SysIdentPy is a Python module for System Identification using NARMAX models built on top of numpy and is distributed under the 3-Clause BSD license.
The update v0.2.0 has been released with major changes and additional features (Fourier basis function, NAR and NFIR models, n-steps ahead prediction for both General Estimators and Neural NARX and more).
There are API modifications and you will need to change your code to have the new (and upcoming) features.
Check the examples of how to use the new version in the documentation page.
For more details, please see the changelog.
- Website: https://sysidentpy.org
SysIdentPy now support NARX Neural Network and General estimators, e.g., sklearn estimators and Catboost.
from torch import nn
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sysidentpy.metrics import root_relative_squared_error
from sysidentpy.utils.generate_data import get_siso_data
# Generate a dataset of a simulated dynamical system
x_train, x_valid, y_train, y_valid = get_siso_data(
n=1000,
colored_noise=False,
sigma=0.001,
train_percentage=80
)from sysidentpy.model_structure_selection import FROLS
from sysidentpy.basis_function import Polynomial
from sysidentpy.utils.display_results import results
from sysidentpy.utils.plotting import plot_residues_correlation, plot_results
from sysidentpy.residues.residues_correlation import compute_residues_autocorrelation
from sysidentpy.residues.residues_correlation import compute_cross_correlation
basis_function=Polynomial(degree=2)
model = FROLS(
order_selection=True,
n_info_values=10,
extended_least_squares=False,
ylag=2,
xlag=2,
info_criteria='aic',
