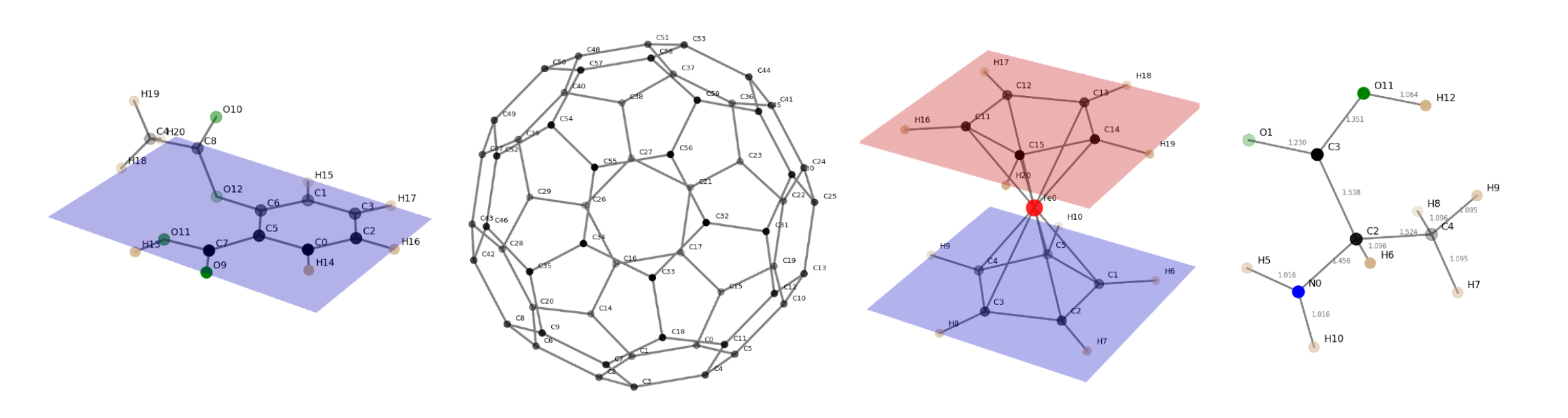
A Python 3 script for printing tables of bond lengths and (dihedral) angles from xyz files to the console. The script furthermore calculates average values, including a variety of statistical parameters, and is able to group bonding parameters. Two best-fit planes through selected or all atoms can be defined and atomic distances and angles between the planes can be calculated. Selected atoms or elements can be excluded from bond or angle tables. Contacts of two or more atoms can be included. The output should result in nicely rendered mark down tables. Molecules (atomic positions & bonds) and planes can be visualized.
pandas (ver. <= 1.5.3 & => 2.1.1), numpy, scipy, tabulate, matplotlib
not compatible with pandas 2.1.0
Start the script with:
python3 xyz2tab.py filename.xyzto open the XYZ. It gives the following output:
Tables with general information. Please note that the covalent radius (column Cov. radius) has been increased by Covalent radius + = 8 % and bonds have been calculated by the sum of the radii given in the column Cov. radius +.
------------------- ------------
Filename : asa.xyz
Number of atoms : 21
Sum formula : C₉H₈O₄
Formula weight : 180.16 g/mol
Excluded atoms : None
Excluded elements : None
Included contacts : None
Covalent radius + : 8.00 %
------------------- ------------
| Element | Atom count | Mass fraction /% | Cov. radius /Å | Cov. radius + /Å |
|-----------|--------------|--------------------|------------------|--------------------|
| C | 9 | 60.00 | 0.76 | 0.82 |
| H | 8 | 4.48 | 0.31 | 0.33 |
| O | 4 | 35.52 | 0.66 | 0.71 |
A table of bond lengths. Please note that the number after the element indicates the position in the xyz file. The numbering starts with zero due to ORCA conventions. This can be changed with the -i option (numberings starts with one).
| Atoms | Bond length /Å |
|---------|------------------|
| C0–C2 | 1.3983 |
| C0–C5 | 1.4051 |
| ... | .... |
A table with summarized general bond lengths.
| Atoms | Bond lengths /Å |
|---------|-------------------|
| C–C | 1.3933 - 1.4993 |
| C–H | 1.0865 - 1.0945 |
| C–O | 1.2189 - 1.3969 |
| O–H | 0.9806 |
A table with statistical parameters.
| Atoms | Count | Mean /Å | Median /Å | Sam. std. dev. | Pop. std. dev. | Std. error | Skewness |
|---------|---------|-----------|-------------|------------------|------------------|--------------|------------|
| C–C | 8 | 1.4221 | 1.4009 | 0.0436 | 0.0408 | 0.0154 | 1.4385 |
| C–H | 7 | 1.09 | 1.0893 | 0.0032 | 0.003 | 0.0012 | 0.289 |
| C–O | 5 | 1.3147 | 1.3438 | 0.0876 | 0.0783 | 0.0392 | -0.3848 |
| O–H | 1 | 0.9806 | 0.9806 | nan | 0 | nan | nan |
Three tables with angles in a likewise manner.
