times CUTIL_REPEAT(4, TEST_2, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10); // repeat `printf("%d", 2);printf("%d", 4); ... printf("%d, 10")` for 4 times
-
generate code like
int arg0, int arg1, int arg2, similar toBOOST_PP_ENUM, up to 25 params-
CUTIL_ENUM(_type, _name, _count)void func(CUTIL_ENUM(var_, int, 3)){ // equivalent to `void func(int var_0, int var_1, int var_2)` }
-
CUTIL_SEQ_ENUM(_action, ...)#define TEST(_x) test_##_x //* Must take exactly 1 argument #define TEST2(_x) test_##_x = 1 int CUTIL_SEQ_ENUM(TEST2, a, b, c, d); // -> int test_a = 1, test_b = 1, test_c = 1, test_d = 1; printf("%d %d %d %d", CUTIL_SEQ_ENUM(TEST, a, b, c, d)); printf("%d %d %d %d", test_a, test_b, test_c, test_d); // equivalent to above
-
-
features with C struct and memory offset/address
CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_OFFSET(_type, _field): calculate the struct address from the member's address, within the typesize_tCUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_SIZE(_type, _field): get the size of a struct memberCUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_CONTAINER(_type, _field, _fieldAddr): use the address of a struct member, to calculate the address of the containing struct object, within the type_type*
//* define a struct type `struct MyStruct`(C) or `MyStruct`(C++) struct MyStruct { uint8_t a; // 0 (+0) uint8_t b; // 1 |--(+1) uint32_t c; // 4 (+4) uint8_t d; // 8 (+4) uint8_t e; // 9 |--(+1) uint8_t f; // 10 |--(+1) uint64_t g; // 16 (+8) uint32_t h; // 24 (+8) }; struct MyStruct myStruct; //* create a struct object `myStruct` //* get the memory offset of a struct member printf("offset: a-%zu", CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_OFFSET(struct MyStruct, a)); // output: `offset: a-0` printf("offset: b-%zu", CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_OFFSET(struct MyStruct, b)); // output: `offset: b-1` printf("offset: c-%zu", CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_OFFSET(struct MyStruct, c)); // output: `offset: c-4` //... // output: `offset: a:0, b:1, c:4, d:8, e:9, f:10, g:16, h:24` // you can simplify the code above with `CUTIL_SEQ_ENUM`, like this: #define MYSTRUCT_OFFSET_OF_ELEMENT(_x) CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_OFFSET(struct MyStruct, _x) printf("offset: a:%zu, b:%zu, c:%zu, zu:%zu, e:%zu, f:%zu, g:%zu, h:%zu \n" , CUTIL_SEQ_ENUM(MYSTRUCT_OFFSET_OF_ELEMENT, a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h) // , CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_OFFSET(struct MyStruct, a) // , CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_OFFSET(struct MyStruct, b) // ... // , CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_OFFSET(struct MyStruct, h) ); // output: `offset: a:0, b:1, c:4, d:8, e:9, f:10, g:16, h:24` //* get the size of a struct member printf("size: a-%zu", CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_SIZE(struct MyStruct, a)); // output: `size: a-1` printf("size: b-%zu", CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_SIZE(struct MyStruct, b)); // output: `size: b-1` printf("size: g-%zu", CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_SIZE(struct MyStruct, g)); // output: `size: g-8` // ... // output: `size: a:1, b:1, c:4, d:1, e:1, f:1, g:8, h:4` // you can simplify the code above with `CUTIL_SEQ_ENUM`, like this: #define MYSTRUCT_SIZE_OF_ELEMENT(_x) CUTIL_FIELD_SIZE(struct MyStruct, _x) printf("size: a:%zu, b:%zu, c:%zu, d:%zu, e:%zu, f:%zu, g:%zu, h:%zu \n" , CUTIL_SEQ_ENUM(MYSTRUCT_SIZE_OF_ELEMENT, a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h) // , CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_SIZE(struct MyStruct, a) // , CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_SIZE(struct MyStruct, b) // ... // , CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_SIZE(struct MyStruct, h) ); // output: `size: a:1, b:1, c:4, d:1, e:1, f:1, g:8, h:4` //* use the address of a struct member, to calculate the address of the containing struct object printf("loc of myStruct: %p %p \n", &myStruct, CUTIL_STRUCT_FIELD_CONTAINER(struct MyStruct, b, &myStruct.b) // [b, &myStruct.b] => &myStruct ); // output: `loc of myStruct: 0000006CE9EFF9D8 0000006CE9EFF9D8`
-
generate getter or setter functions within a class (≥ C++11)
