WAI-ARIA compliant autosuggest component built in React
Check out the Homepage and the Codepen examples.
- WAI-ARIA compliant, with support for ARIA attributes and keyboard interactions
- Plugs in nicely to Flux and redux applications
- Full control over suggestions rendering
- Suggestions can be presented as plain list or multiple sections
- Suggestions can be retrieved asynchronously
- Supports styling using CSS Modules, Radium, Inline styles, global CSS, and more
- You decide when to show suggestions (e.g. when user types 2 or more characters)
- Pass through props to the input field (e.g. placeholder, type, onChange, onBlur)
- onSuggestionSelected hook
- Thoroughly tested
npm install react-autosuggest --saveimport Autosuggest from 'react-autosuggest';
const languages = [
{
name: 'C',
year: 1972
},
{
name: 'Elm',
year: 2012
},
{
name: 'Javascript',
year: 1995
},
{
name: 'Python',
year: 1991
}
];
function getSuggestions(value) {
const escapedValue = escapeRegexCharacters(value.trim()); // See: https://github.com/moroshko/react-autosuggest/blob/master/demo/src/components/utils/utils.js#L2-L4
if (escapedValue === '') {
return [];
}
const regex = new RegExp('^' + escapedValue, 'i');
return languages.filter(language => regex.test(language.name));
}
function getSuggestionValue(suggestion) { // when suggestion selected, this function tells
return suggestion.name; // what should be the value of the input
}
function renderSuggestion(suggestion) {
return (
<span>{suggestion.name}</span>
);
}
class Example extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
value: '',
suggestions: getSuggestions('')
};
this.onChange = this.onChange.bind(this);
this.onSuggestionsUpdateRequested = this.onSuggestionsUpdateRequested.bind(this);
}
onChange(event, { newValue }) {
this.setState({
value: newValue
});
}
onSuggestionsUpdateRequested({ value }) {
this.setState({
suggestions: getSuggestions(value)
});
}
render() {
const { value, suggestions } = this.state;
const inputProps = {
placeholder: 'Type a programming language',
value,
onChange: this.onChange
};
return (
<Autosuggest suggestions={suggestions}
onSuggestionsUpdateRequested={this.onSuggestionsUpdateRequested}
getSuggestionValue={getSuggestionValue}
renderSuggestion={renderSuggestion}
inputProps={inputProps} />
);
}
}suggestionsonSuggestionsUpdateRequestedgetSuggestionValuerenderSuggestioninputPropsshouldRenderSuggestionsmultiSectionrenderSectionTitlegetSectionSuggestionsonSuggestionSelectedfocusInputOnSuggestionClickthemeid
An array of suggestions to display.
For a plain list of suggestions, every item in suggestions should be a single suggestion. It's up to you what shape every suggestion takes. For example:
const suggestions = [
{
text: 'Apple'
},
{
text: 'Banana'
},
{
text: 'Cherry'
},
{
text: 'Grapefruit'
},
{
text: 'Lemon'
}
];To display multiple sections, every item in suggestions should be a single section. Again, it's up to you what shape every section takes. For example:
const suggestions = [
{
title: 'A',
suggestions: [
{
id: '100',
text: 'Apple'
},
{
id: '101',
text: 'Apricot'
}
]
},
{
title: 'B',
suggestions: [
{
id: '102',
text: 'Banana'
}
]
},
{
title: 'C',
suggestions: [
{
id: '103',
text: 'Cherry'
}
]
}
];Note:
- It's totally up to you what shape suggestions take!
- The initial value of
suggestionsshould match the initial value ofinputProps.value. This will make sure that, if input has a non-empty initial value, and it's focused, the right suggestions are displayed.
Normally, you would want to update suggestions as user types. You might also want to update suggestions when user selects a suggestion or the input loses focus (so that, next time the input gets focus, suggestions will be up to date).