Start the script with:
python3 xyz2tab.py filename.xyz > filename.mdwill save the output in markdown format.
Convert markdown to docx (install PANDOC first):
pandoc filename.md -o filename.docxThis will convert the markdown file to a docx file. Open it with your favorite word processor. Convert the file to even more formats such as HTML, PDF or TeX with PANDOC.
filename, required: filename, e.g.my_xyz.xyz, first two lines will be ignored, file format must beelement x y z, cartesian coordinates, units in Å-eaatom(s), optional: exclude atoms, e.g.-ea H18exclude bonds to H18,-ea H18 H19exclude bonds to H18 and H19-eeelements(s), optional: exclude elements, e.g.-ee Hexclude bonds to hydrogen atoms,-ea H Oexclude bonds to hydrogen and oxygen atoms-sa, optional: sort values for bond lengths and angles ascending-sd, optional: sort values for bond lengths and angles descending-sae, optional: ascending alphabetical sort of elements-sde, optional: descending alphabetical sort of elements-icatoms, optional: include contacts of named atoms, e.g.-ic O10 O11, include the distance O10-O11, also include the angles X-O10-O11 and X-O11-O10. Input of more than two atoms is possible, e.g.-ic O10 O11 O12-datom1 atom2 atom3 atom4, optional: calculate the dihedral angle of the selected atoms, e.g.-d C1 C2 O3 N4, calculates the dihedral angle C1-C2-O3-N4-p1atom(s)oratom(s) : atom(s)oratom(s) :or: atom(s)or:, optional: calculate the best-fit plane through selected or all (:) atoms and prints the distance of the selected or all (:) for all atoms to the plane, e.g. an xyz-file containing 5 atoms:-p1 C0 C1 O2 N3 N4, calculates the best-fit plane through C0 C1 O2 N3 and N4 and prints the distances-p1 C0 : N4, calculates the best-fit plane through C0 C1 O2 N3 and N4 and prints the distances-p1 : N4, calculates the best-fit plane through C0 C1 O2 N3 and N4 and prints the distances-p1 C0 :, calculates the best-fit plane through C0 C1 O2 N3 and N4 and prints the distances-p1 :, calculates the best-fit plane through C0 C1 O2 N3 and N4 and prints the distances-p1 C0 : O2 N4, calculates the best-fit plane through C0 C1 O2 and N4 and prints the distances
-p2atom(s)oratom(s) : atom(s)oratom(s) :or: atom(s)or:, optional: calculate the best-fit plane through selected atoms and prints the distance of the selected or atoms to the plane and to the first plane 1 and prints the angle between plane 1 and 2, e.g.-p1 C0 : N4-p2 C11 : N15, calculates the best-fit planes through C0 C1 O2 N3 N4 and C11 C12 O13 N14 N15 and prints the distances and the interplanar angle.-rN, optional: increase the covalent radii byN%, e.g.-r 20.1, increase the covalent radii by 20.1 %. The defaultNis8%. The covalent radii used for the calculation of the bond length (bond length of A-B = rA + rB) is given in the last column of the summary table (Cov. radius +).-s, optional: displays the molecule (atoms & bonds) and planes (if defined). Plane 1 is blue, plane 2 is red colored. Only bonds that have been calculated by the script are shown.-sb, optional: same as-swith labeled bonds.-sn, optional: same as-swith no atom labels.-so, optional: show the orientation of the molecule with respect to the origin (x = 0 , y = 0, z = 0) and the xyz-axes of the cartesian coordinate system. The-sooption can only be given in addition to-s,-sbor-snand has no effect otherwise.-v, optional: include two more tables (tables with general bond lengths and angles)-i, optional: atom index starts with one. The first atom is now atom 1, e.g. C1.
Statistics are derived from the values of the bonding parameters.
Sam. std. dev. = Sample standard deviation, Pop. std. dev. = Population standard deviation, Std. error = Standard error or standard error of mean. Please refer to literature or Wikipedia for the meaning of these terms. The population standard deviation is probably the value you are looking for.
