For training image classifiers like UNI and CTpath as well as Resnet / ViTs, please switch to the train_classifiers branch.
Attention: This repository is currently under construction. Usage might change in the future.
All experiments were run on an Apple MacBook Pro M2 Max 96GB 2023. No special hardware is required, if training vision models is desired a CUDA-compatible GPU may speed up the process.
Please follow the steps below:
- Python Installation: Install Python from source. We used Python 3.11.6 throughout this project.
- Dependency Installation:
Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/Dyke-F/GPT-4V-In-Context-Learning.git
This process might take around 1 minute.
Set up a clean python3 virtual environment, i.e.
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
Install necessary dependencies. :
cd GPT-4V-In-Context-Learning
pip install -r requirements.txt- Repository Structure:
.
├── Datafiles # contains subdirecotories for each dataset with .csv files containing paths to the test samples
│ ├── CRC100K
│ ├── MHIST
│ └── PCam
├── Prompts # contains subdirecotories for each dataset and user and system prompt as .txt file
│ ├── CRC100K
│ ├── MHIST
│ └── PCam
├── README.md
├── Results # Results from running main.py will be stored here as .json file, i.e. Results/PCam/KNN/five_shot/...json
│ ├── CRC100K
│ ├── MHIST
│ └── PCam
├── Stats # similar nested structure like Results, contains a .csv file of the model outputs, a statistics table and plots
│ ├── CRC100K
│ ├── MHIST
│ └── PCam
├── VisionModels # ResNets and Transformers
│ ├── CRC100K
│ ├── MHIST
│ ├── PCam
│ ├── create_embeddings.ipynb # Generate the image embeddings (feature vectors) used for kNN similarity sampling
│ ├── fewshot-histo # Nested Directory, containing source code for Owkin's Phikon Model, used to generate feature vectors (embeddings)
│ ├── make_pcam_imgs.ipynb # Convert PCam h5-files back to .png images to feed into GPT-4V
│ ├── run_finetune.ipynb # alternative fine-tuning of Phikon
│ ├── run_nearest_neighbours.ipynb # alternative nearest-neighours search with Phikon
│ ├── train_classifier.ipynb # train Res-Net and Vision-Transformer for comparison with GPT-4V
│ └── venv
├── Visualisations # Nested directory to create visualisations for Manuscript figures, Mean Accuracy and CIs
│ ├── CRC100K_eval
│ ├── MHIST_eval
│ ├── PCam_eval
│ ├── venv
│ └── visualisations
├── config # Nested directory with .yaml file configuration templates
│ ├── CRC100K
│ ├── MHIST
│ └── PCam
├── data # Directory to store the source data
│ ├── CRC-VAL-HE-7K-png
│ ├── MHIST
│ └── PCam
├── dataset.py # Dataset class, implements zero- and multi shot
├── evaluate.py # Calculates statistics and heatmaps, outputs are stored in Stats/
├── evaluate_for_publication.py # Minor code changes to evaluate.py like color schemes and layouts
├── knn_dataset.py # Similar to dataset.py, implements kNN-sampling (get_topk_similar_per_label)
├── main.py # Runs the GPT-4V evaluation, requires setting a configuration .yaml file
├── make_datasets.ipynb # Helper functions to create test dataset for CRC100K, PCam and MHIST
├── prepare_for_VisionModels.ipynb # Converts GPT-4V sampled data into a training file for VisionModels/
├── requirements.txt
├── text_embeddings.ipynb # Create and visualize text embeddings for Figure 5
├── utils.py # Utility functions
├── venv
└── vision.py # Main class
Using GPT-4V requires access to OpenAIs API. If you do not have one, create an account and generate an API key. Check for further information here: https://openai.com/blog/openai-api
After generating an API key copy it and place it in a .env file in the main directory of this repository. The .env file should look like this:
OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-******************" # Place your API key here
- Download an image dataset and place it in the data directory. The dataset folder should only contain .png images.
- Use make_datasets.ipynb to create a dataset .csv file. For custom datasets not used in our study, the provided functions will need to be modified.
- If you use a custom dataset, change the input prompt to give the model context about your data and the expected outcomes. In the Prompts folder we provide all templates used in our study.
- If using (knn) sampling, create image feature-vectors beforehand.
This can be done with Vision/Models/create_embeddings.ipynb. Open the notebook and follow these steps:
- a. Select a feature extractor.
- b. Set the directory as a key in IMAGE_DIRS.
- c. If not running on MacOS, maybe change the device to CUDA if available.
- d. run create_img_embeddings with the string name of your dataset key in IMAGE_DIRS.
- e. After this is done a .npy file containing feature vectors should be created.
- Set your config file. We provide all configuration files used in our study as templates. Available options are:
project: # Set a project name (i.e. for creating Results folder), ideally dataset name
mode: # i.e. five_shot or random
data:
datafile_path: # path to your dataset .csv file containg the paths to the .png images in a table
save_path: # where to store the results
dataset_vectors_path: # in few-shot sampling: path to .npy Phikon feature embeddings to
# use_tiles: # deprecated, ignore
use_only: # provide a list of labels that should be used, i.e. for debugging or testing
batch_size: # set to 0, increase if OpenAI enables batched inputs in future API releases
num_shots: # number of few-shot examples
show_bbox: # deprecated, ignore
label_replacements: # replace the label encodings in the prompt, i.e replace "..." with "Image of tumor tissue"
"TUM": "..."