Autosuggest will call onSuggestionsUpdateRequested every time it thinks you might want to update suggestions.
onSuggestionsUpdateRequested has the following signature:
function onSuggestionsUpdateRequested({ value, reason })where:
value- The current value of the inputreason- string describing why Autosuggest thinks you might want to update suggestions. The possible values are:'type'- usually means that user typed something, but can also be that they pressed Backspace, pasted something into the field, etc.'click'- user clicked (or tapped) a suggestion'enter'- user pressed Enter'escape'- user pressed Escape'blur'- input lost focus
When user navigates the suggestions using the Up and Down keys, the input should display the highlighted suggestion. You design how suggestion is modelled. Therefore, it's your responsibility to tell Autosuggest how to map suggestions to input values.
This function gets:
suggestion- The suggestion in question
It should return a string. For example:
function getSuggestionValue(suggestion) {
return suggestion.text;
}Use your imagination to define how suggestions are rendered.
renderSuggestion has the following signature:
function renderSuggestion(suggestion, { value, valueBeforeUpDown })where:
suggestion- The suggestion to rendervalue- The current value of the inputvalueBeforeUpDown- The value of the input prior to Up/Down interactions. If user didn't interact with Up/Down yet, it will benull. It is useful if you want to highlight input's value in the suggestion (a.k.a the match), for example.
It should return a ReactElement. For example:
function renderSuggestion(suggestion) {
return (
<span>{suggestion.text}</span>
);
}Autosuggest is a controlled component. Therefore, you should pass at least a value and an onChange callback to the input field. You can pass additional props as well. For example:
const inputProps = {
value: inputValue, // `inputValue` usually comes from application state
onChange: onChange, // called when input value changes
type: 'search',
placeholder: 'Enter city or postcode'
};onChange has the following signature:
function onChange(event, { newValue, method })where:
newValue- the new value of the input fieldmethod- string describing how the change occurred. The possible values are:'down'- user pressed Down'up'- user pressed Up'escape'- user pressed Escape'click'- user clicked (or tapped) on suggestion'type'- none of the methods above (usually means that user typed something, but can also be that they pressed Backspace, pasted something into the field, etc.)
By default, suggestions are rendered when input field isn't blank. Feel free to override this behaviour.
This function gets:
value- The current value of the input
It should return a boolean.
For example, to display suggestions only when input is at least 3 characters long, do:
function shouldRenderSuggestions(value) {
return value.trim().length > 2;
}By default, Autosuggest renders a plain list of suggestions.
If you'd like to have multiple sections (with optional titles), set multiSection={true}.
When rendering multiple sections, you need to tell Autosuggest how to render a section title.
This function gets:
section- The section to render (an item in the suggestions array)
It should return a ReactElement. For example:
function renderSectionTitle(section) {
return (
<strong>{section.title}</strong>
);
}If renderSectionTitle returns null or undefined, section title is not rendered.
When rendering multiple sections, you need to tell Autosuggest where to find the suggestions for a given section.
This function gets:
section- The section to render (an item in the suggestions array)
It should return an array of suggestions to render in the given section. For example:
function getSectionSuggestions(section) {
return section.suggestions;
}Note: Sections with no suggestions are not rendered.
This function is called when suggestion is selected. It has the following signature:
function onSuggestionSelected(event, { suggestion, suggestionValue, method })where:
suggestion- the selected suggestionsuggestionValue- the value of the selected suggestion (equivalent togetSuggestionValue(suggestion))method- string describing how user selected the suggestion. The possible values are:'click'- user clicked (or tapped) on the suggestion'enter'- user selected the suggestion using Enter
By default, focusInputOnSuggestionClick={true}, which means that, every time suggestion is clicked, the input will get the focus back.
To prevent the focus going back to the input, set focusInputOnSuggestionClick={false}.
This may be useful on mobile devices where the keyboard appears when input is focused.
You might want to do something like this:
<Autosuggest focusInputOnSuggestionClick={!isMobile} ... />where isMobile is a boolean describing whether Autosuggest operates on a mobile device or not. You can use kaimallea/isMobile, for example, to determine that.