- Labels are in the format
Element + Position in xyz file, e.g.C11is a carbon atom at position 11 in the xyz file. Counting starts with zero. With the option-icounting starts at one, e.g. the atomC11from the previous example would beC12. - The format of the tabular output can be easily changed in the script using another formatting option of the
tabulatemodule. - With the standard covalent radii, many potential bonds will not be considered. An 8% larger covalent radius includes almost all expected bonds. All C-C distances below 1.6 Å are considered as bonds, for example.
- For extreme cases (like in Jahn-Teller distorted geometries), radii can be increased even more (
-roption) or contacts can be defined (-icoption). -r 0uses the unaltered covalent radii.-d,-p1,-p2and-signore excluded atoms (-ea) or elements (-ee) and sorting (-s...).- Distances are in Å (Angstrom) and angles are in ° (Degree). Input coordinates are assumed to be in Å (Angstrom) as well.
-p1 : N11considers all atoms from the first atom in the xyz file to N11 for plane 1.-p1 N11 :considers all atoms from N11 to the last atom in the xyz file for plane 1.-p1 C0 N11 :considers atom C0 and all atoms from N11 to the last atom in the xyz file for plane 1.-p1 C0 : C4 N11 :considers all atoms from C0 to C4 and all atoms from N11 to the last atom in the xyz file for plane 1.- To print more plane related parameters, remove the appropriate comments in the plane(s) section of the script.
- If the
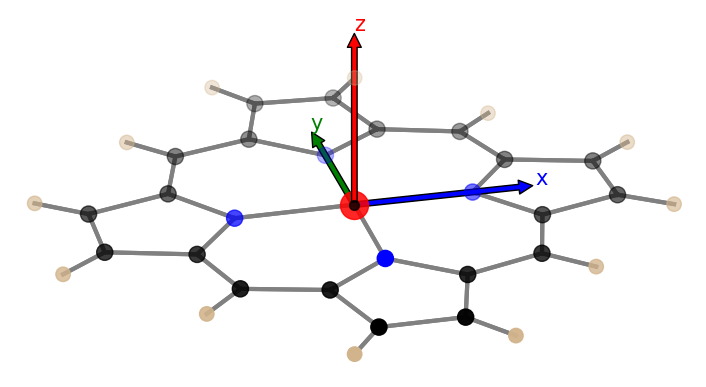
-soption is invoked, the molecule and calculated planes will be shown. Plane 1 is blue colored and plane 2 red. It gives a quick overview over the atomic numbering / labeling and the positions of the planes. One can also check whether all bonds have been calculated or considered and adjust bonding with the-ror-icoptions in case.
- The script makes extensive use of Unicode characters, which can cause problems with output or conversion.
- Verbose output (
-voption) can be very large and confusing (looks nicer after formatting). - When rotating the molecule in the matplotlib window, planes are sometimes misplaced.
- XYZ files containing more than one molecule are not supported. However, if the two header lines between different molecules are removed, the script reads the xyz file as a whole.
python3 xyz2tab.py formaldehyde.xyzOpen formaldehyde.xyz and show tables... Several options are shown.
python3 xyz2tab.py asa.xyz -ee H -sOpen asa.xyz, exclude bonds to hydrogen atoms (-ee H), show tables and the molecule (-s).
Remark: The visualization always shows all atoms, -ee or -ea options are ignored. Included contacts ( -ic option) are shown.
------------------- ------------
Filename : asa.xyz
Number of atoms : 21
Sum formula : C₉H₈O₄
Formula weight : 180.16 g/mol
Excluded atoms : None
Excluded elements : H
Included contacts : None
Covalent radius + : 8.00 %
------------------- ------------
| Element | Atom count | Mass fraction /% | Cov. radius /Å | Cov. radius + /Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 9 | 60.00 | 0.76 | 0.82 |
| H | 8 | 4.48 | 0.31 | 0.33 |
| O | 4 | 35.52 | 0.66 | 0.71 |
| Atoms | Bond length /Å |
|---|---|
| C0–C2 | 1.3983 |
| C0–C5 | 1.4051 |
| ... | ... |
...
