For installation, don't use the env.yml file. Use Option2.
First create conda environment with default python and activate. Install pytorch here (I used CUDA 11.7) https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/ Finally follow the table (skip pytorch). Install specified version if possible
Make sure to test the model before using my code:
python test_gen.py --ckpt ./pretrained/GEN_chair.pt --categories chair# To create a random batch of latent code as npy file:
python latent_random.py
# output saved in /latentCode
# To create some specific latent code as npy file for testing. Edit the python script to specify:
python latent_specific.py
# output saved in /latentCode
# Finally, to generate chair from the created latent code as npy file:
python gen_from_latent.py --ckpt ./pretrained/GEN_chair.pt --categories chair
# output saved in /results# Install WebSockets: (for me the version is 10.4)
conda install websocketsAt project folder, activate the conda environment
python app.pyWait a few seconds for it to load the model architecture
Go to testingWebApp folder and open the main.html file. Now you can click the button and send a batch of random latent code to the sever then receive a batch of generated point cloud. Click again to reroll. The random generation is done on the client side, and the sever generates the point clouds accordingly.
INTEL MKL ERROR: The specified module could not be found. mkl_intel_thread.dll.Solution: install numpy again (I used 1.20.2)
[Paper] [Code] [Demo Created by SerdarHELLI]
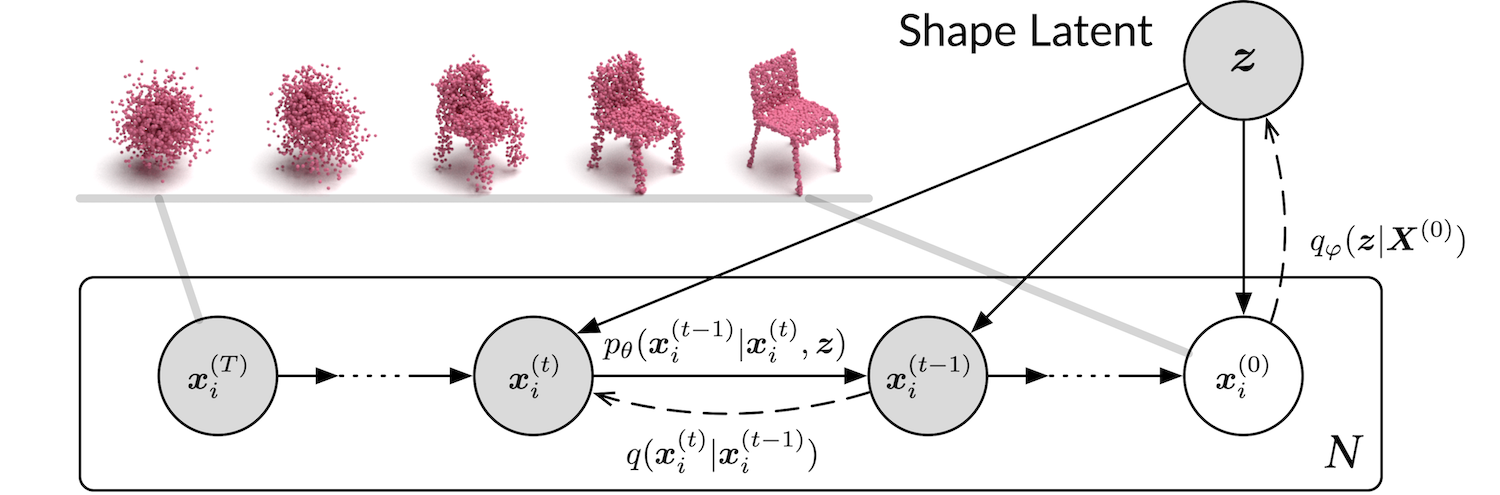
The official code repository for our CVPR 2021 paper "Diffusion Probabilistic Models for 3D Point Cloud Generation".
[Option 1] Install via conda environment YAML file (CUDA 10.1).
# Create the environment
conda env create -f env.yml
# Activate the environment
conda activate dpm-pc-gen[Option 2] Or you may setup the environment manually (If you are using GPUs that only work with CUDA 11 or greater).
Our model only depends on the following commonly used packages, all of which can be installed via conda.
| Package | Version |
|---|---|
| PyTorch | ≥ 1.6.0 |
| h5py | not specified (we used 4.61.1) |
| tqdm | not specified |
| tensorboard | not specified (we used 2.5.0) |
| numpy | not specified (we used 1.20.2) |
| scipy | not specified (we used 1.6.2) |
| scikit-learn | not specified (we used 0.24.2) |
We have removed the EMD module due to GPU compatability issues. The legacy code can be found on the emd-cd branch.
If you have to compute the EMD score or compare our model with others, we strongly advise you to use your own code to compute the metrics. The generation and decoding results will be saved to the results folder after each test run.
Datasets and pretrained models are available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1Su0hCuGFo1AGrNb_VMNnlF7qeQwKjfhZ
# Train an auto-encoder
python train_ae.py
# Train a generator
python train_gen.pyYou may specify the value of arguments. Please find the available arguments in the script.
Note that --categories can take all (use all the categories in the dataset), airplane, chair (use a single category), or airplane,chair (use multiple categories, separated by commas).
Note that the metrics computed during the validation stage in the training script (train_gen.py, train_ae.py) are not comparable to the metrics reported by the test scripts (test_gen.py, test_ae.py). If you train your own models, please evaluate them using the test scripts. The differences include:
- The scale of Chamfer distance in the training script is different. In the test script, we renormalize the bounding boxes of all the point clouds before calculating the metrics (Line 100,
test_gen.py). However, in the validation stage of training, we do not renormalize the point clouds. - During the validation stage of training, we only use a subset of the validation set (400 point clouds) to compute the metrics and generates only 400 point clouds (controlled by the
--test_sizeparameter). Limiting the number to 400 is for saving time. However, the actual size of theairplanevalidation set is 607, larger than 400. Less point clouds mean that it is less likely to find similar point clouds in the validation set for a generated point cloud. Hence, it would lead to a worse Minimum-Matching-Distance (MMD) score even if we renormalize the shapes during the validation stage in the training script.
# Test an auto-encoder
python test_ae.py --ckpt ./pretrained/AE_all.pt --categories all
# Test a generator
python test_gen.py --ckpt ./pretrained/GEN_airplane.pt --categories airplane@inproceedings{luo2021diffusion,
author = {Luo, Shitong and Hu, Wei},
title = {Diffusion Probabilistic Models for 3D Point Cloud Generation},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2021}
}