Autosuggest comes with no styles.
It uses react-themeable to allow you to style your Autosuggest component using CSS Modules, Radium, React Style, JSS, Inline styles, or even global CSS.
For example, to style the Autosuggest using CSS Modules, do:
/* theme.css */
.container { ... }
.input { ... }
.suggestionsContainer { ... }
.suggestion { ... }
.suggestionFocused { ... }
...import theme from 'theme.css';<Autosuggest theme={theme} ... />When not specified, theme defaults to:
{
container: 'react-autosuggest__container',
containerOpen: 'react-autosuggest__container--open',
input: 'react-autosuggest__input',
suggestionsContainer: 'react-autosuggest__suggestions-container',
suggestion: 'react-autosuggest__suggestion',
suggestionFocused: 'react-autosuggest__suggestion--focused',
sectionContainer: 'react-autosuggest__section-container',
sectionTitle: 'react-autosuggest__section-title',
sectionSuggestionsContainer: 'react-autosuggest__section-suggestions-container'
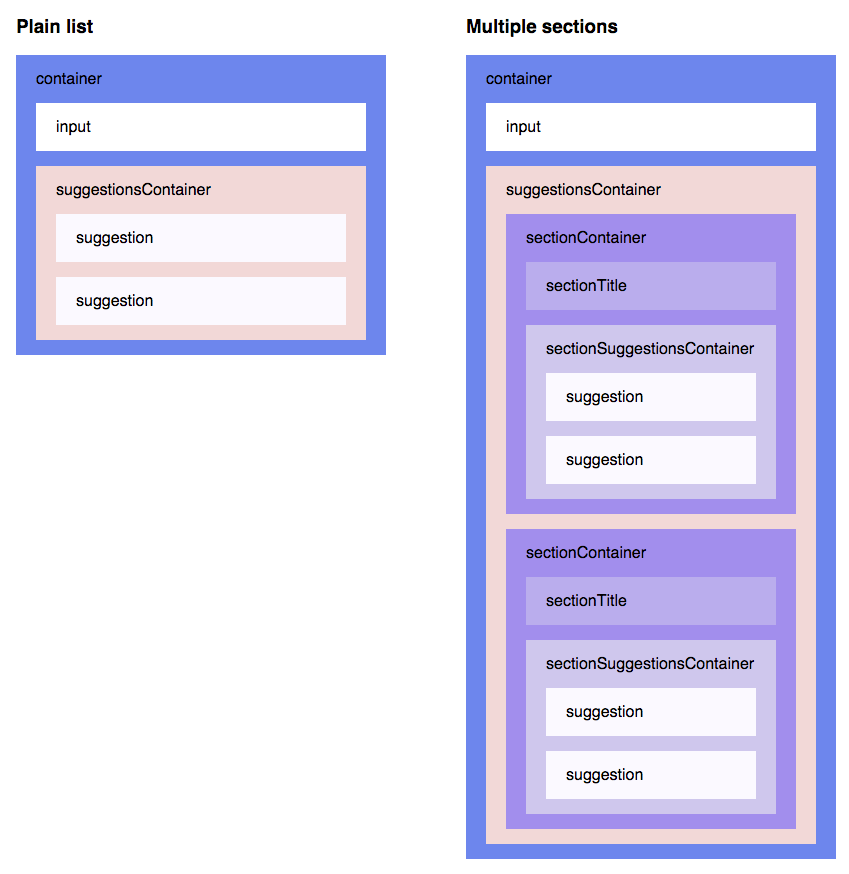
}The following picture illustrates how theme keys correspond to Autosuggest DOM structure:
The only reason id exists, is to set ARIA attributes (they require a unique id).
When rendering a single Autosuggest, don't set the id (it will be set to '1', by default).
When rendering multiple Autosuggest components on a page, make sure to give them unique ids. For example:
<Autosuggest id="source" ... />
<Autosuggest id="destination" ... />npm install
npm startNow, open http://localhost:3000/demo/dist/index.html and start hacking!
npm test