class Test { private: int m_a {}; CUTIL_GETTER(m_a, getA) // public: int getA() {return this->m_a;} CUTIL_SETTER(m_a, setA) // public: void setA(const int& _val) {this->m_a = _val;} private: double m_b {}; CUTIL_MEMBER(m_b, getB, setB) // public: double getB() {return this->m_b;} // public: void setB(const double& _val) {this->m_b = _val;} private: std::string m_c {}; CUTIL_MEMBER(m_c, c) // public: std::string c() {return this->m_c;} // public: void c(const std::string& _val) {this->m_c = _val;} }; Test test; // print fmt::println("Test::m_a = {}", test.getA()); test.setB(3.1615925); fmt::println("Test::m_b = {}", test.getB()); test.c("hello world!"); fmt::println("Test::m_c = {}", test.c());
-
foreach support for C++98
std::vector<int> vec1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}; //* forward iteration CUTIL_ITER(std::vector<int>::iterator, iter, vec1){ // auto it = [vec1.begin() -> vec1.end()] std::cout << *iter << " "; } CUTIL_ITER(std::vector<int>::iterator, iter, vec1.begin(), vec1.end()){ std::cout << *iter << " "; } //* reverse iteration CUTIL_ITER(std::vector<int>::iterator, iter, vec1.rbegin(), vec1.rend()){ // auto it = [vec1.rbegin() -> vec1.rend()] std::cout << *iter << " "; } //* >= C++11 for(auto&& var : vec1){ std::cout << var << " "; } CUTIL_ITER(auto, iter, vec1){ std::cout << *iter << " "; } CUTIL_FOREACH(iter, vec1){ std::cout << *iter << " "; // `iter` is an iterator! } CUTIL_FOREACH(iter, vec1.begin(), vec.end()){ std::cout << *iter << " "; }
-
for loop in range
[0, _end)or[_first, _end)CUTIL_FOR_TYPE(int, i, 5) {} // `for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)`; i <- [0..4]; CUTIL_FOR_TYPE(int, i, 2, 4) {} // `for(int i = 2; i < 4; i++)`; i <- [2..3]; // for C23, GNU C, C++; type of `_var` is deduced from `_end` CUTIL_FOR(i, 5) {} // `for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)`; i <- [0..4]; CUTIL_FOR(i, 0, 10) {} // `for(int i = 2; i < 4; i++)`; i <- [2..3];
-
Mathematical Constants
#define CUTIL_E 2.71828182845904523536 // e #define CUTIL_LOG2E 1.44269504088896340736 // log2(e) #define CUTIL_LOG10E 0.43429448190325182765 // log10(e) #define CUTIL_LN2 0.69314718055994530942 // ln(2) #define CUTIL_LN10 2.30258509299404568402 // ln(10) #define CUTIL_PI 3.14159265358979323846 // pi #define CUTIL_2_PI 6.28318530717958647692 // 2*pi #define CUTIL_3_PI 9.42477796076937971538 // 3*pi #define CUTIL_PI_2 1.57079632679489661923 // pi/2 #define CUTIL_PI_3 1.04719755119659774615 // pi/3 #define CUTIL_PI_4 0.78539816339744830962 // pi/4 #define CUTIL_INV_PI 0.31830988618379067154 // 1/pi #define CUTIL_2_INV_PI 0.63661977236758134308 // 2/pi #define CUTIL_2_SQRT_PI 1.12837916709551257390 // 2/sqrt(pi) #define CUTIL_SQRT_2 1.41421356237309504880 // sqrt(2) #define CUTIL_INV_SQRT_2 0.70710678118654752440 // 1/sqrt(2) #define CUTIL_SQRT_3 1.73205080756887729353 // sqrt(3) #define CUTIL_PHI 1.61803398874989484820 // (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2, golden ratio #define CUTIL_INV_PHI 0.61803398874989484820 // 2 / (1 + sqrt(5)), inversed golden ratio #define CUTIL_EGAMMA 0.57721566490153286060 // Euler-Mascheroni constant
also, you can get float versions with macros with
_Fsuffix:#define CUTIL_E_F 2.71828182845904523536f // e #define CUTIL_LOG2E_F 1.44269504088896340736f // log2(e) #define CUTIL_LOG10E_F 0.43429448190325182765f // log10(e) // ...
-
Power and Factorial for integer variables
std::pow(base, exp) in
<cmath>is for float/double, not for integer.int ret = CUTIL_INTPOW(2, 3); // 2^3 = 8; generates `(2 * 2 * 2)`; arg `exp` must be an constexpr. ret = CUTIL_INTPOW(ret, 2); // 8^2 = 64; generates `(ret * ret)`
C++ versions (template functions):
int ret; ret = cutil::intPow(2, 3); // 2^3 = 8 ret = cutil::intPow<3>(2); // 2^3 = 8 ret = cutil::factorial(3); // 3! = 6 ret = cutil::factorial<3>(); // 3! = 6
-
-
Detect Operating System
OS defined macros Windows (32-bit) CUTIL_OS_WIN32&&CUTIL_OS_WINDOWSWindows (64-bit) CUTIL_OS_WIN32&&CUTIL_OS_WINDOWS&&CUTIL_OS_WIN64Windows (Cygwin) CUTIL_OS_CYGWINLinux CUTIL_OS_LINUXApple CUTIL_OS_APPLEAndroid CUTIL_OS_ANDROID&&CUTIL_OS_LINUX -
Some Macros for Qt Projects:
#include <ConsoleUtil/QtUtil.h> // already wrapped in <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h>, you can include the latter instead.