| Atoms | Bond lengths /Å |
|---|---|
| C–C | 1.3933 - 1.4993 |
| C–O | 1.2189 - 1.3969 |
| Atoms | Count | Mean /Å | Median /Å | Sam. std. dev. | Pop. std. dev. | Std. error | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C–C | 8 | 1.4221 | 1.4009 | 0.0436 | 0.0408 | 0.0154 | 1.4385 |
| C–O | 5 | 1.3147 | 1.3438 | 0.0876 | 0.0783 | 0.0392 | -0.3848 |
| Atoms | Angle /° |
|---|---|
| C2–C0–C5 | 120.83 |
| C3–C1–C6 | 119.91 |
| ... | ... |
...
| Atoms | Angle /° |
|---|---|
| C–C–C | 116.52 - 125.18 |
| C–C–O | 108.76 - 125.02 |
| O–C–O | 120.00 / 126.89 |
| C–O–C | 112.52 |
| Atoms | Count | Mean /° | Median /° | Sam. std. dev. | Pop. std. dev. | Std. error | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C–C–C | 8 | 120.21 | 119.99 | 2.48 | 2.32 | 0.88 | 0.82 |
| C–C–O | 6 | 118.68 | 119.49 | 6.42 | 5.86 | 2.62 | -0.61 |
| O–C–O | 2 | 123.44 | 123.44 | 4.88 | 3.45 | 3.45 | nan |
| C–O–C | 1 | 112.52 | 112.52 | nan | 0 | nan | nan |
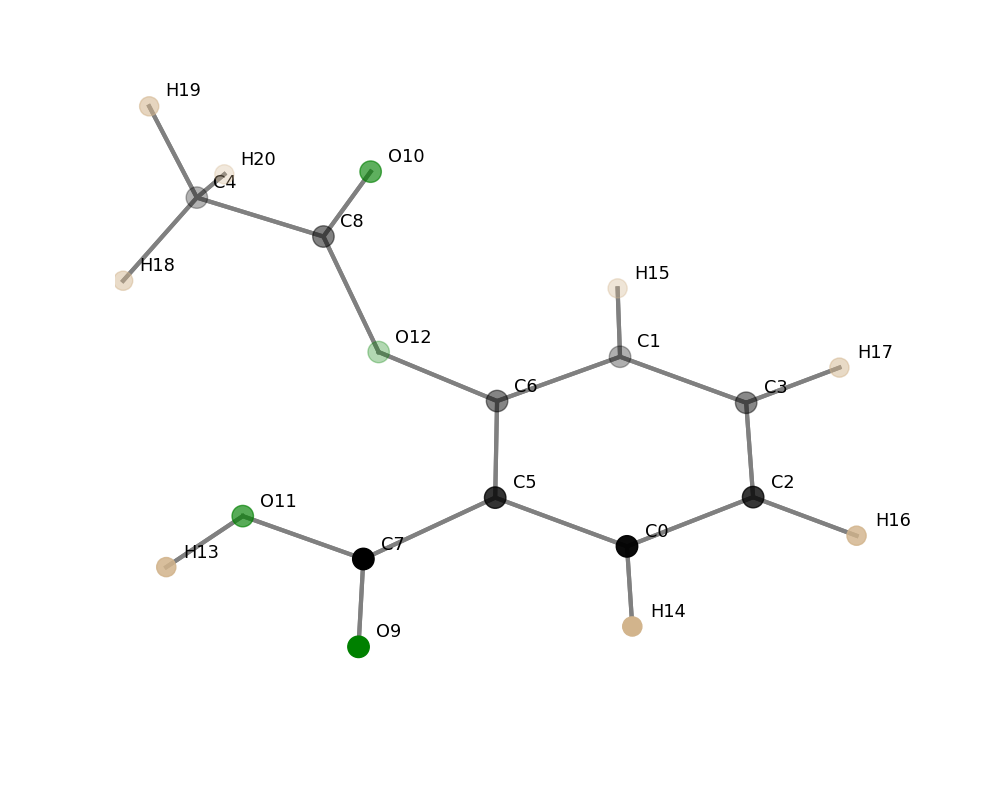
python3 xyz2tab.py asa.xyz -ee H -ic O11 O12 -sa -v -sbOpen asa.xyz, exclude bonds to hydrogen atoms (-ee H), include the contat O11 O12 (-ic O11 O12), sort values ascending (-sa), show verbose tables (-v) and the molecule with bond labels (-sb).