# samples: [] # uncomment to run only on certain samples, i.e. for debugging or testing
most_similar_last: False # if True, sorts the kNN-sampled example images in ascending similarity to the target image in the prompt
model:
model_name: gpt-4-vision-preview # only model currently supported
img_quality: high # check for https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/vision vor further information, can be high or low
model_kwargs: # model hyperparemeters, ... omits for brevity
...
user_args:
system_prompt_path: # path to the system prompt
user_query_path: # path to the user prompt
verbose: # print statistics while running main.py
debug: # if True breaks the script after the first sample, prevents high costs in case outcome is erroneus/unexpected
batched: # not yet supported, see batch_size for details
- Edit main.py. Set @hydra.main(config_path="./config/PCam/knn", config_name="ten_shot", version_base="1.3") to the configuration file you want to use.
- Run the main.py file as a script from the command line.
- Evaluate the results. For this modify the evaluate.py (or evaluate_for_publication.py) file.
At the end of the file set the following: subdir = ... Path to the subdirectory of your results inside the Results/ folder, i.e. subdir = "PCam/knn/ten_shot" In the call to main set the task. This is relevant to create labels for plots etc. If using a custom dataset, you might want to extend the Task class and modify the label encodings. If it is a binary task set multiclass = False. i. e. main(subdir, task=Task.PCAM, multiclass=False)
- To train a image classifier (ResNet or Vision Transformer) first convert your GPT-4 output files into a training dataset. Modify the prepare_for_VisionModels.ipynb to do so. You need a base path to your Results/ folder and a destination folder. The make_train_datafile function works for the provided datasets but might require modification if other datasets are used.
- Modify the VisionModels/train_classifier.ipynb file. Set your directories as indicated. Run the run_train_test function.
-
In order to try out the code, we provide 32 images from the NCT-CRC100K dataset and 2 ready to use config files:
- /config/CRC100K/knn/zero_shot.yaml
- /config/CRC100K/knn/three_shot.yaml
-
To run this simply call:
python3 main.pyfrom the command line. # Modify the main function with the respective config file. -
Once the run is completed, call
python3 evaluate.py. This will only work if the run was completed on all 32 images, as the statistics and visualisation implementations require all labels to be present. # Modify the main function with the respective Results folder name.
CAVE: The few-shot samples file /config/CRC100K/knn/three_shot.yaml will only run if the full CRC100K dataset is placed in the respective image folder and will fail if not, as the sampling requires all images.
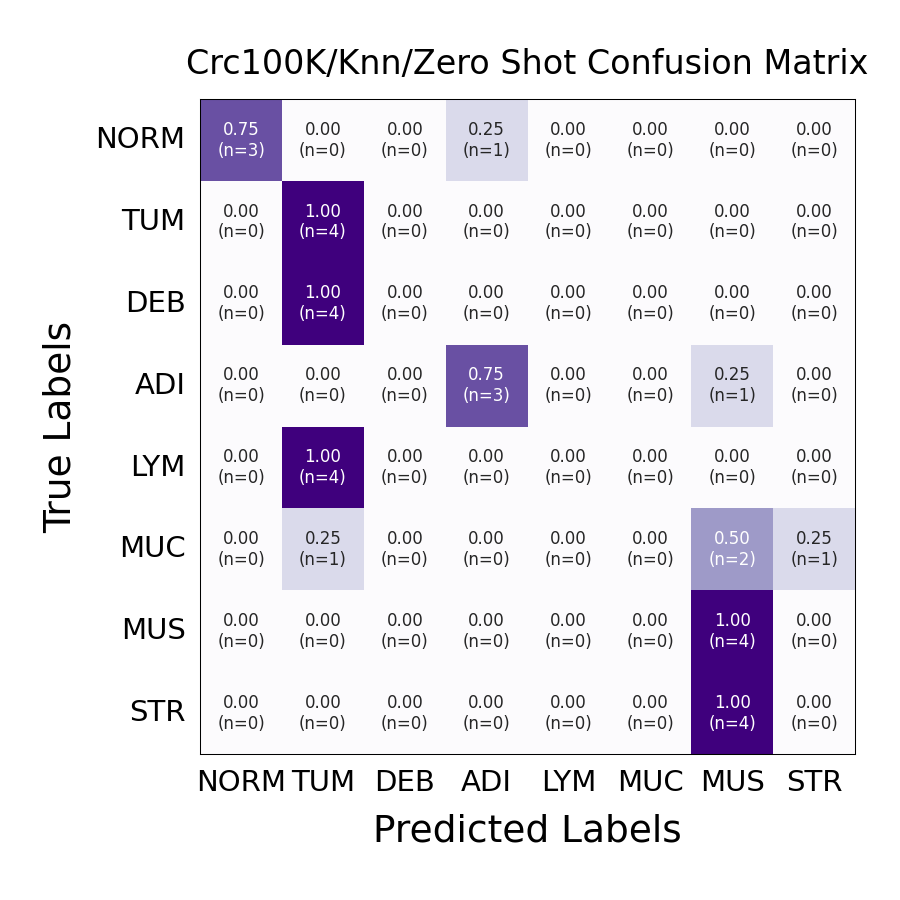
Results for 0-shot prompting on 4 images per label
Results for 3-shot prompting on 4 images per label

The overall performance increases from an accuracy of 0.4375 for zero-shot to 0.71875 for three-shot kNN-prompting.
We see, that using only 3 images as examples for in-context learning are enough to improve prediction on the classes Debris (DEB), Lymphocytes (LYM), Mucus (MUC) and Stroma (STR).
Evaluating on only 4 samples per label might however not be representative and is for illustration purposes only. For n=15 per label, we achieved an accuracy of 0.325 and 0.725 for 0-shot and three-shot sampling respectively.