estimator='least_squares',
basis_function=basis_function
)
model.fit(X=x_train, y=y_train)
yhat = model.predict(X=x_valid, y=y_valid)
rrse = root_relative_squared_error(y_valid, yhat)
print(rrse)
r = pd.DataFrame(
results(
model.final_model, model.theta, model.err,
model.n_terms, err_precision=8, dtype='sci'
),
columns=['Regressors', 'Parameters', 'ERR'])
print(r)
Regressors Parameters ERR
0 x1(k-2) 0.9000 0.95556574
1 y(k-1) 0.1999 0.04107943
2 x1(k-1)y(k-1) 0.1000 0.00335113
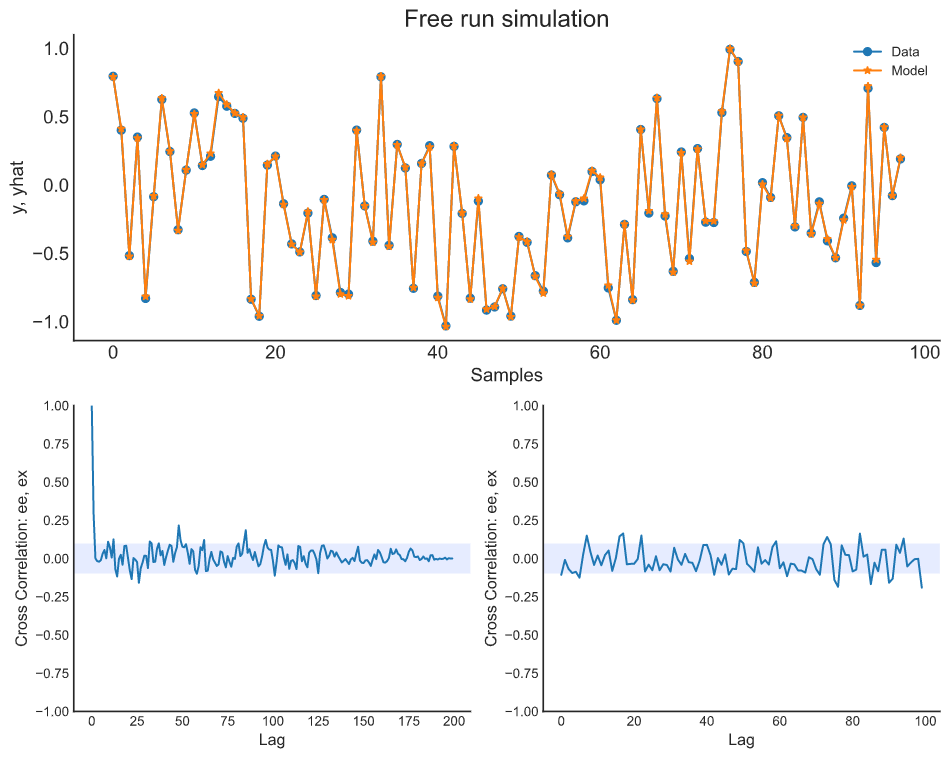
plot_results(y=y_valid, yhat=yhat, n=1000)
ee = compute_residues_autocorrelation(y_valid, yhat)
plot_residues_correlation(data=ee, title="Residues", ylabel="$e^2$")
x1e = compute_cross_correlation(y_valid, yhat, x2_val)
plot_residues_correlation(data=x1e, title="Residues", ylabel="$x_1e$")from sysidentpy.neural_network import NARXNN
from sysidentpy.basis_function import Polynomial
from sysidentpy.utils.plotting import plot_residues_correlation, plot_results
from sysidentpy.residues.residues_correlation import compute_residues_autocorrelation
from sysidentpy.residues.residues_correlation import compute_cross_correlation
class NARX(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.lin = nn.Linear(4, 10)
self.lin2 = nn.Linear(10, 10)
self.lin3 = nn.Linear(10, 1)
self.tanh = nn.Tanh()
def forward(self, xb):
z = self.lin(xb)
z = self.tanh(z)
z = self.lin2(z)
z = self.tanh(z)
z = self.lin3(z)
return z
basis_function=Polynomial(degree=1)
narx_net = NARXNN(
net=NARX(),
ylag=2,
xlag=2,
basis_function=basis_function,
model_type="NARMAX",
loss_func='mse_loss',
optimizer='Adam',
epochs=200,
verbose=False,