-
Enable High DPI Support for Qt5 programs (enable since Qt5.6.0, and fractional scaling since Qt5.14.0). Qt6 supports it by default.
-
Set Qt5 TextCodec Encoding, like UTF-8 or GBK to let qDebug() correctly displays Chinese characters with UTF-8 code page and MSVC compiler.
#include <qglobal.h> #include <QApplication> #include <QDebug> #include <QTextCodec> // include Qt headers first #include <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h> // <ConsoleUtil/QtUtil.h> has been wrapped in this header. int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { CUTIL_QT5_HIGH_DPI(); //* enable Qt5 high DPI support CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_UTF8(); CUTIL_QT5_TEXTCODEC_UTF8(); //* set Qt default text encoding to UTF-8 QApplication app(argc, argv); // you must create QCoreApplication after these macros. return app.exec(); } /* available encodings: CUTIL_QT5_TEXTCODEC_UTF8() CUTIL_QT5_TEXTCODEC_GBK() CUTIL_QT5_TEXTCODEC_BIG5() CUTIL_QT5_TEXTCODEC_EUCKR() CUTIL_QT5_TEXTCODEC_EUCJP() CUTIL_QT5_TEXTCODEC_JIS() */
-
-
Some Macros for CUDA Programs:
#include <ConsoleUtil/CudaUtil.h> // already wrapped in <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h>, you can include the latter instead.
...
-
use
find_package()inCMakeLists.txtof your project to find "ConsoleUtil" CMake package.Set variable "
ConsoleUtil_DIR" previously to the folderConsoleUtil/cmake, with fileConsoleUtilConfig.cmakeinside.set(ConsoleUtil_DIR "D:/3rdlibs/ConsoleUtil/cmake") # there's file `ConsoleUtilConfig.cmake` find_package(ConsoleUtil REQUIRED) # find ConsoleUtil package
-
link "
ConsoleUtil::ConsoleUtil" to your target.project(myProject LANGUAGES CXX) add_executable( ${PROJECT_NAME} "main.cpp") # create a app target target_link_libraries( ${PROJECT_NAME} ConsoleUtil::ConsoleUtil # this header-only Library # fmt::fmt-header-only # other 3rd libraries )
-
include "
ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h" in your source file, and check if there's macroCONSOLE_UTIL_VERSIONequals to version number.#include <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h> // wrapped all 3 below inside // #include <ConsoleUtil/CppUtil.h> // you can include this alone within header files // #include <ConsoleUtil/QtUtil.h> // #include <ConsoleUtil/CudaUtil.h>
#include <print.h> // C++23
#include <windows.h> // include other headers first
#include <fmt/core.h> // include other headers first
#include <ConsoleUtil/ConsoleUtil.h> // include this header at last
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
CUTIL_CHCP_ENCODING_UTF8(); // switch console encoding to UTF-8 (windows)
CUTIL_CONSOLE_TITLE("MyProject"); // set console window title
CUTIL_CONSOLE_SIZE(100, 30); // set console window size to with of 30 chars and height of 30 lines.
CUTIL_CONSOLE_CLEAR(); // clear console (system("cls"))
CUTIL_PRINT_ARGV(argc, argv); // print all argc and argv[n] of main() function
printf(FLGreen "Hello World!\n" CReset); // print "Hello World" with light yellow console color formatting
you should put "CReset" at the end of string to RESET console font color to DEFAULT
printf(CStyle(FLGreen, "Hello World!\n")); // Equivalent
std::cout << FLRed "ERROR\n" CReset; // print "ERROR" with font color light red, "CReset" is also needed to revert font color to default
std::cout << CStyle(FLRed, "ERROR\n");// Equivalent
printf(BRed FGreen CQFlash "test\n" CReset); // Print text with green font and red background, and quickly flashing
printf(CStyle(BRed FGreen CQFlash, "test\n"));// Equivalent
printf(CForward(2)); // move thr cursor 2 characters right
CUTIL_ERROR_MESSAGE("error occurred!"); // print an error message with filename, function name and line number ATTACHED.
CUTIL_CONSOLE_PAUSE(); // system("pause");
return 0;
}Console Effects 控制台效果 :