Remark: The visualization always shows all atoms, -ee or -ea options are ignored. Included contacts (-ic option) are shown.
| Atoms | Bond length /Å |
|---|---|
| C7–O9 | 1.2189 |
| C8–O10 | 1.2241 |
| ... | ... |
| C4–C8 | 1.4993 |
| O11–O12 | 2.6355 |
| Atoms | Bond lengths /Å |
|---|---|
| C–O | 1.2189, 1.2241, 1.3438, 1.3900, 1.3969 |
| C–C | 1.3933, 1.3936, 1.3983, 1.4006, 1.4013, 1.4051, 1.4850, 1.4993 |
| O–O | 2.6355 |
| Atoms | Bond lengths /Å |
|---|---|
| C–O | 1.2189 - 1.3969 |
| C–C | 1.3933 - 1.4993 |
| O–O | 2.6355 |
...
| Atoms | Angle /° |
|---|---|
| C6–O12–O11 | 84.47 |
| C8–O12–O11 | 89.59 |
| C7–O11–O12 | 92.58 |
| ... | ... |
...
python3 xyz2tab.py asa.xyz -d C6 O12 C8 O10Open asa.xyz and calculate the dihedral angle (-d) C6-O12-C8-O10.
...
Dihedral angle C6-O12-C8-O10: 2.85°
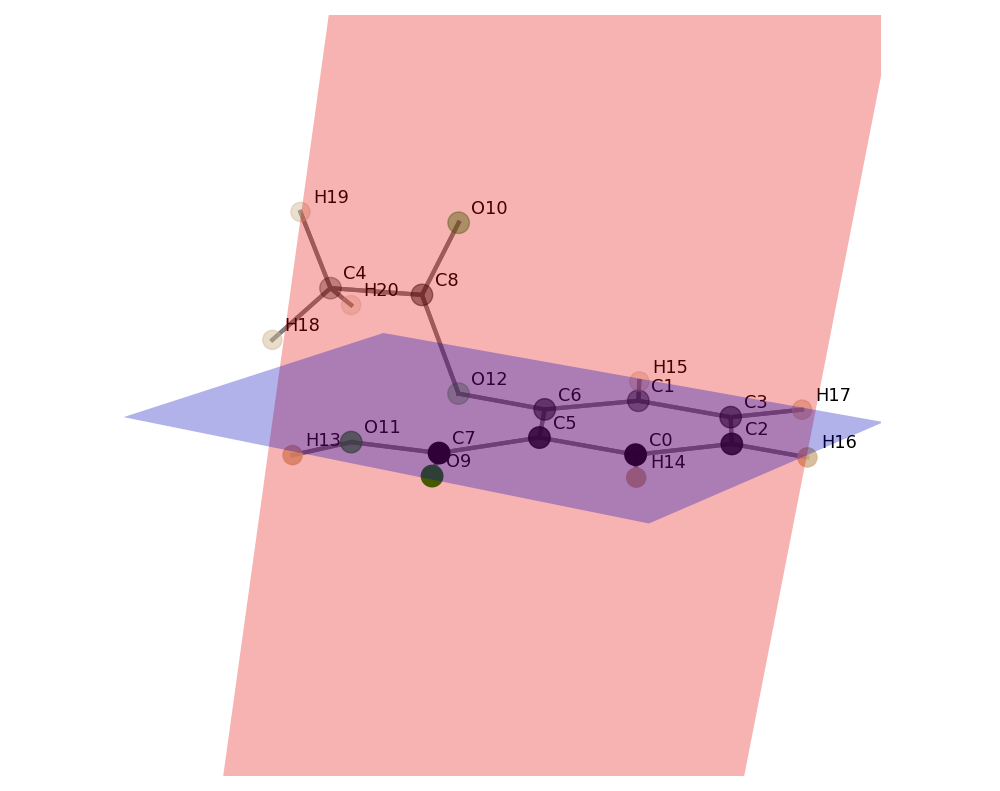
python3 xyz2tab.py asa.xyz -p1 C0 C1 C2 C3 C5 C6 C7 O9 O11 -p2 C4 C8 O10 O12 -sis similar to:
python3 xyz2tab.py asa.xyz -p1 C0 : C3 C5 : C7 O9 O11 -p2 C4 C8 O10 O12 -sOpen asa.xyz and calculate the best-fit plane number one (-p1) through C0, C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, O9, O11 and the the best-fit plane number two (-p2) through C4, C8, O10, O12, print the distances and the angle between the planes and show the molecule and the planes (-s).