optim_params={'betas': (0.9, 0.999), 'eps': 1e-05} # optional parameters of the optimizer
)
narx_net.fit(X=x_train, y=y_train)
yhat = narx_net.predict(X=x_valid, y=y_valid)
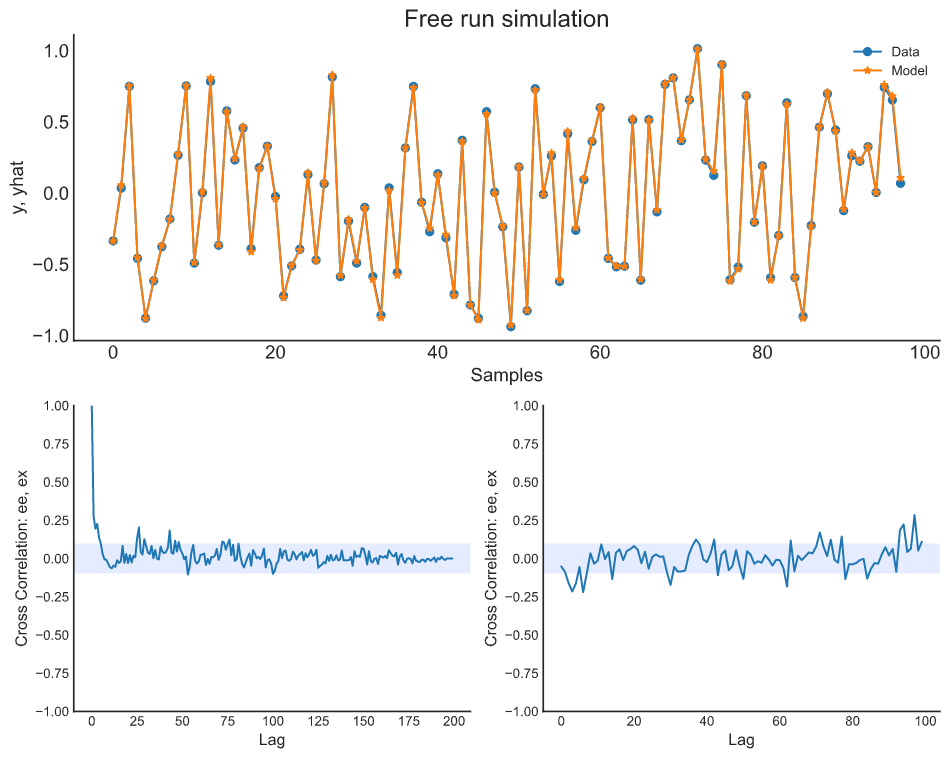
plot_results(y=y_valid, yhat=yhat, n=1000)
ee = compute_residues_autocorrelation(y_valid, yhat)
plot_residues_correlation(data=ee, title="Residues", ylabel="$e^2$")
x1e = compute_cross_correlation(y_valid, yhat, x_valid)
plot_residues_correlation(data=x1e, title="Residues", ylabel="$x_1e$")from catboost import CatBoostRegressor
from sysidentpy.general_estimators import NARX
from sysidentpy.basis_function import Polynomial
from sysidentpy.utils.plotting import plot_residues_correlation, plot_results
from sysidentpy.residues.residues_correlation import compute_residues_autocorrelation
from sysidentpy.residues.residues_correlation import compute_cross_correlation
basis_function=Polynomial(degree=1)
catboost_narx = NARX(
base_estimator=CatBoostRegressor(
iterations=300,
learning_rate=0.1,
depth=6),
xlag=2,
ylag=2,
basis_function=basis_function,
fit_params={'verbose': False}
)
catboost_narx.fit(X=x_train, y=y_train)
yhat = catboost_narx.predict(X=x_valid, y=y_valid)
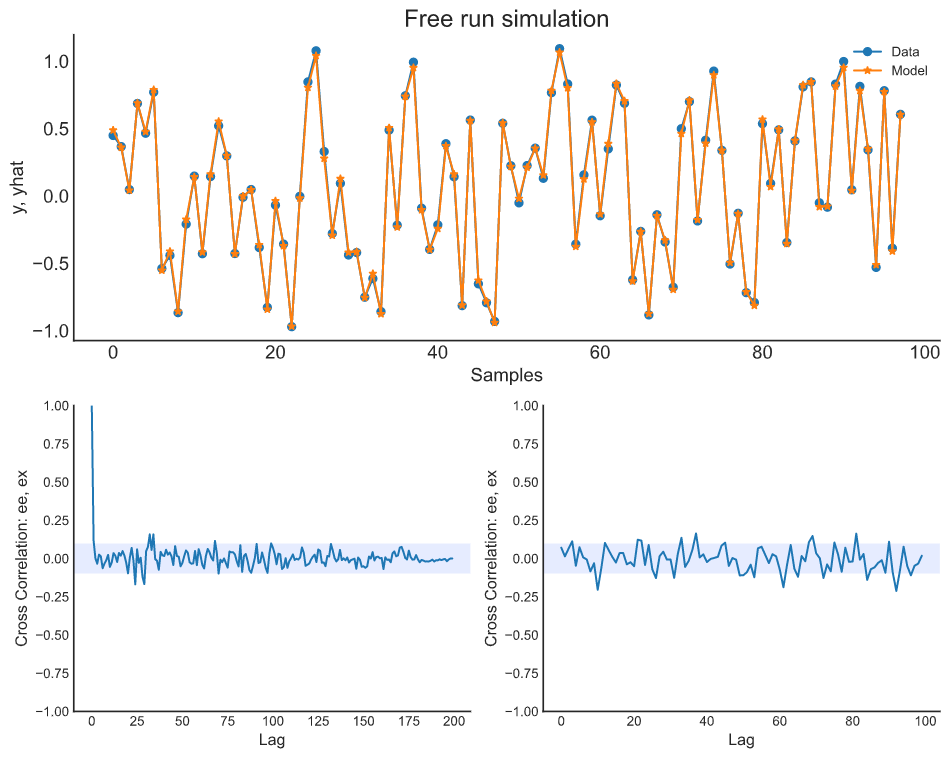
plot_results(y=y_valid, yhat=yhat, n=1000)
ee = compute_residues_autocorrelation(y_valid, yhat)
plot_residues_correlation(data=ee, title="Residues", ylabel="$e^2$")
x1e = compute_cross_correlation(y_valid, yhat, x_valid)
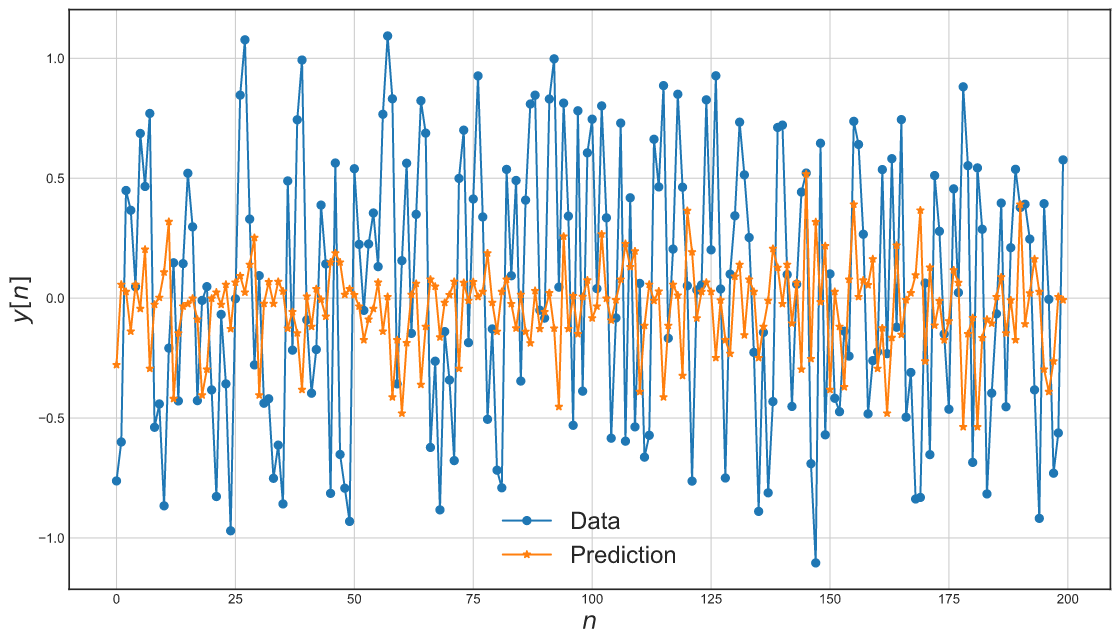
plot_residues_correlation(data=x1e, title="Residues", ylabel="$x_1e$")The following is the Catboost performance without the NARX configuration.
def plot_results_tmp(y_valid, yhat):
_, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(14, 8))
ax.plot(y_valid[:200], label='Data', marker='o')
ax.plot(yhat[:200], label='Prediction', marker='*')
ax.set_xlabel("$n$", fontsize=18)
ax.set_ylabel("$y[n]$", fontsize=18)
ax.grid()
ax.legend(fontsize=18)
plt.show()
catboost = CatBoostRegressor(
iterations=300,
learning_rate=0.1,
depth=6
)
catboost.fit(x_train, y_train, verbose=False)
plot_results_tmp(y_valid, catboost.predict(x_valid))The examples directory has several Jupyter notebooks with tutorials of how to use the package and some specific applications of sysidentpy. Try it out!
SysIdentPy requires:
- Python (>= 3.7)
- NumPy (>= 1.5.0) for all numerical algorithms
- Matplotlib >= 1.5.2 for static plotting and visualizations
- Pytorch (>=1.7.1) for building feed-forward neural networks
| Platform | Status |
|---|---|
| Linux | ok |
| Windows | ok |
| macOS | ok |
SysIdentPy do not to support Python 2.7.
A few examples require pandas >= 0.18.0. However, it is not required to use sysidentpy.
The easiest way to get sysidentpy running is to install it using pip
pip install sysidentpy
We will make it available at conda repository as soon as possible.
See the changelog for a history of notable changes to SysIdentPy.
We welcome new contributors of all experience levels. The sysidentpy community goals are to be helpful, welcoming, and effective.
Note: we use the pytest package for testing. The test functions are located in tests subdirectories at each folder inside SysIdentPy, which check the validity of the algorithms.
Run the pytest in the respective folder to perform all the tests of the corresponding sub-packages.
Currently, we have around 81% of code coverage.
You can install pytest using
pip install -U pytest
Open a terminal emulator of your choice and go to a subdirectory, e.g,
\sysidentpy\metrics\
Just type pytest and you get a result like
========== test session starts ==========
platform linux -- Python 3.7.6, pytest-5.4.2, py-1.8.1, pluggy-0.13.1
rootdir: ~/sysidentpy
plugins: cov-2.8.1
collected 12 items
tests/test_regression.py ............ [100%]
========== 12 passed in 2.45s ==================
You can also see the code coverage using the pytest-cov package. First, install pytest-cov using
pip install pytest-cov
Run the command below in the SysIdentPy root directory, to generate the report.
pytest --cov=.
-
Official source code repo: https://github.com/wilsonrljr/sysidentpy
-
Download releases: https://pypi.org/project/sysidentpy/
You can check the latest sources with the command::
git clone https://github.com/wilsonrljr/sysidentpy.git
The project was started by Wilson R. L. Junior, Luan Pascoal and Samir A. M. Martins as a project for System Identification discipline. Samuel joined early in 2019.
The project is actively maintained by Wilson R. L. Junior and looking for contributors.
-
Discord server: https://discord.gg/8eGE3PQ
-
Website: http://sysidentpy.org
If you use SysIdentPy on your project, please drop me a line.
If you use SysIdentPy on your scientific publication, we would appreciate citations to the following paper:
- Lacerda et al., (2020). SysIdentPy: A Python package for System Identification using NARMAX models. Journal of Open Source Software, 5(54), 2384, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.02384
@article{Lacerda2020,
doi = {10.21105/joss.02384},
url = {https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.02384},
year = {2020},
publisher = {The Open Journal},
volume = {5},
number = {54},
pages = {2384},
author = {Wilson Rocha Lacerda Junior and Luan Pascoal Costa da Andrade and Samuel Carlos Pessoa Oliveira and Samir Angelo Milani Martins},
title = {SysIdentPy: A Python package for System Identification using NARMAX models},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software}
}
The documentation and structure (even this section) is openly inspired by sklearn, einsteinpy, and many others as we used (and keep using) them to learn.