Best-fit Plane 1 through 9 atoms.
| Atom | Distance to Plane 1 /Å |
|---------|---------------------------|
| C0 | -0.0056 |
| C1 | 0.0079 |
| C2 | -0.0204 |
| C3 | -0.0170 |
| C5 | 0.0167 |
| C6 | 0.0399 |
| C7 | 0.0040 |
| O9 | 0.0276 |
| O11 | -0.0532 |
Best-fit Plane 2 through 4 atoms.
| Atom | Distance to Plane 2 /Å | Distance to Plane 1 /Å |
|---------|---------------------------|---------------------------|
| C4 | -0.0006 | 1.2181 |
| C8 | 0.0023 | 1.3202 |
| O10 | -0.0009 | 2.3736 |
| O12 | -0.0007 | 0.0405 |
Angle between Plane 1 and Plane 2: 93.69°
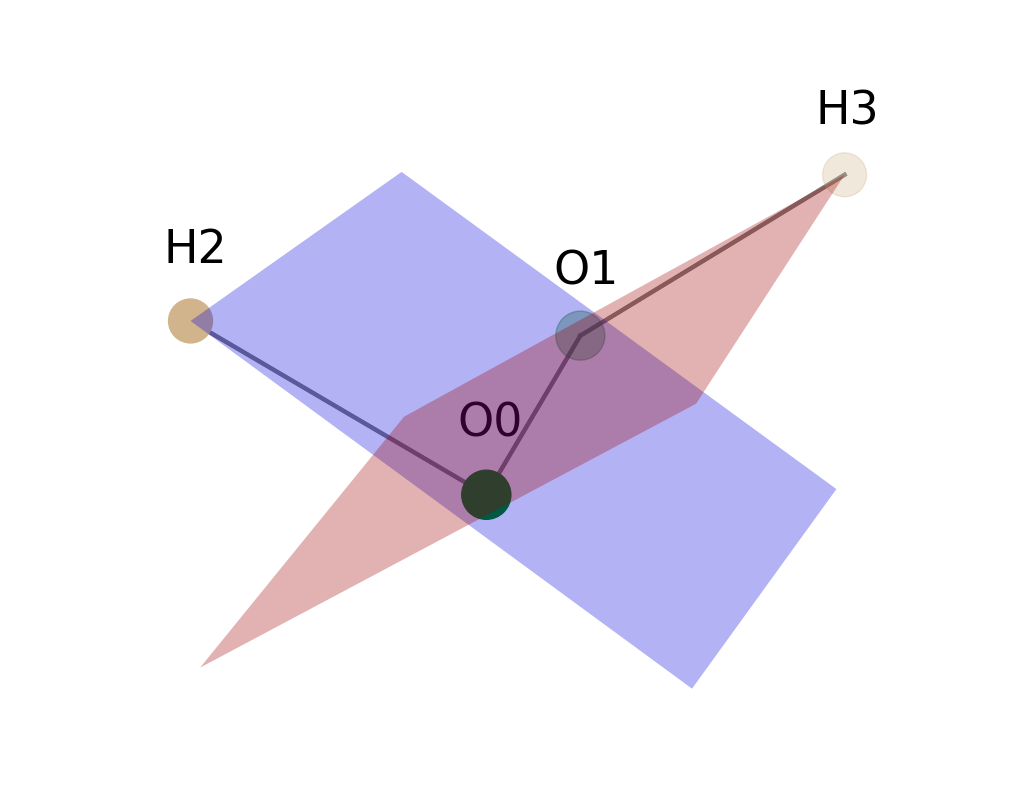
python3 xyz2tab.py h2o2.xyz -r 10 -d H2 O0 O1 H3 -p1 O0 O1 H2 -p2 O0 O1 H3 -sOpen h2o2.xyz, add +10% to radii (-r), calculate the dihedral angle (-d) H2-O0-O1-H3 and calculate the best-fit plane number one (-p1) through O0, O1, H3 and the best-fit plane number two (-p2) through O0, O1, H3, print the distances and the angle between the planes and show the molecule and the planes (-s).
Dihedral angle H2-O0-O1-H3: 113.89°
Best-fit Plane 1 through 3 atoms.
| Atom | Distance to Plane 1 /Å |
|---------|---------------------------|
| O0 | 0.0000 |
| O1 | -0.0000 |
| H2 | 0.0000 |
Best-fit Plane 2 through 3 atoms.
| Atom | Distance to Plane 2 /Å | Distance to Plane 1 /Å |
|---------|---------------------------|---------------------------|
| O0 | -0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| O1 | -0.0000 | -0.0000 |
| H3 | 0.0000 | 0.8686 |
Angle between Plane 1 and Plane 2: 113.89°
python3 xyz2tab.py nipor.xyz -sn -soOpen nipor.xyz, show the molecule with no labels (-sn) and show the orientation (-so).